Abstract
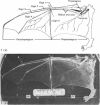
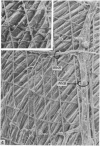
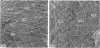
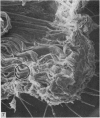
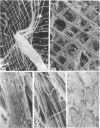
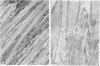
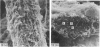
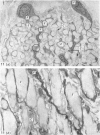
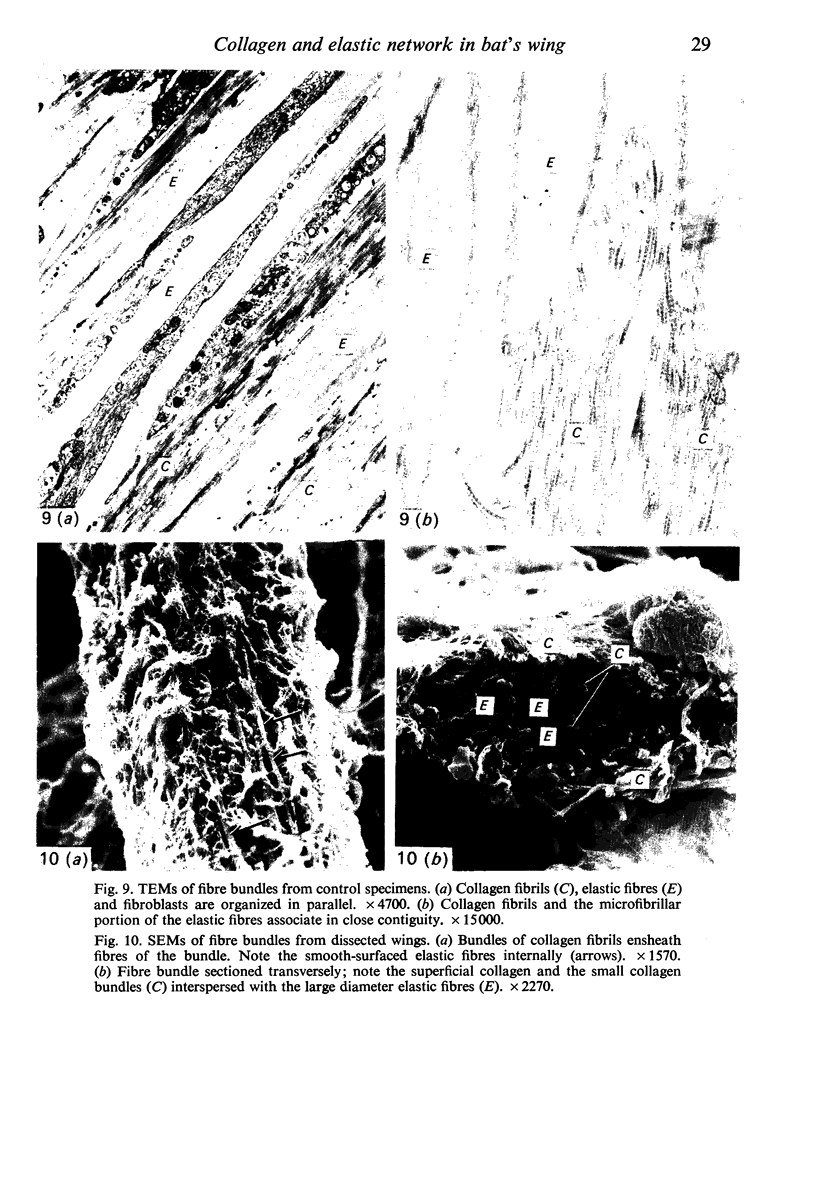
Bundles of collagen fibrils, elastic fibres and fibroblasts are organized into a network that lies in the plane of a large portion of the bat wing. By ultrastructural (TEM and SEM) and biochemical analyses it was found that individual bundles of the net are similar to elastic ligaments. Although elastic fibres predominate, they are integrated and aligned in parallel with small bundles of collagen. A reticulum of fibroblasts, joined by focal junctions, forms a cellular framework throughout each bundle. Because of the unique features of the fibre bundles of the bat's wing, in particular their accessibility, and the parallel alignment of the collagen fibrils and elastic fibres in each easily isolatable fibre bundle, they should prove a most valuable model for connective tissue studies, particularly for the study of collagen-elastin interactions.
Full text
PDF
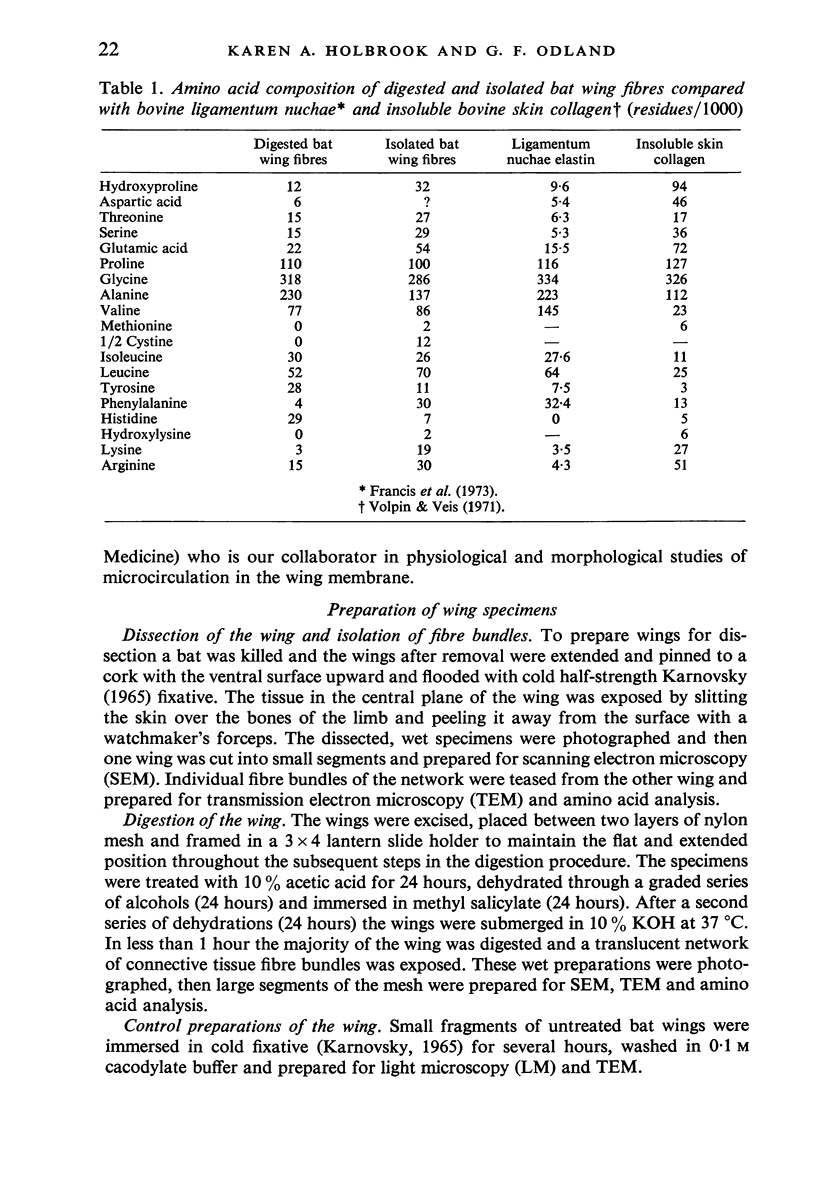
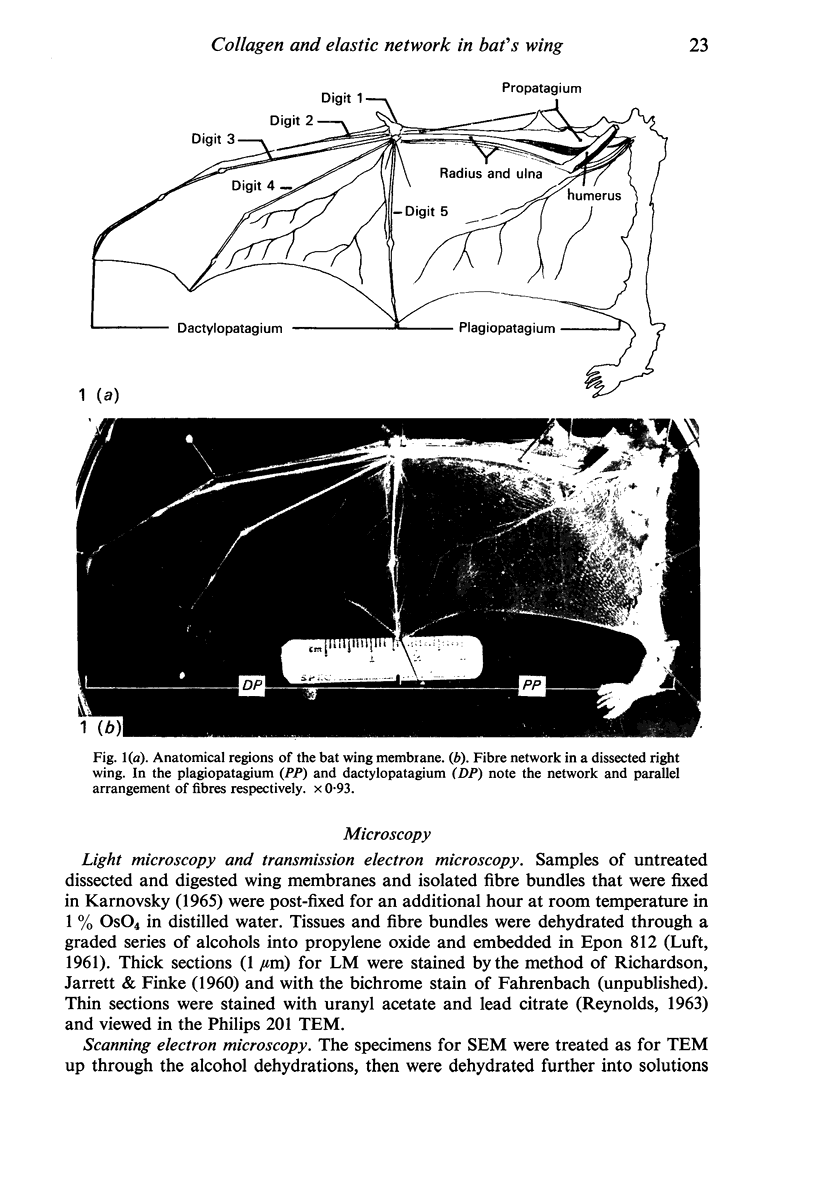
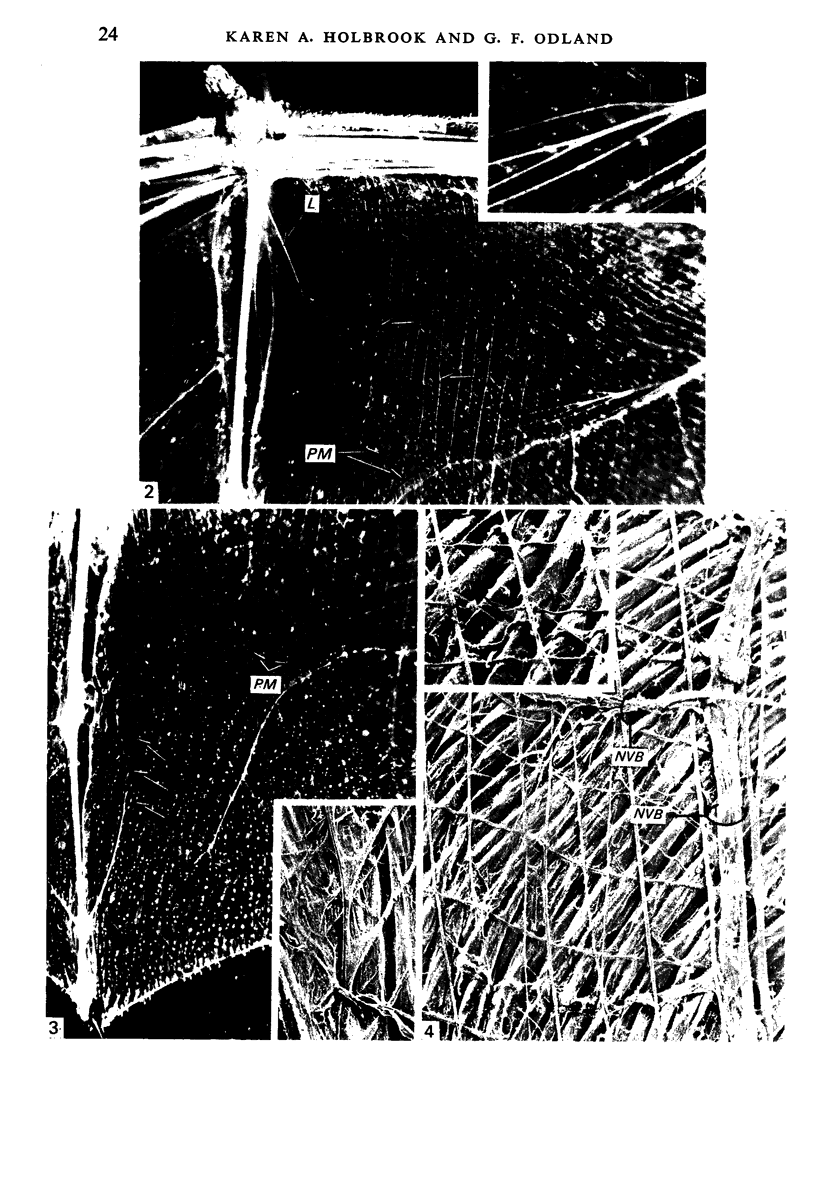











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FULLMER H. M. Differential staining of connective tissue fibers in areas of stress. Science. 1958 May 23;127(3308):1240–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3308.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G., John R., Thomas J. Biosynthetic pathway of desmosines in elastin. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):45–55. doi: 10.1042/bj1360045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawlik Z. Morphological and morphochemical properties of the elastic system in the motor organ of man. Folia Histochem Cytochem (Krakow) 1965;3(3):233–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee T. K., Jr, Ross R. The development of the rat flexor digital tendon, a fine structure study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 May;18(3):354–376. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen O. H., Bhangoo K. S., Hansen K. Control of epidermal cell renewal in the bat web. A study of the cell number, cell size and mitotic rate in the epidermis on both sides of the web after the removal of the epidermis on the ventral side only, with special emphasis on growth control theories. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1974;16(2):157–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER H. E. Electron microscope study of developing chick embryo aorta. J Ultrastruct Res. 1960 Dec;4:420–454. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(60)80032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayasi T. Electron microscopy of the elastic fibers and the dermal membrane in normal human skin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1968;48(4):303–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Bornstein P. The elastic fiber. I. The separation and partial characterization of its macromolecular components. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):366–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Greenlee T. K., Jr Electron microscopy: attachment sites between connective tissue cells. Science. 1966 Aug 26;153(3739):997–999. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3739.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARZ W. ELEKTRONENMIKROSKOPISCHE UNTERSUCHUNGEN UEBER DIE BILDUNG ELASTISCHER FASERN IN DER GEWEBEKULTUR. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1964 Aug 18;63:636–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpin D., Veis A. Differences between CNBr peptides of soluble and insoluble bovine collagens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):804–812. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90782-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]