Abstract
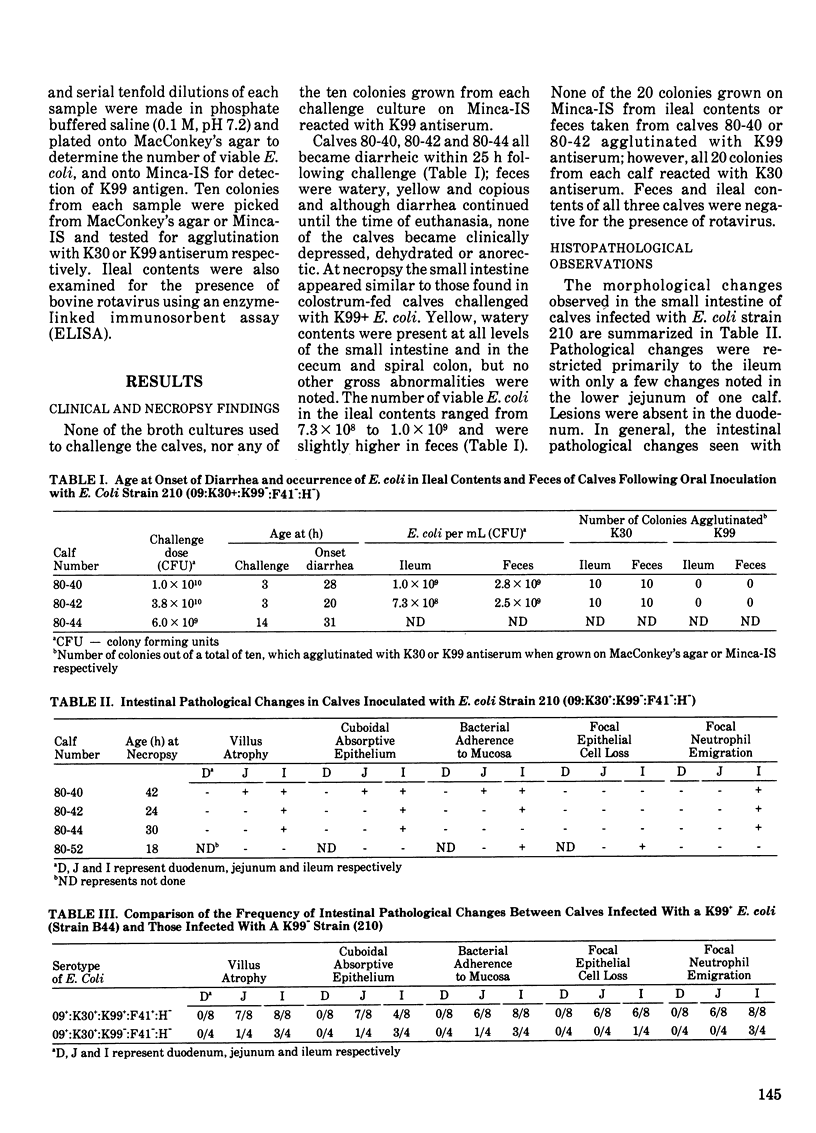
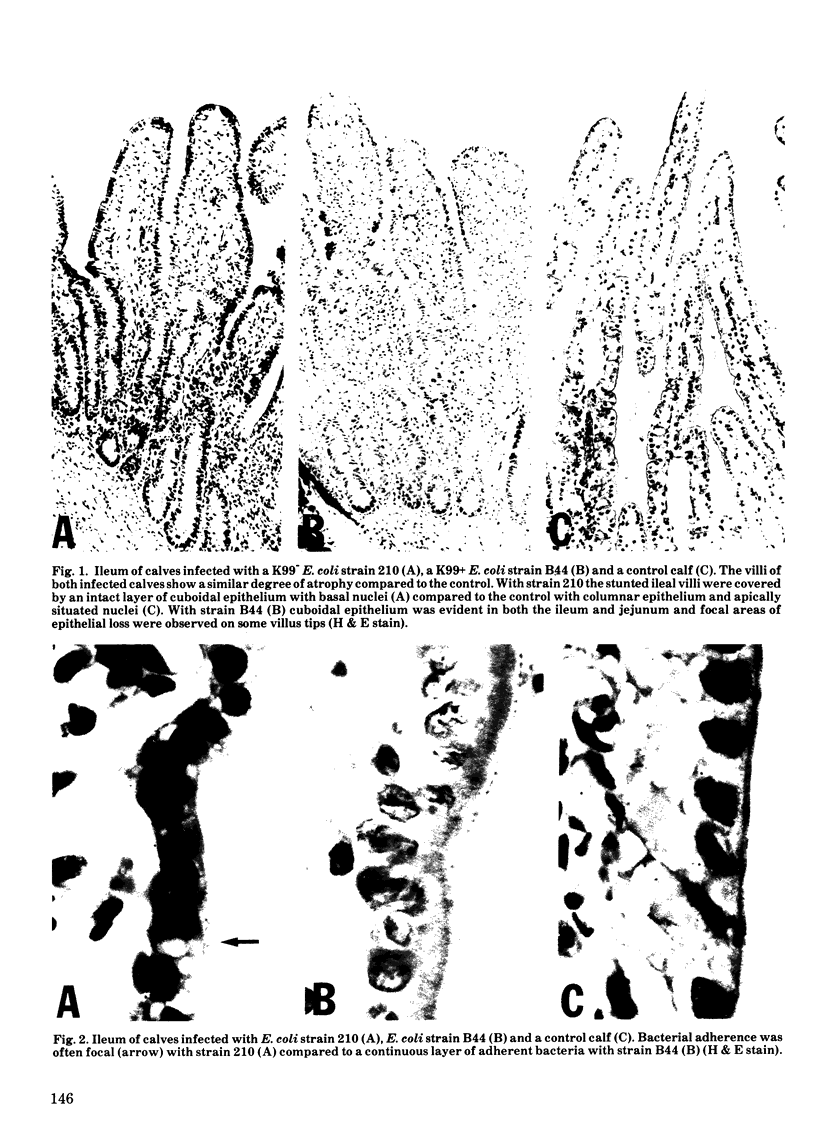
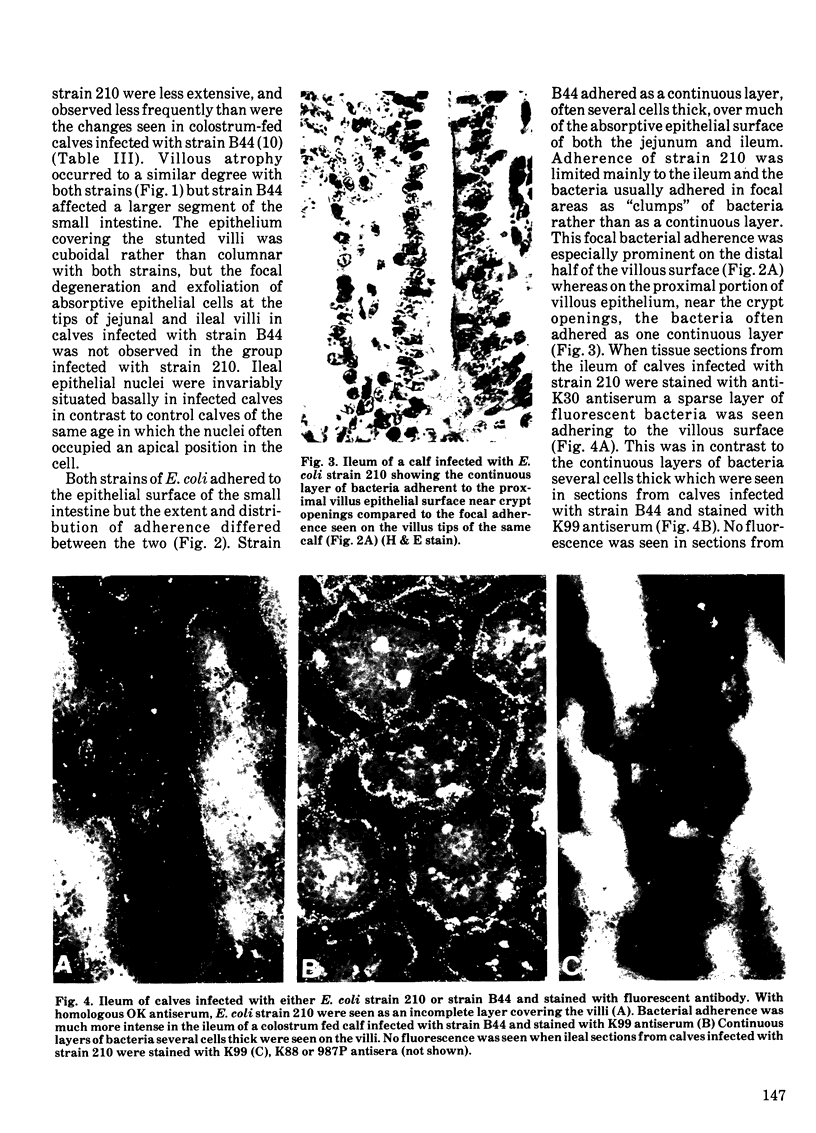
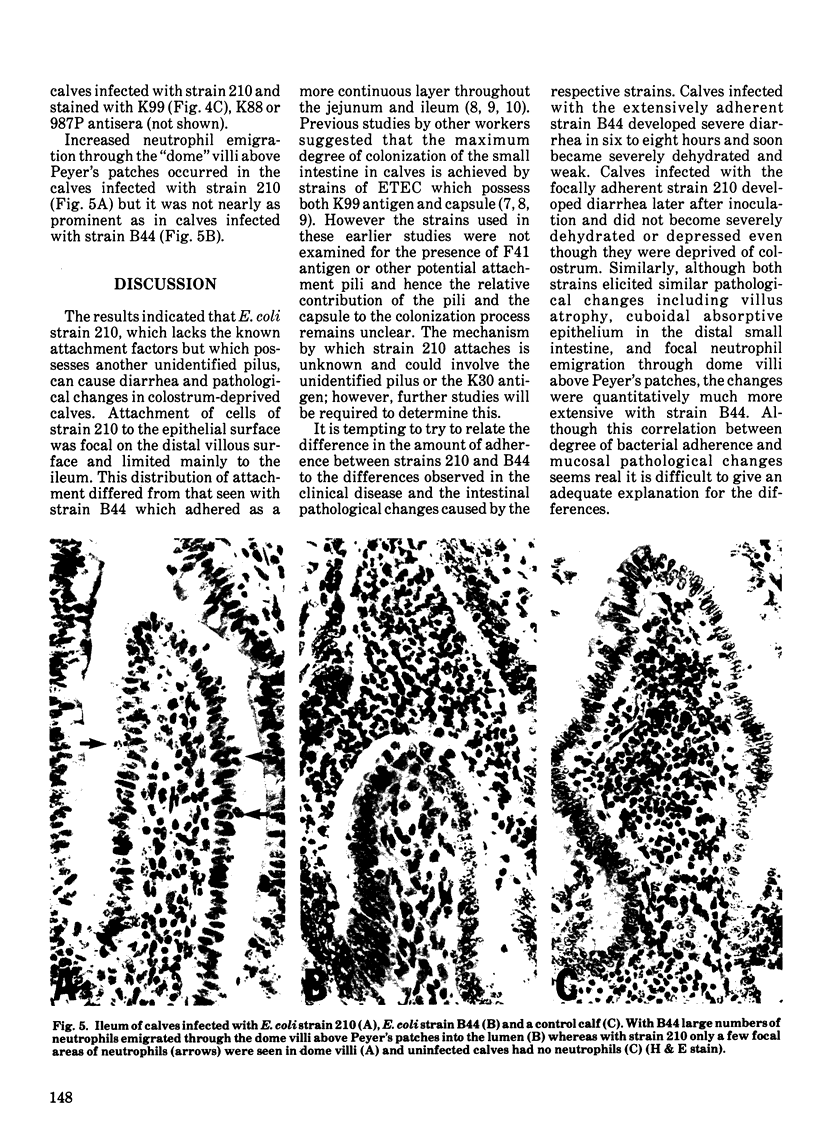
Enterotoxigenic colibacillosis was experimentally produced in four colostrum-deprived calves given 10(10) Escherichia coli strain 210 (serotype 09+:K30+:K99-:F41-:H-) orally and the histopathological changes compared to those seen in colostrum-fed calves infected in an earlier study with strain B44 (serotype 09+:K30+:K99+:F41+:H-). Escherichia coli strain 210 caused diarrhea, atrophic villi with cuboidal epithelium, and focal accumulations of a few neutrophils in the dome villi above Peyer's patches but neither the clinical nor the histopathological changes were as pronounced as with strain B44. The extent and distribution of adherence to the mucosal surface differed between the two strains. Strain B44 adhered as a continuous layer over most of the absorptive epithelial surface of both the jejunum and ileum. Adherence of strain 210 was restricted to the ileum and the bacteria often adhered focally in "clumps" rather than as a continuous layer, especially on the distal half of the villous surface.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellamy J. E., Acres S. D. Enterotoxigenic colibacillosis in colostrum-fed calves: pathologic changes. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Oct;40(10):1391–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy J. E., Nielsen N. O. Immune-mediated emigration of neutrophils into the lumen of the small intestine. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):615–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.615-619.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R., Acres S. D., Costerton J. W. Use of specific antibody to demonstrate glycocalyx, K99 pili, and the spatial relationships of K99+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in the ileum of colostrum-fed calves. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1170–1180. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1170-1180.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R., Lian C. J., Costerton J. W., Acres S. D. The use of specific antibodies to demonstrate the glycocalyx and spatial relationships of a K99-, F41- enterotoxigenic strain of Escherichia coli colonizing the ileum of colostrum-deprived calves. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Apr;47(2):150–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardeau J. P. A new in vitro technique for attachment to intestinal villi using enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 Jul-Aug;131B(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadad J. J., Gyles C. L. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of the small intestine of colostrum-fed calves infected with selected strains of Escherichia coli. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jan;43(1):41–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadad J. J., Gyles C. L. The role of K antigens of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in colonization of the small intestine of calves. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jan;46(1):21–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A., Thorns C. J., Sojka W. J. Evidence for two adhesive antigens on the K99 reference strain Escherichia coli B41. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 May;118(1):107–113. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A., Thorns C., Scott A. C., Sojka W. J., Wells G. A. Adhesion in vitro and in vivo associated with an adhesive antigen (F41) produced by a K99 mutant of the reference strain Escherichia coli B41. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1146–1153. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1146-1153.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Smith H. W., Sojka W. J. The establishment of K99, a thermolabile, transmissible escherichia coli K antigen, previously called "Kco", possessed by calf and lamb enteropathogenic strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Feb;83(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Logan E. F. The rate of development of postmortem artefact in the small intestine of neonatal calves. Br J Exp Pathol. 1978 Apr;59(2):178–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S., Logan E. F. Pathological changes in the small intestine of neonatal calves with enteric colibacillosis. Vet Pathol. 1978 Jan;15(1):92–101. doi: 10.1177/030098587801500111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Huggins M. B. The influence of plasmid-determined and other characteristics of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli on their ability to proliferate in the alimentary tracts of piglets, calves and lambs. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Nov;11(4):471–492. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-4-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Roorda I. Production, purification, and characterization of the fimbrial adhesive antigen F41 isolated from calf enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain B41M. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):751–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.751-758.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]