Abstract
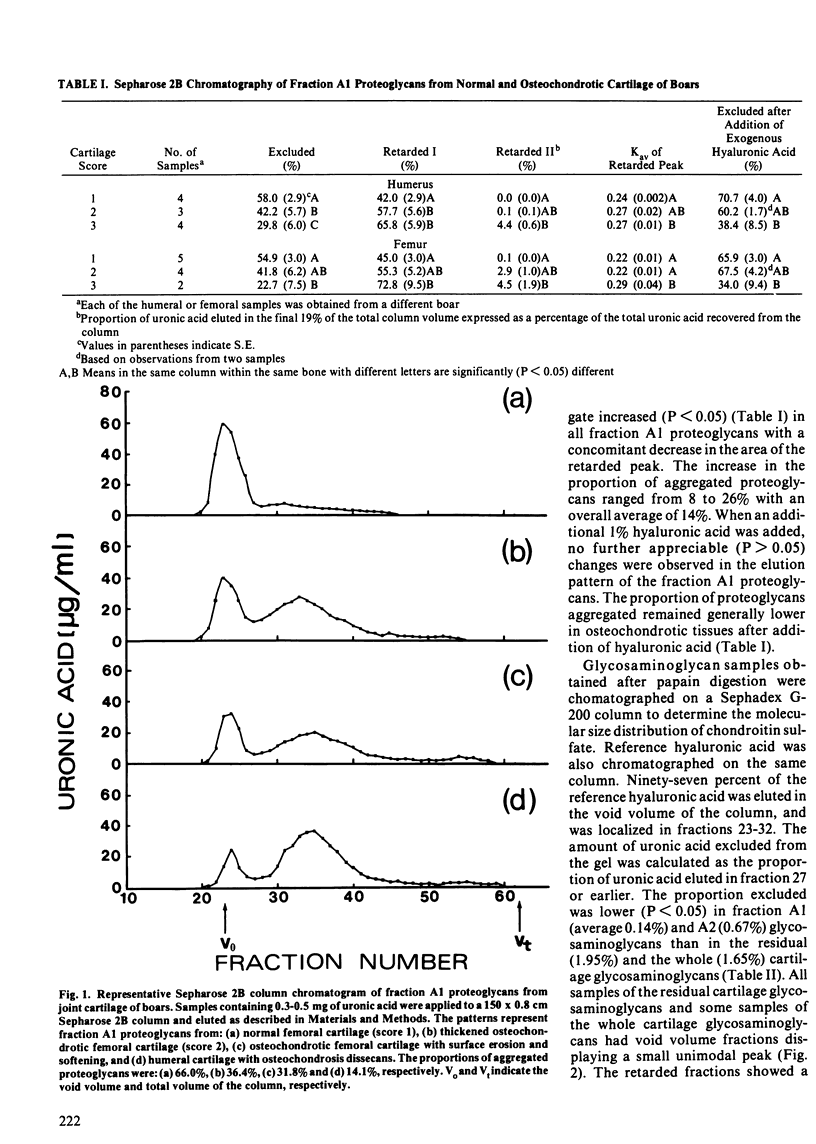
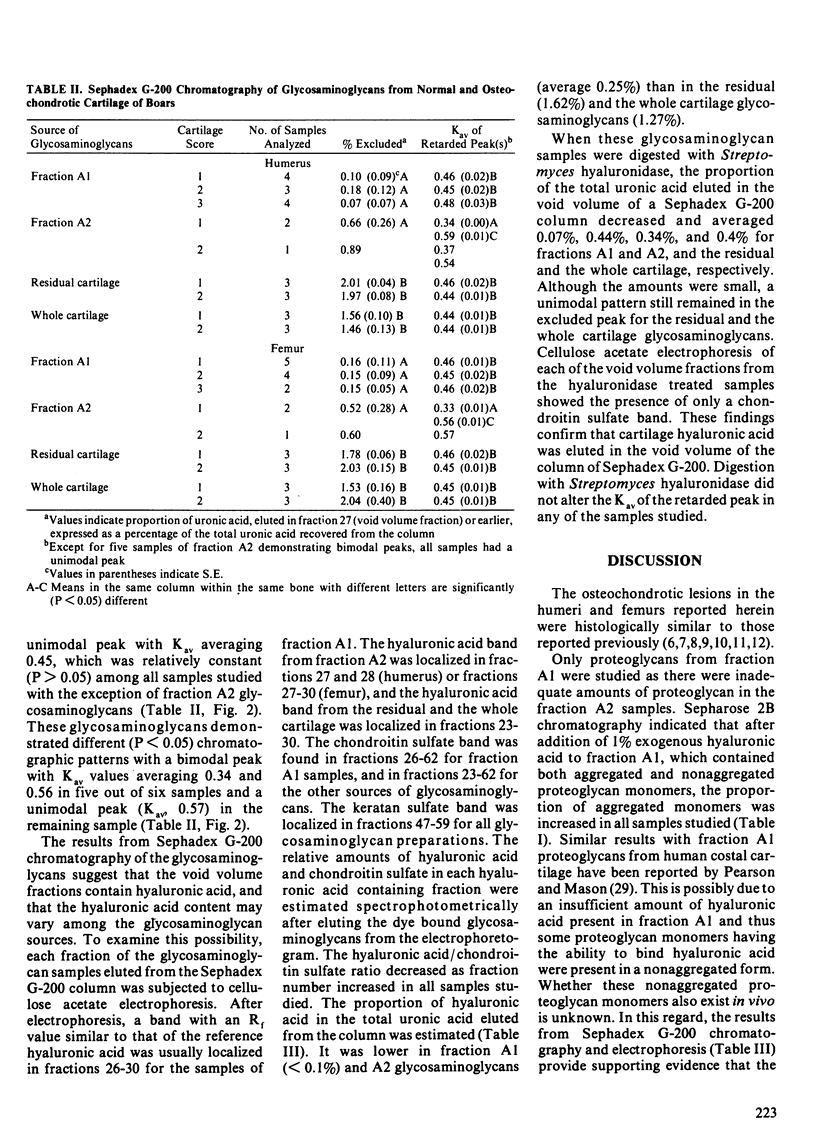
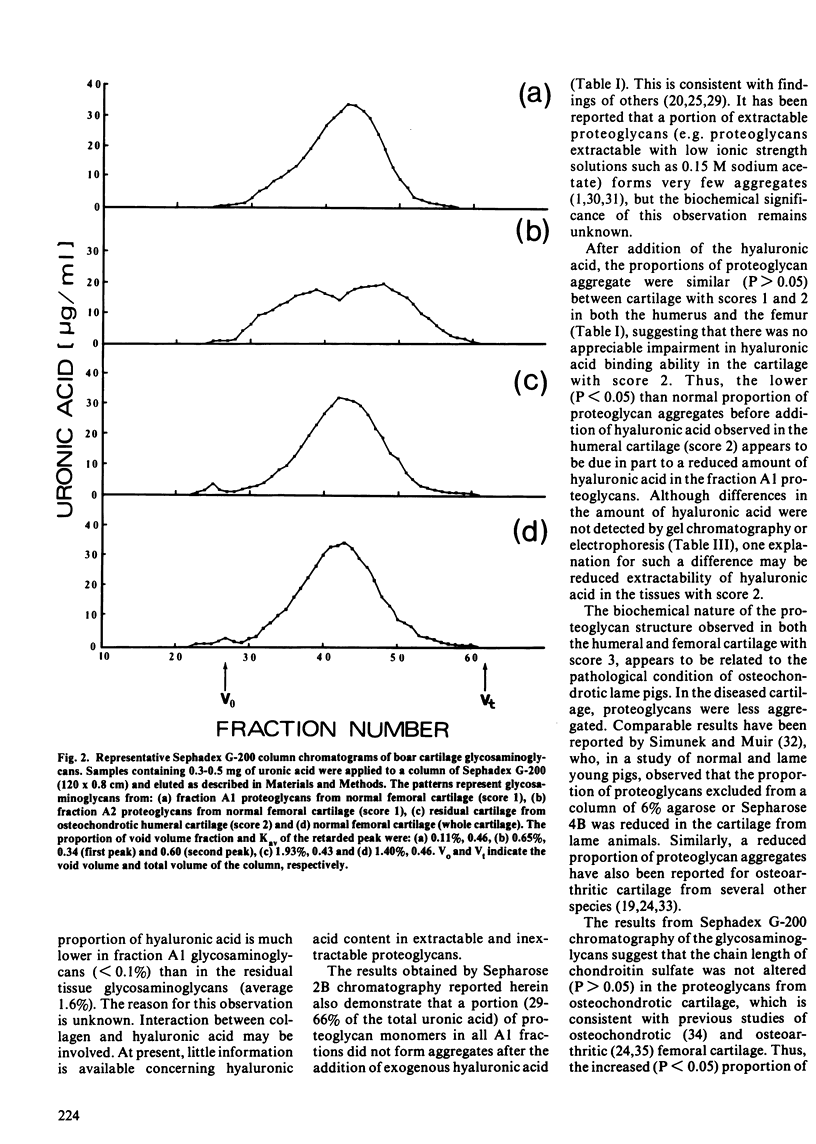
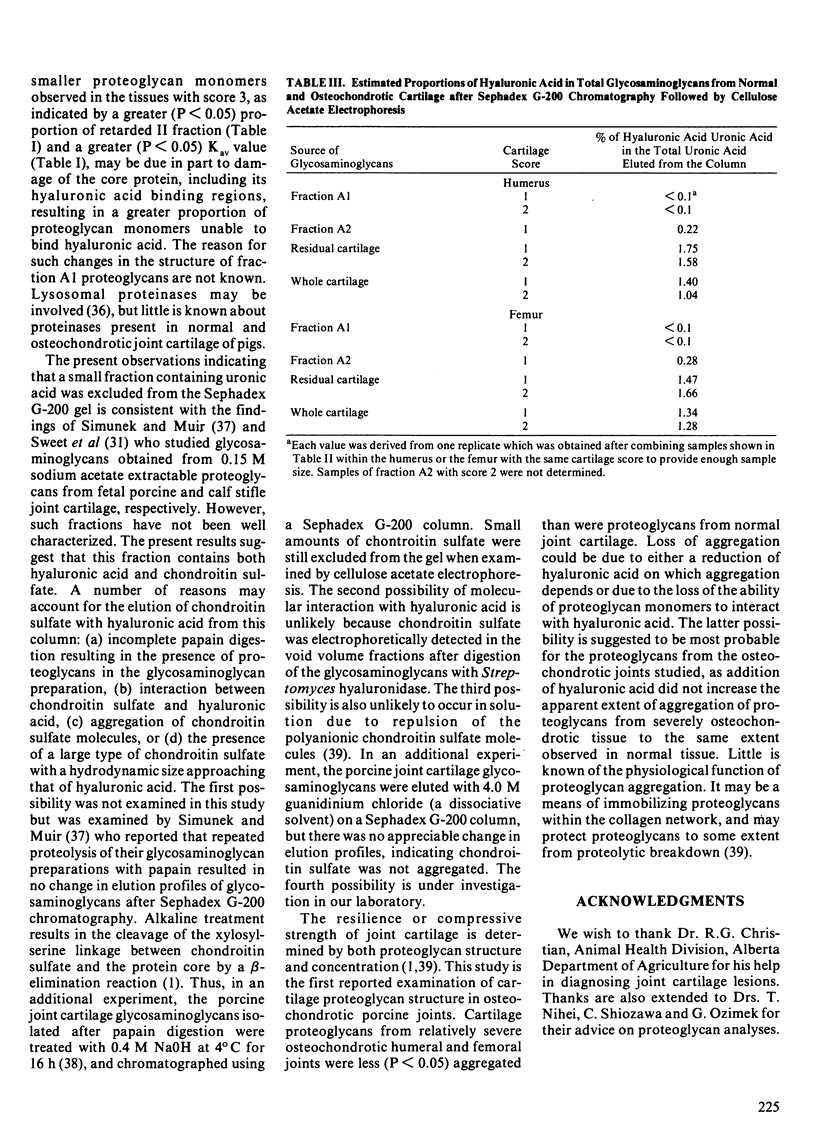
Modern pigs grow fast but are highly susceptible to degenerative joint abnormalities, including osteochondrosis. Normal and osteochondrotic humeri and femurs were obtained from five normal and ten lame adolescent boars to study cartilage proteoglycans. Histological examination of joints indicated a locally-reduced intensity of proteoglycan staining by safranin-O in lesion areas of cartilage. Cartilage proteoglycans extracted with 4.0 M guanidinium chloride were studied using Sepharose 2B gel chromatography. The proteoglycans from severely osteochondrotic joints were less (P less than 0.05) aggregated and contained a greater (P less than 0.05) proportion of smaller monomers than those from normal joints. Loss or damage of core protein, including its hyaluronic acid-binding regions, may account for the greater proportion of small monomers. The results also indicated that the proportion of hyaluronic acid in the total glycosaminoglycan uronic acid fraction, estimated by Sephadex G-200 chromatography and cellulose acetate electrophoresis, was lower (P less than 0.05) for the extracted proteoglycans than for the residual or the whole cartilage proteoglycans in all joints studied.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Palmoski M. J., Perricone E. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. II Evidence for the presence of a hyaluronate-binding region on proteoglycans from osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Nov-Dec;19(6):1308–1314. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Palmoski M. Organization of ground substance proteoglycans in normal and osteoarthritic knee cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Mar-Apr;19(2):209–215. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingle J. T., Barrett A. J., Weston P. D. Cathepsin D. Characteristics of immunoinhibition and the confirmation of a role in cartilage breakdown. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj1230001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén A., Heinegård D., Reiland S., Olsson S. E. Proteoglycans and calcification of cartilage in the femoral head epiphysis of the immature rat. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982 Apr;64(4):558–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedegebuure S. A., Häni H. J., van der Valk P. C., van der Wal P. G. Osteochondrosis in six breeds of slaughter pigs. I. A morphological investigation of the status of osteochondrosis in relation to breed and level of feeding. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 1980 Jan 15;105(2):28–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grondalen T. Osteochondrosis and arthrosis in pigs. I. Incidence in animals up to 120 kg live weight. Acta Vet Scand. 1974;15(1):1–25. doi: 10.1186/BF03547490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Ewins R. J., Muir H. Cartilage proteoglycans. Structure and heterogeneity of the protein core and the effects of specific protein modifications on the binding to hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):127–143. doi: 10.1042/bj1570127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Hyaluronic acid in cartilage and proteoglycan aggregation. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):565–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1390565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C. Interaction of cartilage proteoglycans with hyaluronic acid. J Supramol Struct. 1977;7(1):101–120. doi: 10.1002/jss.400070110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata R., Nagai Y. A micro colorimetric determination of acidic glycosaminoglycans by two dimensional electrophoresis on a cellulose acetate strip. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):652–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata R., Nagai Y. A rapid and micro method for separation of acidic glycosaminoglycans by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1972 Feb;45(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Extraction, fractionation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine tracheal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inerot S., Heinegård D., Audell L., Olsson S. E. Articular-cartilage proteoglycans in aging and osteoarthritis. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):143–156. doi: 10.1042/bj1690143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G., Pronsky W. Glycosaminoglycan contents of normal and degenerative articular cartilage from dogs. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Jul;39(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir H. Heberden Oration, 1976. Molecular approach to the understanding of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Jun;36(3):199–208. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.3.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata K., Yokoyama Y. Acidic glycosaminoglycan, lipid and water contents in human coronary arterial branches. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Oct;45(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Thompson J. R., Aherne F. X., Christian R. G. Observations of abnormalities and age-related changes in the anconeal processes of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Oct;43(10):1840–1844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Thompson J. R., Aherne F. X. Molecular size of chondroitin sulfate from normal and osteochondrotic joint cartilage of adolescent boars. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Oct;46(4):395–399. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya T., Kaneko Y. Novel hyaluronidase from streptomyces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 18;198(3):607–609. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. P., Mason R. M. Proteoglycan aggregates in adult human costal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 3;583(4):512–526. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiland S. Morphology of osteochondrosis and sequelae in pigs. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1978;358:45–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiland S. Pathology of so-called leg weakness in the pig. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1978;358:23–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiland S. The effect of decreased growth rate on frequency and severity of osteochondrosis in pigs. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1978;358:107–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. Chemical basis for the histological use of safranin O in the study of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Jan;53(1):69–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. E. Aliphatic ammonium salts in the assay of acidic polysaccharides from tissues. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:145–197. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simůnek Z., Muir H. Changes in the protein-polysaccharides of pig articular cartilage during prenatal life, development and old age. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):515–523. doi: 10.1042/bj1260515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simůnek Z., Muir H. Proteoglycans of the knee-joint cartilage of young normal and lame pigs. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):181–187. doi: 10.1042/bj1300181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet M. B., Thonar E. J., Immelman A. R. Anatomically determined polydispersity of proteoglycans of immature articular cartilage. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jul;189(1):28–36. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasan N. Proteoglycans in normal and severely osteoarthritic human cartilage. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):781–787. doi: 10.1042/bj1870781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


