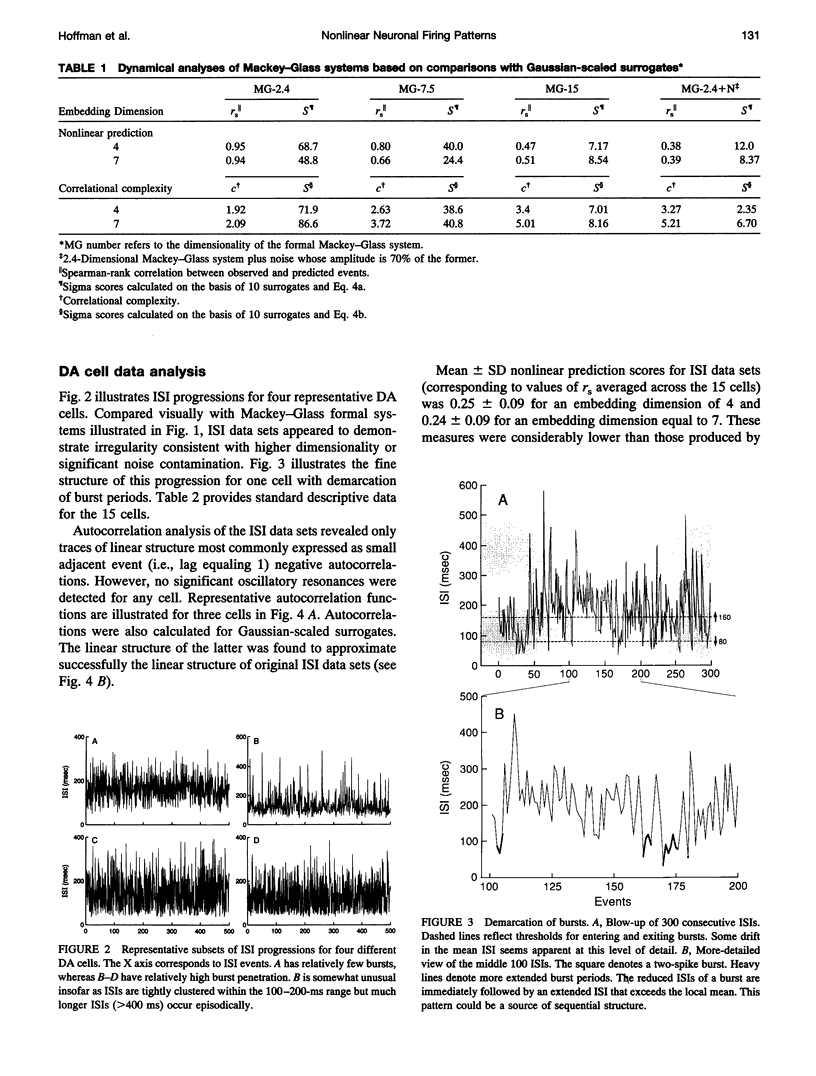
Abstract
Firing patterns of 15 dopamine neurons in the rat substantia nigra were studied. These cells alternated between two firing modes, single-spike and bursting, which interwove to produce irregular, aperiodic interspike interval (ISI) patterns. When examined by linear autocorrelation analysis, these patterns appeared to reflect a primarily stochastic or random process. However, dynamical analysis revealed that the sequential behavior of a majority of these cells expressed "higher-dimensional" nonlinear deterministic structure. Dimensionality refers to the number of degrees of freedom or complexity of a time series. Bursting was statistically associated with some aspects of nonlinear ISI sequence dependence. Controlling for the effects of nonstationarity substantially increased overall predictability of ISI sequences. We hypothesize that the nonlinear deterministic structure of ISI firing patterns reflects the neuron's response to coordinated synaptic inputs emerging from neural circuit interactions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander G. E., Crutcher M. D. Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):266–271. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90107-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean A. J., Roth R. H. Extracellular dopamine and neurotensin in rat prefrontal cortex in vivo: effects of median forebrain bundle stimulation frequency, stimulation pattern, and dopamine autoreceptors. J Neurosci. 1991 Sep;11(9):2694–2702. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-09-02694.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney B. S., Aghajanian G. K. Dopamine and norepinephrine innervated cells in the rat prefrontal cortex: pharmacological differentiation using microiontophoretic techniques. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 1;19(11):1783–1789. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney B. S., Chiodo L. A., Grace A. A. Midbrain dopamine system electrophysiological functioning: a review and new hypothesis. Synapse. 1991 Oct;9(2):79–94. doi: 10.1002/syn.890090202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney B. S., Walters J. R., Roth R. H., Aghajanian G. K. Dopaminergic neurons: effect of antipsychotic drugs and amphetamine on single cell activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jun;185(3):560–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T., Schiff S. J., Sauer T., Gossard J. P., Burke R. E. Stochastic versus deterministic variability in simple neuronal circuits: I. Monosynaptic spinal cord reflexes. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):671–683. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80526-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton T. A., Diamond G. A. Can the analytic techniques of nonlinear dynamics distinguish periodic, random and chaotic signals? Comput Biol Med. 1991;21(4):243–263. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(91)90006-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser AM, Swinney HL. Independent coordinates for strange attractors from mutual information. Phys Rev A Gen Phys. 1986 Feb;33(2):1134–1140. doi: 10.1103/physreva.33.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. S., Bunney B. S. Activity of A9 and A10 dopaminergic neurons in unrestrained rats: further characterization and effects of apomorphine and cholecystokinin. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 3;405(1):46–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90988-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonon F. G. Nonlinear relationship between impulse flow and dopamine released by rat midbrain dopaminergic neurons as studied by in vivo electrochemistry. Neuroscience. 1988 Jan;24(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace A. A., Bunney B. S. Induction of depolarization block in midbrain dopamine neurons by repeated administration of haloperidol: analysis using in vivo intracellular recording. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Sep;238(3):1092–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace A. A., Bunney B. S. Intracellular and extracellular electrophysiology of nigral dopaminergic neurons--2. Action potential generating mechanisms and morphological correlates. Neuroscience. 1983 Oct;10(2):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace A. A., Bunney B. S. Nigral dopamine neurons: intracellular recording and identification with L-dopa injection and histofluorescence. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):654–656. doi: 10.1126/science.7433992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace A. A., Bunney B. S. Opposing effects of striatonigral feedback pathways on midbrain dopamine cell activity. Brain Res. 1985 May 6;333(2):271–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91581-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace A. A., Bunney B. S. The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: burst firing. J Neurosci. 1984 Nov;4(11):2877–2890. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-11-02877.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace A. A., Bunney B. S. The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: single spike firing. J Neurosci. 1984 Nov;4(11):2866–2876. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-11-02866.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legéndy C. R., Salcman M. Bursts and recurrences of bursts in the spike trains of spontaneously active striate cortex neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Apr;53(4):926–939. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.4.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. F., Gotthelf T. Sensory inattention in rats with 6-hydroxydopamine-induced degeneration of ascending dopaminergic neurons: apomorphine-induced reversal of deficits. Exp Neurol. 1979 Aug;65(2):398–411. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(79)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinerie JM, Albano AM, Mees AI, Rapp PE. Mutual information, strange attractors, and the optimal estimation of dimension. Phys Rev A. 1992 May 15;45(10):7058–7064. doi: 10.1103/physreva.45.7058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp P. E., Zimmerman I. D., Vining E. P., Cohen N., Albano A. M., Jiménez-Montaño M. A. The algorithmic complexity of neural spike trains increases during focal seizures. J Neurosci. 1994 Aug;14(8):4731–4739. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-08-04731.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp PE, Albano AM, Schmah TI, Farwell LA. Filtered noise can mimic low-dimensional chaotic attractors. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1993 Apr;47(4):2289–2297. doi: 10.1103/physreve.47.2289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera M. K., Trulson M. E., German D. C. Electrophysiological properties of mouse dopamine neurons: in vivo and in vitro studies. Neuroscience. 1984 Jul;12(3):793–801. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff S. J., Jerger K., Chang T., Sauer T., Aitken P. G. Stochastic versus deterministic variability in simple neuronal circuits: II. Hippocampal slice. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80527-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. S. Responses of striatal neurons to peripheral sensory stimulation in symptomatic MPTP-exposed cats. Brain Res. 1991 Mar 29;544(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sesack S. R., Bunney B. S. Pharmacological characterization of the receptor mediating electrophysiological responses to dopamine in the rat medial prefrontal cortex: a microiontophoretic study. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):1323–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard P. D., Bunney B. S. Effects of apamin on the discharge properties of putative dopamine-containing neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1988 Nov 1;463(2):380–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90414-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva N. L., Bunney B. S. Intracellular studies of dopamine neurons in vitro: pacemakers modulated by dopamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 May 10;149(3):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. D., Grace A. A. Role of the subthalamic nucleus in the regulation of nigral dopamine neuron activity. Synapse. 1992 Dec;12(4):287–303. doi: 10.1002/syn.890120406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks D. L., Mays L. E. Movement fields of saccade-related burst neurons in the monkey superior colliculus. Brain Res. 1980 May 19;190(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara G., May R. M. Nonlinear forecasting as a way of distinguishing chaos from measurement error in time series. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):734–741. doi: 10.1038/344734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidd C. W., Olsen L. F., Schaffer W. M. The case for chaos in childhood epidemics. II. Predicting historical epidemics from mathematical models. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 Dec 22;254(1341):257–273. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vives F., Mogenson G. J. Electrophysiological study of the effects of D1 and D2 dopamine antagonists on the interaction of converging inputs from the sensory-motor cortex and substantia nigra neurons in the rat. Neuroscience. 1986 Feb;17(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G., Lovinger D. M., Weight F. F. Transient low-threshold Ca2+ current triggers burst firing through an afterdepolarizing potential in an adult mammalian neuron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6802–6806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):86–97. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Stewart M. Different firing patterns generated in dendrites and somata of CA1 pyramidal neurones in guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1992 Nov;457:675–687. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeomans J. S., Maidment N. T., Bunney B. S. Excitability properties of medial forebrain bundle axons of A9 and A10 dopamine cells. Brain Res. 1988 May 31;450(1-2):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]