Abstract
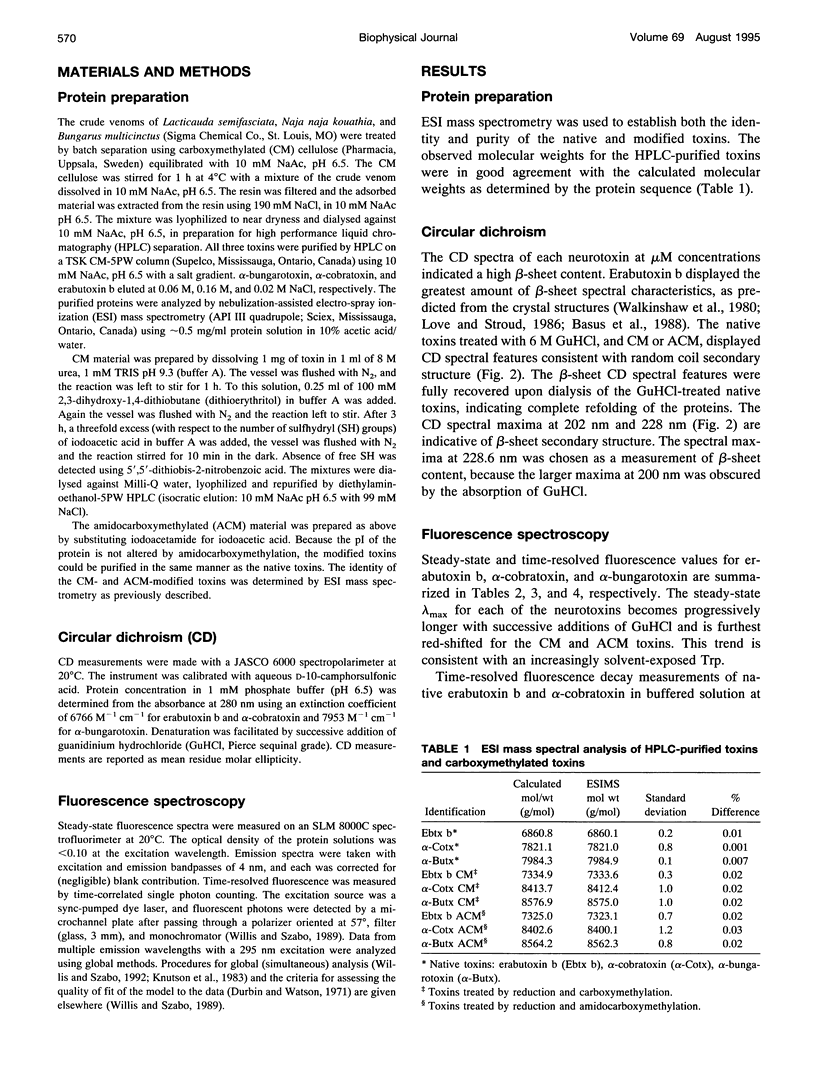
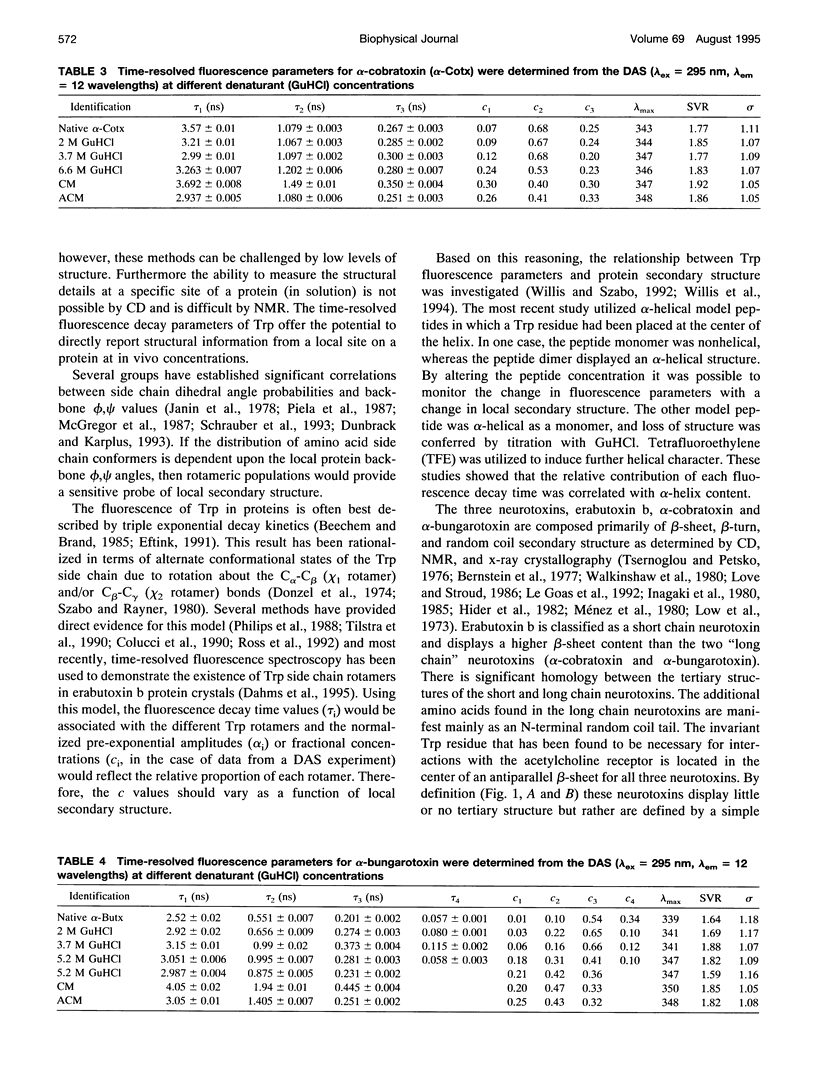
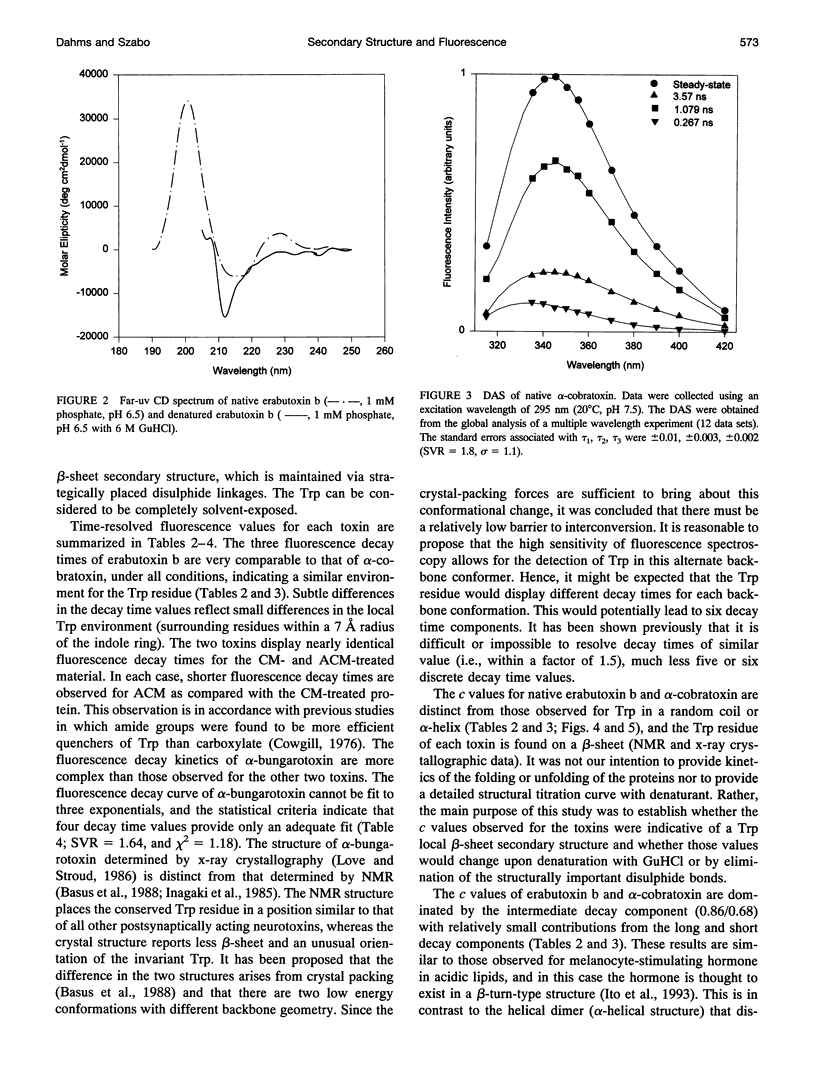
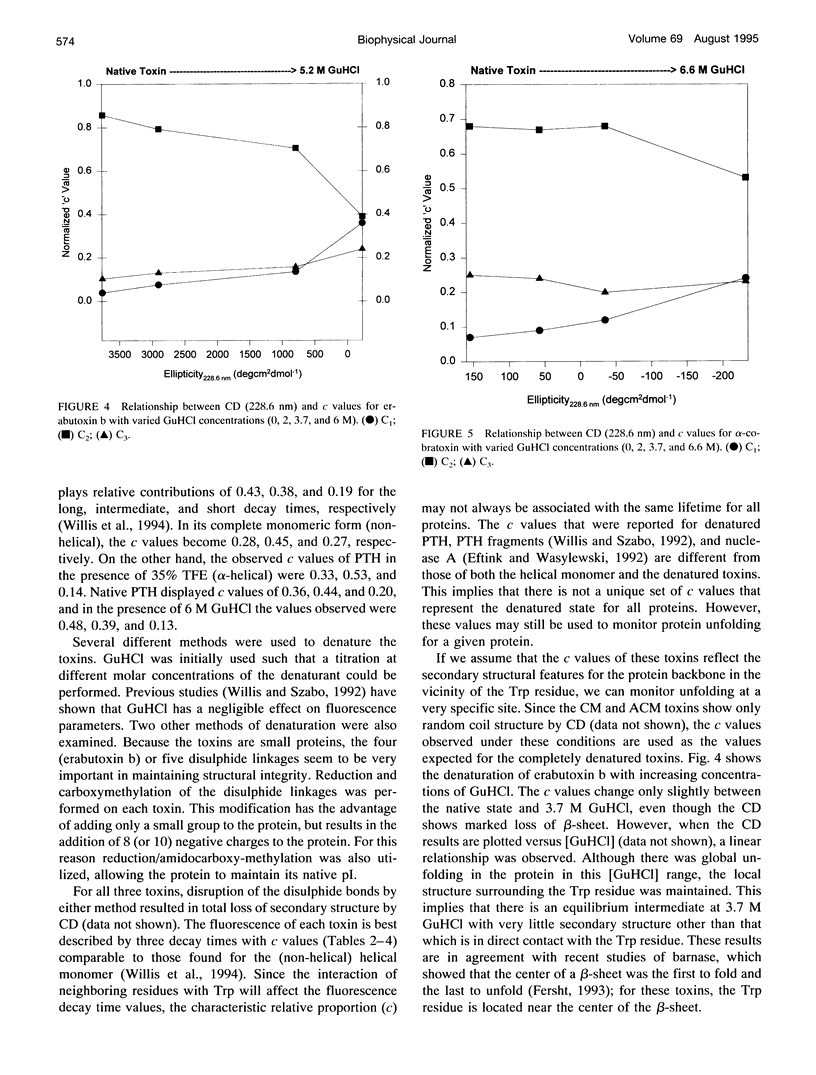
The relationship between beta-sheet secondary structure and intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence parameters of erabutoxin b, alpha-cobratoxin, and alpha-bungarotoxin were examined. Nuclear magnetic resonance and x-ray crystallography have shown that these neurotoxins have comparable beta-sheet, beta-turn, and random coil secondary structures. Each toxin contains a single tryptophan (Trp) residue within its beta-sheet. The time-resolved fluorescence properties of native erabutoxin b and alpha-cobratoxin are best described by triple exponential decay kinetics, whereas native alpha-bungarotoxin exhibits more than four lifetimes. The disulphide bonds of each toxin were reduced to facilitate carboxymethylation and amidocarboxymethylation. The two different toxin derivatives of all three neurotoxins displayed triple exponential decay kinetics and were completely denatured as evidenced by circular dichroism (random coil). The concentration (c) values of the three fluorescence decay times (time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy (TRFS)) were dramatically different from those of the native toxins. Each neurotoxin, treated with different concentrations of guanidinium hydrochloride (GuHCl), was studied both by circular dichroism and TRFS. Disappearance of the beta-sheet secondary structural features with increasing concentrations of GuHCl was accompanied by a shift in the relative contribution (c value) of each fluorescence decay time (TRFS). It was found that certain disulphide residues confer added stability to the beta-sheet secondary structure of these neurotoxins and that the center of the beta-sheet is last to unfold. These titrations show that Trp can be used as a very localized probe of secondary structure.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basus V. J., Billeter M., Love R. A., Stroud R. M., Kuntz I. D. Structural studies of alpha-bungarotoxin. 1. Sequence-specific 1H NMR resonance assignments. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2763–2771. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechem J. M., Brand L. Time-resolved fluorescence of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:43–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunbrack R. L., Jr, Karplus M. Backbone-dependent rotamer library for proteins. Application to side-chain prediction. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):543–574. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R. Fluorescence techniques for studying protein structure. Methods Biochem Anal. 1991;35:127–205. doi: 10.1002/9780470110560.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fersht A. R. The sixth Datta Lecture. Protein folding and stability: the pathway of folding of barnase. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 28;325(1-2):5–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81405-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hider R. C., Drake A. F., Inagaki F., Williams R. J., Endo T., Miyazawa T. Molecular conformation of alpha-cobratoxin as studied by nuclear magnetic resonance and circular dichroism. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):275–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki F., Hider R. C., Hodges S. J., Drake A. F. Molecular conformation of alpha-bungarotoxin as studied by nuclear magnetic resonance and circular dichroism. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):575–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90173-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki F., Tamiya N., Miyazawa T. Molecular conformation and function of erabutoxins as studied by nuclear magnetic resonance. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):129–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A. S., Castrucci A. M., Hruby V. J., Hadley M. E., Krajcarski D. T., Szabo A. G. Structure-activity correlations of melanotropin peptides in model lipids by tryptophan fluorescence studies. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 16;32(45):12264–12272. doi: 10.1021/bi00096a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Wodak S. Conformation of amino acid side-chains in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 5;125(3):357–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goas R., LaPlante S. R., Mikou A., Delsuc M. A., Guittet E., Robin M., Charpentier I., Lallemand J. Y. Alpha-cobratoxin: proton NMR assignments and solution structure. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4867–4875. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love R. A., Stroud R. M. The crystal structure of alpha-bungarotoxin at 2.5 A resolution: relation to solution structure and binding to acetylcholine receptor. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):37–46. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. W., Preston H. S., Sato A., Rosen L. S., Searl J. E., Rudko A. D., Richardson J. S. Three dimensional structure of erabutoxin b neurotoxic protein: inhibitor of acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2991–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor M. J., Islam S. A., Sternberg M. J. Analysis of the relationship between side-chain conformation and secondary structure in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):295–310. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménez A., Montenay-Garestier T., Fromageot P., Hélène C. Conformation of two homologous neurotoxins. Fluorescence and circular dichroism studies. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5202–5208. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piela L., Nemethy G., Scheraga H. A. Conformational constraints of amino acid side chains in alpha-helices. Biopolymers. 1987 Aug;26(8):1273–1286. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. B., Wyssbrod H. R., Porter R. A., Schwartz G. P., Michaels C. A., Laws W. R. Correlation of tryptophan fluorescence intensity decay parameters with 1H NMR-determined rotamer conformations: [tryptophan2]oxytocin. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1585–1594. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrauber H., Eisenhaber F., Argos P. Rotamers: to be or not to be? An analysis of amino acid side-chain conformations in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):592–612. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Corfield P. W., Hendrickson W. A., Low B. W. Refinement at 1.4 A resolution of a model of erabutoxin b: treatment of ordered solvent and discrete disorder. Acta Crystallogr A. 1988 May 1;44(Pt 3):357–368. doi: 10.1107/s0108767388000303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. The crystal structure of a post-synaptic neurotoxin from sea snake at A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkinshaw M. D., Saenger W., Maelicke A. Three-dimensional structure of the "long" neurotoxin from cobra venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2400–2404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis K. J., Neugebauer W., Sikorska M., Szabo A. G. Probing alpha-helical secondary structure at a specific site in model peptides via restriction of tryptophan side-chain rotamer conformation. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1623–1630. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80954-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis K. J., Szabo A. G. Conformation of parathyroid hormone: time-resolved fluorescence studies. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):8924–8931. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]