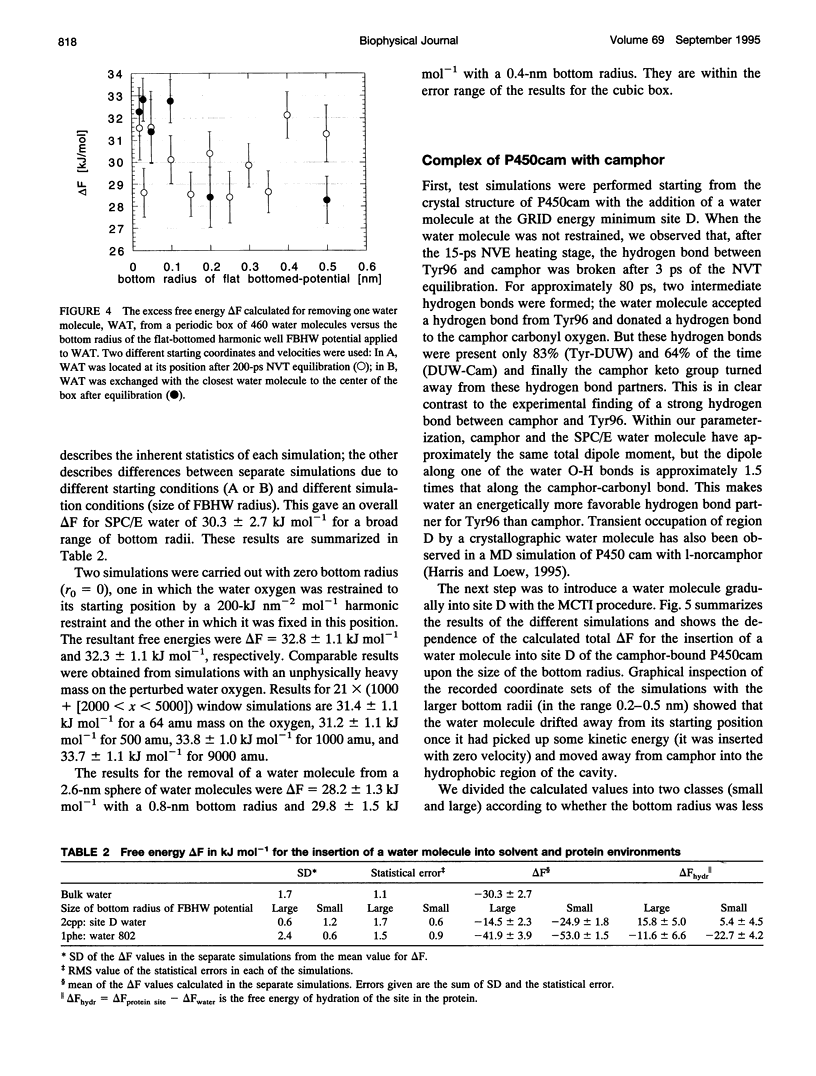
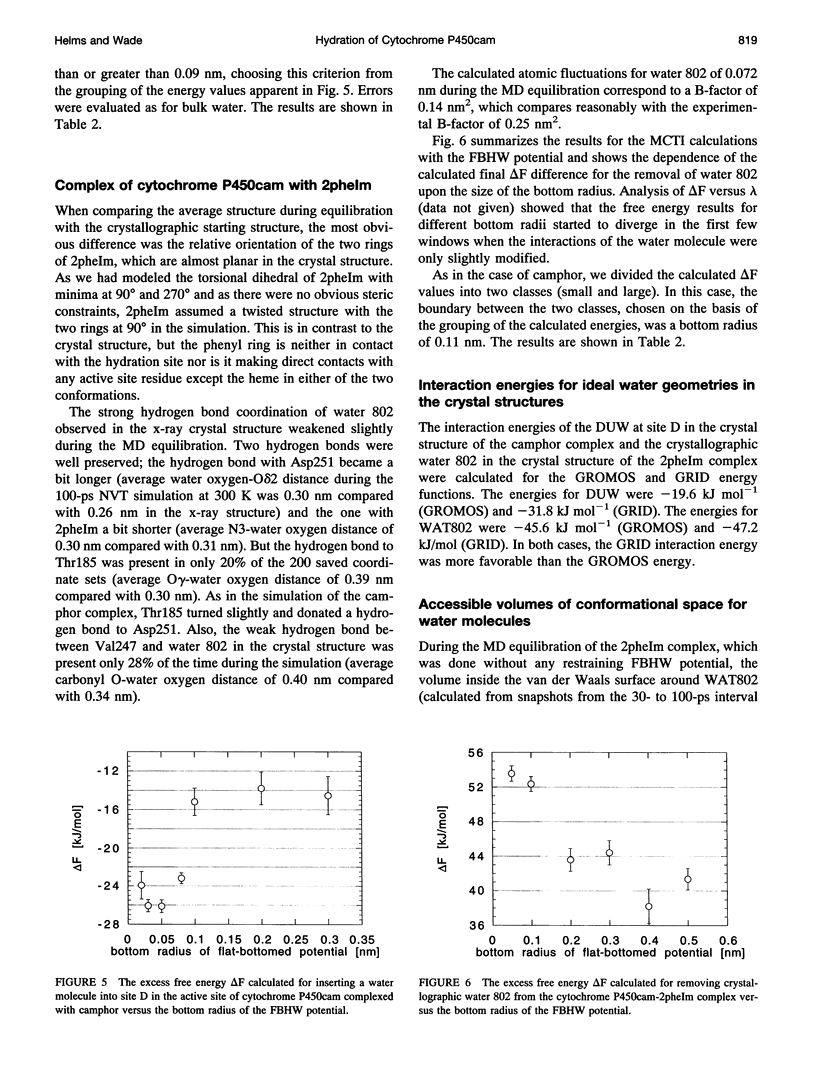
Abstract
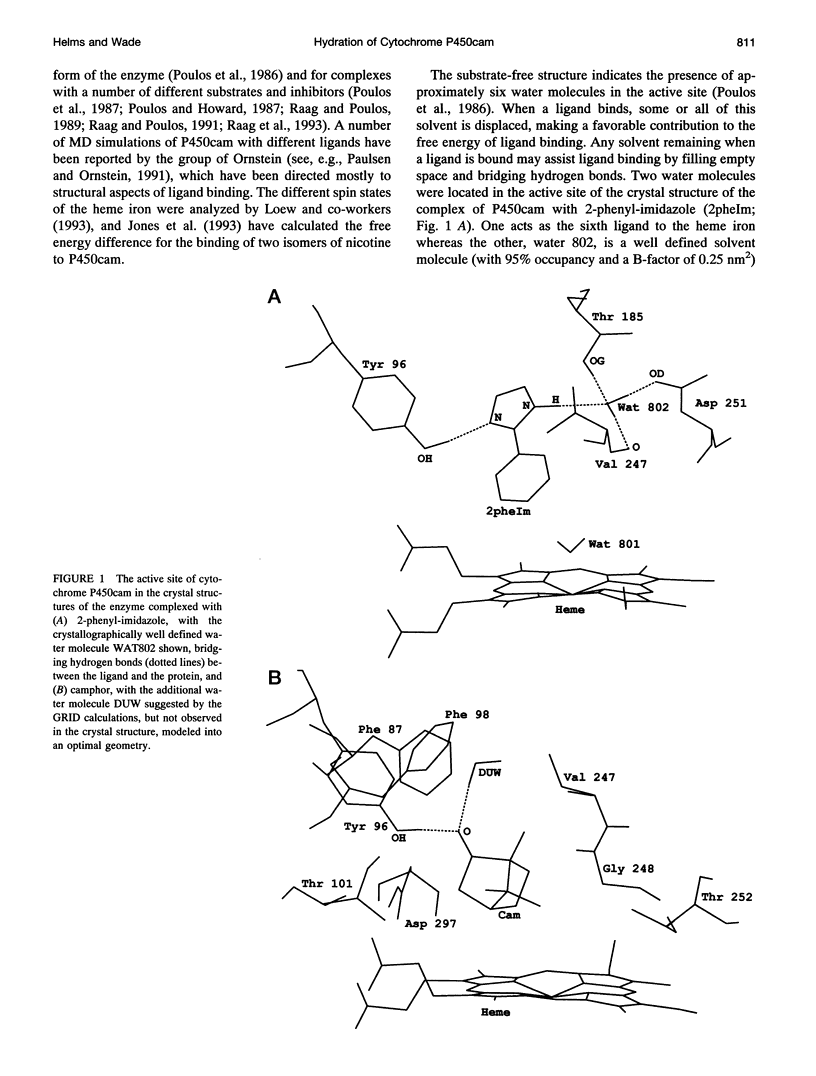
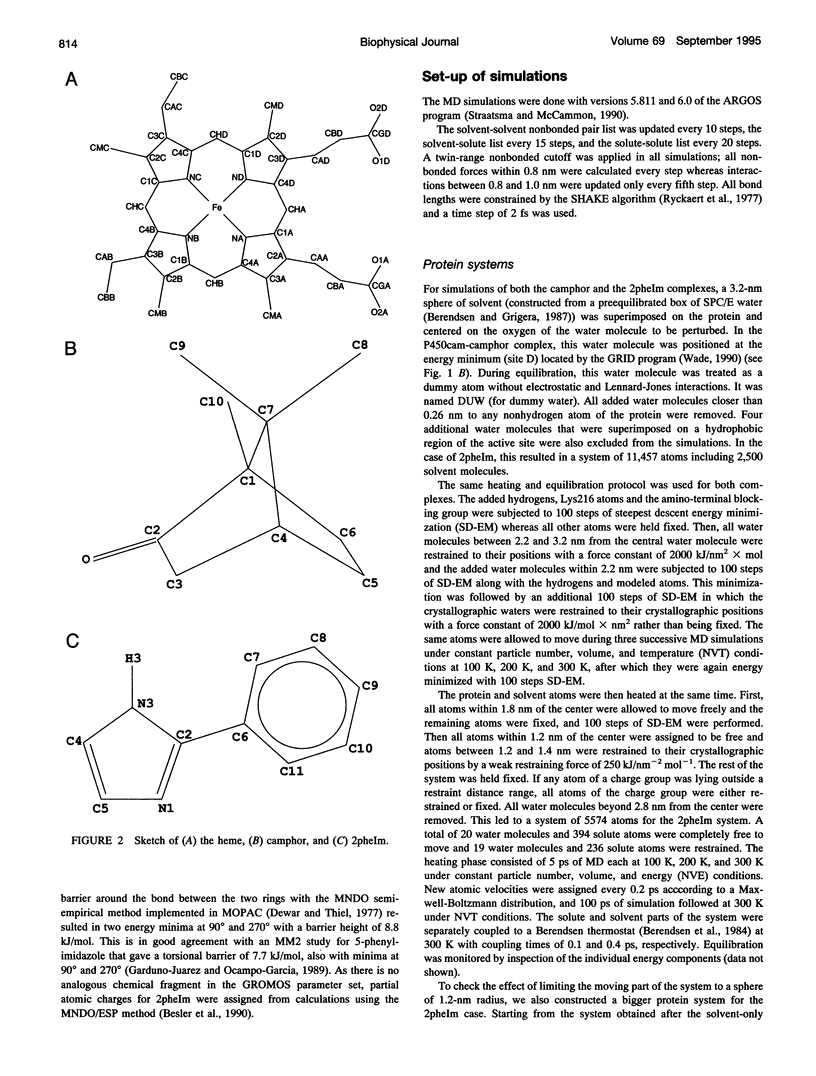
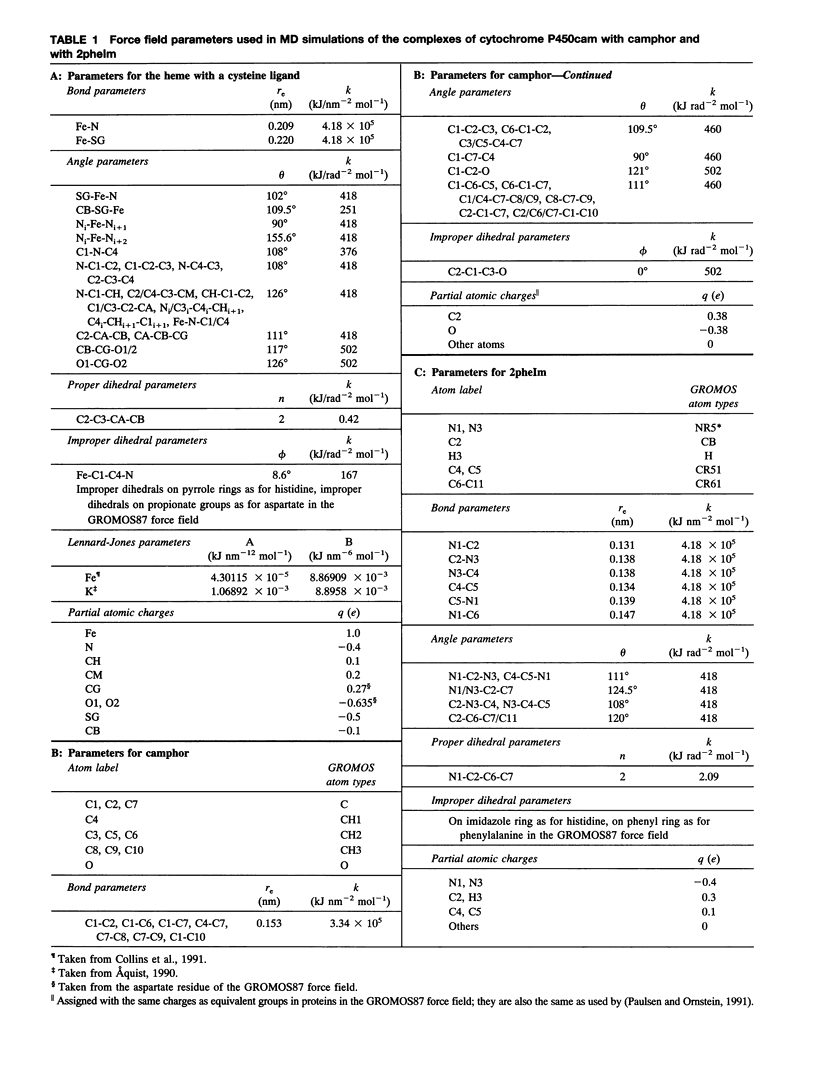
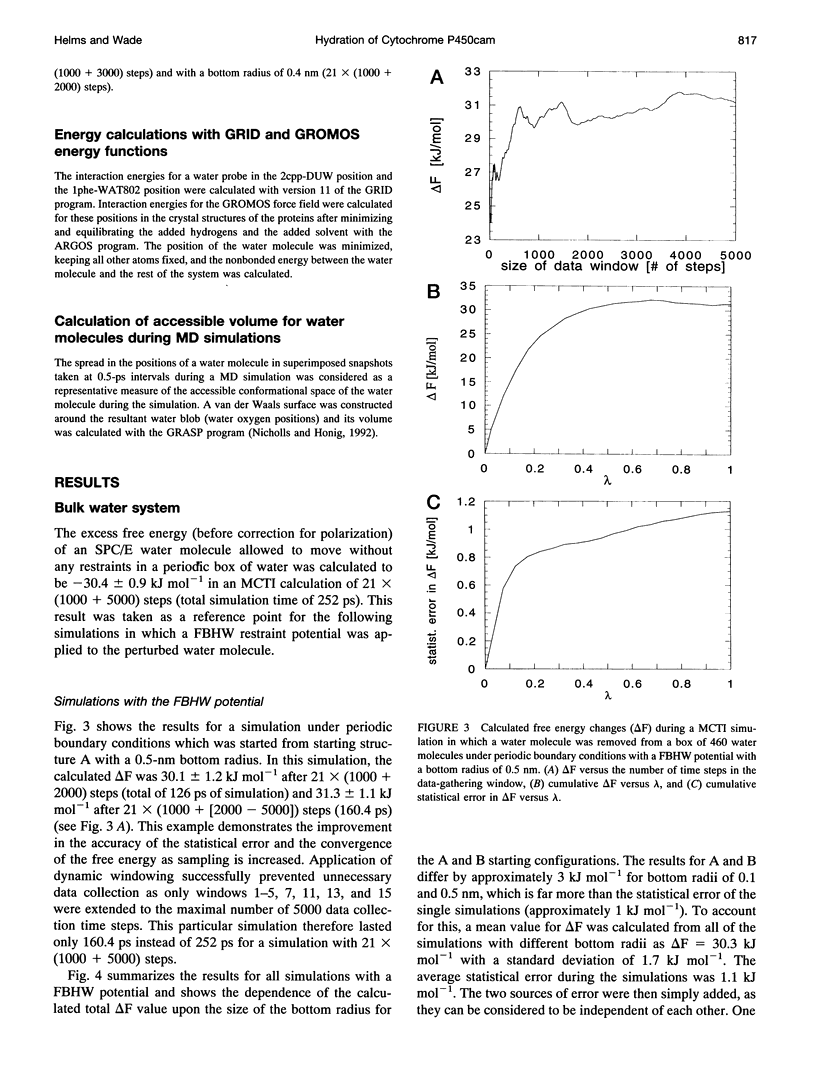
Ordered water molecules are observed by crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance to mediate protein-ligand interactions. Here, we examine the energetics of hydrating cavities formed at protein-ligand interfaces using molecular dynamics simulations. The free energies of hydrating two cavities in the active site of two liganded complexes of cytochrome P450cam were calculated by multiconfigurational thermodynamic integration. The complex of cytochrome P450cam with 2-phenyl-imidazole contains a crystallographically well defined water molecule mediating hydrogen bonds between the protein and the inhibitor. We calculate that this water molecule is stabilized by a binding free energy of -11.6 +/- kJ/mol. The complex of cytochrome P450cam with its natural substrate, camphor, contains a cavity that is empty in the crystal structure although a water molecule in it could make a hydrogen bond to camphor. Here, solvation of this cavity is calculated to be unfavorable by +15.8 +/- 5.0 kJ/mol. The molecular dynamics simulations can thus distinguish a hydrated interfacial cavity from an empty one. They also provide support for the notion that protein-ligand complexes can accommodate empty interfacial cavities and that such cavities are likely to be unhydrated unless more than one hydrogen bond can be made to a water molecule in the cavity.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beamer L. J., Pabo C. O. Refined 1.8 A crystal structure of the lambda repressor-operator complex. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 5;227(1):177–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90690-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge D. L., DiCapua F. M. Free energy via molecular simulation: applications to chemical and biomolecular systems. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:431–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat T. N., Bentley G. A., Boulot G., Greene M. I., Tello D., Dall'Acqua W., Souchon H., Schwarz F. P., Mariuzza R. A., Poljak R. J. Bound water molecules and conformational stabilization help mediate an antigen-antibody association. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boobbyer D. N., Goodford P. J., McWhinnie P. M., Wade R. C. New hydrogen-bond potentials for use in determining energetically favorable binding sites on molecules of known structure. J Med Chem. 1989 May;32(5):1083–1094. doi: 10.1021/jm00125a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Bax A., Omichinski J. G., Gronenborn A. M. Localization of bound water in the solution structure of a complex of the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 with DNA. Structure. 1994 Feb 15;2(2):89–94. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan S. W., Newcomer M. E., Jones T. A. Crystallographic refinement of human serum retinol binding protein at 2A resolution. Proteins. 1990;8(1):44–61. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Primo C., Hui Bon Hoa G., Douzou P., Sligar S. G. Heme-pocket-hydration change during the inactivation of cytochrome P-450camphor by hydrostatic pressure. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 15;209(2):583–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Primo C., Hui Bon Hoa G., Douzou P., Sligar S. Mutagenesis of a single hydrogen bond in cytochrome P-450 alters cation binding and heme solvation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5361–5363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunitz J. D. The entropic cost of bound water in crystals and biomolecules. Science. 1994 Apr 29;264(5159):670–670. doi: 10.1126/science.264.5159.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A. E., Baase W. A., Wozniak J. A., Matthews B. W. A cavity-containing mutant of T4 lysozyme is stabilized by buried benzene. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):371–373. doi: 10.1038/355371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A. E., Baase W. A., Zhang X. J., Heinz D. W., Blaber M., Baldwin E. P., Matthews B. W. Response of a protein structure to cavity-creating mutations and its relation to the hydrophobic effect. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):178–183. doi: 10.1126/science.1553543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst J. A., Clubb R. T., Zhou H. X., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Demonstration of positionally disordered water within a protein hydrophobic cavity by NMR. Science. 1995 Mar 24;267(5205):1813–1817. doi: 10.1126/science.7892604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M. M., Churchill M. J., McRee D. E., Goodin D. B. Small molecule binding to an artificially created cavity at the active site of cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 5;33(13):3807–3818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodford P. J. A computational procedure for determining energetically favorable binding sites on biologically important macromolecules. J Med Chem. 1985 Jul;28(7):849–857. doi: 10.1021/jm00145a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. J., Argos P. Cavities and packing at protein interfaces. Protein Sci. 1994 Dec;3(12):2194–2206. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. J., Gross K. H., Argos P. Intramolecular cavities in globular proteins. Protein Eng. 1994 May;7(5):613–626. doi: 10.1093/protein/7.5.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaLonde J. M., Bernlohr D. A., Banaszak L. J. X-ray crystallographic structures of adipocyte lipid-binding protein complexed with palmitate and hexadecanesulfonic acid. Properties of cavity binding sites. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 26;33(16):4885–4895. doi: 10.1021/bi00182a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenders R., van Gunsteren W. F., Berendsen H. J., Visser A. J. Molecular dynamics simulations of oxidized and reduced Clostridium beijerinckii flavodoxin. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):634–645. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80837-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Vrielink A., Brick P., Blow D. M. Crystal structure of cholesterol oxidase complexed with a steroid substrate: implications for flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent alcohol oxidases. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 2;32(43):11507–11515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen M. D., Bass M. B., Ornstein R. L. Analysis of active site motions from a 175 picosecond molecular dynamics simulation of camphor-bound cytochrome P450cam. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Oct;9(2):187–203. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen M. D., Ornstein R. L. A 175-psec molecular dynamics simulation of camphor-bound cytochrome P-450cam. Proteins. 1991;11(3):184–204. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T. D., Coon M. J. Cytochrome P-450. Multiplicity of isoforms, substrates, and catalytic and regulatory mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13469–13472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Finzel B. C., Howard A. J. Crystal structure of substrate-free Pseudomonas putida cytochrome P-450. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5314–5322. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Finzel B. C., Howard A. J. High-resolution crystal structure of cytochrome P450cam. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):687–700. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Howard A. J. Crystal structures of metyrapone- and phenylimidazole-inhibited complexes of cytochrome P-450cam. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8165–8174. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A., Wilson D. K., Vyas N. K. Substrate specificity and affinity of a protein modulated by bound water molecules. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):404–407. doi: 10.1038/340404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raag R., Li H., Jones B. C., Poulos T. L. Inhibitor-induced conformational change in cytochrome P-450CAM. Biochemistry. 1993 May 4;32(17):4571–4578. doi: 10.1021/bi00068a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raag R., Poulos T. L. Crystal structures of cytochrome P-450CAM complexed with camphane, thiocamphor, and adamantane: factors controlling P-450 substrate hydroxylation. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 12;30(10):2674–2684. doi: 10.1021/bi00224a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raag R., Poulos T. L. The structural basis for substrate-induced changes in redox potential and spin equilibrium in cytochrome P-450CAM. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):917–922. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Fuller N. L., Butko P., Francis G., Nicholls P. Measured change in protein solvation with substrate binding and turnover. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 15;32(23):5925–5929. doi: 10.1021/bi00074a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel T. J., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R. Refined structure of the hirudin-thrombin complex. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):583–601. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakked Z., Guzikevich-Guerstein G., Frolow F., Rabinovich D., Joachimiak A., Sigler P. B. Determinants of repressor/operator recognition from the structure of the trp operator binding site. Nature. 1994 Mar 31;368(6470):469–473. doi: 10.1038/368469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. E., van Gunsteren W. F. Translational and rotational diffusion of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 18;236(2):629–636. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varadarajan R., Richards F. M. Crystallographic structures of ribonuclease S variants with nonpolar substitution at position 13: packing and cavities. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12315–12327. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade R. C., Clark K. J., Goodford P. J. Further development of hydrogen bond functions for use in determining energetically favorable binding sites on molecules of known structure. 1. Ligand probe groups with the ability to form two hydrogen bonds. J Med Chem. 1993 Jan 8;36(1):140–147. doi: 10.1021/jm00053a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade R. C., Goodford P. J. Further development of hydrogen bond functions for use in determining energetically favorable binding sites on molecules of known structure. 2. Ligand probe groups with the ability to form more than two hydrogen bonds. J Med Chem. 1993 Jan 8;36(1):148–156. doi: 10.1021/jm00053a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade R. C., Mazor M. H., McCammon J. A., Quiocho F. A. A molecular dynamics study of thermodynamic and structural aspects of the hydration of cavities in proteins. Biopolymers. 1991 Jul;31(8):919–931. doi: 10.1002/bip.360310802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade R. C. Solvation of the active site of cytochrome P450-cam. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 1990 Jun;4(2):199–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00125318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. A., Goodfellow J. M., Thornton J. M. Buried waters and internal cavities in monomeric proteins. Protein Sci. 1994 Aug;3(8):1224–1235. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R., Radzicka A. On the probability of finding a water molecule in a nonpolar cavity. Science. 1994 Aug 12;265(5174):936–937. doi: 10.1126/science.8052849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias M., Straatsma T. P., McCammon J. A., Quiocho F. A. Inversion of receptor binding preferences by mutagenesis: free energy thermodynamic integration studies on sugar binding to L-arabinose binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 27;32(29):7428–7434. doi: 10.1021/bi00080a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gunsteren W. F., Mark A. E. On the interpretation of biochemical data by molecular dynamics computer simulation. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 15;204(3):947–961. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


