Abstract
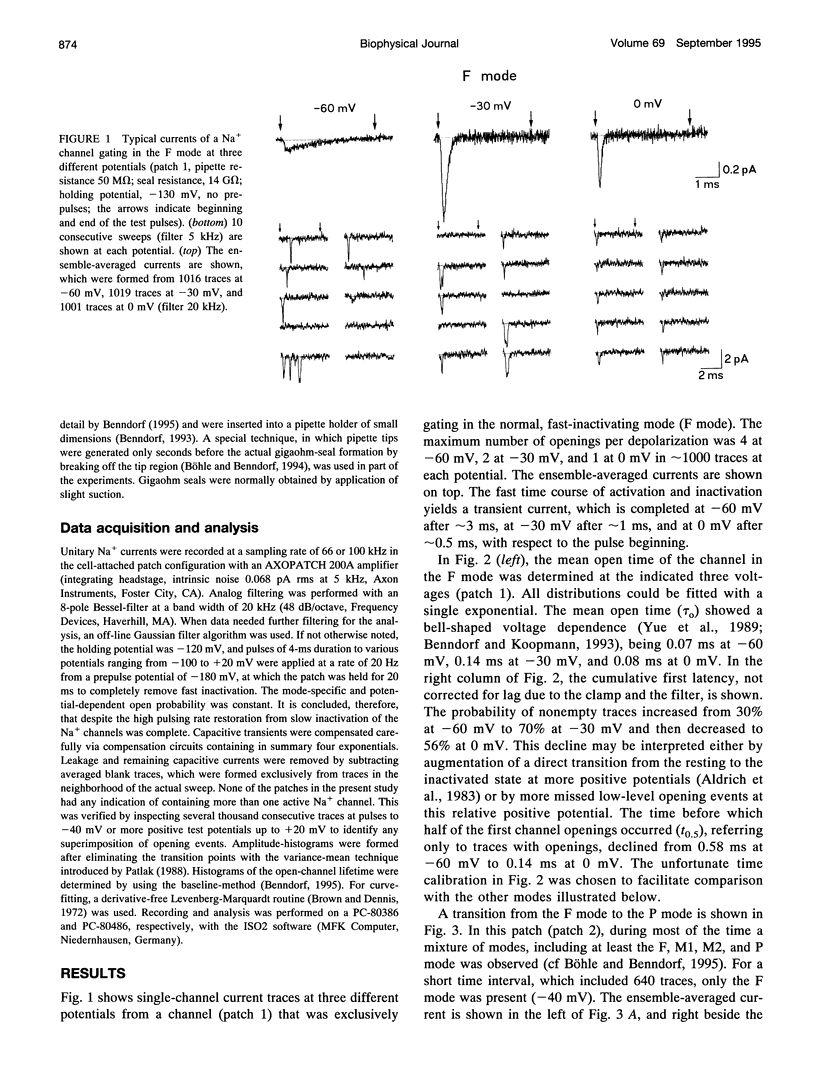
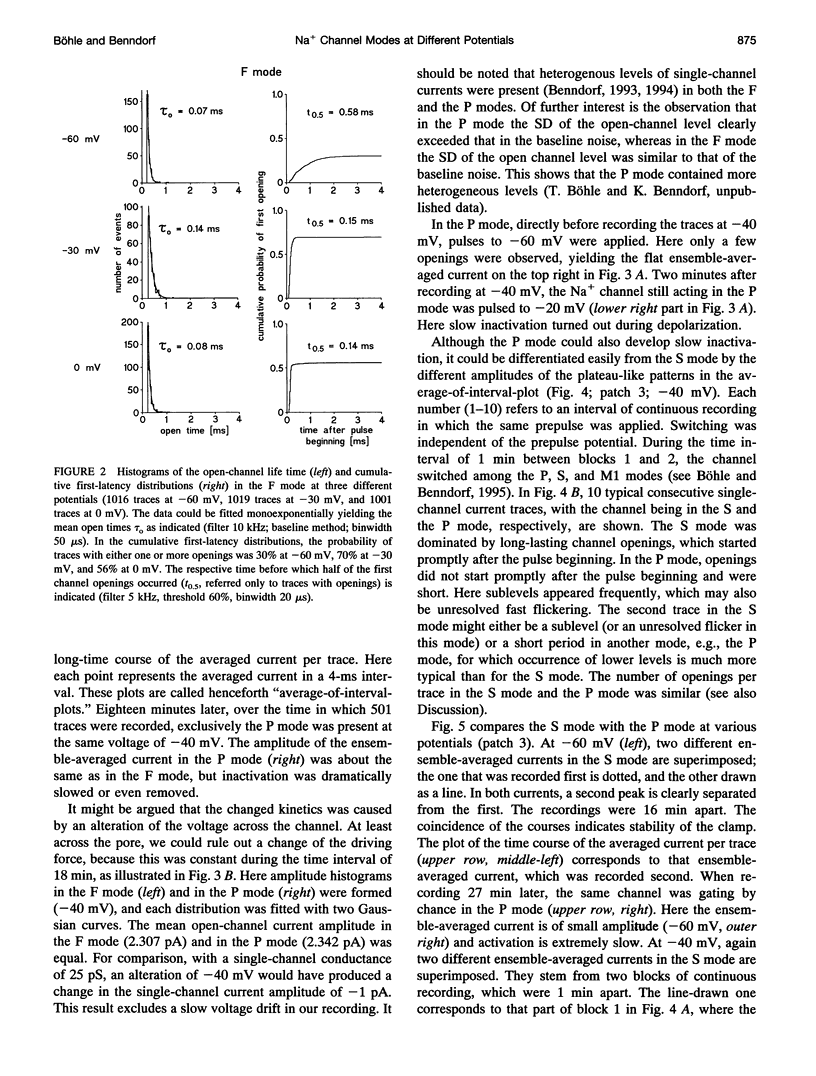
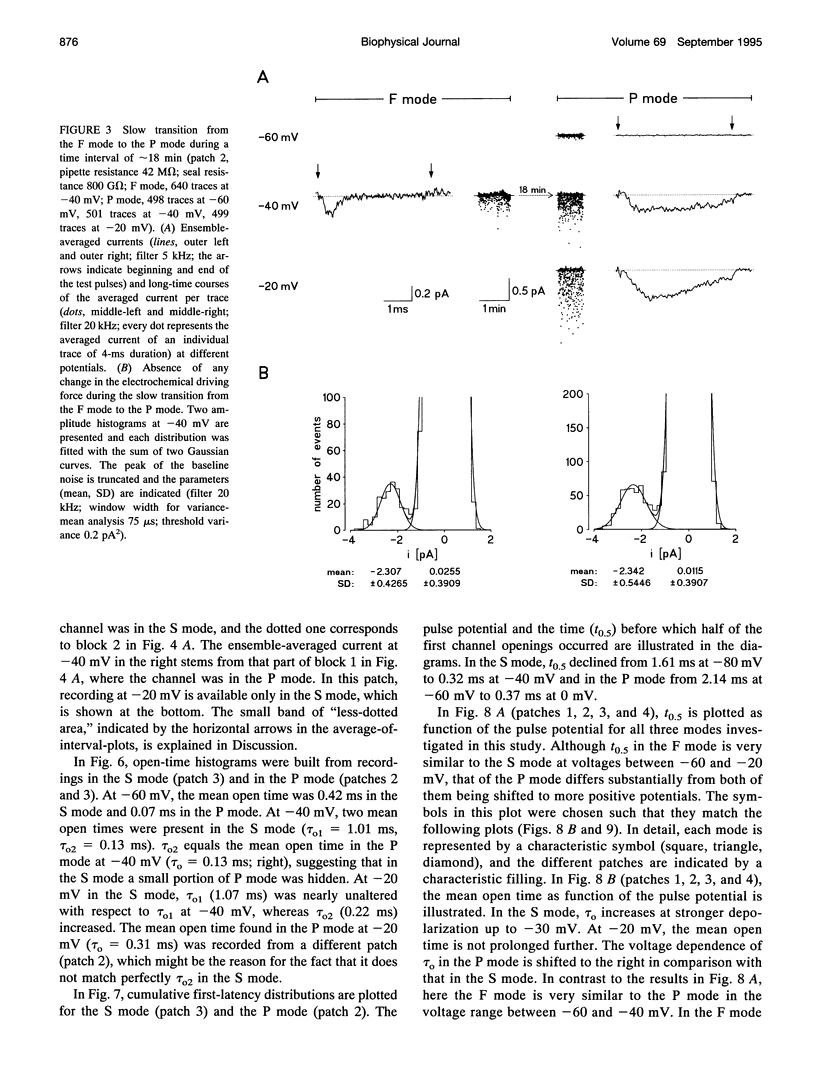
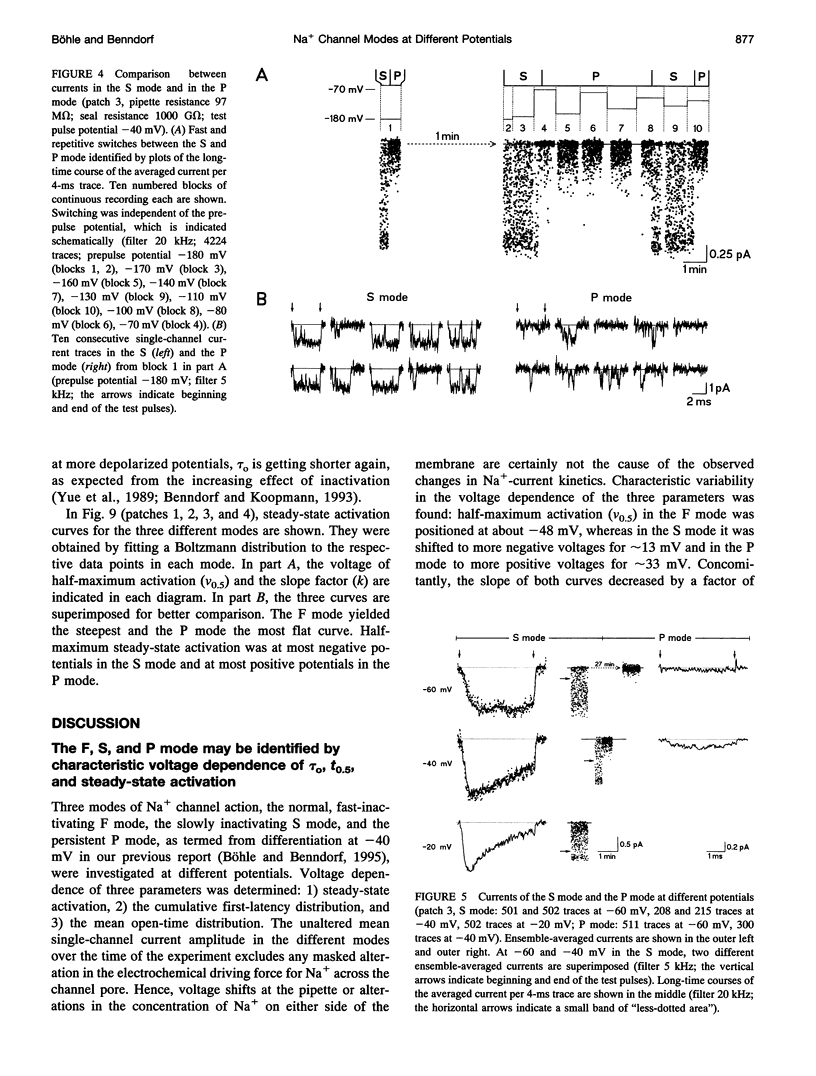
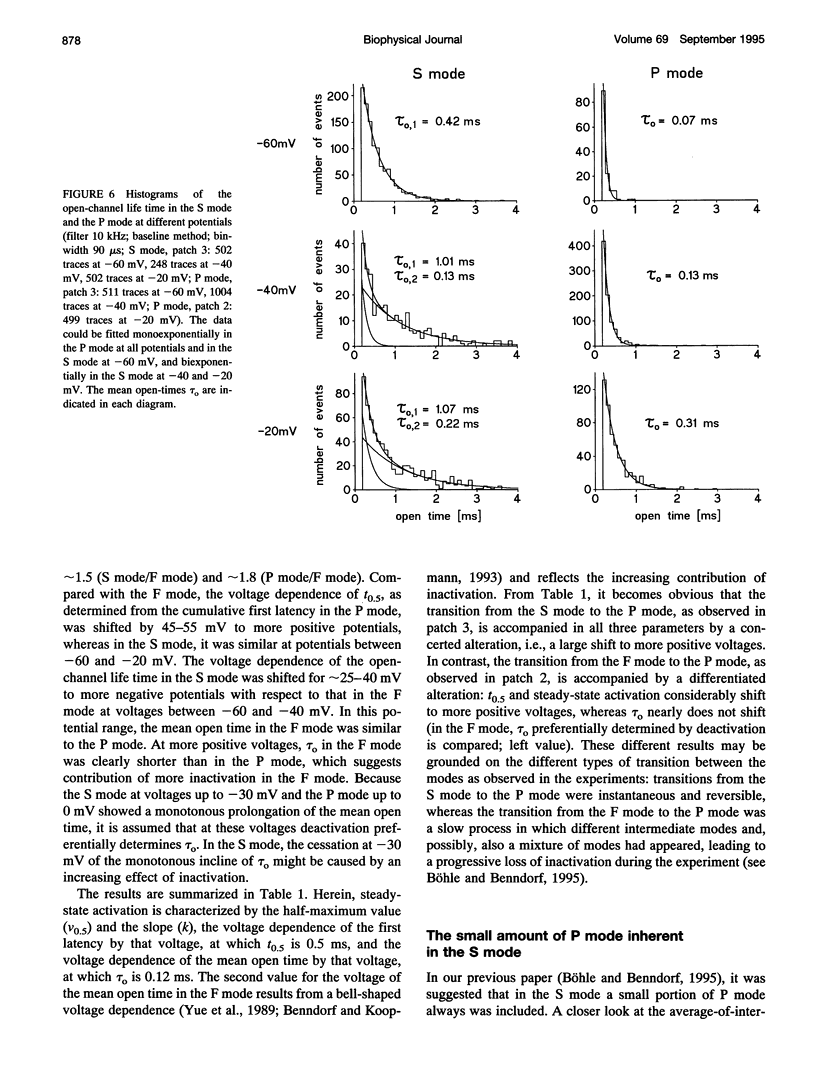
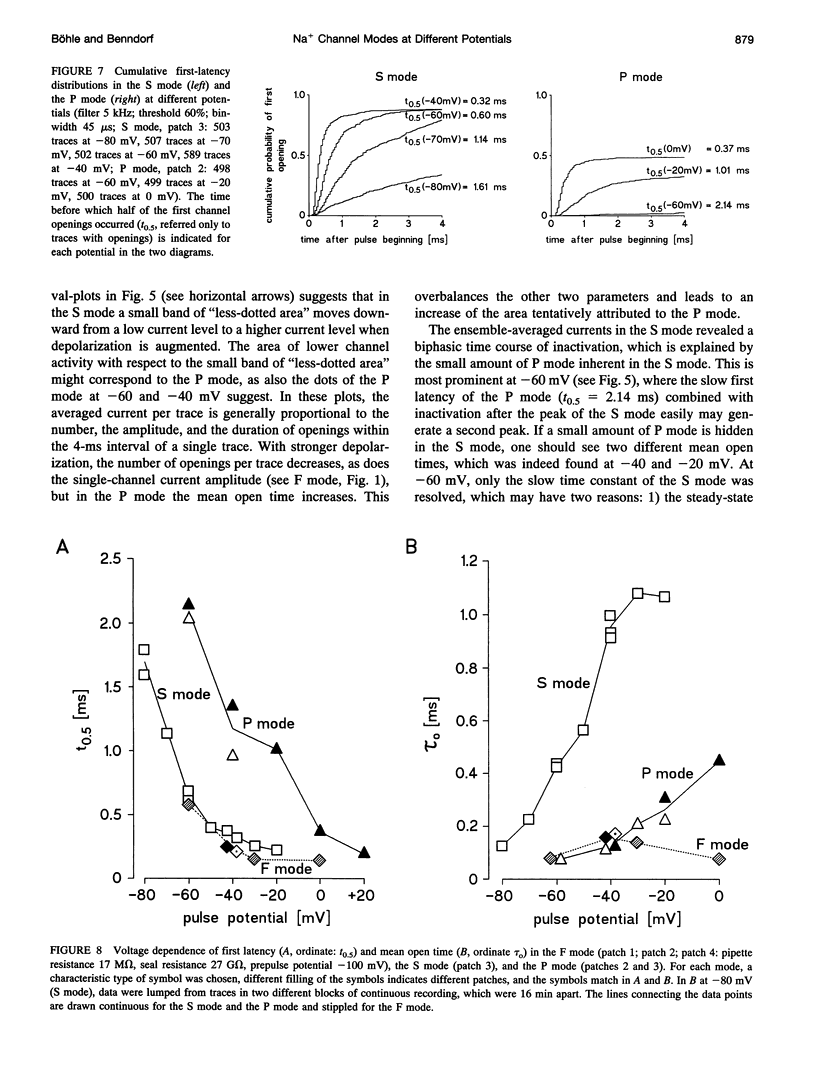
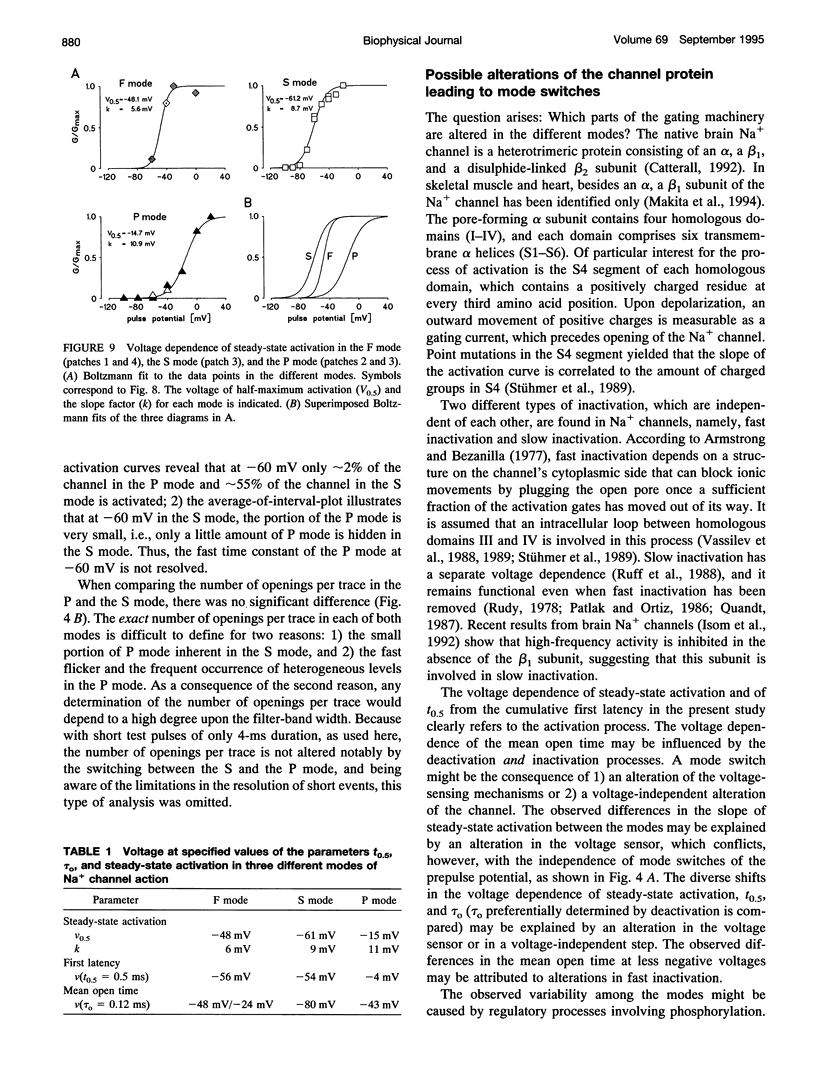
Three different modes of Na+ channel action, the F mode (fast inactivating), the S mode (slowly inactivating), and the P mode (persistent), were studied at different potentials in exceptionally small cell-attached patches containing one and only one channel. Switching between the modes was independent of voltage. In the F mode, the mean open time (tau o) at -30 and -40 mV was 0.14 and 0.16 ms, respectively, which was significantly larger than at -60 and 0 mV, where the values were 0.07 and 0.08 ms, respectively. The time before which half of the first channel openings occurred (t 0.5), decreased from 0.58 ms at -60 mV to 0.14 ms at 0 mV. The fit of steady-state activation with a Boltzmann function yielded a half-maximum value (V 0.5) at -48.1 mV and a slope (k) of 5.6 mV. The mean open time in the S mode increased steadily from 0.12 ms at -80 mV to 1.09 ms at -30 mV, but was not prolonged further at -20 mV (1.07 ms). Concomitantly, t 0.5 decreased from 1.61 ms at -80 mV to 0.22 ms at -20mV. Here the midpoint of steady-state activation was found at -61.2 mV, and the slope was 8.7 mV. The mean open time in the P mode increased from 0.07 ms at -60 mV to 0.45 ms at 0 mV and t 0.5 declined from 2.14 ms at -60 mV to 0.19 ms at +20 mV. Steady-state activation had its midpoint at -14.7 mV, and the slope was 10.9 mV. It is concluded that a single Na+ channel may switch among the F, S, and P mode and that the three modes differ by a characteristic pattern of voltage dependence of tau 0, t 0.5, and steady-state activation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldrich R. W., Corey D. P., Stevens C. F. A reinterpretation of mammalian sodium channel gating based on single channel recording. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):436–441. doi: 10.1038/306436a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):567–590. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Cohen I., Eisner D., Ohba M., Ojeda C. The steady state TTX-sensitive ("window") sodium current in cardiac Purkinje fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Mar 16;379(2):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00586939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benndorf K., Koopmann R. Thermodynamic entropy of two conformational transitions of single Na+ channel molecules. Biophys J. 1993 Oct;65(4):1585–1589. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81197-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benndorf K. Multiple levels of native cardiac Na+ channels at elevated temperature measured with high-bandwidth/low-noise patch clamp. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Feb;422(5):506–515. doi: 10.1007/BF00375079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benndorf K., Nilius B. Inactivation of sodium channels in isolated myocardial mouse cells. Eur Biophys J. 1987;15(2):117–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00257505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benndorf K. Properties of single cardiac Na channels at 35 degrees C. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Nov;104(5):801–820. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.5.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Lee K. S., Powell T. Sodium current in single rat heart muscle cells. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:479–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N. A., Undrovinas A. I., Fleidervish I. A., Rosenshtraukh L. V. Ischemic poison lysophosphatidylcholine modifies heart sodium channels gating inducing long-lasting bursts of openings. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Oct;415(1):124–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00373151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhle T., Benndorf K. Facilitated giga-seal formation with a just originated glass surface. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Jul;427(5-6):487–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00374265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhle T., Benndorf K. Multimodal action of single Na+ channels in myocardial mouse cells. Biophys J. 1995 Jan;68(1):121–130. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80166-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachelin A. B., De Peyer J. E., Kokubun S., Reuter H. Sodium channels in cultured cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:389–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello H. F., Stow J. L., Prat A. G., Ausiello D. A. Actin filaments regulate epithelial Na+ channel activity. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):C882–C888. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.5.C882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E. Slow inactivation of the sodium current in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Jan;408(1):18–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00581835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S15–S48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):50–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2459775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corr P. B., Cain M. E., Witkowski F. X., Price D. A., Sobel B. E. Potential arrhythmogenic electrophysiological derangements in canine Purkinje fibers induced by lysophosphoglycerides. Circ Res. 1979 Jun;44(6):822–832. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.6.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corr P. B., Gross R. W., Sobel B. E. Arrhythmogenic amphiphilic lipids and the myocardial cell membrane. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1982 Nov;14(11):619–626. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(82)90159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corr P. B., Witkowski F. X., Sobel B. E. Mechanisms contributing to malignant dysrhythmias induced by ischemia in the cat. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):109–119. doi: 10.1172/JCI108908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M. R., Casnellie J. E., Catterall W. A. Selective phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the sodium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7918–7921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M. R., Catterall W. A. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the sodium channel in synaptic nerve ending particles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8210–8218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M. R., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the sodium channel by protein kinase C. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1984 Sep;4(3):291–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00733592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant A. O., Starmer C. F., Strauss H. C. Unitary sodium channels in isolated cardiac myocytes of rabbit. Circ Res. 1983 Dec;53(6):823–829. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.6.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlhardt M., Fröbe U., Herzig J. W. Properties of normal and non-inactivating single cardiac Na+ channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Oct 22;232(1266):71–93. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze D. L., Lacerda A. E., Wilson D. L., Brown A. M. Cardiac Na currents and the inactivating, reopening, and waiting properties of single cardiac Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):691–719. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Weeks T. A., Kao R. L., Akaike N., Brown A. M. Sodium current in single heart muscle cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):269–271. doi: 10.1038/278269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., West J. W., Numann R., Murphy B. J., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Convergent regulation of sodium channels by protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1993 Sep 10;261(5127):1439–1442. doi: 10.1126/science.8396273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. M., DeFelice L. J., Mazzanti M. Na channels that remain open throughout the cardiac action potential plateau. Biophys J. 1992 Sep;63(3):654–662. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81635-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makita N., Bennett P. B., Jr, George A. L., Jr Voltage-gated Na+ channel beta 1 subunit mRNA expressed in adult human skeletal muscle, heart, and brain is encoded by a single gene. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7571–7578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzanti M., DeFelice L. J. Na channel kinetics during the spontaneous heart beat in embryonic chick ventricle cells. Biophys J. 1987 Jul;52(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83192-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. J., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of purified rat brain Na+ channel reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16129–16134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R., Catterall W. A., Scheuer T. Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):115–118. doi: 10.1126/science.1656525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Fozzard H. A., Hanck D. A. Mechanism of cAMP-dependent modulation of cardiac sodium channel current kinetics. Circ Res. 1993 Apr;72(4):807–815. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.4.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Ortiz M. Slow currents through single sodium channels of the adult rat heart. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jul;86(1):89–104. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Ortiz M. Two modes of gating during late Na+ channel currents in frog sartorius muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Feb;87(2):305–326. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B. Sodium channel subconductance levels measured with a new variance-mean analysis. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Oct;92(4):413–430. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. Molecular kinetics of voltage-dependent Na+ channels. Physiol Rev. 1991 Oct;71(4):1047–1080. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.4.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N. Burst kinetics of sodium channels which lack fast inactivation in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:563–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossie S., Catterall W. A. Cyclic-AMP-dependent phosphorylation of voltage-sensitive sodium channels in primary cultures of rat brain neurons. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12735–12744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Simoncini L., Stühmer W. Slow sodium channel inactivation in mammalian muscle: a possible role in regulating excitability. Muscle Nerve. 1988 May;11(5):502–510. doi: 10.1002/mus.880110514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppersberg J. P., Stocker M., Pongs O., Heinemann S. H., Frank R., Koenen M. Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian IK(A) channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):711–714. doi: 10.1038/352711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokabe M., Sachs F., Jing Z. Q. Quantitative video microscopy of patch clamped membranes stress, strain, capacitance, and stretch channel activation. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):722–728. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82285-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):597–603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunami A., Fan Z., Nakamura F., Naka M., Tanaka T., Sawanobori T., Hiraoka M. The catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase directly inhibits sodium channel activities in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Oct;419(3-4):415–417. doi: 10.1007/BF00371125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P. M., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Identification of an intracellular peptide segment involved in sodium channel inactivation. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Inhibition of inactivation of single sodium channels by a site-directed antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8147–8151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellis D. P., DeFelice L. J., Mazzanti M. Outward sodium current in beating heart cells. Biophys J. 1990 Jan;57(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82505-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue D. T., Lawrence J. H., Marban E. Two molecular transitions influence cardiac sodium channel gating. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):349–352. doi: 10.1126/science.2540529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


