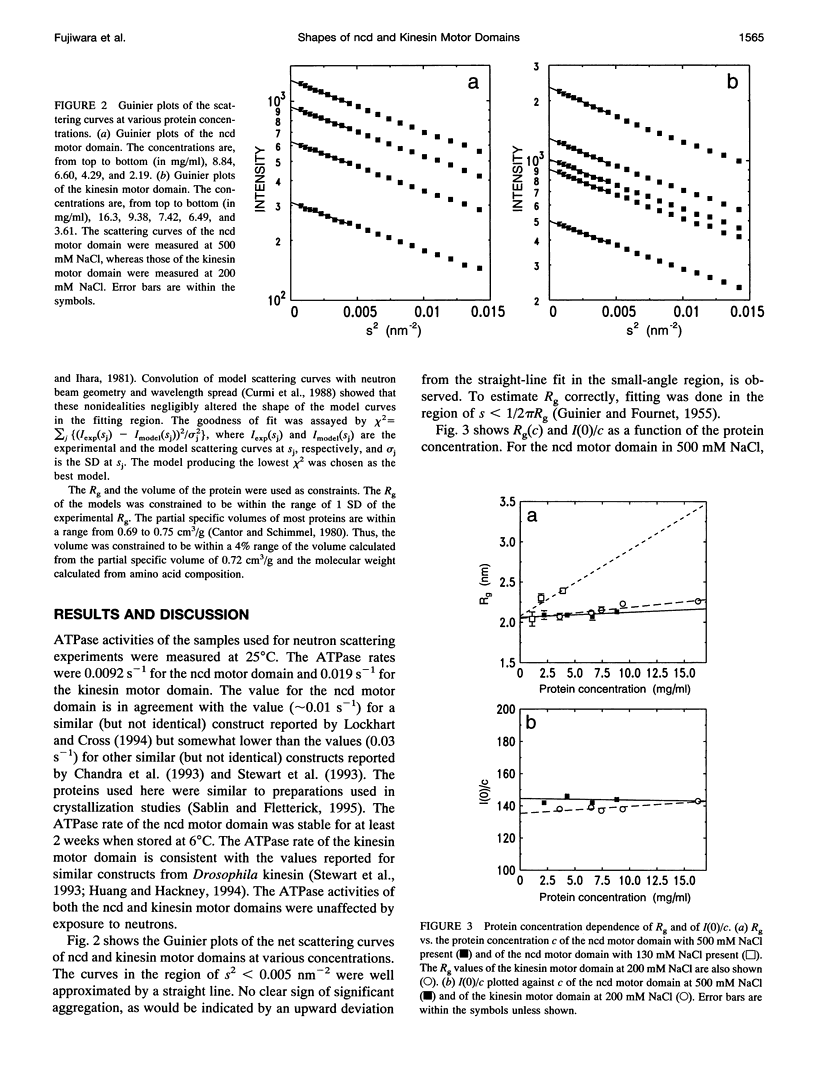
Abstract
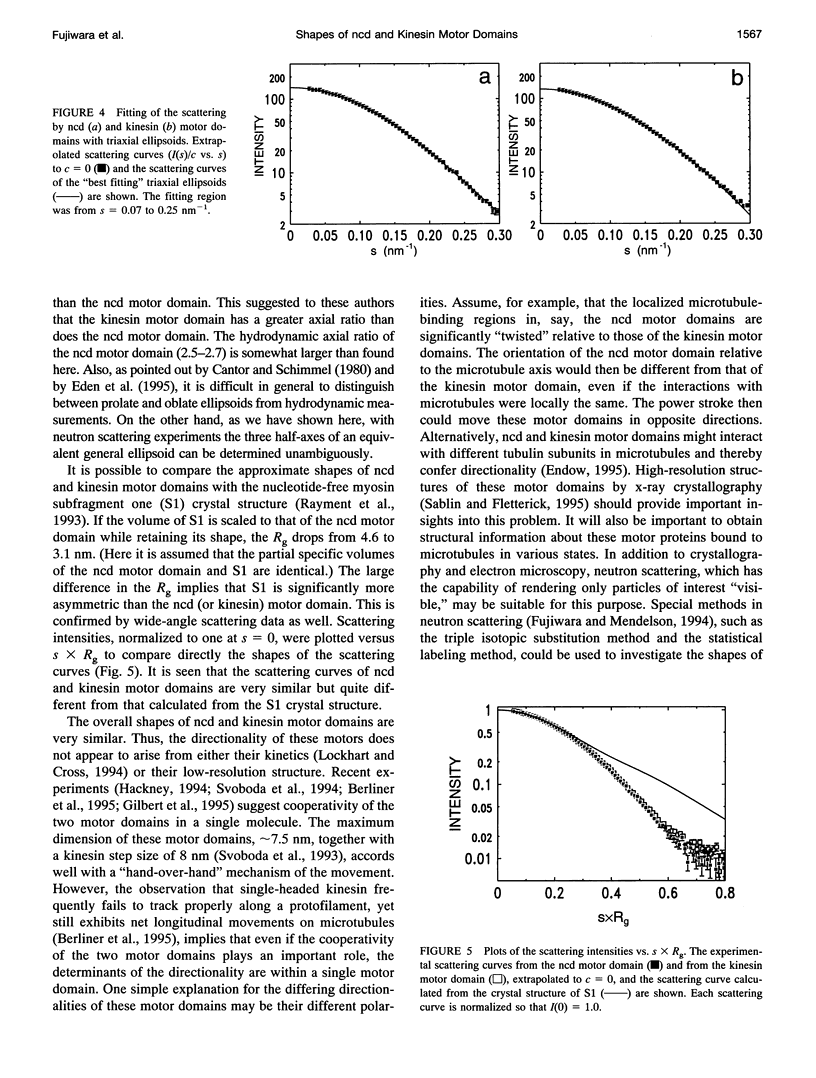
The shapes of the motor domains of kinesin and ncd, which move in opposite directions along microtubules, have been investigated. Using proteins expressed in Escherichia coli, it was found that at high salt (> 200 mM) Drosophila ncd motor domain (R335-K700) and human kinesin motor domain (M1-E349) were both sufficiently monomeric to allow an accurate determination of their radii of gyration (Rg) and their molecular weights. The measured Rg values of the ncd and kinesin motor domains in D2O were 2.06 +/- 0.06 and 2.05 +/- 0.04 nm, respectively, and the molecular weights were consistent with those computed from the amino acid compositions. Fitting of the scattering curves to approximately 3.5 nm resolution showed that the ncd and kinesin motor domains can be described adequately by triaxial ellipsoids having half-axes of 1.42 +/- 0.38, 2.24 +/- 0.44, and 3.65 +/- 0.22 nm, and half-axes of 1.52 +/- 0.23, 2.00 +/- 0.25, and 3.73 +/- 0.10 nm, respectively. Both motor domains are described adequately as somewhat flattened prolate ellipsoids with a maximum dimension of approximately 7.5 nm. Thus, it appears that the overall shapes of these motor domains are not the major determinants of the directionality of their movement along microtubules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berliner E., Young E. C., Anderson K., Mahtani H. K., Gelles J. Failure of a single-headed kinesin to track parallel to microtubule protofilaments. Nature. 1995 Feb 23;373(6516):718–721. doi: 10.1038/373718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra R., Salmon E. D., Erickson H. P., Lockhart A., Endow S. A. Structural and functional domains of the Drosophila ncd microtubule motor protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):9005–9013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curmi P. M., Stone D. B., Schneider D. K., Spudich J. A., Mendelson R. A. Comparison of the structure of myosin subfragment 1 bound to actin and free in solution. A neutron scattering study using actin made "invisible" by deuteration. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):781–798. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden D., Luu B. Q., Zapata D. J., Sablin E. P., Kull F. J. Solution structure of two molecular motor domains: nonclaret disjunctional and kinesin. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):59S–65S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A. Determinants of motor polarity in the kinesin proteins. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):271S–274S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endow S. A., Henikoff S., Soler-Niedziela L. Mediation of meiotic and early mitotic chromosome segregation in Drosophila by a protein related to kinesin. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):81–83. doi: 10.1038/345081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert S. P., Webb M. R., Brune M., Johnson K. A. Pathway of processive ATP hydrolysis by kinesin. Nature. 1995 Feb 23;373(6516):671–676. doi: 10.1038/373671a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodson H. V., Kang S. J., Endow S. A. Molecular phylogeny of the kinesin family of microtubule motor proteins. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jul;107(Pt 7):1875–1884. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.7.1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D. Evidence for alternating head catalysis by kinesin during microtubule-stimulated ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6865–6869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. G., Hackney D. D. Drosophila kinesin minimal motor domain expressed in Escherichia coli. Purification and kinetic characterization. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16493–16501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. G., Suhan J., Hackney D. D. Drosophila kinesin motor domain extending to amino acid position 392 is dimeric when expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16502–16507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibel K. Comparison of neutron and X-ray scattering of dilute myoglobin solutions. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart A., Cross R. A. Origins of reversed directionality in the ncd molecular motor. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):751–757. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald H. B., Goldstein L. S. Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a kinesin-like protein in Drosophila. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):991–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90064-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sablin E. P., Fletterick R. J. Crystallization and preliminary structural studies of the ncd motor domain. Proteins. 1995 Jan;21(1):68–69. doi: 10.1002/prot.340210108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenborn B. P. Advantages of neutron scattering for biological structure analysis. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1976 May;(27):110–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. J., Thaler J. P., Goldstein L. S. Direction of microtubule movement is an intrinsic property of the motor domains of kinesin heavy chain and Drosophila ncd protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5209–5213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda K., Mitra P. P., Block S. M. Fluctuation analysis of motor protein movement and single enzyme kinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):11782–11786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.11782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda K., Schmidt C. F., Schnapp B. J., Block S. M. Direct observation of kinesin stepping by optical trapping interferometry. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):721–727. doi: 10.1038/365721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., Salmon E. D., Endow S. A. The Drosophila claret segregation protein is a minus-end directed motor molecule. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):780–782. doi: 10.1038/347780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D. Special instrumentation and techniques for kinetic studies of contractile systems. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):698–708. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]