Abstract
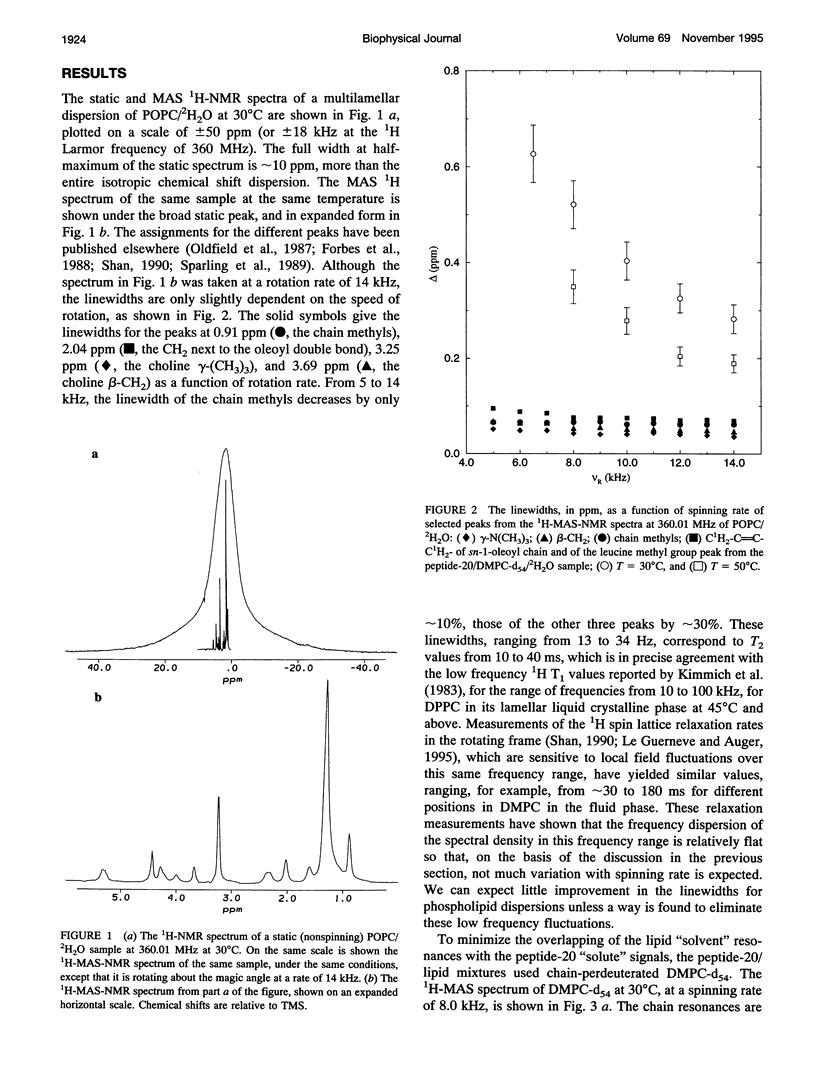
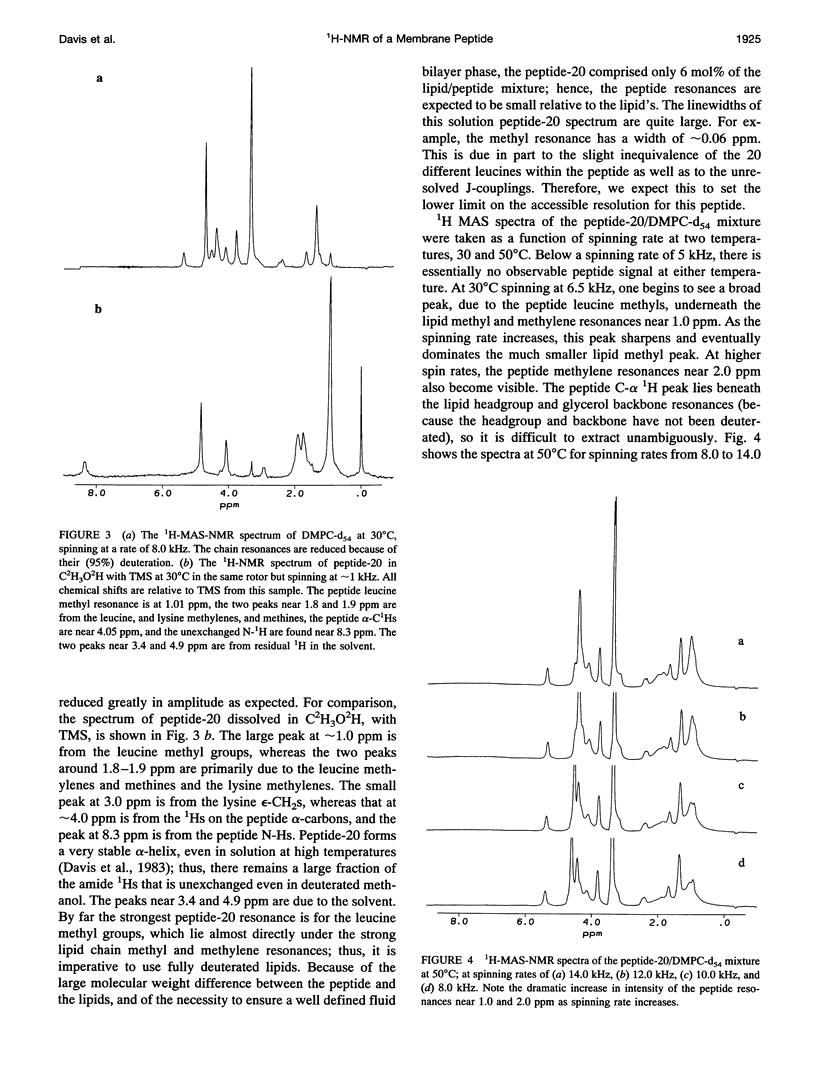
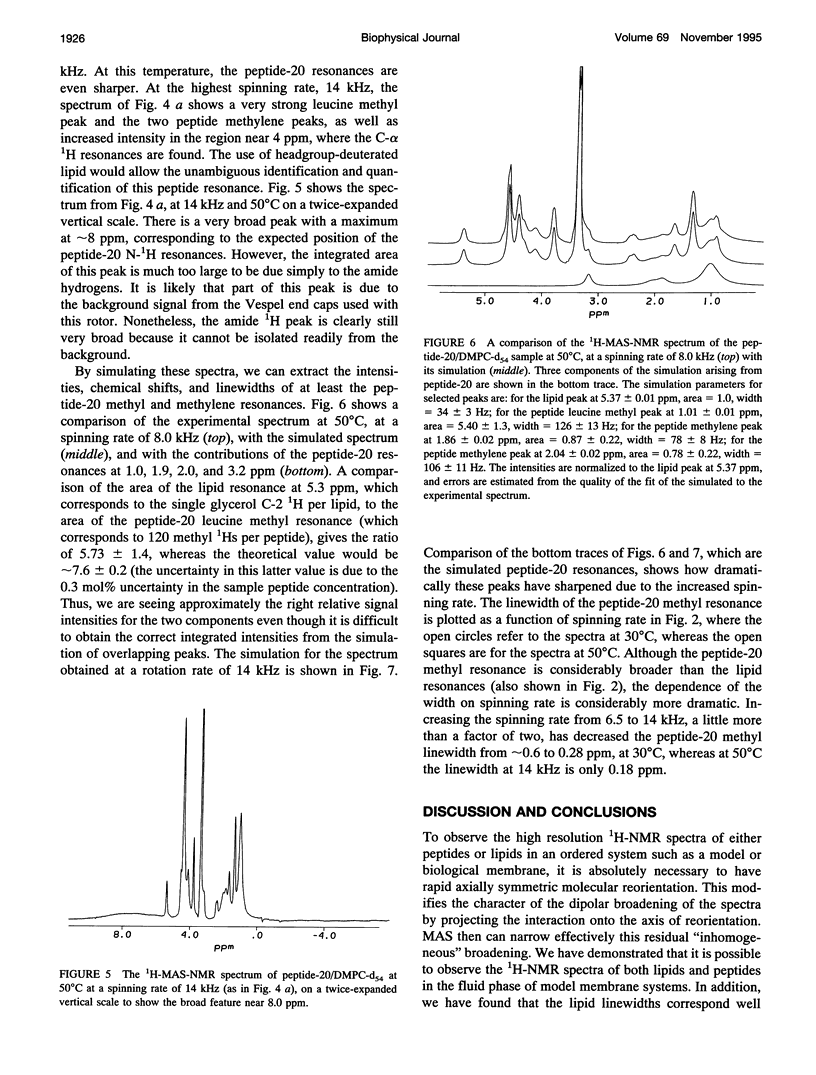
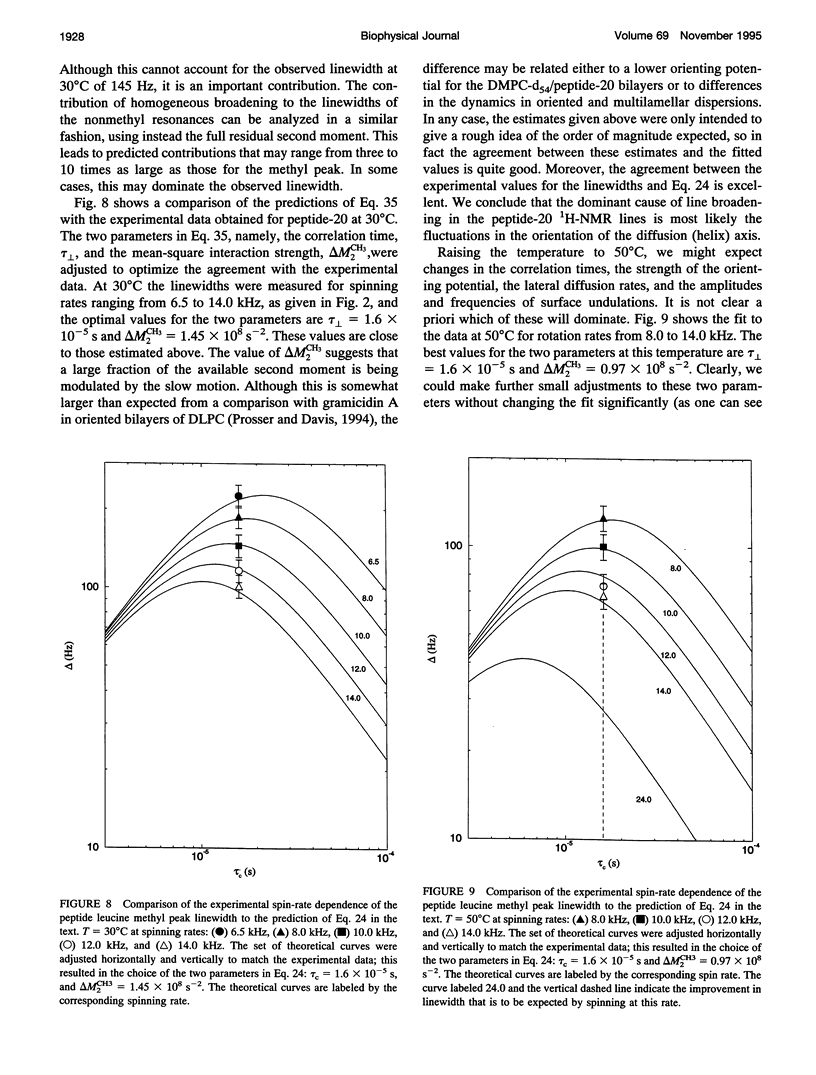
Although the strong 1H-1H dipolar interaction is known to result in severe homogeneous broadening of the 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra of ordered systems, in the fluid phase of biological and model membranes the rapid, axially symmetric reorientation of the molecules about the local bilayer normal projects the dipolar interaction onto the motional symmetry axis. Because the linewidth then scales as (3 cos2 theta-1)/2, where theta is the angle between the local bilayer normal and the magnetic field, the dipolar broadening has been reduced to an "inhomogeneous" broadening by the rapid axial reorientation. It is then possible to obtain high resolution 1H-NMR spectra of membrane components by using magic angle spinning (MAS). Although the rapid axial reorientation effectively eliminates the homogeneous dipolar broadening, including that due to n = 0 rotational resonances, the linewidths observed in both lipids and peptides are dominated by low frequency motions. For small peptides the most likely slow motions are either a "wobble" or reorientation of the molecular diffusion axis relative to the local bilayer normal, or the reorientation of the local bilayer normal itself through surface undulations or lateral diffusion over the curved surface. These motions render the peptide 1H-NMR lines too broad to be observed at low spinning speeds. However, the linewidths due to these slow motions are very sensitive to spinning rate, so that at higher speeds the lines become readily visible. The synthetic amphiphilic peptide K2GL20K2A-amide (peptide-20) has been incorporated into bilayers of 1,2-di-d 27-myristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC-d54) and studied by high speed 1H-MAS-NMR. The linewidths observed for this transbilayer peptide, although too broad to be observable at spinning rates below -5 kHz, are reduced to 68 Hz at a spinning speed of 14 kHz (at 500C). Further improvements in spinning speed and modifications in sample composition designed to reduce the effectiveness of the slow motions responsible for the linewidth should result in significant further reduction in peptide linewidths. With this technique, there is now the potential for the use of 1H-MAS-NMR for the study of conformation, folding, and dynamics of small membrane peptides and protein fragments.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cowan S. W., Schirmer T., Rummel G., Steiert M., Ghosh R., Pauptit R. A., Jansonius J. N., Rosenbusch J. P. Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. coli porins. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):727–733. doi: 10.1038/358727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creuzet F., McDermott A., Gebhard R., van der Hoef K., Spijker-Assink M. B., Herzfeld J., Lugtenburg J., Levitt M. H., Griffin R. G. Determination of membrane protein structure by rotational resonance NMR: bacteriorhodopsin. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):783–786. doi: 10.1126/science.1990439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datema K. P., Pauls K. P., Bloom M. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of the exchangeable sites on gramicidin A and gramicidin S in multilamellar vesicles of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3796–3803. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H. 2H nuclear magnetic resonance of exchange-labeled gramicidin in an oriented lyotropic nematic phase. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):428–436. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H. The description of membrane lipid conformation, order and dynamics by 2H-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):117–171. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Michel H. The Photosynthetic Reaction Center from the Purple Bacterium Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1463–1473. doi: 10.1126/science.245.4925.1463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin R. G. Solid state nuclear magnetic resonance of lipid bilayers. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:108–174. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta C. M., Radhakrishnan R., Khorana H. G. Glycerophospholipid synthesis: improved general method and new analogs containing photoactivable groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4315–4319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. D., Sykes B. D. Assignment of amide 1H and 15N NMR resonances in detergent-solubilized M13 coat protein: a model for the coat protein dimer. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 16;31(23):5284–5297. doi: 10.1021/bi00138a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. H., Lee C. W., Das Gupta S. K., Blume A., Griffin R. G. A 13C and 2H nuclear magnetic resonance study of phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol interactions: characterization of liquid-gel phases. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 7;32(48):13277–13287. doi: 10.1021/bi00211a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karslake C., Piotto M. E., Pak Y. K., Weiner H., Gorenstein D. G. 2D NMR and structural model for a mitochondrial signal peptide bound to a micelle. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 23;29(42):9872–9878. doi: 10.1021/bi00494a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketchem R. R., Hu W., Cross T. A. High-resolution conformation of gramicidin A in a lipid bilayer by solid-state NMR. Science. 1993 Sep 10;261(5127):1457–1460. doi: 10.1126/science.7690158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda D., Inagaki F. Structure of epidermal growth factor bound to perdeuterated dodecylphosphocholine micelles determined by two-dimensional NMR and simulated annealing calculations. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 28;31(3):677–685. doi: 10.1021/bi00118a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Guernevé C., Auger M. New approach to study fast and slow motions in lipid bilayers: application to dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine-cholesterol interactions. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1952–1959. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80372-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay A. L. A proton NMR moment study of the gel and liquid-crystalline phases of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84791-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay A. L., Burnell E. E., Bienvenue A., Devaux P. F., Bloom M. Flexibility of membrane proteins by broad-line proton magnetic resonance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 9;728(3):460–462. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Seelig J. Dynamic properties of gramicidin A in phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2357–2364. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott A. E., Creuzet F., Gebhard R., van der Hoef K., Levitt M. H., Herzfeld J., Lugtenburg J., Griffin R. G. Determination of internuclear distances and the orientation of functional groups by solid-state NMR: rotational resonance study of the conformation of retinal in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1994 May 24;33(20):6129–6136. doi: 10.1021/bi00186a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E., Bowers J. L., Forbes J. High-resolution proton and carbon-13 NMR of membranes: why sonicate? Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6919–6923. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opella S. J., Stewart P. L., Valentine K. G. Protein structure by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Q Rev Biophys. 1987 Feb;19(1-2):7–49. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orekhov VYu, Abdulaeva G. V., Musina LYu, Arseniev A. S. 1H-15N-NMR studies of bacteriorhodopsin Halobacterium halobium. Conformational dynamics of the four-helical bundle. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 15;210(1):223–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orekhov VYu, Pervushin K. V., Arseniev A. S. Backbone dynamics of (1-71)bacterioopsin studied by two-dimensional 1H-15N NMR spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Feb 1;219(3):887–896. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascal S. M., Cross T. A. Structure of an isolated gramicidin A double helical species by high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1101–1109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91055-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls K. P., MacKay A. L., Söderman O., Bloom M., Tanjea A. K., Hodges R. S. Dynamic properties of the backbone of an integral membrane polypeptide measured by 2H-NMR. Eur Biophys J. 1985;12(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00254089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pervushin K. V., Orekhov VYu, Popov A. I., Musina LYu, Arseniev A. S. Three-dimensional structure of (1-71)bacterioopsin solubilized in methanol/chloroform and SDS micelles determined by 15N-1H heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):571–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. R., Dekker N., van den Berg L., Boelens R., Kaptein R., Slotboom A. J., de Haas G. H. Conformational changes in phospholipase A2 upon binding to micellar interfaces in the absence and presence of competitive inhibitors. A 1H and 15N NMR study. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 20;31(41):10024–10030. doi: 10.1021/bi00156a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picot D., Loll P. J., Garavito R. M. The X-ray crystal structure of the membrane protein prostaglandin H2 synthase-1. Nature. 1994 Jan 20;367(6460):243–249. doi: 10.1038/367243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser R. S., Daleman S. I., Davis J. H. The structure of an integral membrane peptide: a deuterium NMR study of gramicidin. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1415–1428. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80932-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser R. S., Davis J. H. Dynamics of an integral membrane peptide: a deuterium NMR relaxation study of gramicidin. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1429–1440. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80933-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser R. S., Davis J. H., Mayer C., Weisz K., Kothe G. Deuterium NMR relaxation studies of peptide-lipid interactions. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 6;31(39):9355–9363. doi: 10.1021/bi00154a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. R., 2nd Solid state 13C NMR of unlabeled phosphatidylcholine bilayers: spectral assignments and measurement of carbon-phosphorus dipolar couplings and 13C chemical shift anisotropies. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81352-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance and the head group structure of phospholipids in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 31;515(2):105–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Seelig A. Lipid conformation in model membranes and biological membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Feb;13(1):19–61. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shon K. J., Kim Y., Colnago L. A., Opella S. J. NMR studies of the structure and dynamics of membrane-bound bacteriophage Pf1 coat protein. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1303–1305. doi: 10.1126/science.1925542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Thomas D. E., Separovic F., Atkins A. R., Cornell B. A. Determination of the structure of a membrane-incorporated ion channel. Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance studies of gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1989 Aug;56(2):307–314. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82677-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. O., Hamilton J., Salmon A., Bormann B. J. Rotational resonance NMR determination of intra- and intermolecular distance constraints in dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1994 May 24;33(20):6327–6333. doi: 10.1021/bi00186a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. O., Jonas R., Braiman M., Bormann B. J. Structure and orientation of the transmembrane domain of glycophorin A in lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1994 May 24;33(20):6334–6341. doi: 10.1021/bi00186a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling M. L., Zidovetzki R., Muller L., Chan S. I. Analysis of membrane lipids by 500 MHz 1H NMR. Anal Biochem. 1989 Apr;178(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. K., McDermott A. E., Raap J., van der Wielen C. M., Lugtenburg J., Herzfeld J., Griffin R. G. Rotational resonance NMR study of the active site structure in bacteriorhodopsin: conformation of the Schiff base linkage. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 1;31(34):7931–7938. doi: 10.1021/bi00149a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich A. S., Heyn M. P., Watts A. Structure determination of the cyclohexene ring of retinal in bacteriorhodopsin by solid-state deuterium NMR. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 27;31(42):10390–10399. doi: 10.1021/bi00157a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. N., Kühlbrandt W., Sarabia V. E., Reithmeier R. A. Two-dimensional structure of the membrane domain of human band 3, the anion transport protein of the erythrocyte membrane. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2233–2239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05876.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz K., Gröbner G., Mayer C., Stohrer J., Kothe G. Deuteron nuclear magnetic resonance study of the dynamic organization of phospholipid/cholesterol bilayer membranes: molecular properties and viscoelastic behavior. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 4;31(4):1100–1112. doi: 10.1021/bi00119a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetta L., Consonni R., De Marco A., Longhi R., Manera E., Vecchio G. Opioid peptides in micellar systems: conformational analysis by CD and by one-dimensional and two-dimensional 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1990;30(9-10):899–909. doi: 10.1002/bip.360300905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


