Abstract
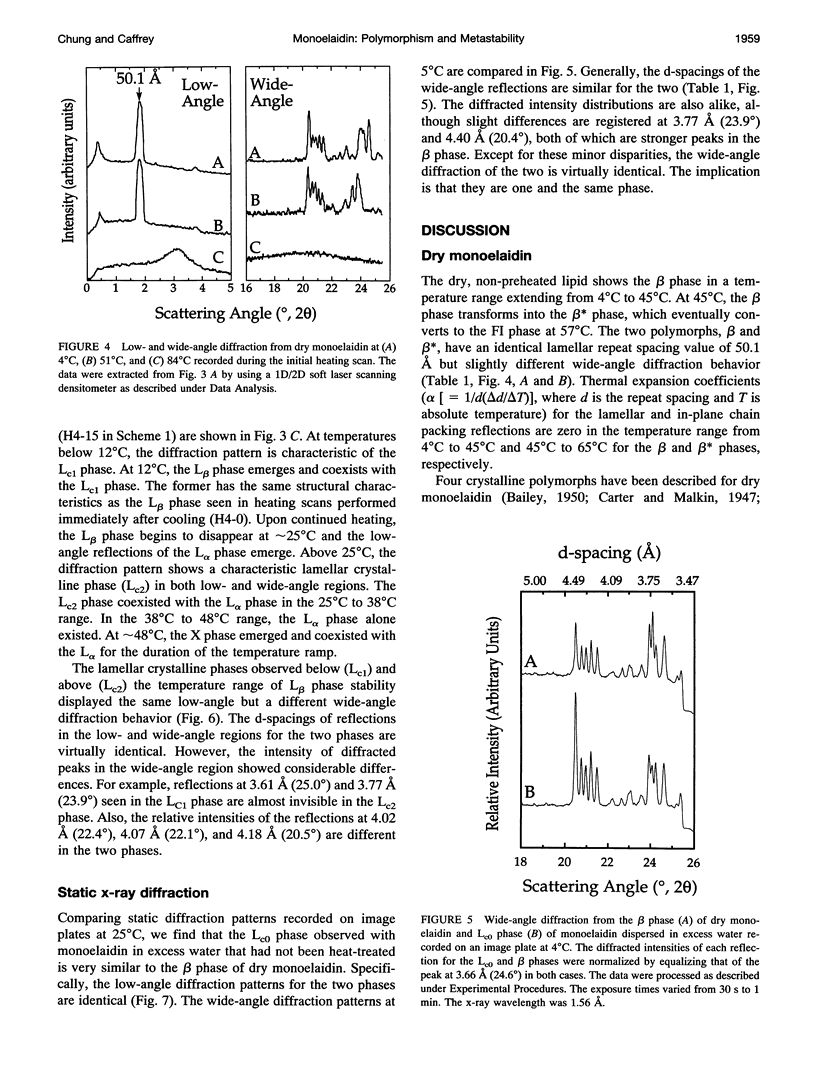
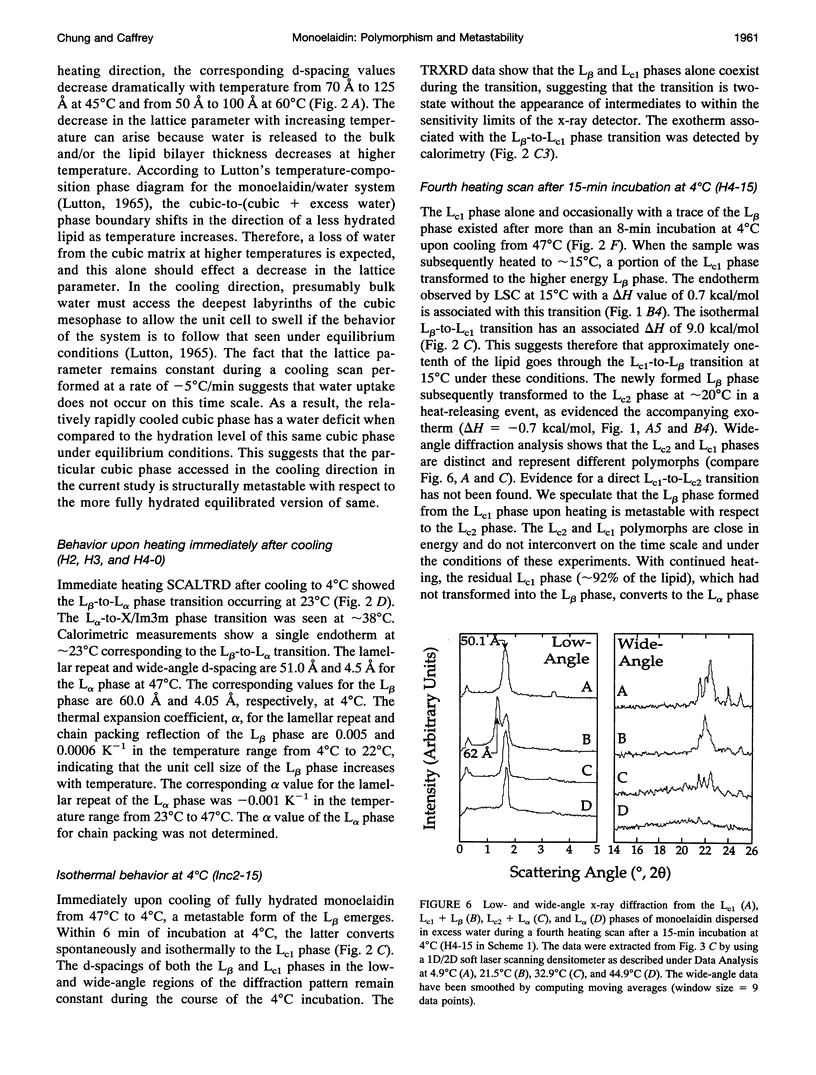
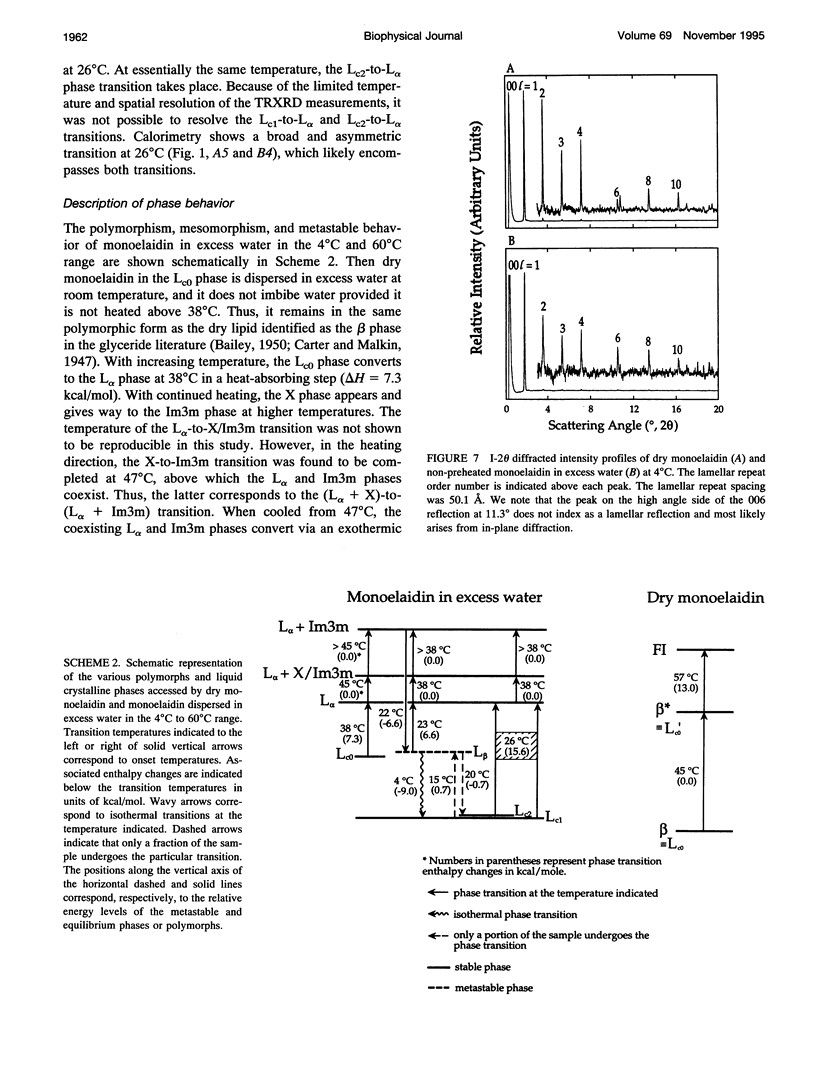
The polymorphic and metastable phase behavior of monoelaidin dry and in excess water was studied by using high-sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry and time-resolved x-ray diffraction in the temperature range of 4 degrees C to 60 degrees C. To overcome problems associated with a pronounced thermal history-dependent phase behavior, simultaneous calorimetry and time-resolved x-ray diffraction measurements were performed on individual samples. Monoelaidin/water samples were prepared at room temperature and stored at 4 degrees C for up to 1 week before measurement. The initial heating scan from 4 degrees C to 60 degrees C showed complex phase behavior with the sample in the lamellar crystalline (Lc0) and cubic (Im3m, Q229) phases at low and high temperatures, respectively. The Lc0 phase transforms to the lamellar liquid crystalline (L alpha) phase at 38 degrees C. At 45 degrees C, multiple unresolved lines appeared that coexisted with those from the L alpha phase in the low-angle region of the diffraction pattern that have been assigned previously to the so-called X phase (Caffrey, 1987, 1989). With further heating the X phase converts to the Im3m cubic phase. Regardless of previous thermal history, cooling calorimetric scans revealed a single exotherm at 22 degrees C, which was assigned to an L alpha+cubic (Im3m, Q229)-to-lamellar gel (L beta) phase transition. The response of the sample to a cooling followed by a reheating or isothermal protocol depended on the length of time the sample was incubated at 4 degrees C. A model is proposed that reconciles the complex polymorphic, mesomorphic, and metastability interrelationships observed with this lipid/water system. Dry monoelaidin exists in the lamellar crystalline (beta) phase in the 4 degrees C to 45 degrees C range. The beta phase transforms to a second lamellar crystalline polymorph identified as beta* at 45 degrees C that subsequently melts at 57 degrees C. The beta phase observed with dry monoelaidin is identical to the LcO phase formed by monoelaidin that was dispersed in excess water and that had not been previously heated.
Full text
PDF



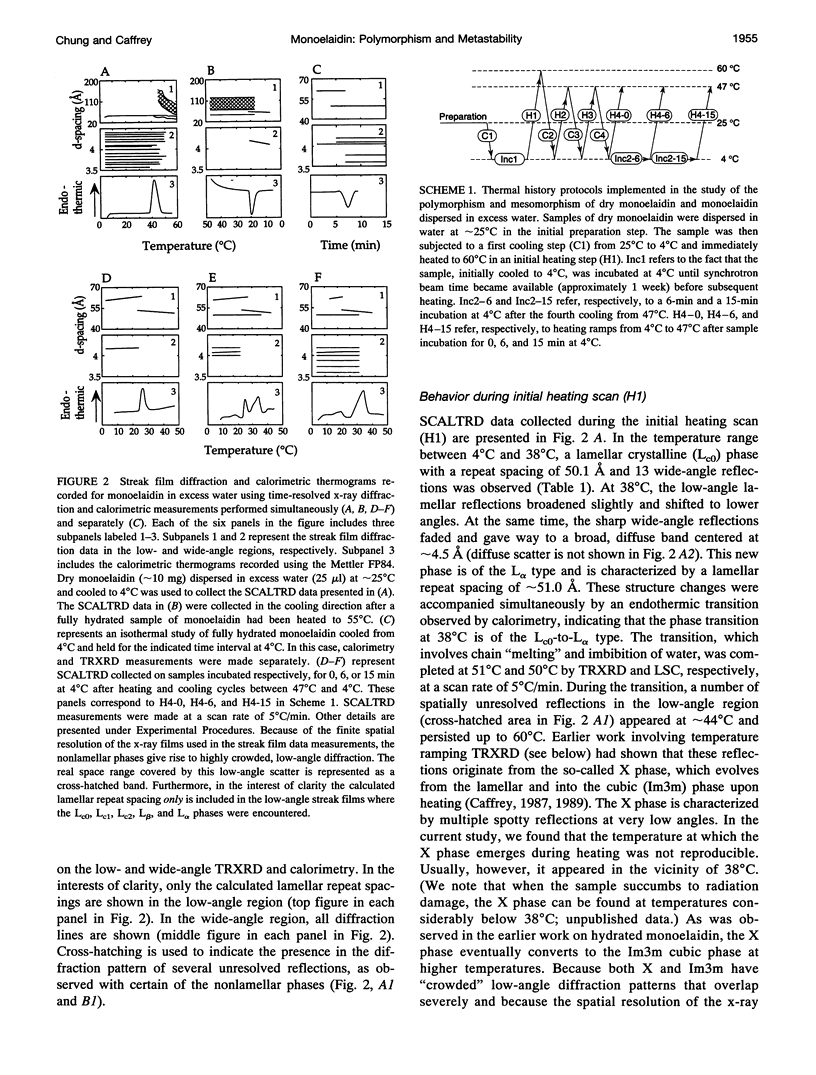
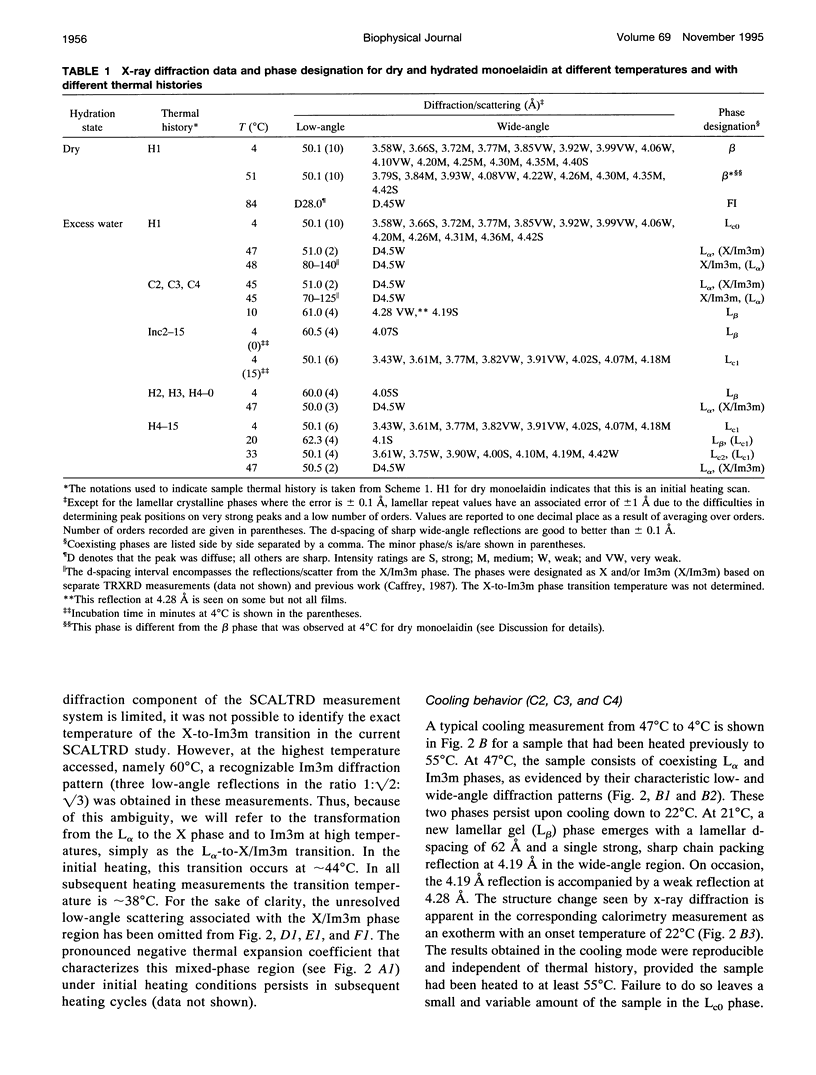

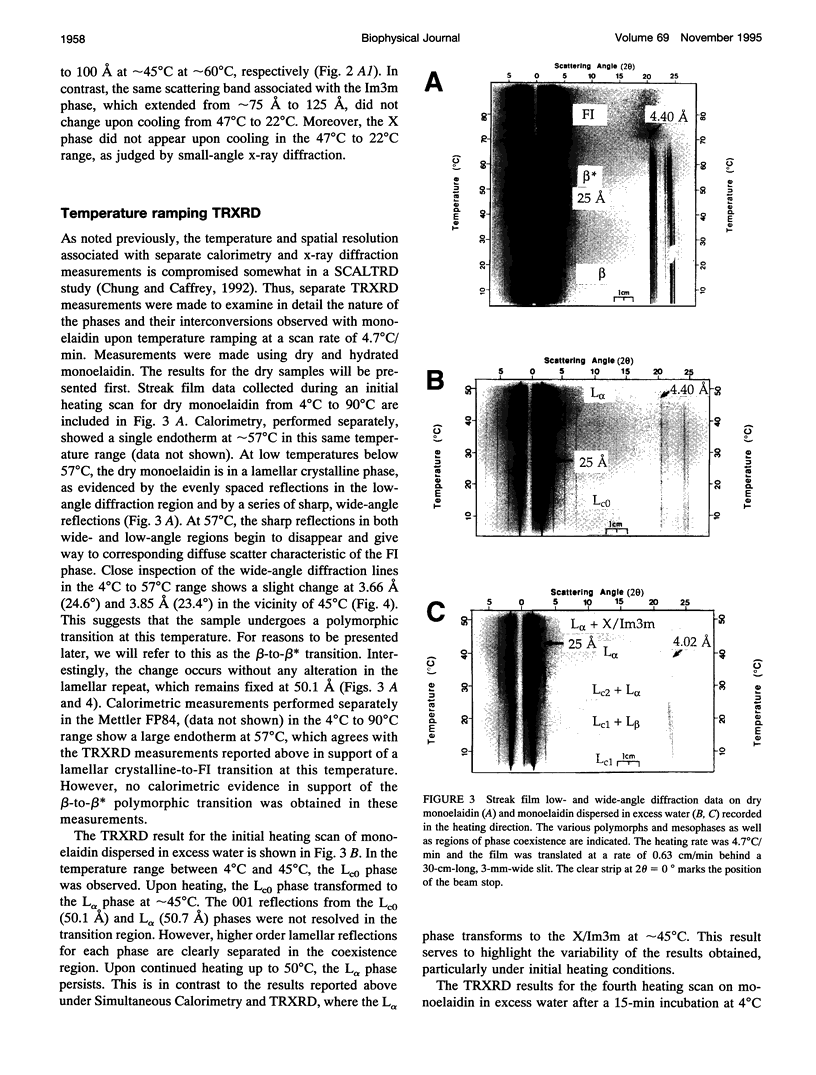


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briggs J., Caffrey M. The temperature-composition phase diagram of monomyristolein in water: equilibrium and metastability aspects. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):573–587. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80847-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey M. A lyotrope gradient method for liquid crystal temperature-composition-mesomorph diagram construction using time-resolved x-ray diffraction. Biophys J. 1989 Jan;55(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82779-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey M. Kinetics and mechanism of the lamellar gel/lamellar liquid-crystal and lamellar/inverted hexagonal phase transition in phosphatidylethanolamine: a real-time X-ray diffraction study using synchrotron radiation. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4826–4844. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey M. Kinetics and mechanism of transitions involving the lamellar, cubic, inverted hexagonal, and fluid isotropic phases of hydrated monoacylglycerides monitored by time-resolved X-ray diffraction. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6349–6363. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng A. C., Hogan J. L., Caffrey M. X-rays destroy the lamellar structure of model membranes. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):291–294. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung H., Caffrey M. Direct correlation of structure changes and thermal events in hydrated lipid established by simultaneous calorimetry and time-resolved x-ray diffraction. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):438–447. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81621-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutton E. S. Phase behavior of aqueous systems of monoglycerides. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Dec;42(12):1068–1070. doi: 10.1007/BF02636909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani P., Luzzati V., Delacroix H. Cubic phases of lipid-containing systems. Structure analysis and biological implications. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):165–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90607-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Magid A. D., Simon S. A. Repulsive interactions between uncharged bilayers. Hydration and fluctuation pressures for monoglycerides. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):897–904. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82888-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]