Abstract
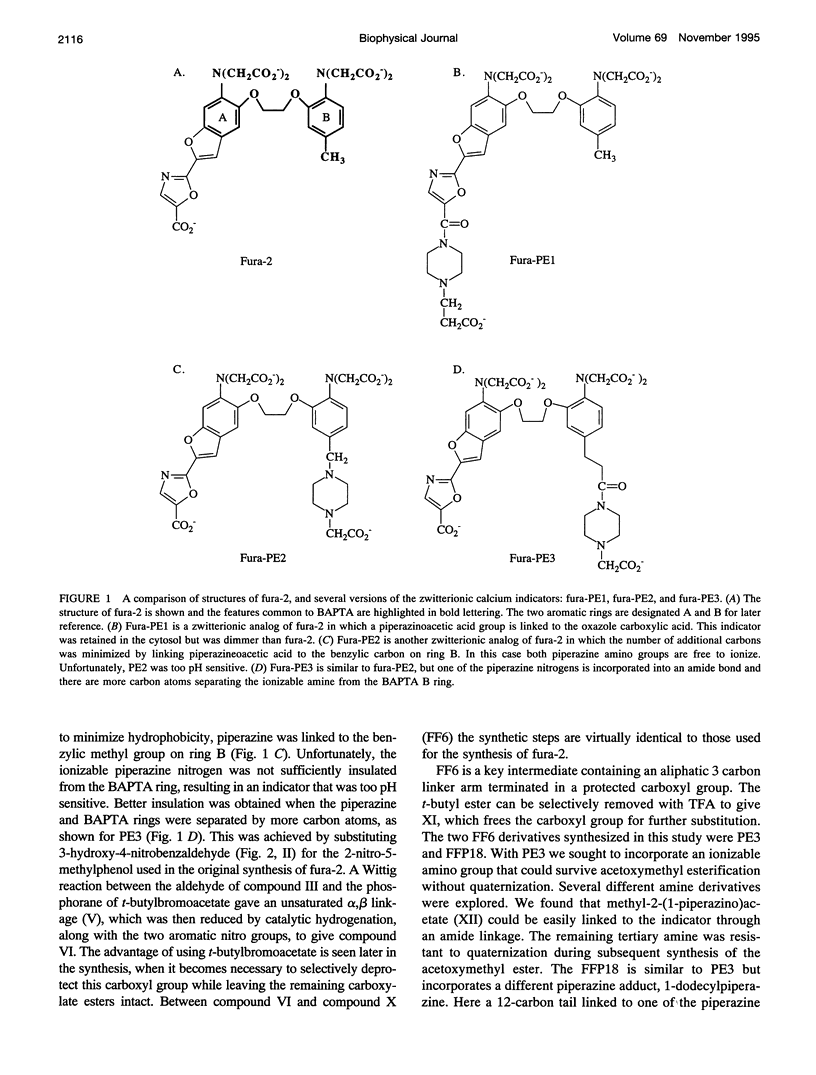
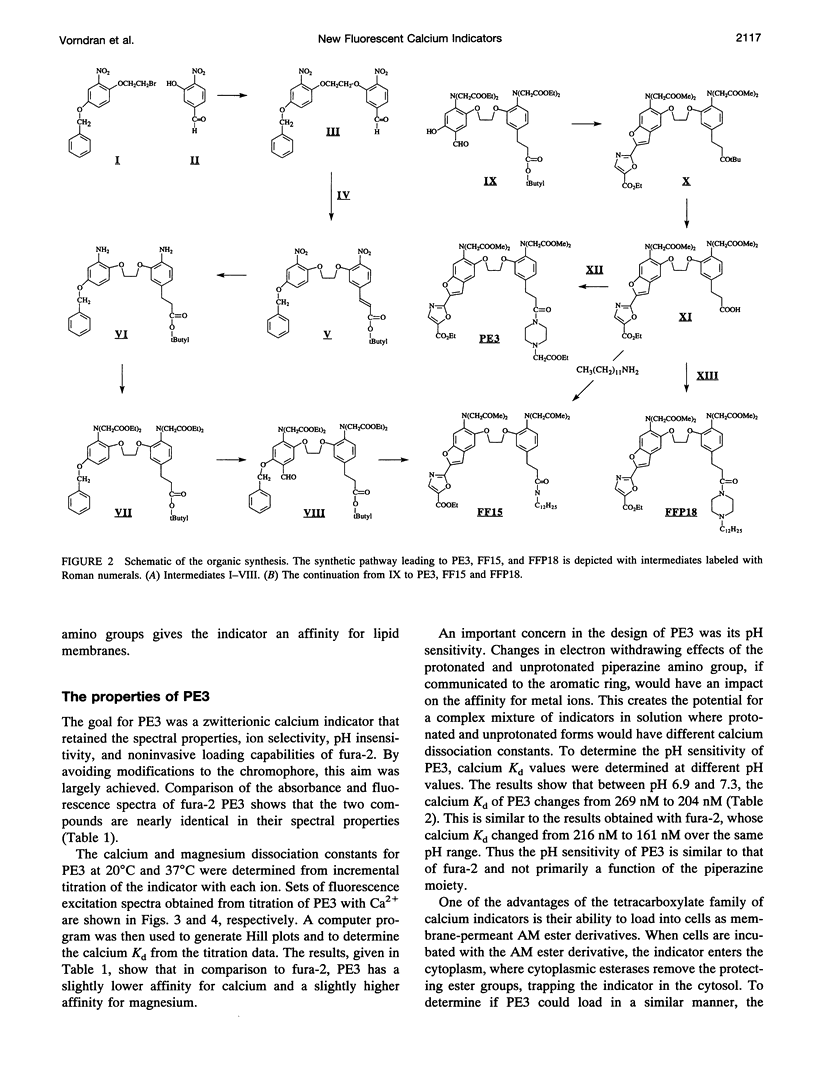
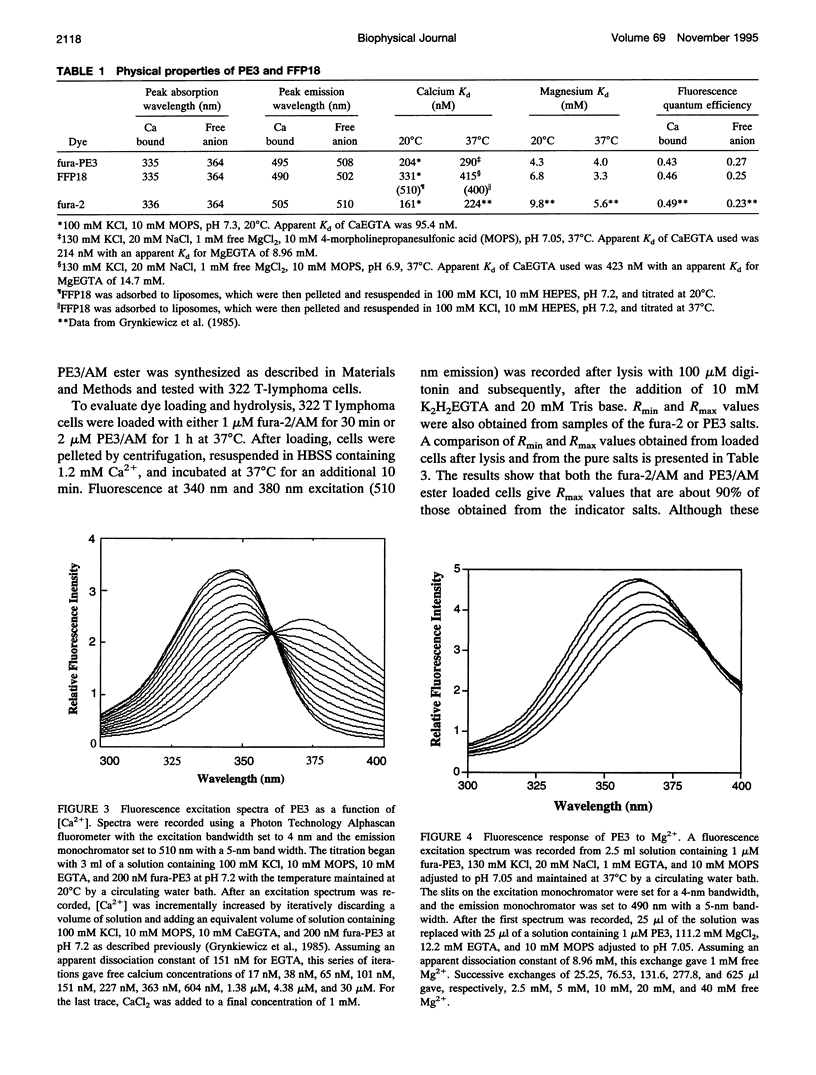
A new family of fluorescent calcium indicators has been developed based on a new analog of BAPTA called FF6. This new BAPTA analog serves as a versatile synthetic intermediate for developing Ca2+ indicators targeted to specific intracellular environments. Two of these new Ca2+ indicators, fura-PE3 and fura-FFP18, are described in this report. Fura-PE3 is a zwitterionic indicator that resists the rapid leakage and compartmentalization seen with fura-2 and other polycarboxylate calcium indicators. In contrast to results obtained with fura-2, cells loaded with PE3 remain brightly loaded and responsive to changes in concentration of cytosolic free calcium for hours. Fura-FFP18 is an amphipathic indicator that to binds to liposomes and to cell membranes. Studies to be detailed later indicate that FFP18 functions as a near-membrane Ca2+ indicator and that calcium levels near the plasma membrane rise faster and higher than in the cytosol.
Full text
PDF



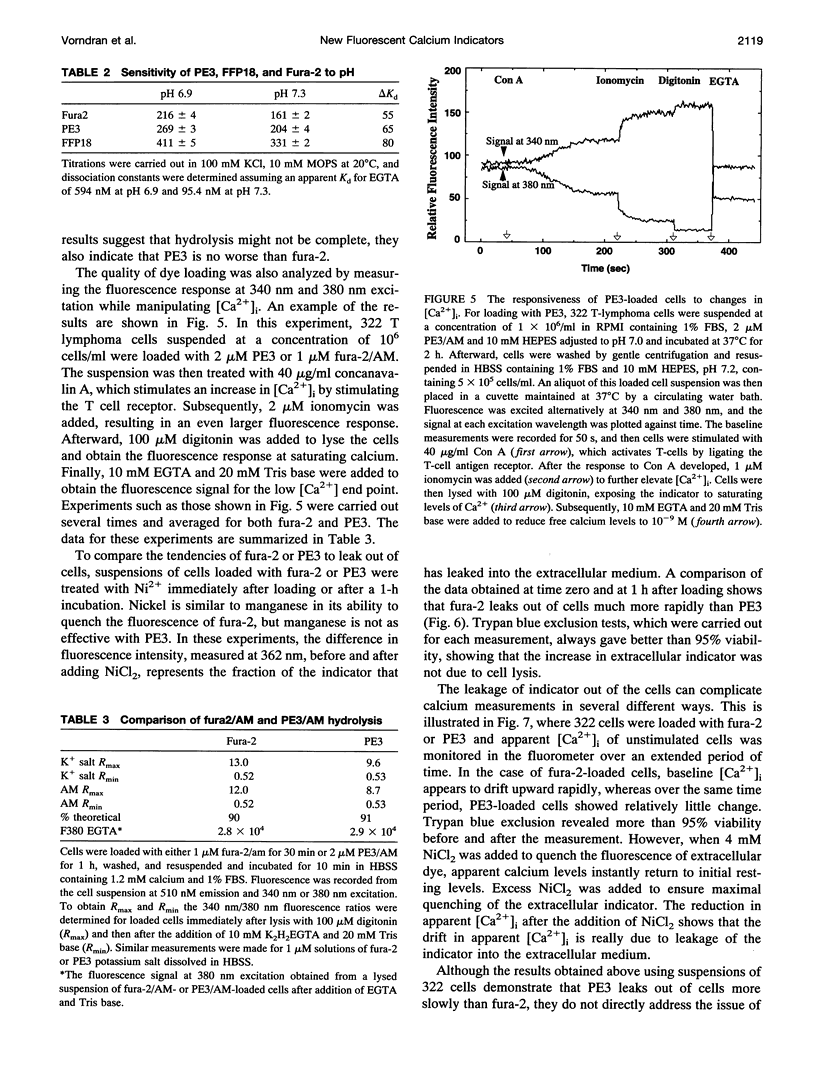
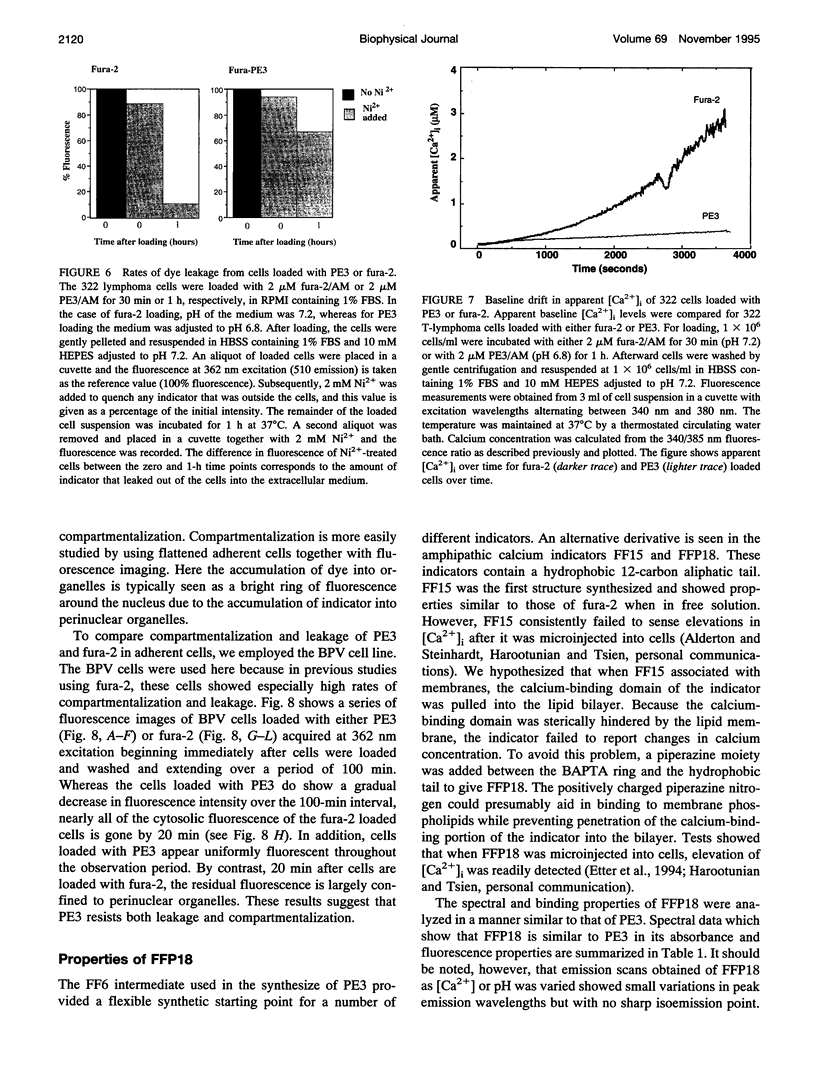

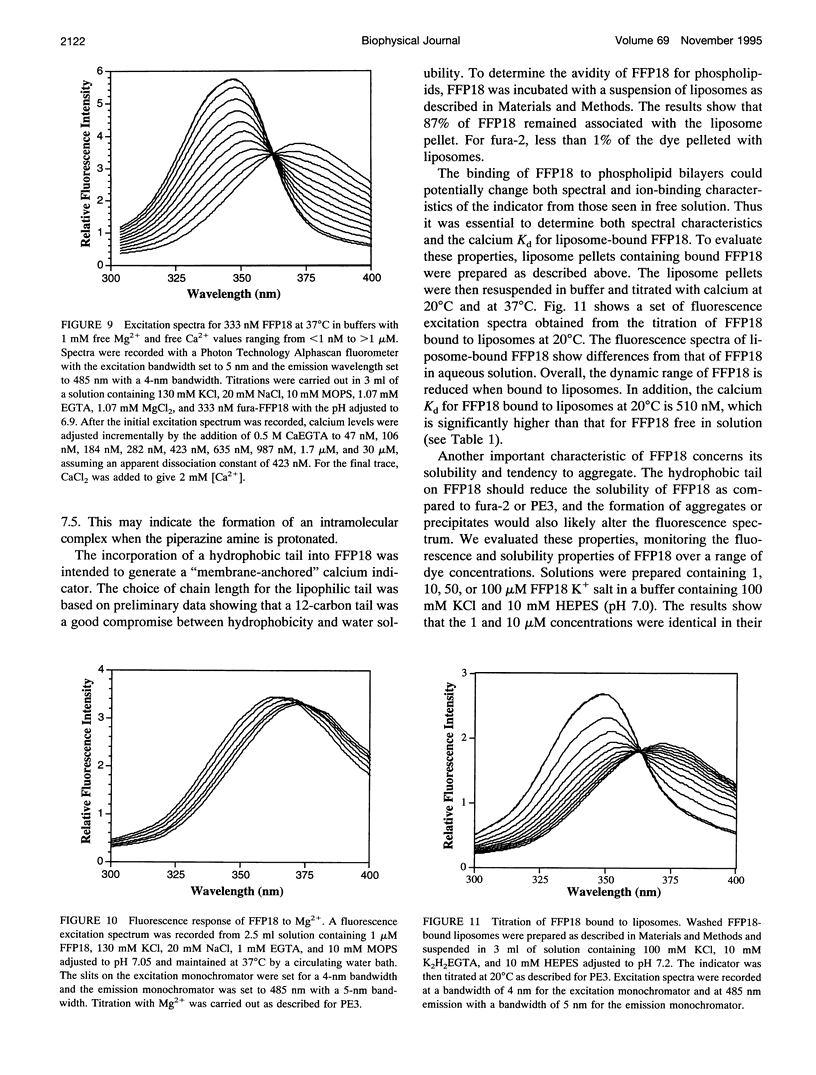


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Neher E. Calcium requirements for secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:247–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Steinberg T. H., Silverstein S. C. Inhibition of Fura-2 sequestration and secretion with organic anion transport blockers. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Steinberg T. H., Swanson J. A., Silverstein S. C. Fura-2 secretion and sequestration in macrophages. A blocker of organic anion transport reveals that these processes occur via a membrane transport system for organic anions. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):915–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etter E. F., Kuhn M. A., Fay F. S. Detection of changes in near-membrane Ca2+ concentration using a novel membrane-associated Ca2+ indicator. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):10141–10149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelson A. L., Zucker R. S. Presynaptic calcium diffusion from various arrays of single channels. Implications for transmitter release and synaptic facilitation. Biophys J. 1985 Dec;48(6):1003–1017. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83863-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goligorsky M. S., Hruska K. A., Loftus D. J., Elson E. L. Alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation and cytoplasmic free calcium concentration in cultured renal proximal tubular cells: evidence for compartmentalization of quin-2 and fura-2. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Sep;128(3):466–474. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Cruz A., Sala F., Adams P. R. Subcellular calcium transients visualized by confocal microscopy in a voltage-clamped vertebrate neuron. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):858–862. doi: 10.1126/science.2154851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P., Alderton J. M., Tsien R. Y., Steinhardt R. A. Active involvement of Ca2+ in mitotic progression of Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):183–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Simon B. J., Szucs G., Schneider M. F. Simultaneous recording of calcium transients in skeletal muscle using high- and low-affinity calcium indicators. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):971–988. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83178-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. Microdomains of high calcium concentration in a presynaptic terminal. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1350109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Milani D., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Fura-2 measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in monolayers and suspensions of various types of animal cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Steinhardt R., Tsien R. Calcium rises abruptly and briefly throughout the cell at the onset of anaphase. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):886–889. doi: 10.1126/science.3755550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M. Alteration of intracellular Fura-2 fluorescence by viscosity: a simple correction. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90062-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen C. D., Means A. R. Calmodulin is involved in regulation of cell proliferation. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3961–3968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02738.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richie E. R., McEntire B., Phillips J., Allison J. P. Altered expression of lymphocyte differentiation antigens on phorbol ester-activated CD4+8+ T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4115–4122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R., Brini M., Murgia M., Pozzan T. Microdomains with high Ca2+ close to IP3-sensitive channels that are sensed by neighboring mitochondria. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):744–747. doi: 10.1126/science.8235595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala F., Hernández-Cruz A. Calcium diffusion modeling in a spherical neuron. Relevance of buffering properties. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82533-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon M., Williams D. A., Fay F. S. A Ca2+-insensitive form of fura-2 associated with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Assessment and accurate Ca2+ measurement. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6308–6312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Llinás R. R. Compartmentalization of the submembrane calcium activity during calcium influx and its significance in transmitter release. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):485–498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83804-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speksnijder J. E., Miller A. L., Weisenseel M. H., Chen T. H., Jaffe L. F. Calcium buffer injections block fucoid egg development by facilitating calcium diffusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6607–6611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S. F., Bilezikian J. P., Al-Awqati Q. Fura-2 fluorescence is localized to mitochondria in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 1):C744–C747. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.5.C744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Neutral carrier ion-selective microelectrodes for measurement of intracellular free calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):623–638. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J., Poenie M. Measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in individual small cells using fluorescence microscopy with dual excitation wavelengths. Cell Calcium. 1985 Apr;6(1-2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(85)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R., Pozzan T. Measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ with quin2. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:230–262. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]