Abstract
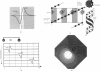
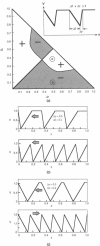
Many molecular motors move unidirectionally along a DNA strand powered by nucleotide hydrolysis. These motors are multimeric ATPases with more than one hydrolysis site. We present here a model for how these motors generate the requisite force to process along their DNA track. This novel mechanism for force generation is based on a fluctuating electrostatic field driven by nucleotide hydrolysis. We apply the principle to explain the motion of certain DNA helicases and the portal protein, the motor that bacteriophages use to pump the genome into their capsids. The motor can reverse its direction without reversing the polarity of its electrostatic field, that is, without major structural modifications of the protein. We also show that the motor can be driven by an ion gradient; thus the mechanism may apply as well to the bacterial flagellar motor and to ATP synthase.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams J. P., Leslie A. G., Lutter R., Walker J. E. Structure at 2.8 A resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature. 1994 Aug 25;370(6491):621–628. doi: 10.1038/370621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astumian RD, Bier M. Fluctuation driven ratchets: Molecular motors. Phys Rev Lett. 1994 Mar 14;72(11):1766–1769. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.72.1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Turner L. Torque generated by the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):2201–2216. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81278-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-controlled macromolecular interactions. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:131–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carazo J. M., Donate L. E., Herranz L., Secilla J. P., Carrascosa J. L. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the connector of bacteriophage phi 29 at 1.8 nm resolution. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):853–867. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., Wyckoff E., Hayden M., Sampson L., Eppler K., Randall S., Moreno E. T., Serwer P. Bacteriophage P22 portal protein is part of the gauge that regulates packing density of intravirion DNA. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 20;224(4):1055–1074. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90469-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering CR, Horsthemke W, Riordan J. Nonequilibrium fluctuation-induced transport. Phys Rev Lett. 1994 May 9;72(19):2984–2987. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.72.2984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donate L. E., Carrascosa J. L. Characterization of a versatile in vitro DNA-packaging system based on hybrid lambda/phi 29 proheads. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):534–544. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90594-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube P., Tavares P., Lurz R., van Heel M. The portal protein of bacteriophage SPP1: a DNA pump with 13-fold symmetry. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1303–1309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Casjens S. R. DNA packaging by the double-stranded DNA bacteriophages. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelman E. H., Yu X., Wild R., Hingorani M. M., Patel S. S. Bacteriophage T7 helicase/primase proteins form rings around single-stranded DNA that suggest a general structure for hexameric helicases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3869–3873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert S. P., Webb M. R., Brune M., Johnson K. A. Pathway of processive ATP hydrolysis by kinesin. Nature. 1995 Feb 23;373(6516):671–676. doi: 10.1038/373671a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Koshland D. E., Jr Sensitivity amplification in biochemical systems. Q Rev Biophys. 1982 Aug;15(3):555–591. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo P., Peterson C., Anderson D. Prohead and DNA-gp3-dependent ATPase activity of the DNA packaging protein gp16 of bacteriophage phi 29. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney D. D. Evidence for alternating head catalysis by kinesin during microtubule-stimulated ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6865–6869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Symmetry mismatch and DNA packaging in large bacteriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4779–4783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingorani M. M., Patel S. S. Interactions of bacteriophage T7 DNA primase/helicase protein with single-stranded and double-stranded DNAs. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 23;32(46):12478–12487. doi: 10.1021/bi00097a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M. Escherichia coli DNA helicases: mechanisms of DNA unwinding. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(1):5–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnasco MO. Forced thermal ratchets. Phys Rev Lett. 1993 Sep 6;71(10):1477–1481. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk B. C., Feng W. C., Marshall C. J., Seto-Young D., Na S., Haber J. E., Perlin D. S. Modeling a conformationally sensitive region of the membrane sector of the fungal plasma membrane proton pump. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1994 Feb;26(1):101–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00763222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. S., Hingorani M. M., Ng W. M. The K318A mutant of bacteriophage T7 DNA primase-helicase protein is deficient in helicase but not primase activity and inhibits primase-helicase protein wild-type activities by heterooligomer formation. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 28;33(25):7857–7868. doi: 10.1021/bi00191a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. S., Hingorani M. M. Nucleotide binding studies of bacteriophage T7 DNA helicase-primase protein. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):186S–190S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peskin C. S., Oster G. Coordinated hydrolysis explains the mechanical behavior of kinesin. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):202S–211S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel A. D., Berg H. C. Fluctuation analysis of rotational speeds of the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3502–3506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwer P. The source of energy for bacteriophage DNA packaging: an osmotic pump explains the data. Biopolymers. 1988 Jan;27(1):165–169. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda K., Block S. M. Force and velocity measured for single kinesin molecules. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):773–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda K., Mitra P. P., Block S. M. Fluctuation analysis of motor protein movement and single enzyme kinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):11782–11786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.11782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valpuesta J. M., Carrascosa J. L. Structure of viral connectors and their function in bacteriophage assembly and DNA packaging. Q Rev Biophys. 1994 May;27(2):107–155. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valpuesta J. M., Fujisawa H., Marco S., Carazo J. M., Carrascosa J. L. Three-dimensional structure of T3 connector purified from overexpressing bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90579-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong I., Lohman T. M. Allosteric effects of nucleotide cofactors on Escherichia coli Rep helicase-DNA binding. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):350–355. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]