Abstract
Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of the human diarrheal disease cholera, is a motile bacterium with a single polar flagellum, and motility has been inferred to be an important aspect of virulence. The V. cholerae flagellar hierarchy is organized into four classes of genes. The expression of each class of genes within a flagellar hierarchy is generally tightly regulated in other bacteria by both positive and negative regulatory elements. To further elucidate flagellar biogenesis in V. cholerae, we characterized the roles of the three putative regulatory genes, flhF, flhG, and VC2061. V. cholerae flhF and flhG mutants appeared nonmotile in a soft agar assay. Electron microscopy revealed that the flhF mutant lacked a polar flagellum, while interestingly, the flhG mutant possessed multiple (8 to 10) polar flagella per cell. The transcriptional activity of class III and class IV gene promoters in the flhF mutant was decreased, suggesting that FlhF acts as a positive regulator of class III gene transcription. The transcription of all four classes of flagellar promoters was increased in the flhG mutant, suggesting that FlhG acts as a negative regulator of class I gene transcription. Additionally, the ability to colonize the infant mouse intestine was reduced for the flhG mutant (∼10-fold), indicating that the negative regulation of class I flagellar genes enhances virulence. The V. cholerae VC2061 mutant was motile and produced a polar flagellum indistinguishable from that of the wild type, and the transcriptional activities of the four classes of flagellar promoters were similar to that of the wild type. Our results indicate that FlhG and FlhF regulate class I and class III flagellar transcription, respectively, while VC2061 plays no detectable role in V. cholerae flagellar biogenesis.
The diarrheal disease cholera is acquired by the ingestion of food or water contaminated with Vibrio cholerae. This gram-negative bacterium is highly motile by means of a single polar flagellum, and several studies have linked motility and flagellar synthesis to aspects of V. cholerae virulence (5, 11, 12, 26, 39), but it has been difficult to elucidate the contribution of the flagellum to cholera pathogenesis.
Assembly of the bacterial flagellum occurs in a stepwise fashion that is initiated by the insertion of a type III export apparatus into the cytoplasmic membrane (reviewed in reference 27). Flagellar components are then secreted through this export machinery to be added to the growing end of the flagellum in the specific order in which they are assembled (reviewed in reference 46). The transcription of flagellar genes generally occurs in a hierarchical fashion, that is, genes encoding early flagellar components are transcribed prior to the genes encoding late flagellar components, such as flagellin subunits (23).
Flagellar gene transcription in V. cholerae is organized into a transcriptional hierarchy that is comprised of four classes of genes (37). Class I is composed solely of the gene encoding the σ54-dependent activator FlrA, which along with the σ54 holoenzyme form of RNA polymerase, activates the expression of class II genes. These genes include structural components of the MS (membrane/supramembrane) ring, switch, and export apparatus as well as the regulatory genes encoding FlrB, FlrC, and FliA (σ28). FlrC, along with the σ54 holoenzyme, activates the expression of class III genes, which encode the basal body, hook, and the “core” flagellin, FlaA. Finally, the σ28 holoenzyme activates the expression of class IV genes, which include additional filament genes as well as motor genes.
Additional levels of regulation of flagellar transcription are predicted to exist to ensure the correct temporal expression of flagellar components. For example, the flagellar regulatory factors are likely to have mechanisms to downregulate inappropriate transcriptional activity. In fact, the anti-σ28 factor FlgM appears to regulate class IV gene transcription in V. cholerae, similar to FlgM of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (4). FlgM binds to σ28 and prevents its association with RNA polymerase until the hook-basal-body structure is complete, at which time FlgM is secreted outside the cell, releasing σ28 and allowing the transcription of σ28-dependent genes (class III in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium and class IV in V. cholerae). FlrC, the activator of class III genes, must be phosphorylated by FlrB to activate transcription (5), suggesting that the regulation of phospho-FlrC might be another mechanism to downregulate inappropriate flagellar transcription.
In other bacteria with polar flagella, additional factors not found in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium are involved in the regulation of flagellar transcription. FlhF, a protein with homology to GTP-binding signal recognition particle (SRP) pathway proteins, is required for flagellar synthesis in Bacillus subtilis (3), Campylobacter jejuni, and Helicobacter pylori (18, 34) and for polar flagellar placement in Pseudomonas putida (36). It has been demonstrated with C. jejuni that flhF positively influences the transcription of class III flagellar genes (18). FleN, a protein with homology to MinD-related proteins, plays a role in regulating the flagellar number in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, since its mutation leads to multiple polar flagella (1). FleN has been demonstrated to interact with the flagellar master regulator, FleQ (a V. cholerae FlrA homologue), and to downregulate class II gene transcription (7).
In V. cholerae, flhF and fleN homologues are transcribed within a class II (FlrA-dependent) operon that also includes fliA (encodes σ28), a number of che genes essential for chemotaxis (2, 14, 26), and VC2061, a gene that shares homology with parA. The initiation of flagellar assembly is tied to cell division in Caulobacter crescentus (24) and Escherichia coli (38), suggesting a potential role in V. cholerae flagellar synthesis for one of the ParA family members, which are normally involved in chromosome segregation during cell division (13, 40).
For this study, we characterized the role of flhF, flhG (the V. cholerae fleN homologue), and VC2061 in V. cholerae flagellar biogenesis. The results demonstrate that flhF is a positive regulator of class III gene transcription, flhG is a negative regulator of class I gene transcription and flagellar number, and VC2061 plays little role in V. cholerae flagellar synthesis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and media.
E. coli strain DH5α (16) was used for cloning manipulations, and SM10λpir (31) was used to transfer plasmids to V. cholerae by conjugation. The V. cholerae strains used for this study are listed in Table 1. The construction of chromosomal deletions/insertions using pKEK229, a pCVD442 derivative with the sacB gene (9), has been described previously (5). The correct construction of all strains was verified by PCR and sequencing.
TABLE 1.
Bacterial strains, plasmids, and oligonucleotides used for this study
| Strain, plasmid, or oligonucleotide | Relevant genotype or sequence (5′-3′) | Source or reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| V. cholerae strains | |||
| O395 | Wild-type classical Ogawa | 28 | |
| KKV598 | O395, ΔlacZ | 5 | |
| KKV1560 | 0395, ΔflhF ΔlacZ | This study | |
| KKV1701 | 0395, ΔflhG ΔlacZ | This study | |
| KKV1721 | 0395, Δorf2061 ΔlacZ | This study | |
| Plasmids | |||
| pRS551 | Transcriptional lacZ fusion vector, Ampr Kanr | 41 | |
| pKEK72 | flrB promoter-lacZ fusion in pRS551 | 21 | |
| pKEK73 | flrA promoter-lacZ fusion in pRS551 | 21 | |
| pKEK76 | flaC promoter-lacZ fusion in pRS551 | 20 | |
| pKEK77 | flaD promoter-lacZ fusion in pRS551 | 20 | |
| pKEK79 | flaB promoter-lacZ fusion in pRS551 | 20 | |
| pKEK80 | flaA promoter-lacZ fusion in pRS551 | 20 | |
| pKEK81 | flaE promoter-lacZ fusion in pRS551 | 20 | |
| pKEK327 | fliE promoter-lacZ fusion in pRS551 | 37 | |
| pKEK331 | flgK promoter-lacZ fusion in pRS551 | 37 | |
| pKEK229 | R6K ori sacB mob Ampr | 5 | |
| pKEK516 | ΔflhF in pKEK229 | 25 | |
| pKEK579 | ΔflhG in pKEK229 | This study | |
| pKEK591 | Δorf2061 in pKEK229 | This study | |
| pBAD24 | ColE1 ori AmpraraBAD promoter | 15 | |
| pKEK553 | flhF in pBAD24 | This study | |
| pKEK509 | flhF′ (lacking C-terminal 14 aa) in pBAD24 | This study | |
| Oligonucleotides | |||
| FLHG1 | GCGGATCCGAGCATTTCAGAAGGATACCG
|
||
| FLHG2 | GCGAAGCTTCATAGGTTTCAAAGCTCGCGC
|
||
| ΔFLHGUp | CTCACCATATTCTGCAGTAAAACATGGCCTAGGTTACG
|
||
| ΔFLHGDown | CCATGTTTTACTGAATATGGTGAGAAGTTATCGT
|
||
| VC2061-1 | GCGGATCCATCGATGGTGGCGACCGCATG
|
||
| VC2061-2 | GCGCGTCGACTTCAACAACGCTGCAGGGCTG
|
||
| ΔVC2061Up | ACGAAGCGCGGAATTCTTCACGTAACTGGAACAAGTC
|
||
| ΔVC2061Down | GTTACGTGAAGAATTCCGCGCTTCGTTGCAGACATTG
|
||
| FlhFMet | GCGGATCCATGGAAATAAAACGATTTTTTGCCAAG
|
||
| FlhFXhoI | GCGCTCGAGCTAGAATCTCTCGAATCACTG | ||
Luria broth was used for both liquid and agar media. Antibiotics were added when appropriate at the following concentrations: ampicillin, 50 μg/ml; chloramphenicol, 2 or 20 μg/ml (for V. cholerae and E. coli, respectively); and streptomycin, 100 μg/ml. Agar plates consisting of LB with 0.3% agar were used to measure motility, and 0.05% arabinose was added when appropriate. For counterselection with sacB-containing plasmids, LB without NaCl and with 10% sucrose was used.
Plasmid construction.
All plasmids and oligonucleotide primers used for this study are listed in Table 1. V. cholerae O395 chromosomal DNA was used as the template for PCR amplifications. All primer sequences were designed based on the complete V. cholerae genome sequence (17). In-frame deletions of flhG and VC2061 were constructed by first amplifying the 5′ fragment using the corresponding oligonucleotides (FLHG1 and ΔFLHGUp or VC2061-1 and ΔVC2061Up), digesting the amplified product with PstI or EcoRI and BamHI, and ligating the product into similarly digested pWSK30 (44) to form pKEK558 and pKEK559, respectively. The 3′ fragment of each gene was PCR amplified using the corresponding oligonucleotides FLHG2 and ΔFLHGDown or VC2061-2 and ΔVC2061Down. The 3′ flhG PCR fragment was digested with PstI and HindIII and ligated into similarly digested pKEK558 to form pKEK564 (ΔflhG); the deleted sequence corresponds to amino acids 41 to 211 of FlhG. The 3′ VC2061 PCR fragment was digested with SalI and EcoRI and ligated into similarly digested pKEK559 to form pKEK565 (ΔVC2061); the deleted sequence corresponds to amino acids 68 to 193 of the VC2061 protein. pKEK564 (ΔflhG) was digested with XhoI and NotI, and pKEK565 (ΔVC2061) was digested with SalI and NotI for subsequent ligation into plasmid pKEK229 digested with SalI and NotI to form pKEK579 and pKEK591, respectively. Plasmids pKEK579 (ΔflhG), pKEK591 (ΔVC2061), and pKEK516 (ΔflhF), which was described previously (25), were used to recombine the corresponding mutation back into the chromosome of V. cholerae strain KKV598, generating KKV1701, KKV1721, and KKV1560, respectively. All plasmids and V. cholerae strains constructed were confirmed to be correct by DNA sequencing.
For complementation of V. cholerae ΔflhF, we constructed plasmids pKEK509 and pKEK553. pKEK509 and pKEK553 were constructed by PCR amplifying flhF using the oligonucleotides FlhFMet and FlhFSalI (pKEK509) or FlhFXhoI (pKEK553), digesting the products with NcoI and SalI or XhoI, and ligating the products into pBAD24 that had been digested with the same enzymes. We were unaware of a SalI site present within the C terminus of the flhF gene, and thus pKEK509 expresses a truncated FlhF protein lacking the last 14 amino acids (aa) of the protein.
β-Galactosidase assays.
V. cholerae strains were transformed with the promoter-lacZ fusion-containing plasmids listed in Table 1, grown in LB plus ampicillin, and harvested at an optical density at 600 nm of ∼0.4 to 0.6. Bacterial cells were permeabilized with chloroform and sodium dodecyl sulfate and assayed for β-galactosidase activity following the method of Miller (30). All experiments were performed at least three separate times.
Electron microscopy.
Strains were grown to mid-log phase in LB, centrifuged, and resuspended in 0.15 M NaCl. Samples were adhered to a carbon-coated grid and stained with 1% uranyl acetate before microscopy with a JOEL 1230 microscope.
In vitro/in vivo virulence assays.
Cholera toxin (CT) was measured by a GM1-ganglioside-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, as described previously (42). Toxin-coregulated pilus (TCP) was measured using transduction with CTXΦ-Kan (a kind gift from M. Waldor) as described previously (43). The infant mouse colonization assay has been described previously (12). The inocula consisted of ∼106 CFU for both wild-type and mutant strains.
RESULTS
The production of flagella represents a highly energy-demanding process for the bacterial cell, so tight regulation of this process ensures proper energy expenditure. The regulation of flagellar production in V. cholerae is poorly understood. We have shown that phosphorylation of FlrC is important for the expression of class III genes (5) and also that the expression of class IV genes is controlled through modulation of the activity of σ28 by an anti-σ28 factor, FlgM (4). To ascertain the function of putative flagellar regulatory genes whose function has been inferred from studies of other bacterial species, we constructed mutations in the flhF, flhG, and VC2061 V. cholerae genes.
FlhF acts as a positive regulator of class III flagellar gene transcription.
The FlrA- and σ54-dependent (i.e., class II) promoter that lies upstream of flhA (encoding an export apparatus component) appears to drive the transcription of an operon that also contains several regulatory genes (37). We have already shown that one of the genes in this operon, fliA, encodes σ28, which is required for the transcription of class IV flagellar genes (37). Also found within this operon are genes predicted to encode proteins found only in polar flagellates (flhF and flhG), the chemotaxis genes cheYZABW, a gene encoding a ParA homologue (VC2061), and two additional genes annotated as encoding hypothetical proteins. Although there are multiple chemotaxis genes within the V. cholerae genome, the chemotaxis genes within this operon have been demonstrated to be necessary and sufficient for chemotaxis (2, 14, 26). Given the critical role of other genes found within this operon, we investigated the role of the three putative regulatory genes flhF, flhG, and VC2061 in flagellar gene transcription and biogenesis.
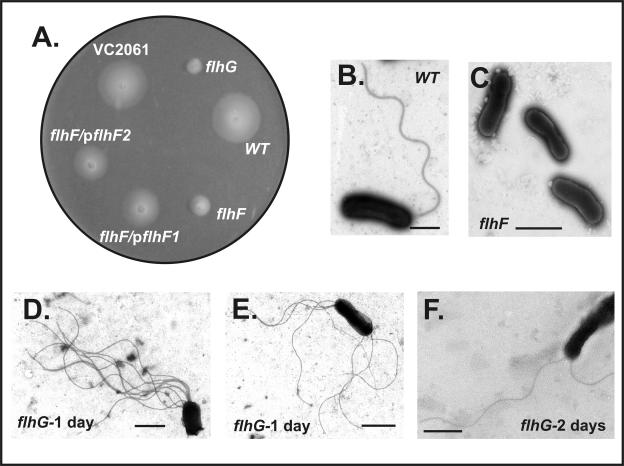
A V. cholerae ΔflhF (with a deletion of VC2068) strain was constructed as described in Materials and Methods. The ΔflhF strain exhibited growth in LB similar to that of the wild-type strain. The ΔflhF strain was nonmotile, as determined by inoculation into motility agar (Fig. 1A) and observation by wet mount, and it lacked polar flagella, as determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (Fig. 1C). Motility was restored by complementation of the ΔflhF strain with a plasmid carrying either the entire flhF gene or a version of flhF missing the last 42 bp (resulting in a truncated protein lacking the C-terminal 14 aa) expressed from the arabinose-inducible promoter PBAD (pKEK553 and pKEK509, respectively) (Fig. 1A). These results indicate that FlhF is required for flagellar synthesis in V. cholerae but that the last 14 aa of FlhF are not necessary for this function.
FIG. 1.
Motility phenotypes and electron micrographs of V. cholerae wild-type and mutant strains. (A) V. cholerae strains KKV598 (wild type, WT), KKV1560 (flhF), KKV1701 (flhG), KKV1721 (VC2061), KKV1694 (flhF/pflhF1, complementing plasmid containing a truncated flhF gene lacking the last 42 bp), and KKV1696 (flhF/pflhF2, complementing plasmid containing the entire flhF gene) were inoculated into motility agar plus 0.05% arabinose and incubated at 30°C for 15 h. (B) KKV598 (wild type, WT); (C) KKV1560 (flhF); (D and E) KKV1701 (flhG), first day; (F) KKV1701 (flhG), second day. Bars, 500 nm.
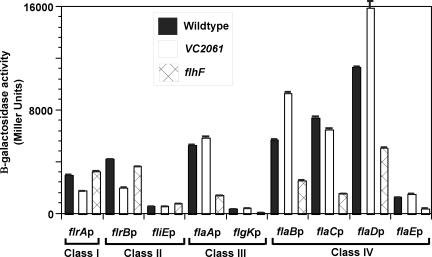
To determine whether FlhF affects the transcription of flagellar genes, plasmids containing promoters belonging to the four classes of the flagellar hierarchy fused to lacZ were transformed into the ΔflhF strain. Analyses of the β-galactosidase activity of the flagellar promoters in the ΔflhF strain showed wild-type levels of transcriptional activity for class I and class II promoters (Fig. 2). In contrast, the transcriptional activities of class III and class IV promoters were reduced two- to sixfold in the ΔflhF strain compared to the wild type. These results demonstrate that FlhF positively regulates class III and class IV gene transcription. Because of the hierarchical nature of flagellar transcription in V. cholerae, these results suggest that FlhF may exert its function through the regulation of the activity of FlrC, the class III flagellar activator.
FIG. 2.
Expression of representative class I, class II, class III, and class IV flagellar promoters in flhF and VC2061 mutant V. cholerae strains. V. cholerae strains KKV598 (wild type), KKV1560 (flhF), and KKV1721 (VC2061) carrying plasmids pKEK73 (flrAp-lacZ), pKEK72 (flrBp-lacZ), pKEK327 (fliEp-lacZ), pKEK80 (flaAp-lacZ), pKEK331 (flgKp-lacZ), pKEK79 (flaBp-lacZ), pKEK76 (flaCp-lacZ), pKEK77 (flaDp-lacZ), and pKEK81 (flaEp-lacZ) were assayed for β-galactosidase activity during logarithmic growth in LB. Assays were performed in triplicate, and standard deviations are shown.
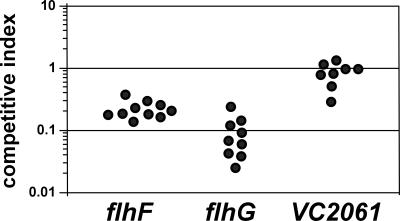
The ΔflhF strain was analyzed for virulence defects by utilizing an infant mouse intestinal colonization assay. The competitive index of ΔflhF versus that of the wild-type strain was 0.39 (see Fig. 4), indicating a modest defect in colonization of the infant mouse intestine. When the ΔflhF strain was grown under in vitro virulence factor-inducing conditions, CT and TCP expression levels were similar to those seen in the wild-type strain (not shown).
FIG. 4.
Intestinal colonization of flhF, flhG, and VC2061 mutant V. cholerae strains. Mutant strains KKV1560 (flhF), KKV1701 (flhG), and KKV1721 (VC2061) were coinoculated with O395 (wild type) perorally into infant mice at a ratio of ∼1:1. The competitive index is given as the output mutant/wild-type ratio divided by the input mutant/wild-type ratio. Each data point represents an individual mouse.
FlhG controls class I flagellar gene transcription and flagellar number.
A V. cholerae ΔflhG strain was constructed as described in Materials and Methods. The ΔflhG strain exhibited growth in LB similar to that of the wild-type strain. Immediately following the construction of this strain, it was analyzed for motility phenotypes. Interestingly, the ΔflhG strain appeared significantly less motile than the parental wild-type strain in motility agar, suggesting a reduced flagellar function (Fig. 1A). However, examination by TEM revealed that the ΔflhG cells had 8 to 10 flagella localized mainly at one of the poles (Fig. 1D), although some cells were observed with multiple flagella at both poles (Fig. 1E). Differences in flagellar width could be observed in flagella emanating from the same cell, suggesting that some of the flagella lacked a sheath. When observed with phase-contrast microscopy, the ΔflhG cells showed a markedly reduced motility and appeared to be in large aggregates due to entanglement of the multiple flagella.
This pronounced phenotype of the ΔflhG strain was noticeably unstable. Upon prolonged incubation (>1 day) of the ΔflhG strain in motility agar, an apparent increase in motility could be observed (not shown) that correlated with a reduction in the flagellar number on the individual cells (Fig. 1F), with most cells having one or two flagella. The unstable nature of the multiflagellate phenotype for this strain was reproducible; the ΔflhG strain was constructed several times, and each time the initial strain appeared poorly motile with multiple (8 to 10) flagella per cell, but after 1 to 2 days of incubation, the strain regained motility and reduced its flagellar number. This change in phenotype occurred in broth cultures as well as cultures on solid media, and all the cells in the population showed reduced flagellar numbers, suggesting an adaptive behavior rather than the appearance of suppressor mutations. Complementation of the flhG mutant was not performed, since it would be difficult to ascertain whether the restored motility phenotype was due to complementation or due to the unstable nature of the mutant phenotype.
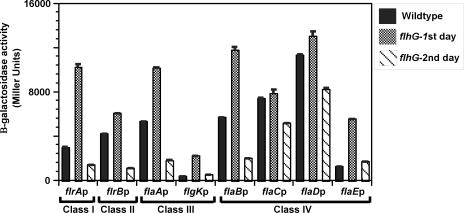
To determine the effect of FlhG upon flagellar transcription, the ΔflhG strain was transformed immediately upon construction with plasmids containing promoters belonging to the four classes of the flagellar hierarchy fused to lacZ. β-Galactosidase activity was measured in the ΔflhG strain immediately following transformation (1 day), when the cells displayed a multiflagellate phenotype, as well as 2 days after transformation, when the cells displayed a predominantly monoflagellate phenotype (Fig. 3). When the cells displayed the multiflagellate phenotype (1 day), there was a more-than-threefold increase in transcription of the class I flrA promoter. In general, the transcription of class II, class III, and class IV promoters was also increased in the ΔflhG mutant, although the increases ranged from modest (flrBp, flaCp, and flaDp) to two- to threefold (flaAp, flgKp, flaBp, and flaEp). Given the hierarchical nature of flagellar transcription, the increased expression of the master regulator FlrA may be the cause of the general increase in all flagellar gene transcription and the multiflagellate phenotype.
FIG. 3.
Expression of representative class I, class II, class III, and class IV flagellar promoters in the flhG mutant V. cholerae strain. V. cholerae strains KKV598 (wild type) and KKV1701 (flhG) were transformed with the plasmids pKEK73 (flrAp-lacZ), pKEK72 (flrBp-lacZ), pKEK80 (flaAp-lacZ), pKEK331 (flgKp-lacZ), pKEK79 (flaBp-lacZ), pKEK76 (flaCp-lacZ), pKEK77 (flaDp-lacZ) and pKEK81 (flaEp-lacZ). β-Galactosidase activity was assayed during logarithmic growth in LB on the first and second days after transformation of the flhG mutant. Assays were performed in triplicate, and standard deviations are shown.
β-Galactosidase activity was also measured in the ΔflhG strain 2 days after transformation, when the cells displayed a predominantly monoflagellate phenotype (Fig. 3). Notably, the transcription of all flagellar promoters was reduced more than twofold from the previous day's activities. The most dramatic reduction in transcription was observed for flrAp, whose transcription was reduced sevenfold from that seen in the multiflagellate cells. The reduction in expression of the master regulator FlrA seen in the monoflagellate cells may be the cause for the general reduction in all of the classes of flagellar promoters. Our results suggest that FlhG exerts its influence on the flagellar hierarchy by negatively regulating the transcription of flrA and that the absence of FlhG (and hence increased flagellar transcription) is deleterious to the cell and leads to compensatory mechanisms that downregulate flrA transcription.
The ΔflhG mutant strain (in the multiflagellate state, i.e., 1 day after construction) was analyzed for virulence properties by the infant mouse colonization assay. The ΔflhG strain showed an approximately 10-fold defect in its ability to colonize the infant mouse intestine (competitive index, 0.15) (Fig. 4). This colonization defect is consistent with a previous report in which a V. cholerae El Tor strain with a transposon insertion in flhG was identified as attenuated for intestinal colonization in a signature-tagged mutagenesis screen (29). Measurements of CT and TCP under in vitro virulence factor-inducing conditions revealed wild-type levels of CT and TCP in the ΔflhG mutant (not shown).
The ParA homologue VC2061 has little effect on flagellar transcription.
The third putative regulatory gene investigated from the flhA operon was VC2061, which encodes a ParA family protein. A V. cholerae strain with a deletion of VC2061 was constructed as described in Materials and Methods and analyzed for its motility phenotype. The VC2061 deletion strain exhibited growth in LB similar to that of the wild-type strain. The motility and flagellar morphology of the VC2061 deletion mutant resembled those of the parental wild-type strain, as determined by a motility agar assay (Fig. 1A), wet mounting, and TEM (data not shown). The transcriptional activity of the flagellar promoter-lacZ fusions was measured in the VC2061 deletion mutant (Fig. 2). Modest (less than twofold) reductions in transcription compared to the wild-type strain were detected at the flrA (class I) and flrB (class II) promoters, while the other flagellar promoters tested showed essentially wild-type levels of transcription. These results indicate that VC2061 has little effect on the motility and transcriptional activation of flagellar promoters in V. cholerae. Moreover, the VC2061 deletion mutant showed nearly wild-type levels of colonization of the infant mouse intestine (competitive index, 0.83) (Fig. 4) and expressed wild-type levels of CT and TCP under in vitro virulence factor-inducing conditions. Our results failed to demonstrate any critical role for VC2061 in either flagellar synthesis or virulence of V. cholerae.
DISCUSSION
The production of the bacterial flagellum is a highly energy-demanding process involving more than 40 genes that are organized into classes that are transcribed in a hierarchical fashion. Flagellar synthesis has been studied in great detail for S. enterica serovar Typhimurium, and elegant studies by multiple investigators have allowed for a tremendous understanding of flagellum-based motility in this peritrichously flagellated organism. Less is known about flagellar synthesis in polar flagellates, with the notable exception of C. crescentus, where flagellar synthesis is intimately connected to the developmental cycle (35). The V. cholerae flagellar transcription hierarchy consists of a combination of regulatory elements found within the flagellar hierarchies of both S. enterica serovar Typhimurium and C. crescentus and is quite similar to the flagellar hierarchy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (8, 23, 45).
Within S. enterica serovar Typhimurium and C. crescentus, multiple levels of regulation are present to ensure the correct temporal expression of flagellar subunits that must be assembled in a precise manner. We know considerably less about the regulation of V. cholerae flagellar transcription but infer that such complex regulation must exist to ensure that only a single flagellum is assembled at the pole in the most efficient manner. In the present study, we analyzed the roles of three putative regulatory genes found only in polar flagellates, namely, flhF, flhG, and VC2061, in V. cholerae flagellar synthesis. These three genes are located within an apparent class II (FlrA- and σ54-dependent) operon (37) that also contains the genes for σ28 as well as critical chemotaxis regulatory genes (cheA2 and cheY3) (2, 14).
FlhF as a regulator of class III transcription.
We have previously shown that the transcription of class III flagellar genes in V. cholerae requires phosphorylation of the σ54-dependent activator FlrC by the histidine kinase FlrB (5). FlrC binds directly to enhancer elements in class III promoters to stimulate transcription (4a). Thus, one potential checkpoint controlling the class II-III transition would be the phosphorylation of FlrC, which is probably induced upon completion of the MS-ring-switch-export apparatus. Homologues of FlrC that regulate a similar set of flagellar genes and that contain both the response regulatory (phosphorylation) domain and the σ54 activation domain can be found in other polar flagellates, such as P. aeruginosa and C. jejuni (8, 18). The mechanism linking flagellar assembly to the transcriptional activity of these FlrC homologues might also be conserved between these bacteria.
Our results revealed a reduction in the transcription of class III and IV flagellar genes in a V. cholerae ΔflhF mutant, indicating that FlhF positively regulates class III transcription. Since FlrC is the direct activator of class III genes, we suggest that FlhF exerts its positive regulatory function by stimulating FlrB phosphorylation of FlrC by an interaction with either FlrB or FlrC (Fig. 5). FlhF has homology with the SRP54 family of signal recognition particle proteins, in the domain predicted to encode GTP-binding activity (located in approximately the C-terminal half of FlhF) (19). While constructing a plasmid to complement the ΔflhF mutant, we inadvertently removed the C-terminal 42 nucleotides of the flhF gene. This truncated FlhF protein retained the ability to complement for FlhF function, indicating that the C-terminal 14 aa are not necessary for its activity. However, an N-terminal maltose binding protein (MBP) fusion to the full-length FlhF protein was not able to complement for FlhF function (presumably due to steric hindrance caused by the presence of MBP), suggesting that the amino terminus of FlhF might interact with some other cellular component (data not shown).
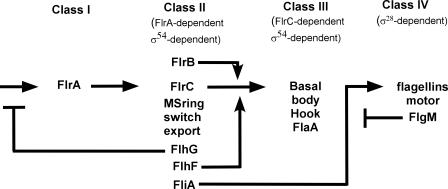
FIG. 5.
Proposed model of regulation of the V. cholerae flagellar transcription hierarchy. The results presented here indicate that FlhG acts as a negative regulator of class I (flrA) transcription, while FlhF acts as positive regulator of class III flagellar promoters, perhaps exerting its function through the modulation of FlrC activity. We have previously shown that FlrB is a positive regulator of class III gene transcription by facilitating the phosphorylation of FlrC (5) and that FlgM is a negative regulator of class IV gene transcription through its function as an anti-σ28 factor (4). flgM is transcribed from a class IV promoter (as shown here) and also from a flagellum-independent promoter (37).
FlhF homologues in H. pylori and C. jejuni have been demonstrated to be required for flagellar synthesis. In both H. pylori and C. jejuni, FlhF appears to stimulate transcription of the flagellar gene class regulated by the FlrC homologue FlgR (18, 34); thus, it appears that FlhF function may be conserved between V. cholerae, H. pylori, and C. jejuni. In P. putida, ΔflhF mutants appear nonmotile but display a random (rather than polar) placement of flagella and additionally show defects in stress resistance (36). Conflicting reports have shown either a requirement or a lack of a requirement for FlhF in Bacillus subtilis flagellar synthesis (3, 47). In C. crescentus, transcription by the FlrC homologue FlbD requires assembly of the MS ring-export-switch apparatus, and coupling assembly to FlbD activity is accomplished by an interaction with the transactivator FliX (32, 33). While FliX is not a clear FlhF homologue per se, it contains a GTP-binding SRP54 motif, suggesting that this may be the salient feature common to the regulation of FlrC homologues in various bacteria. By analogy with FliX, we would therefore predict that FlhF directly interacts with FlrC to regulate its transcriptional activity.
FlhG as a regulator of class I transcription.
The σ54-dependent activator FlrA is the master regulator of the V. cholerae flagellar hierarchy. As such, it is the sole class I flagellar gene, and until now no regulatory factors have been identified that modulate its transcription, which is σ54 and σ28 independent (37). The results presented here demonstrate that FlhG negatively regulates flrA transcription, since the transcription of flrA (and the other three classes of flagellar promoters) is increased in a ΔflhG mutant; we presume that the effects on class II, III, and IV transcription are due to increased FlrA levels. Because flhG is transcribed by an FlrA-dependent (class II) promoter, an autoregulatory loop exists in which FlrA transcribes a factor that shuts down its own synthesis. The ΔflhG mutant cells had the unusual phenotype of multiple (typically 8 to 10) polar flagella and were observed to be nonmotile in a soft agar assay, primarily due to entanglement of the flagella causing large aggregates of bacteria. Interestingly, the multiflagellate phenotype of the ΔflhG strain was unstable, and after several days the cells were observed to regain motility in a soft agar assay, which was correlated with a reduction in the number of flagella per cell and a decrease in flrA (and class II, III, and IV) transcription. Due to the unstable phenotype, we constructed the ΔflhG strain several times, and each time we observed the same initial multiflagellate nonmotile state followed by a motile state with a reduction in flagellar number. Flagellar synthesis requires a significant amount of energy expenditure, and thus the multiflagellate phenotype of the ΔflhG mutant likely induces some type of adaptation to reduce the energy cost to the cell.
The multiflagellate phenotype was also seen in a P. aeruginosa fleN (homologue of V. cholerae flhG) mutant (1), suggesting that the function of FlhG is conserved between P. aeruginosa and V. cholerae. However, Dasgupta and Ramphal (7) demonstrated that FleN has no effect on the transcription of fleQ (the flrA homologue), but rather physically interacts with FleQ and inhibits its transcriptional activity; thus, a fleN mutant has elevated levels of class II, III, and IV transcription but normal class I transcription. We have not yet determined whether FlhG also interacts with FlrA to inhibit its transcriptional activity, but our experiments clearly showed effects of FlhG on flrA transcription, indicating that the functions of FlhG may differ between P. aeruginosa and V. cholerae. This difference could be due to the presence of 30 aa in the amino terminus of V. cholerae FlhG that are missing in P. aeruginosa FleN.
While FlhG represses flrA expression, regulatory factors that activate its transcription are not yet known. The expression of the master flagellar regulator, CtrA, in C. crescentus is regulated by cell cycle cues (35). In E. coli, S. enterica serovar Typhimurium, and P. aeruginosa, the master flagellar regulator (flhDC or fleQ) is controlled by a σ70-dependent promoter (6, 22). We predict that flrA is likely also transcribed from a σ70-dependent promoter and that cell division cues contribute to its regulation, which may be relayed through the negative influence of FlhG.
Lack of effect of VC2061 on flagellar synthesis.
A third potential regulatory gene, VC2061, is located within the putative operon that also contains flhF and flhG. The gene product is annotated as a ParA family protein and has homology with the cell division ATPase MinD, which is involved in septum-site determination (10, 13). Because a single flagellum is synthesized per V. cholerae cell, we have hypothesized that cell division cues might contribute to flagellar regulation and hence the potential involvement of a MinD homologue. However, a VC2061 mutant produced polar flagella indistinguishable from those of the wild-type strain, and there was little effect on flagellar transcription in the VC2061 deletion strain. Clearly, VC2061 does not play an essential role in flagellar synthesis; its function may be redundant with other factors, and thus its inactivation results in a subtle phenotype.
Flagellar regulation and intestinal colonization.
Our previous results have shown that alteration of the transcriptional activity of the class III flagellar regulator, FlrC, alters the ability of V. cholerae to colonize the infant mouse intestine (5). The results presented here demonstrate that FlhG also contributes to intestinal colonization, since a flhG mutant exhibited an ∼10-fold colonization defect. This result is consistent with the previous identification of a flhG mutant as being attenuated in a signature-tagged mutagenesis screen of V. cholerae utilizing an infant mouse model (29). The defect in intestinal colonization indicates that the downregulation of flagellar transcription contributes to virulence, but it is not clear why, since this strain expressed wild-type levels of CT and TCP under inducing conditions within the laboratory. Possibly, increased flagellar synthesis causes a metabolic imbalance that is deleterious within the intestinal environment, or perhaps the aggregated state of the multiflagellate bacteria prevents access to preferred colonization sites.
The lack of FlhF only caused a modest defect (approximately threefold) in intestinal colonization, which is reminiscent of the approximately threefold defect of a ΔflrC mutant (5). Since our results suggest that FlhF exerts its positive effects through FlrC, one might anticipate that a ΔflhF ΔflrC mutant would exhibit similar colonization behavior. The VC2061 mutant exhibited a colonization behavior similar to that of the wild-type strain. Our results establish a significant role for FlhG, a modest role for FlhF, and no detectable role for VC2061 in intestinal colonization.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grant AI43486 to K.E.K.
REFERENCES
- 1.Arora, S. K., N. Dasgupta, S. Lory, and R. Ramphal. 2000. Identification of two distinct types of flagellar cap proteins, FliD, in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 68:1474-1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Butler, S. M., and A. Camilli. 2004. Both chemotaxis and net motility greatly influence the infectivity of Vibrio cholerae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:5018-5023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Carpenter, P. B., D. W. Hanlon, and G. W. Ordal. 1992. flhF, a Bacillus subtilis flagellar gene that encodes a putative GTP-binding protein. Mol. Microbiol. 6:2705-2713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Correa, N. E., J. R. Barker, and K. E. Klose. 2004. The Vibrio cholerae FlgM homologue is an anti-sigma 28 factor that is secreted through the sheathed polar flagellum. J. Bacteriol. 186:4613-4619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4a.Correa, N. E., and K. E. Klose. 2005. Characterization of enhancer binding by the Vibrio cholerae flagellar regulatory protein FlrC. J. Bacteriol. 187:3158-3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Correa, N. E., C. M. Lauriano, R. McGee, and K. E. Klose. 2000. Phosphorylation of the flagellar regulatory protein FlrC is necessary for Vibrio cholerae motility and enhanced colonization. Mol. Microbiol. 35:743-755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dasgupta, N., E. P. Ferrell, K. J. Kanack, S. E. West, and R. Ramphal. 2002. fleQ, the gene encoding the major flagellar regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, is sigma 70 dependent and is downregulated by Vfr, a homolog of Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein. J. Bacteriol. 184:5240-5250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dasgupta, N., and R. Ramphal. 2001. Interaction of the antiactivator FleN with the transcriptional activator FleQ regulates flagellar number in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 183:6636-6644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dasgupta, N., M. C. Wolfgang, A. L. Goodman, S. K. Arora, J. Jyot, S. Lory, and R. Ramphal. 2003. A four-tiered transcriptional regulatory circuit controls flagellar biogenesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 50:809-824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Donnenberg, M. S., and J. B. Kaper. 1991. Construction of an eae deletion mutant of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by using a positive-selection suicide vector. Infect. Immun. 59:4310-4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Easter, J., Jr., and J. W. Gober. 2002. ParB-stimulated nucleotide exchange regulates a switch in functionally distinct ParA activities. Mol. Cell 10:427-434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Freter, R., and P. C. O'Brien. 1981. Role of chemotaxis in the association of motile bacteria with intestinal mucosa: fitness and virulence of nonchemotactic Vibrio cholerae mutants in infant mice. Infect. Immun. 34:222-233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gardel, C. L., and J. J. Mekalanos. 1996. Alterations in Vibrio cholerae motility phenotypes correlate with changes in virulence factor expression. Infect. Immun. 64:2246-2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Godfrin-Estevenon, A. M., F. Pasta, and D. Lane. 2002. The parAB gene products of Pseudomonas putida exhibit partition activity in both P. putida and Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 43:39-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gosink, K. K., R. Kobayashi, I. Kawagishi, and C. C. Hase. 2002. Analyses of the roles of the three cheA homologs in chemotaxis of Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 184:1767-1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Guzman, L.-M., D. Belin, M. J. Carson, and J. Beckwith. 1995. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol. 177:4121-4130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hanahan, D. 1983. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J. Mol. Biol. 166:577-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Heidelberg, J. F., J. A. Eisen, W. C. Nelson, R. A. Clayton, M. L. Gwinn, R. J. Dodson, D. H. Haft, E. K. Hickey, J. D. Peterson, L. Umayam, S. R. Gill, K. E. Nelson, T. D. Read, H. Tettelin, D. Richardson, M. D. Ermolaeva, J. Vamathevan, S. Bass, H. Qin, I. Dragoi, P. Sellers, L. McDonald, T. Utterback, R. D. Fleishmann, W. C. Nierman, O. White, S. L. Salzberg, H. O. Smith, R. R. Colwell, J. J. Mekalanos, J. C. Venter, and C. M. Fraser. 2000. DNA sequence of both chromosomes of the cholera pathogen Vibrio cholerae. Nature 406:477-483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hendrixson, D. R., and V. J. DiRita. 2003. Transcription of sigma54-dependent but not sigma28-dependent flagellar genes in Campylobacter jejuni is associated with formation of the flagellar secretory apparatus. Mol. Microbiol. 50:687-702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Keenan, R. J., D. M. Freymann, R. M. Stroud, and P. Walter. 2001. The signal recognition particle. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70:755-775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Klose, K. E., and J. J. Mekalanos. 1998. Differential regulation of multiple flagellins in Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 180:303-316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Klose, K. E., and J. J. Mekalanos. 1998. Distinct roles of an alternative sigma factor during both free-swimming and colonizing phases of the Vibrio cholerae pathogenic cycle. Mol. Microbiol. 28:501-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kutsukake, K. 1997. Autogenous and global control of the flagellar master operon, flhD, in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Gen. Genet. 254:440-448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kutsukake, K., Y. Ohya, and T. Iino. 1990. Transcriptional analysis of the flagellar regulon of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 172:741-747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Laub, M. T., S. L. Chen, L. Shapiro, and H. H. McAdams. 2002. Genes directly controlled by CtrA, a master regulator of the Caulobacter cell cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:4632-4637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lauriano, C. M., C. Ghosh, N. E. Correa, and K. E. Klose. 2004. The sodium-driven flagellar motor controls exopolysaccharide expression in Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 186:4864-4874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee, S. H., S. M. Butler, and A. Camilli. 2001. Selection for in vivo regulators of bacterial virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:6889-6894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Macnab, R. M. 2003. How bacteria assemble flagella. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57:77-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mekalanos, J. J., R. J. Collier, and W. R. Romig. 1979. Enzymic activity of cholera toxin. II. Relationships to proteolytic processing, disulfide bond reduction, and subunit composition. J. Biol. Chem. 254:5855-5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Merrell, D. S., D. L. Hava, and A. Camilli. 2002. Identification of novel factors involved in colonization and acid tolerance of Vibrio cholerae. Mol. Microbiol. 43:1471-1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miller, J. H. 1992. A short course in bacterial genetics, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, N.Y.
- 31.Miller, V. L., and J. J. Mekalanos. 1988. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J. Bacteriol. 170:2575-2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Muir, R. E., and J. W. Gober. 2004. Regulation of FlbD activity by flagellum assembly is accomplished through direct interaction with the trans-acting factor, FliX. Mol. Microbiol. 54:715-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Muir, R. E., T. M. O'Brien, and J. W. Gober. 2001. The Caulobacter crescentus flagellar gene, fliX, encodes a novel trans-acting factor that couples flagellar assembly to transcription. Mol. Microbiol. 39:1623-1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Niehus, E., H. Gressmann, F. Ye, R. Schlapbach, M. Dehio, C. Dehio, A. Stack, T. F. Meyer, S. Suerbaum, and C. Josenhans. 2004. Genome-wide analysis of transcriptional hierarchy and feedback regulation in the flagellar system of Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 52:947-961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Osley, M. A., M. Sheffery, and A. Newton. 1977. Regulation of flagellin synthesis in the cell cycle of caulobacter: dependence on DNA replication. Cell 12:393-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pandza, S., M. Baetens, C. H. Park, T. Au, M. Keyhan, and A. Matin. 2000. The G-protein FlhF has a role in polar flagellar placement and general stress response induction in Pseudomonas putida. Mol. Microbiol. 36:414-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Prouty, M. G., N. E. Correa, and K. E. Klose. 2001. The novel sigma54- and sigma28-dependent flagellar gene transcription hierarchy of Vibrio cholerae. Mol. Microbiol. 39:1595-1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pruss, B. M., and P. Matsumura. 1997. Cell cycle regulation of flagellar genes. J. Bacteriol. 179:5602-5604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Richardson, K. 1991. Roles of motility and flagellar structure in pathogenicity of Vibrio cholerae: analysis of motility mutants in three animal models. Infect. Immun. 59:2727-2736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rothfield, L. I., Y. L. Shih, and G. King. 2001. Polar explorers: membrane proteins that determine division site placement. Cell 106:13-16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Simons, R. W., F. Houman, and N. Kleckner. 1987. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene 53:85-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Svennerholm, A. M., and J. Holmgren. 1978. Identification of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin by means of a ganglioside immunosorbent assay (GM1-ELISA) procedure. Curr. Microbiol. 1:19-23. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Waldor, M. K., and J. J. Mekalanos. 1996. Lysogenic conversion by a filamentous phage encoding cholera toxin. Science 272:1910-1914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wang, R. F., and S. Kushner. 1991. Construction of versatile low-copy-number vectors for cloning, sequencing and gene expression in Escherichia coli. Gene 100:195-199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wu, J., and A. Newton. 1997. Regulation of the Caulobacter flagellar gene hierarchy; not just for motility. Mol. Microbiol. 24:233-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yonekura, K., S. Maki-Yonekura, and K. Namba. 2002. Growth mechanism of the bacterial flagellar filament. Res. Microbiol. 153:191-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zanen, G., H. Antelmann, H. Westers, M. Hecker, J. M. van Dijl, and W. J. Quax. 2004. FlhF, the third signal recognition particle-GTPase of Bacillus subtilis, is dispensable for protein secretion. J. Bacteriol. 186:5956-5960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]