Abstract
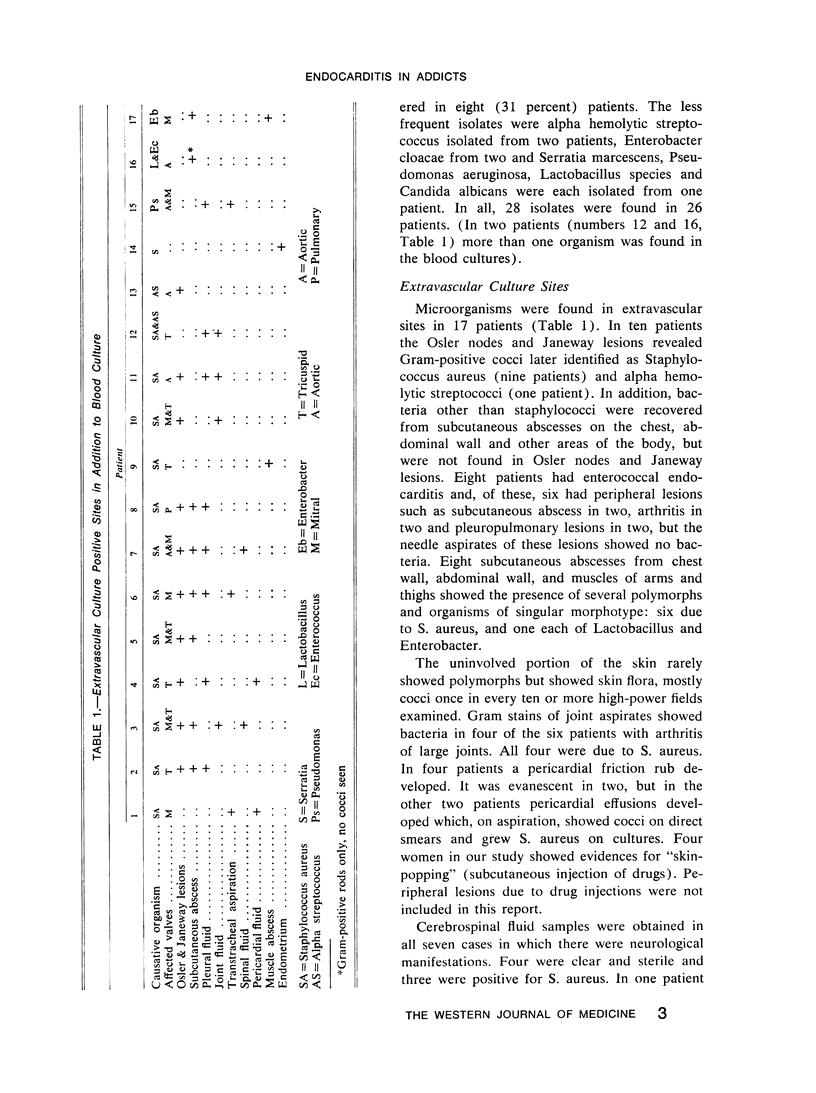
Gram stains and cultures of multiple extravascular sites showed the infecting organisms in 17 of 26 heroin addicts with endocarditis. In addition to routine blood cultures, the etiologic agent was cultured from Osler nodes and Janeway lesions in ten patients, subcutaneous abscesses in eight, pleural fluids in eight, joint aspirates in three, spinal fluids in three, pericardial fluids in two, muscle abscesses in two and endometrium in one patient. Gram-positive cocci were found in extravascular lesions in 11 of 12 patients with staphy-lococcal endocarditis and from as many as four different sites. In contrast, no Gram-positive cocci were seen in extravascular sites in any of eight patients with enterococcal endocarditis although six of them had peripheral lesions. Gram stain and culture of multiple extravascular sites appears to provide a valuable early clue to the nature of the etiologic agent in addict endocarditis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks G. F., Pribble A. H., Beaty H. N. Early diagnosis of bacteremia by buffy-coat examinations. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Nov;132(5):673–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowder J. G., White A. Teichoic acid antibodies in staphylococcal and nonstaphylococcal endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Jul;77(1):87–90. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helpern M., Rho Y. M. Deaths from narcotism in New York City. Incidence, circumstances, and postmortem findings. N Y State J Med. 1966 Sep 15;66(18):2391–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. R., Jr, Siekert R. G., Geraci J. E. Neurologic manifestations of bacterial endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Jul;71(1):21–28. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-71-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner P. I., Weinstein L. Infective endocarditis in the antibiotic era. N Engl J Med. 1966 Feb 3;274(5):259–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196602032740506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louria D. B., Hensle T., Rose J. The major medical complications of heroin addiction. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jul;67(1):1–22. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menda K. B., Gorbach S. L. Favorable experience with bacterial endocarditis in heroin addicts. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Jan;78(1):25–32. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANKEY G. A. Subacute bacterial endocarditis at the University of Minnesota Hospital, 1939 through 1959. Ann Intern Med. 1961 Oct;55:550–561. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-55-4-550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers D. L., Mandell G. L. Intraleukocytic bacteria in endocarditis patients. JAMA. 1974 Jan 21;227(3):312–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U., Sheagren J. N. Staphlococcal endocarditis in parenteral drug abusers: source of the organism. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):788–790. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Gemmingen G. R., Winkelmann R. K. Osler's node of subacute bacterial endocarditis. Focal necrotizing vaculitis of the glomus body. Arch Dermatol. 1967 Jan;95(1):91–94. doi: 10.1001/archderm.95.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


