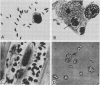
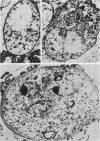
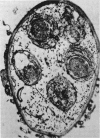
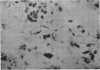
Abstract
Pneumocystis carinii and Toxoplasma gondii are the two major parasitic protozoan pathogens in the immunocompromised host. Both organisms cause latent infection in humans and many animals. Cats are the definitive hosts for toxoplasmosis; the animal vector for pneumocystis (if any) has not been defined. Toxoplasma is an obligate intracellular parasite, whereas the available evidence suggests that Pneumocystis carinii exists primarily extracellularly. In compromised hosts, pneumocystis infection usually involves only lungs, whereas toxoplasma causes a generalized infection with encephalitis being the principal clinical manifestation. Both types of infection are treated with combinations of folate antagonists (trimethoprim or pyrimethamine with sulfonamide). Both parasites are associated with cytomegalovirus infection in immunosuppressed hosts, an association which may be due to symbiosis between parasites, or to an additive immunosuppressive effect of dual infection on the hosts.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. E., Remington J. S. The diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. South Med J. 1975 Nov;68(11):1433–1443. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197511000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awen C. F., Baltzan M. A. Systemic dissemination of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Can Med Assoc J. 1971 May 8;104(9):809–812. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKE B. A., KROVETZ L. J., GOOD R. A. Occurrence of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in children with agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics. 1961 Aug;28:196–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford C. R. Toxoplasmosis mimicking a brain abscess in an adult with treated scleroderma. Neurology. 1975 Apr;25(4):343–345. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.4.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett R. N., Hull J. G., Vortel V., Schwarz J. Pneumocystis carinii in lymph nodes and spleen. Arch Pathol. 1969 Aug;88(2):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
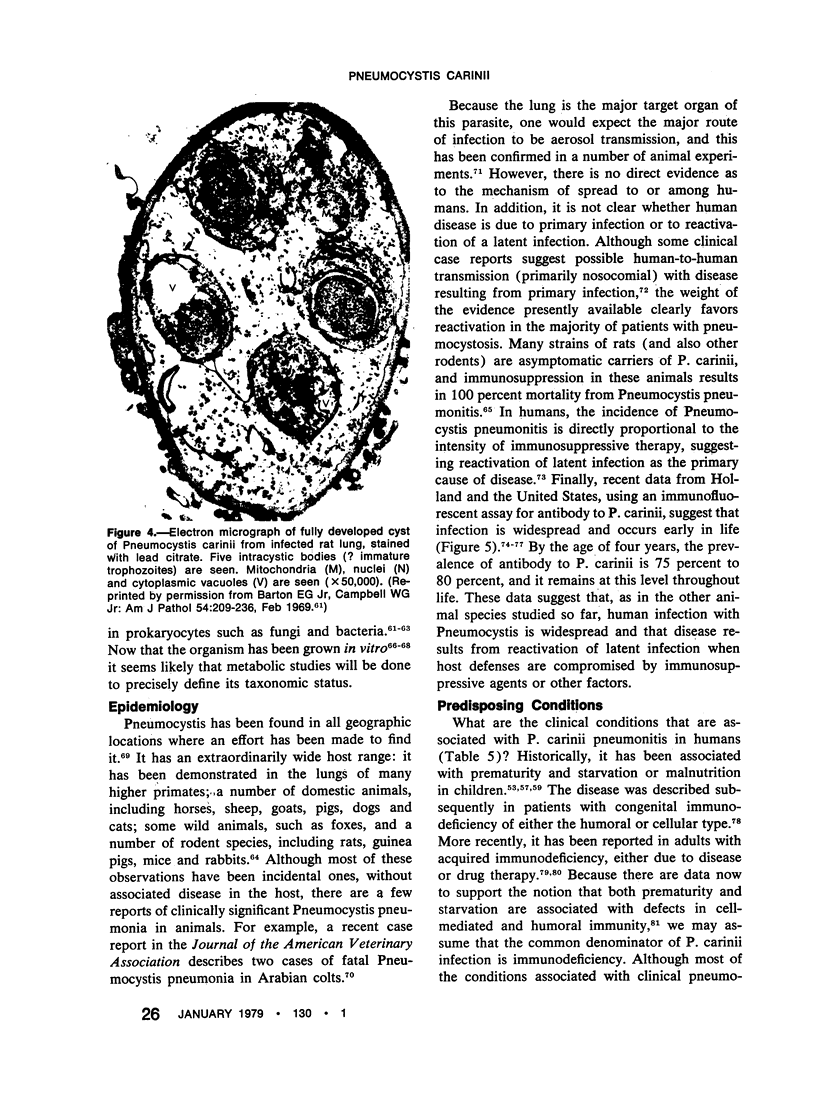
- Barton E. G., Jr, Campbell W. G., Jr Further observations on the ultrastructure of pneumocystis. Arch Pathol. 1967 Jun;83(6):527–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommer W., Höfling K. H., Heunert H. H. Lebendebeobachtungen über das Eindringen von Toxoplasmen in die Wirtszelle. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1968 Dec 6;93(49):2365–passim. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1110941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B. A., Good R. A. Pneumocystis carinii infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Jan;52(1):23–51. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197301000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd R. B., Horn B. R. Infection due to Pneumocystis carinii simulating lobar bacterial pneumonia. Chest. 1976 Jul;70(1):91–92. doi: 10.1378/chest.70.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. M., Kimball A. C., Armstrong D., Lieberman P. H. Toxoplasmosis. Clinical experiences in a cancer hospital. Am J Med. 1973 Jan;54(1):30–38. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino R. A. Percutaneos pulmonary needle diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Oct;43:137–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Couvreur J. Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy and its transmission to the fetus. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1974 Feb;50(2):146–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman R. F., Remington J. S. Value of lymph-node biopsy in the diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 25;289(17):878–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310252891702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Finley T. N., Mintz L., Klein H. Z. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia by bronchopulmonary lavage. JAMA. 1974 Nov 4;230(5):713–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubey J. P., Miller N. L., Frenkel J. K. Characterization of the new fecal form of Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1970 Jun;56(3):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDMAN H. A., MILLER L. T. Serological study of toxoplasmosis prevalence. Am J Hyg. 1956 Nov;64(3):320–335. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K. Adoptive immunity to intracellular infection. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1309–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
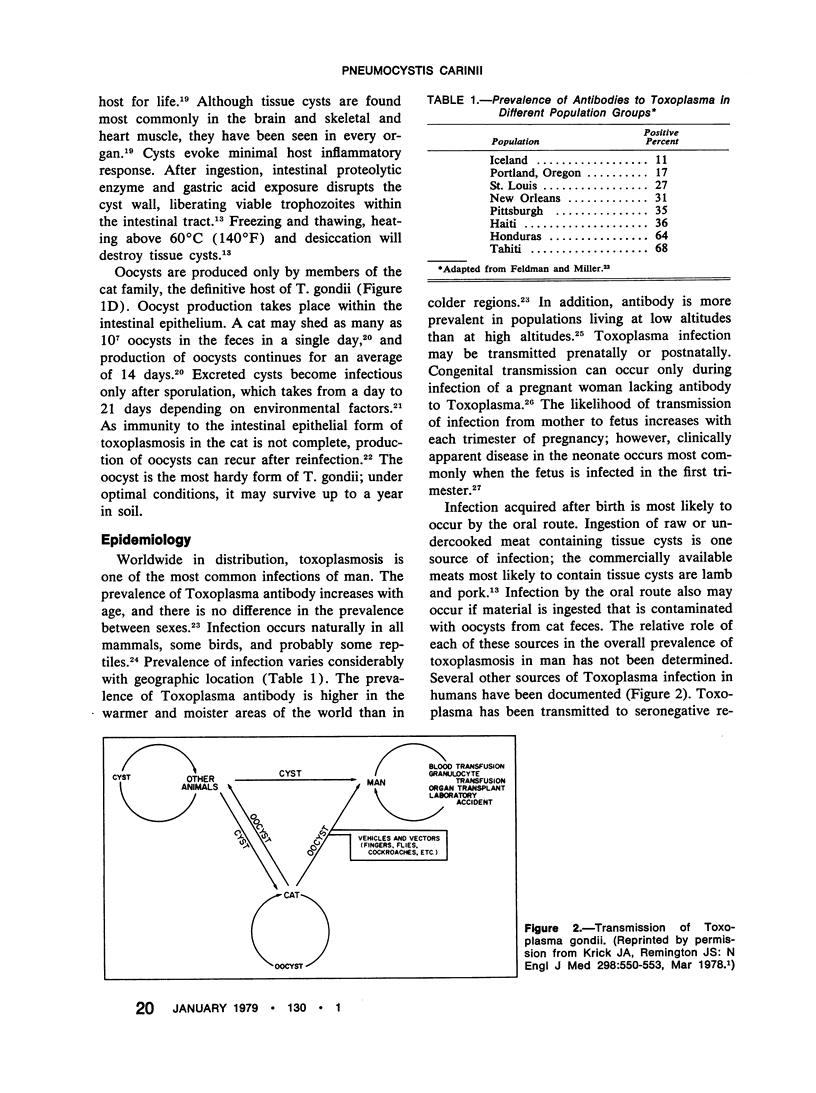
- Frenkel J. K., Dubey J. P., Miller N. L. Toxoplasma gondii in cats: fecal stages identified as coccidian oocysts. Science. 1970 Feb 6;167(3919):893–896. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3919.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Dubey J. P., Miller N. L. Toxoplasma gondii: fecal forms separated from eggs of the nematode Toxocara cati. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):432–433. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B. A., Wenglin B. D., Hyland R. N., Rifkind D. Roentgenographically atypical Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Jan;111(1):89–96. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAJDUSEK D. C. Pneumocystis carinii; etiologic agent of interstitial plasma cell pneumonia of premature and young infants. Pediatrics. 1957 Apr;19(4 Pt 1):543–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARD S., MAGNUSSON J. H. A glandular form of toxoplasmosis in connection with pregnancy. Acta Med Scand. 1951;141(1):59–64. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1951.tb14195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O., Ruskin J., Remington J. S. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Problems in diagnosis and therapy in 24 cases. Calif Med. 1972 Apr;116(4):6–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell B., Jacobs J. B., Powell R. D., DeVita V. T. Pneumocystis carinii: the spectrum of diffuse interstitial pneumonia in patients with neoplastic diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Mar;72(3):337–340. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-72-3-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. L., Maher E. Four uncommon infections in Hodgkin's disease. JAMA. 1966 Dec 5;198(10):1129–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEMSATH F. A., PINKERTON H. Disseminated cytomegalic inclusion disease and disseminated toxoplasmosis in an adult with myeloid metaplasia; report of a case. Am J Clin Pathol. 1956 Jan;26(1):36–41. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/26.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. O., Weller T. H. Activation and transmission in rats of infection with Pneumocystis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1401–1404. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Feldman S., Aur R. J., Verzosa M. S., Hustu H. O., Simone J. V. Intensity of immunosuppressive therapy and the incidence of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2004–2009. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Feldman S., Chaudhary S. C., Ossi M. J., Cox F., Sanyal S. K. Comparison of pentamidine isethionate and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Pediatr. 1978 Feb;92(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Kuhn S., Chaudhary S., Feldman S., Verzosa M., Aur R. J., Pratt C., George S. L. Successful chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 29;297(26):1419–1426. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712292972602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Price R. A., Kim H. K., Coburn T. P., Grigsby D., Feldman S. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in children with malignancies. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):404–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Price R. A., Sisko F., Havron W. S., Kafatos A. G., Schonland M., Smythe P. M. Protein-calorie malnutrition. A host determinant for Pneumocystis carinii infection. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Jul;128(1):44–52. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110260046008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVADY G., PALDY L. Ein neues Behandlungsverfahren der interstitiellen plasmazelligen Pneumonie Frühgeborener mit fünfwertigem Stibium und aromatischen Diamidinen. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1958 Jan;106(1):10–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVADY G., PALDY L., UNGER G. WEITERE ERFAHRUNGEN BEI DER BEHANDLUNG DER INTERSTITIELLEN PLASMACELLULAEREN PNEUMONIE MIT PENTAMIDIN. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1963 Aug;111:297–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS L., REMINGTON J. S., MELTON M. L. The resistance of the encysted form of Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1960 Feb;46:11–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES T. C., KEAN B. H., KIMBALL A. C. TOXOPLASMIC LYMPHADENITIS. JAMA. 1965 Apr 5;192:1–5. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080140007001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Yeh S., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. I. Mechanism of entry and intracellular fate of the parasite. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1157–1172. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagen L. J., Kimball A. C., Christian C. L. Serologic evidence of toxoplasmosis among patients with polymyositis. Am J Med. 1974 Feb;56(2):186–191. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90596-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Hughes W. T. Comparison of methods for identification of Pneumocystis carinii in pulmonary aspirates. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Oct;60(4):462–466. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.4.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby H. B., Kenamore B., Guckian J. C. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia treated with pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Oct;75(4):505–509. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-4-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krick J. A., Remington J. S. Toxoplasmosis in the adult--an overview. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 9;298(10):550–553. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803092981006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUDLAM G. B., BEATTIE C. P. PULMONARY TOXOPLASMOSIS? Lancet. 1963 Nov 30;2(7318):1136–1138. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90789-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre C. R., Sulzer A. J., Norman L. G. Serial propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in cell line cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1204–1206. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1204-1206.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeGolvan D. P., Heidelberger K. P. Disseminated, granulomatous Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Arch Pathol. 1973 May;95(5):344–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna M. A., Lichtiger B. Disseminated toxoplasmosis and cytomegalovirus infection complicating Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Apr;55(4):499–505. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke E., Carlberg K., Norrby R. Interactions between Toxoplasma gondii and its host cells: function of the penetration-enhancing factor of toxoplasma. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):853–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.853-861.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud A. A., Strickland G. T., Warren K. S. Toxoplasmosis and the host-parasite relationship in murine schistosomiasis mansoni. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):408–413. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Jones T. C. The interaction in vitro of Pneumocystis carinii with macrophages and L-cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):157–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G. Some observations on the serology of Pneumocystis carinii infections in the United States. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.317-321.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor G. R. Manifestations and management of ocular toxoplasmosis. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1974 Feb;50(2):192–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Blazkovec A. A., Walker D. L. Immunosuppression during acute murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):835–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Woods D., Hughes W. T. Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in Vero cell culture. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):66–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.66-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi S. A. Disseminated Pneumocystis carinii in thymic alymphoplasia. Arch Pathol. 1974 Mar;97(3):162–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M., Steiner P., Victoria M. S., James P., Fikrig S., Goldenberg L., Kassner E. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Occurrence in a healthy American infant. JAMA. 1977 Nov 21;238(21):2301–2301. doi: 10.1001/jama.238.21.2301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Gentry L. O. Acquired toxoplasmosis: infection versus diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):1006–1017. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S. Toxoplasmosis in the adult. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1974 Feb;50(2):211–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repsher L. H., Schröter G., Hammond W. S. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis by means of endobronchial brush biopsy. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 17;287(7):340–341. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208172870708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Zamvil L., Remington J. S. Recurrent Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in a child with hypogammaglobulinemia. Am J Dis Child. 1973 Jan;125(1):102–103. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1973.04160010068015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D., Faris T. D., Hill R. B., Jr Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Studies on the diagnosis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Nov;65(5):943–956. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-65-5-943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P. P., Martini N., Armstrong D. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Diagnosis by lung biopsy. Am J Med. 1975 Jun;58(6):794–802. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90634-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P., Armstrong D., Ramos C. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. A clinicopathologic study of twenty patients with neoplastic diseases. Am J Med. 1972 Oct;53(4):428–436. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin J., Remington J. S. Toxoplasmosis in the compromised host. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Feb;84(2):193–199. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-2-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryning F. W., Remington J. S. Effect of cytochalasin D on Toxoplasma gondii cell entry. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):739–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.739-743.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. N., Dellers R. W., Buergelt C. D., Hsu F. S., Kabelac L. P., Moe K. K., Tennant B., Vaughan J. T. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in two foals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1973 Apr 15;162(8):648–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel S. E., Lunde M. N., Gelderman A. H., Halterman R. H., Brown J. A., Levine A. S., Graw R. G., Jr Transmission of toxoplasmosis by leukocyte transfusion. Blood. 1971 Apr;37(4):388–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C. Endocytic uptake of particles by mononuclear phagocytes and the penetration of obligate intracellular parasites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):161–169. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P., Schottenfeld D. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: a cluster of eleven cases. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):772–777. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Allison A. C. Role of T lymphocytes in recovery from murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):458–462. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.458-462.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzberg J. E., Remington J. S. Transmission of Toxoplasma. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jul;129(7):777–779. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120440005002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUNEMATSU Y., SHIOIRI K., KUSANO N. THREE CASES OF LYMPHADENOPATHIA TOXOPLASMOTICA WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE APPLICATION OF FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY TECHNIQUE FOR DETECTION OF TOXOPLASMA IN TISSUE. Jpn J Exp Med. 1964 Aug;34:216–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologides A., Kennedy B. J. Toxoplasmic myocarditis and pericarditis. Am J Med. 1969 Aug;47(2):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENEK J., JIROVEC O., LUKES J. Interstitial plasma cell pneumonia in infants. Ann Paediatr. 1953 Jan;180(1):1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vietzke W. M., Gelderman A. H., Grimley P. M., Valsamis M. P. Toxoplasmosis complicating malignancy. Experience at the National Cancer Institute. Cancer. 1968 May;21(5):816–827. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196805)21:5<816::aid-cncr2820210506>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer T. L., Bernheim C., Engelbrecht E. Two cases of hepatitis due to Toxoplasma gondii. Lancet. 1967 Oct 28;2(7522):919–921. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel C. L., Cohen M. H., Powell R. D., Jr, DeVita V. T. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jan;68(1):97–108. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vossen M. E., Beckers P. J., Meuwissen J. H., Stadhouders A. M. Developmental biology of Pneumocystis carinii, and alternative view on the life cycle of the parasite. Z Parasitenkd. 1978 Apr 20;55(2):101–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00384826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton B. C., De Arjona I., Benchoff B. M. Relationship of Toxoplasma antibodies to altitude. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Jul;15(4):492–495. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Schnelle V., Armstrong D., Rosen P. P. Nude mouse: a new experimental model for Pneumocystis carinii infection. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.301657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N. S., Huang S. N., Thurlbeck W. M. Combined Pneumocystis carinii and cytomegalovirus infection. Arch Pathol. 1970 Dec;90(6):529–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W. R., Askin F. B., Dehner L. P. Lung biopsy in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: a histopathologic study of typical and atypical features. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jan;67(1):11–19. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/67.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Western K. A., Perera D. R., Schultz M. G. Pentamidine isethionate in the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Nov;73(5):695–702. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-5-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb M. E., Schwarz M. I., Charles M. A., Larson P. H. Interstitial fibrosis after Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Nov;73(5):761–765. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-5-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Krick J. A., Remington J. S. Pulmonary infection in the compromised host: part I. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Aug;114(2):359–394. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]