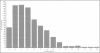
Abstract
BACKGROUND: There is considerable variation in prescribing, and existing standards against which primary care prescribing is routinely judged consist largely of local or national averages. There is thus a need for more sophisticated standards, which must be widely applicable and have credibility among the general practice profession. AIM: A study aimed to develop a range of criteria of prescribing quality, to set standards of performance for these criteria, and apply these standards to practices. METHOD: A consensus group consisting of eight general practitioners and a resource team was convened to develop and define criteria and set standards of prescribing performance using prescribing analyses and cost (PACT) data. The standards were applied to 1992-93 prescribing data from all 518 practices in the former Northern Regional Health Authority. RESULTS: The group developed criteria and set numeric standards for 13 aspects of prescribing performance in four areas: generic prescribing, prescribing within specific therapeutic groups, drugs of limited clinical value and standards based on prescribing volume. Except for generic prescribing, standards for individual criteria were achieved by between 9% and 34% of practices. For each criterion, a score was allocated based on whether the standard was achieved or not. Total scores showed considerable variation between practices. The distribution of scores was similar between fundholding and non-fundholding practices, and also between dispensing and non-dispensing practices. CONCLUSION: Using a consensus group of general practitioners it is possible to agree criteria and standards of prescribing performance. This novel approach offers a professionally driven method for assessing the quality of prescribing in primary care.
Full text
PDF

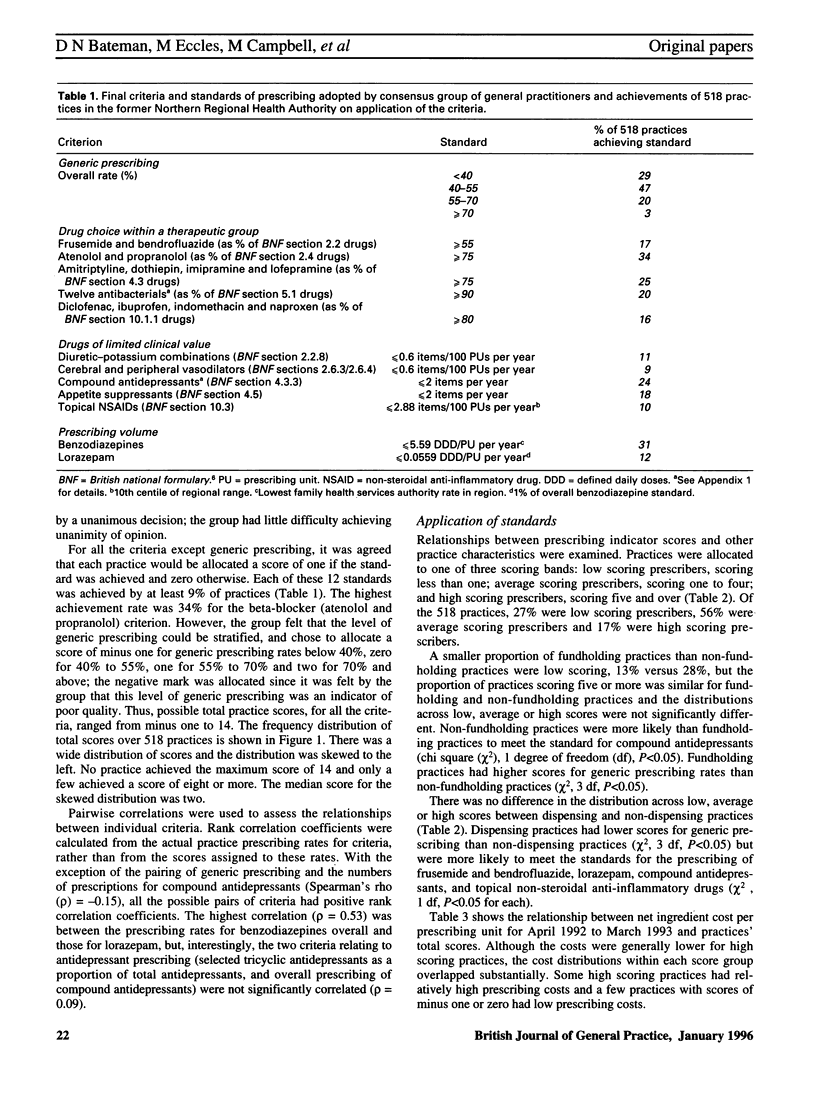



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brook R. H., Kosecoff J. B., Park R. E., Chassin M. R., Winslow C. M., Hampton J. R. Diagnosis and treatment of coronary disease: comparison of doctors' attitudes in the USA and the UK. Lancet. 1988 Apr 2;1(8588):750–753. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91550-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catford J. C. Quality of prescribing for children in general practice. Br Med J. 1980 Jun 14;280(6229):1435–1437. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6229.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leape L. L., Park R. E., Kahan J. P., Brook R. H. Group judgments of appropriateness: the effect of panel composition. Qual Assur Health Care. 1992 Jun;4(2):151–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell M., Heaney D., Howie J. G., Noble S. General practice fundholding: observations on prescribing patterns and costs using the defined daily dose method. BMJ. 1993 Nov 6;307(6913):1190–1194. doi: 10.1136/bmj.307.6913.1190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlynn E. A., Kosecoff J., Brook R. H. Format and conduct of consensus development conferences. Multi-nation comparison. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 1990;6(3):450–469. doi: 10.1017/s0266462300001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Brink G., Bollen C. W., Van de Wall O. E., Hoeve L. J., Porsius A. J. A drug use review study in patients with obstructive lung disease. Assessment of the quality of drug therapy. Pharm Weekbl Sci. 1992 Oct 16;14(5):311–315. doi: 10.1007/BF01977619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zwanenberg T. D., Grant G. B., Gregory D. A. Can rational prescribing be assessed? J R Coll Gen Pract. 1987 Jul;37(300):308–310. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]