Abstract
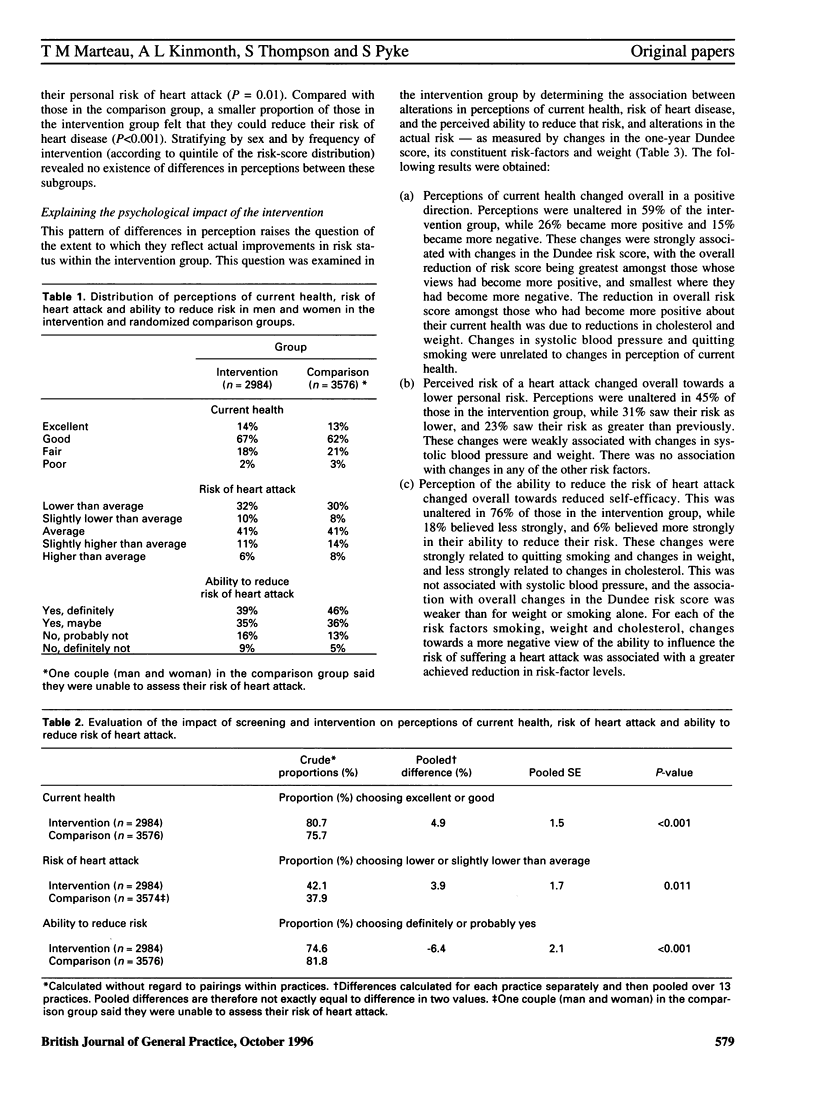
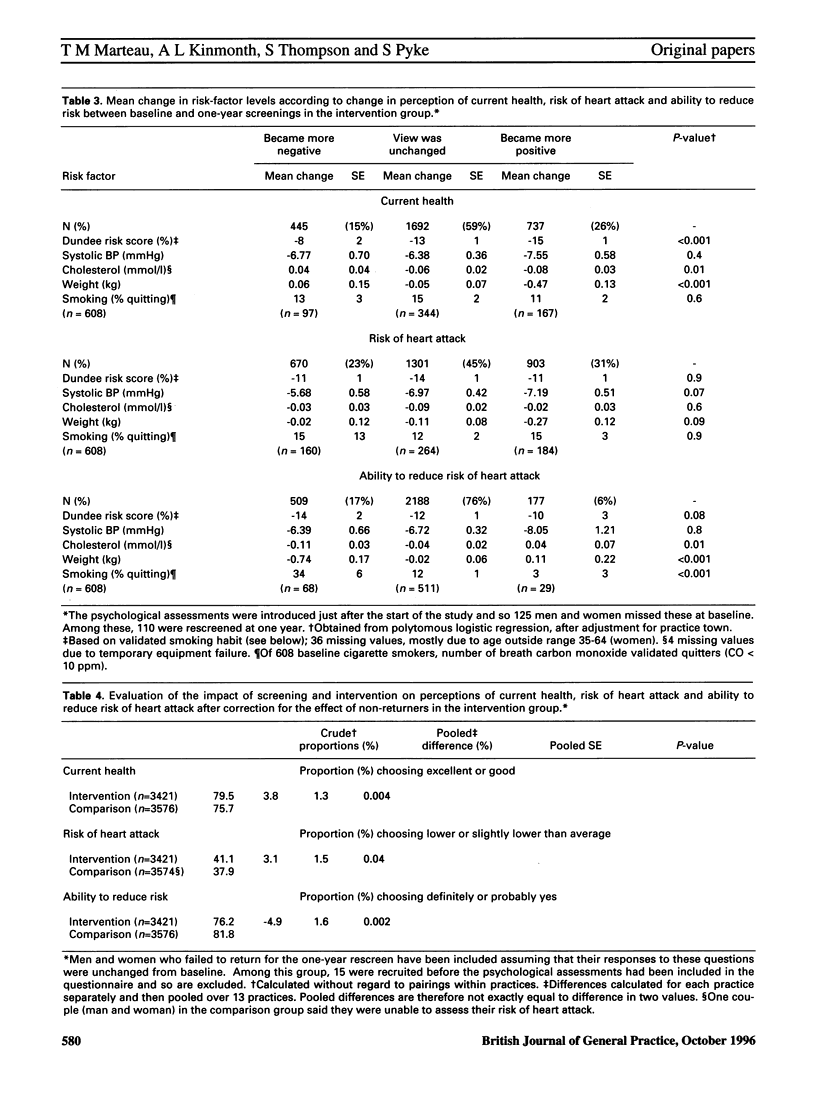
BACKGROUND: There have been many reports of the adverse psychological effects of screening. Here we discuss the results of a randomized controlled study--one of the first to address this issue. AIM: To determine the extent to which participation in a population-based intervention programme that aims to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases raises concerns about health, or undermines a belief in the ability to reduce that risk. METHOD: A randomized controlled trial involving 13 general practices in England, Wales and Scotland was conducted. Two thousand, nine hundred and eighty-four middle-aged men and women undergoing cardiovascular risk-screening and intervention, and a randomized comparison group of 3,576 men and women from the same practices, who were not offered the intervention, were compared on three outcomes: perception of current health, perceived risk of suffering a heart attack, and perceived ability to reduce the risk of suffering a heart attack. RESULTS: We found no evidence to suggest that participation in this one-year, population-based intervention programme, to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease raised concerns about health or risk of a heart attack; indeed, those in the intervention group were slightly more optimistic about their health. Alterations in perceptions of current health and the risk of suffering a heart attack were associated directly with true alterations in risk factors. A more noticeable effect on participants in this intervention programme was a reduction in their perceived ability to further reduce their risks of a heart attack. This was associated with a decrease in weight and with quitting smoking. CONCLUSION: Contemporary screening and intervention programmes in primary care, aimed at reducing risk of cardiovascular disease, do not necessarily lead to raised anxiety or concern about health. A more subtle effect of screening would appear to be one of reassurance in the face of continuing, albeit reduced, risk.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DerSimonian R., Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986 Sep;7(3):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlay S., Heller R. F. Effectiveness and hazards of case finding for a high cholesterol concentration. BMJ. 1990 Jun 16;300(6739):1545–1547. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6739.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathoo V. Investigation of non-responders at a cervical cancer screening clinic in Manchester. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Apr 9;296(6628):1041–1042. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6628.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd P., Price M. G., Graham L. E., Beilstein B. A., Tarbell S. J., Bacchetti P., Fortmann S. P. Consequences of worksite hypertension screening. Differential changes in psychosocial function. Am J Med. 1986 May;80(5):853–860. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90628-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper A. G., Pocock S. J., Phillips A. N., Walker M. A scoring system to identify men at high risk of a heart attack. Health Trends. 1987 May;19(2):37–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoate H. G. Can health screening damage your health? J R Coll Gen Pract. 1989 May;39(322):193–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunstall-Pedoe H. The Dundee coronary risk-disk for management of change in risk factors. BMJ. 1991 Sep 28;303(6805):744–747. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6805.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tymstra T., Bieleman B. The psychosocial impact of mass screening for cardiovascular risk factors. Fam Pract. 1987 Dec;4(4):287–290. doi: 10.1093/fampra/4.4.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. E., Jr, Sherbourne C. D. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992 Jun;30(6):473–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


