Abstract
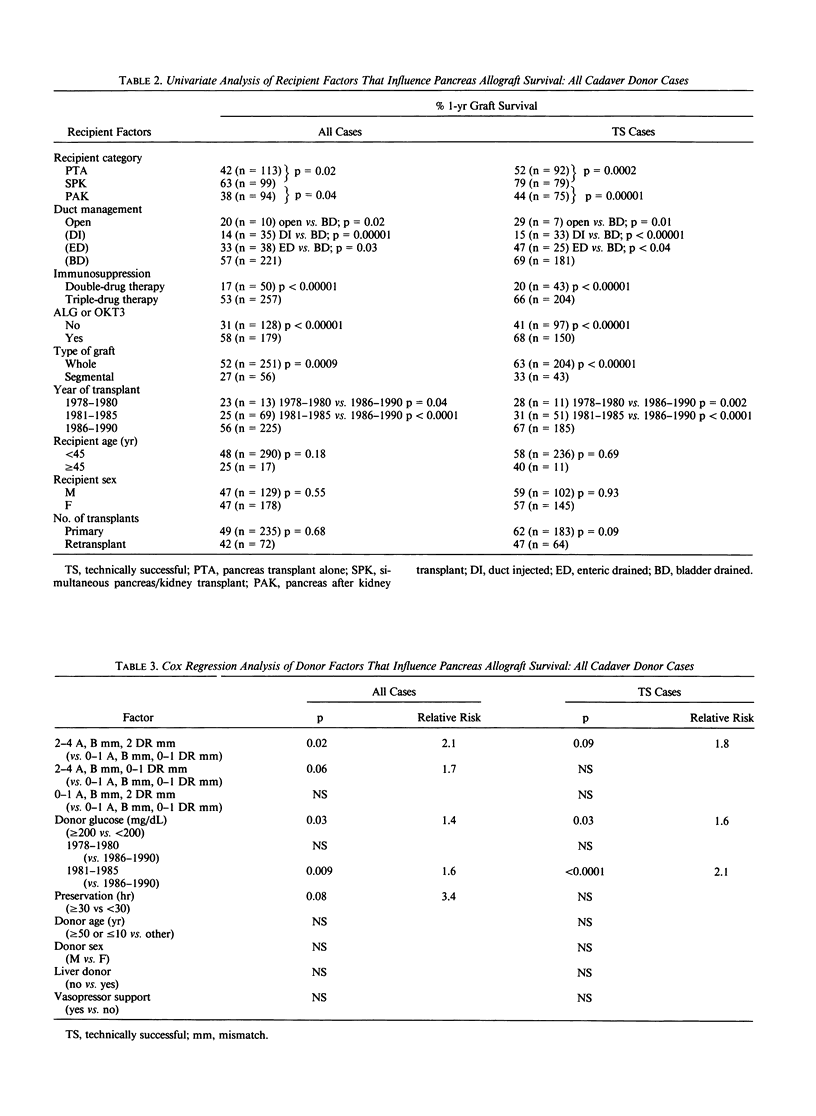
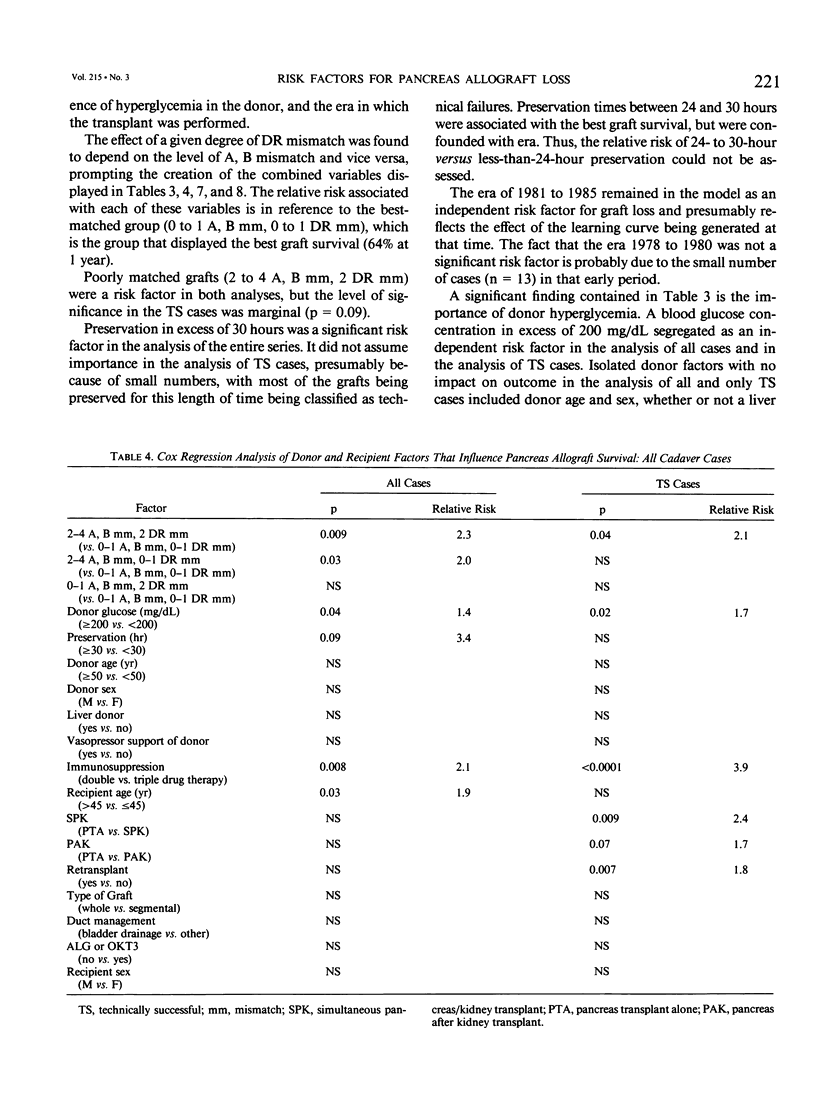
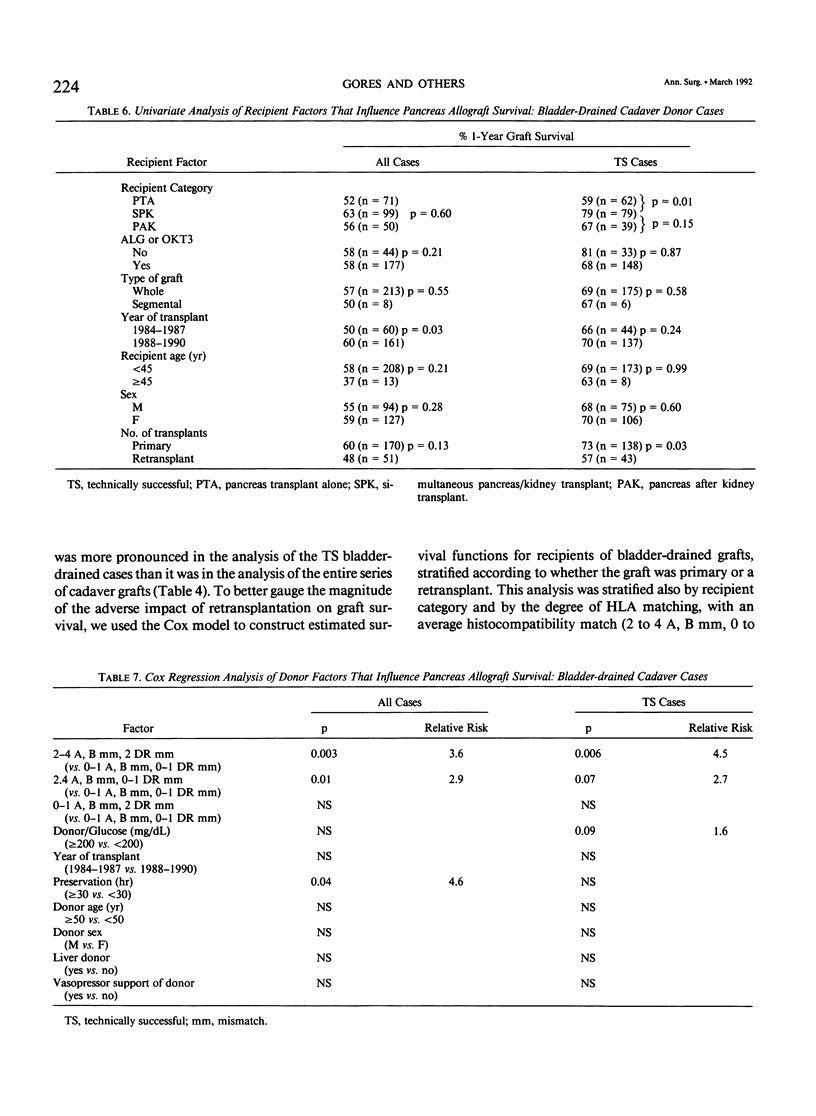
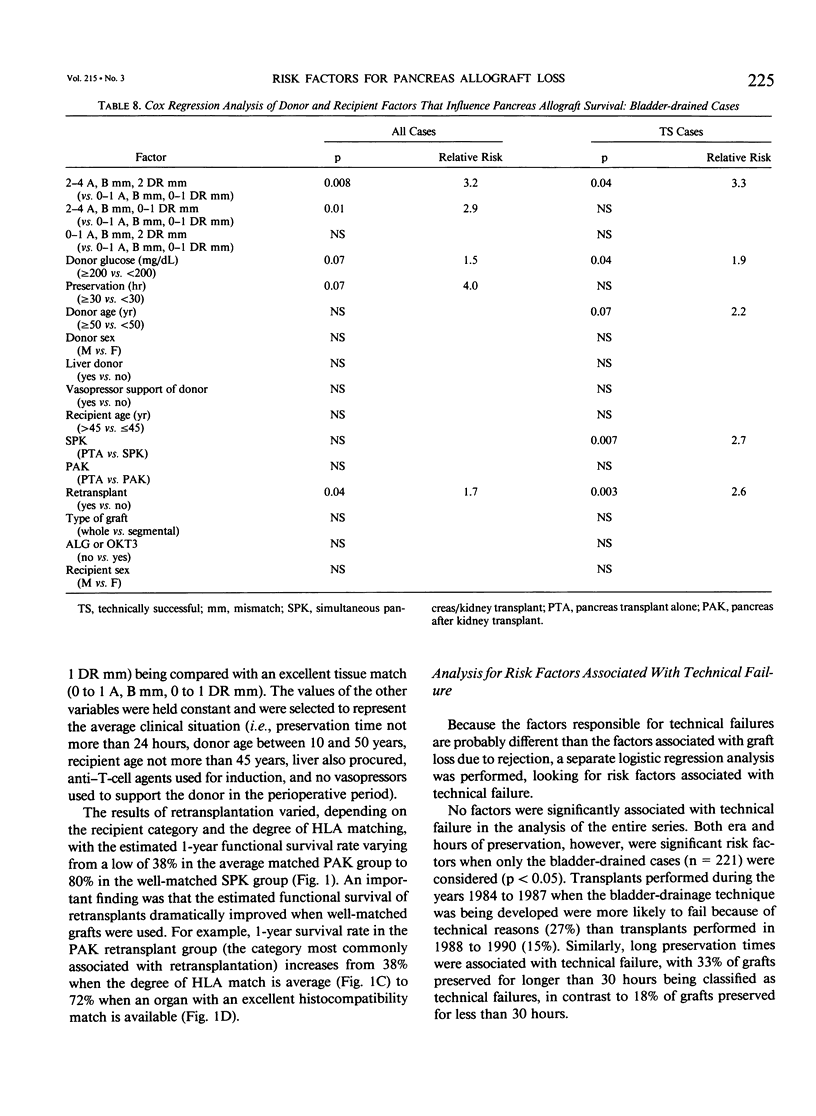
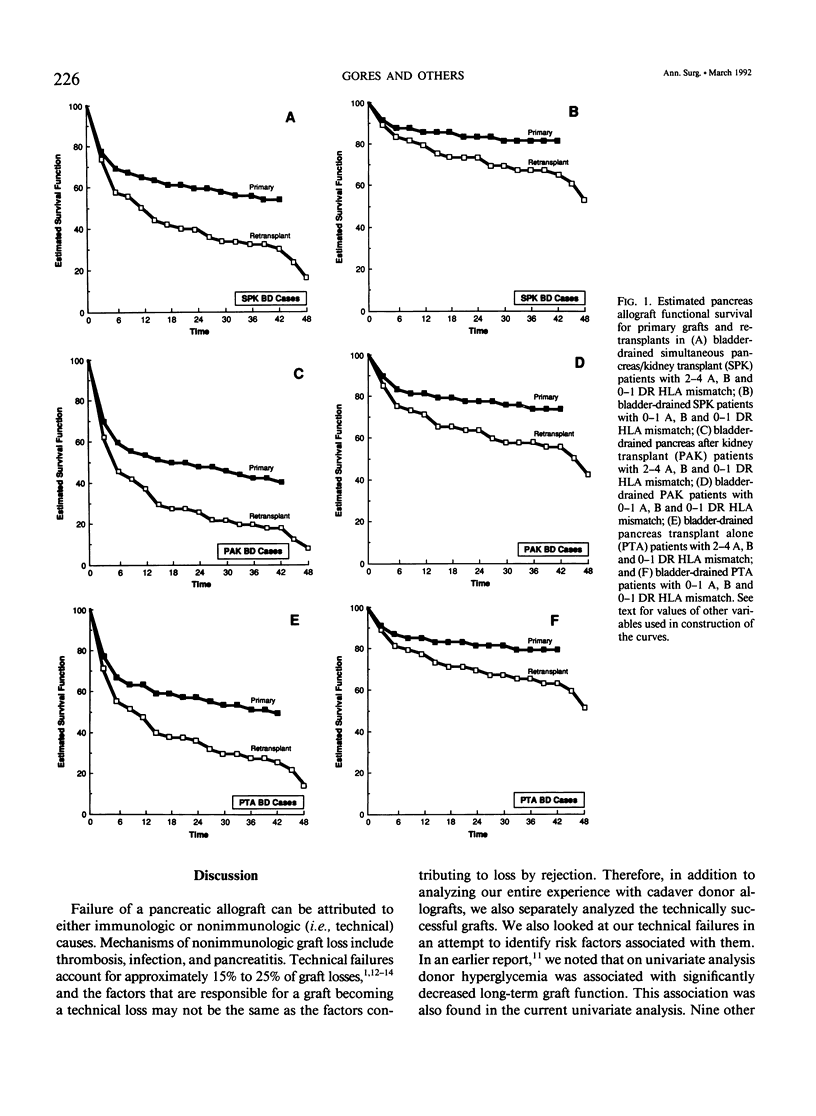
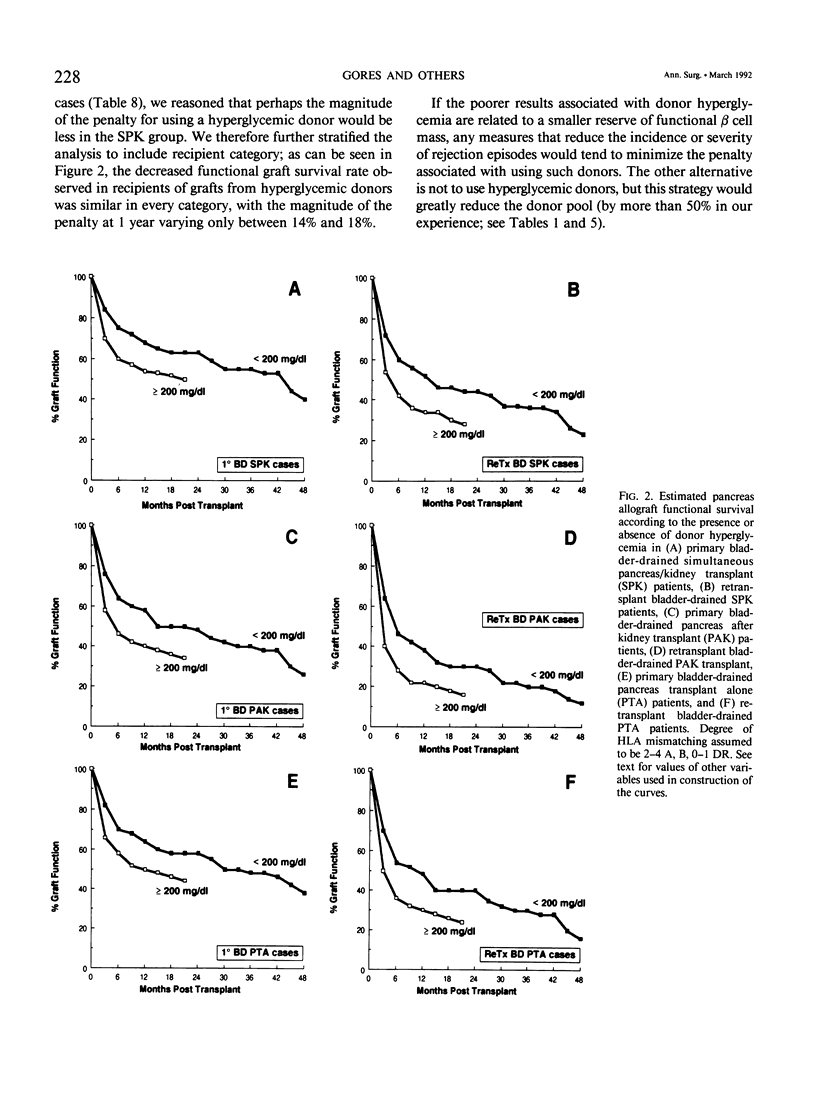
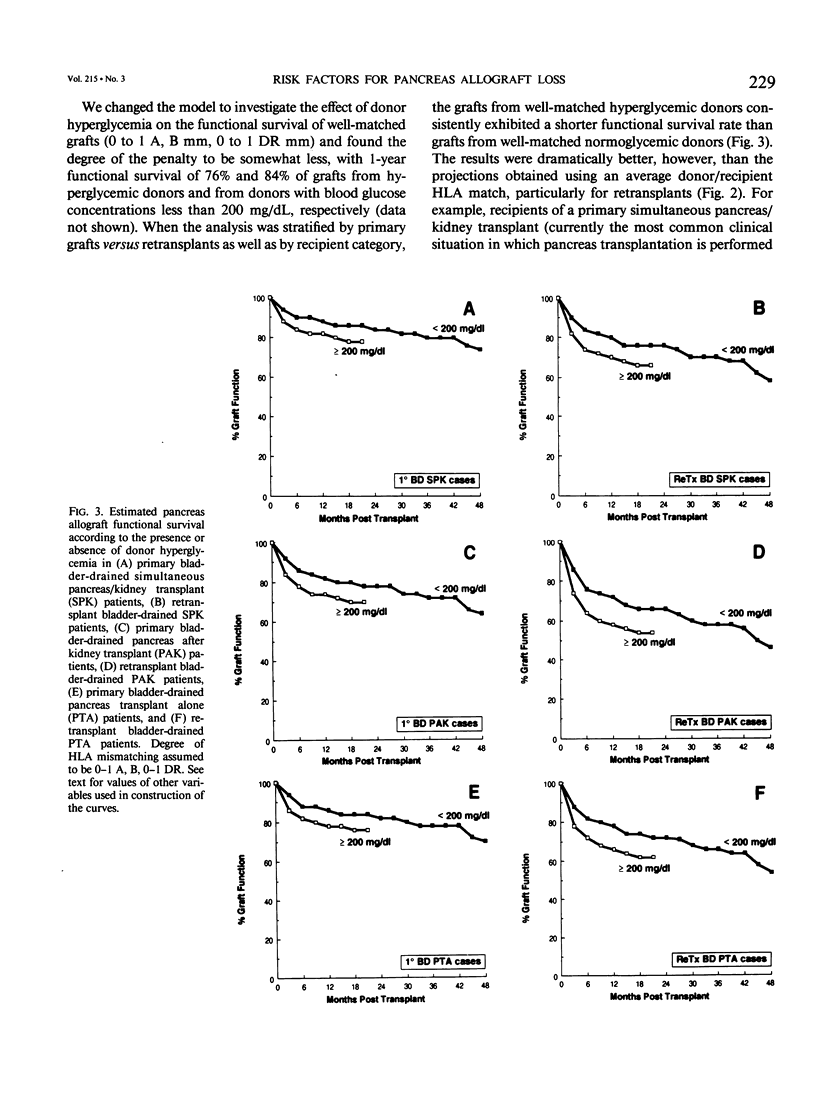
The impact of multiple donor and recipient variables on functional survival of 307 cadaveric pancreas allografts transplanted in 253 recipients at the authors' institution between July 25, 1978 and September 4, 1990 was determined using the Cox proportional hazards regression model. Relative risk of graft loss was calculated for all cases as well as for technically successful (TS) ones. Factors with an impact in descending order of significance for TS cases were immunosuppression (RR = 3.9 for double-drug versus triple-drug maintenance, p less than 0.0001); recipient category (RR = 2.4 for pancreas alone versus simultaneous pancreas/kidney, p = 0.009); retransplantation (RR = 1.8 for retransplants versus primary grafts, p = 0.007); donor hyperglycemia (RR = 1.7 for blood glucose greater than or equal to 200 versus less than 200 mg/dL, p = 0.02); human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching (RR = 2.1 for poor versus a good match, p = 0.04). A logistic regression analysis also was performed to determine which factors predisposed to technical failure; none were identified. To make the model as relevant as possible to their current program, the authors analyzed only the bladder-drained cases (n = 221; 1984 to 1990). All patients received triple therapy. Recipient category, retransplantation, donor hyperglycemia, and degree of HLA matching remained as significant risk factors. Construction of estimated survival curves showed that the results of retransplantation were significantly improved, and the penalty incurred by using hyperglycemic donors was partially ameliorated by using well-matched donors. Because preservation times up to 30 hours did not exert an adverse effect on outcome, an argument is made to share pancreata between centers to achieve good matches.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fasola C. G., Fryd D. S., Fischel R. J., Ascher N. L., Payne W. D., Najarian J. S. Adult kidney retransplantation: evolution of treatment and results over 25 years at the University of Minnesota. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 2):2165–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEHAN E. A. A GENERALIZED WILCOXON TEST FOR COMPARING ARBITRARILY SINGLY-CENSORED SAMPLES. Biometrika. 1965 Jun;52:203–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gores P. F., Viste A., Hesse U. J., Moudry-Munns K. C., Dunn D. L., Sutherland D. E. The influence of donor hyperglycemia and other factors on long-term pancreatic allograft survival. Transplant Proc. 1990 Apr;22(2):437–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruessner R. W., Manivel C., Dunn D. L., Sutherland D. E. Pancreaticoduodenal transplantation with enteric drainage following native total pancreatectomy for chronic pancreatitis: a case report. Pancreas. 1991 Jul;6(4):479–488. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199107000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse U. J., Gores P. F., Sutherland D. E. Serum amylase and plasma glucose levels in pancreas cadaver donors: correlation with functional status of the pancreatic graft. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 3):2765–2766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriett J. M., Kaye M. P. The Registry of the International Society for Heart Transplantation: seventh official report--1990. J Heart Transplant. 1990 Jul-Aug;9(4):323–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margreiter R., Klima G., Bösmüller C., Königsrainer A., Schmid T., Steiner E. Rejection of kidney and pancreas after pancreas-kidney transplantation. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38 (Suppl 1):79–81. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.s79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel P., Moudry-Munns K., Najarian J. S., Gruessner R., Dunn D. L., Sutherland D. E. Influence of preservation time on outcome and metabolic function of bladder-drained pancreas transplants. Transplantation. 1990 Feb;49(2):294–303. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199002000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel P., Schlumpf R., Dunn D. L., Moudry-Munns K., Najarian J. S., Sutherland D. E. Pancreas retransplants compared with primary transplants. Transplantation. 1991 Apr;51(4):825–833. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199104000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto M., Sutherland D. E., Fernandez-Cruz L., Heil J., Najarian J. S. Experimental and clinical experience with urine amylase monitoring for early diagnosis of rejection in pancreas transplantation. Transplantation. 1987 Jan;43(1):73–79. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198701000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto M., Sutherland D. E., Goetz F. C., Rosenberg M. E., Najarian J. S. Pancreas transplant results according to the technique of duct management: bladder versus enteric drainage. Surgery. 1987 Oct;102(4):680–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw B. W., Jr, Wood R. P. Improved results with retransplantation of the liver. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 2):2407–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So S. K., Minford E. J., Moudry-Munns K. C., Gillingham K., Sutherland D. E. DR matching improves cadaveric pancreas transplant results. Transplant Proc. 1990 Apr;22(2):687–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollinger H. W., Cook K., Kamps D., Glass N. R., Belzer F. O. Clinical and experimental experience with pancreaticocystostomy for exocrine pancreatic drainage in pancreas transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1984 Jun;16(3):749–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollinger H. W., Stratta R. J., D'Alessandro A. M., Kalayoglu M., Pirsch J. D., Belzer F. O. Experience with simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation. Ann Surg. 1988 Oct;208(4):475–483. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198810000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollinger H. W., Stratta R. J., Kalayoglu M., Pirsch J. D., Belzer F. O. Pancreas transplantation with pancreaticocystostomy and quadruple immunosuppression. Surgery. 1987 Oct;102(4):674–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Dunn D. L., Goetz F. C., Kennedy W., Ramsay R. C., Steffes M. W., Mauer S. M., Gruessner R., Moudry-Munns K. C., Morel P. A 10-year experience with 290 pancreas transplants at a single institution. Ann Surg. 1989 Sep;210(3):274–288. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198909000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Goetz F. C., Najarian J. S. One hundred pancreas transplants at a single institution. Ann Surg. 1984 Oct;200(4):414–440. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198410000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Moudry-Munns K. C. International Pancreas Transplant Registry report. Clin Transpl. 1988:53–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tydén G., Brattström C., Lundgren G., Ostman J., Gunnarsson R., Groth C. G. Improved results in pancreatic transplantation by avoidance of nonimmunological graft failures. Transplantation. 1987 May;43(5):674–676. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198705000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tydén G., Reinholt F., Brattström C., Lundgren G., Wilczek H., Bolinder J., Ostman J., Groth C. G. Diagnosis of rejection in recipients of pancreatic grafts with enteric exocrine diversion by monitoring pancreatic juice cytology and amylase excretion. Transplant Proc. 1987 Oct;19(5):3892–3894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Grundy S. Hyperglycaemia as an inducer as well as a consequence of impaired islet cell function and insulin resistance: implications for the management of diabetes. Diabetologia. 1985 Mar;28(3):119–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00273856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


