Abstract
The records of 92 patients with symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts referred for surgical management over a 27-year period were retrospectively reviewed to compare outcome in 42 patients managed with operative internal drainage procedures (group I) with that in 52 patients managed with computed tomography-directed percutaneous catheter drainage (PCD) (group II). The two groups were similar for patient age, sex, pseudocyst location, and cause. The frequency of antecedent pseudocyst-associated complications was less in group I (16.7 versus 38.5%, p less than 0.05). Seven group I patients and four group II patients had major complications (16.7 versus 7.7%, not significant). Group II mean duration of catheter drainage was 42.1 days, and the drain track infection rate was 48.1%. The frequency of antecedent operative cyst drainage was similar (14.2 versus 13.5%), as was the frequency of subsequent operations for complications related to chronic pancreatitis (9.5 versus 19.2%, not significant). Mortality rate was greater in group I (7.1% versus 0%, p less than 0.05). Pseudocysts can be effectively managed either by open operation with internal drainage or by PCD. Drawbacks of PCD include the controlled external pancreatic fistula and the risk of drain track infection. Percutaneous catheter drainage has the following advantages: (1) low mortality rate, (2) does not require a major operation, (3) does not violate the operative field in cases when subsequent retrograde duct drainage procedures are required. Neither PCD nor internal drainage is definitive, and with either technique subsequent correction of underlying pancreatic pathology may be necessary.
Full text
PDF
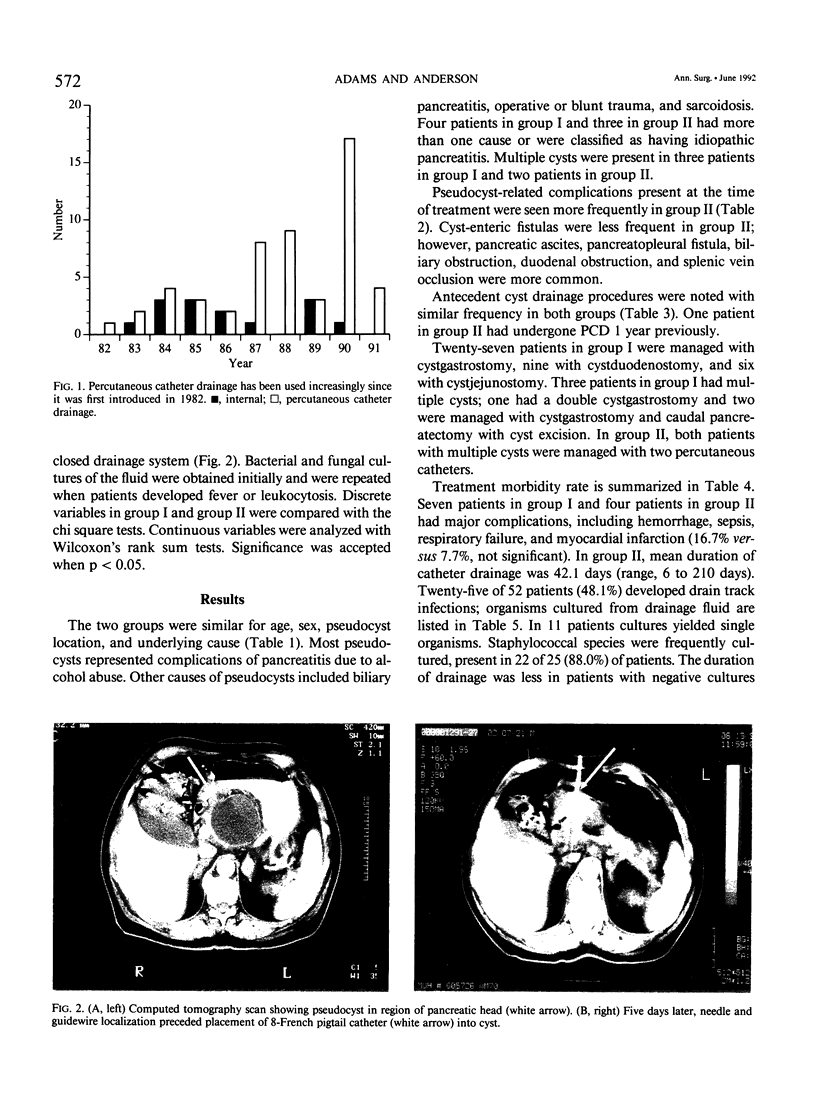
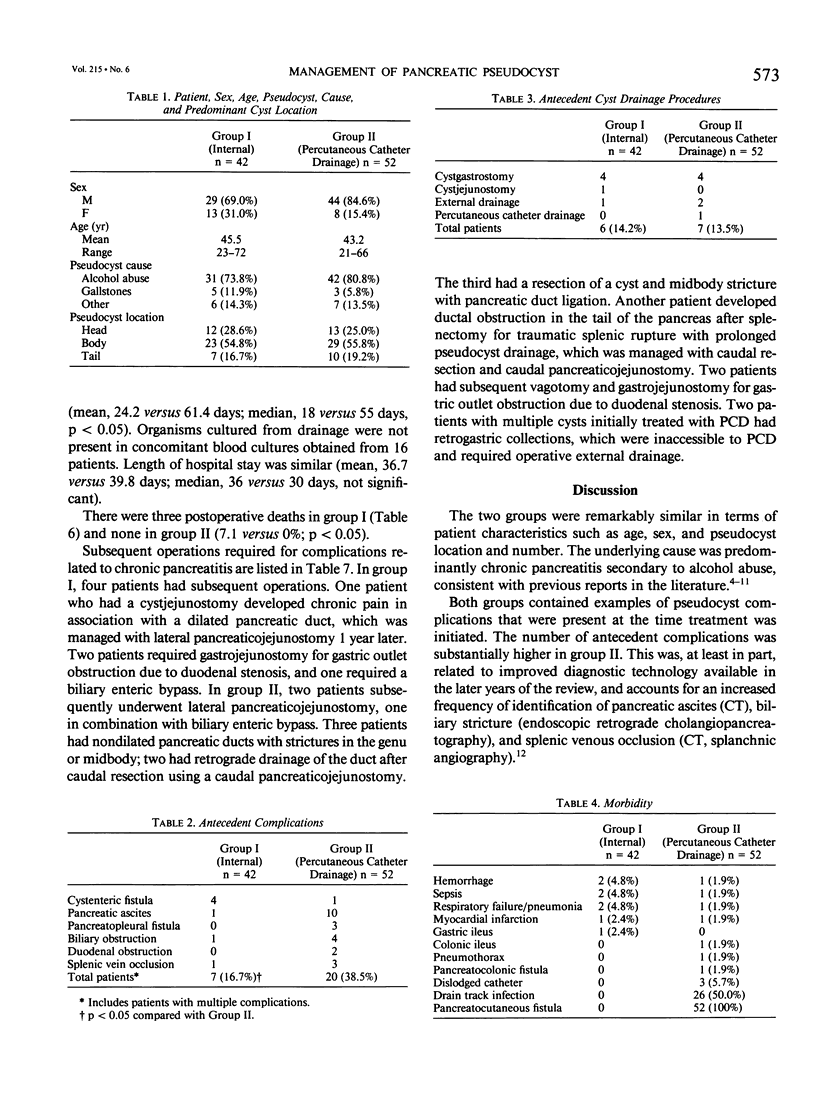



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acocella G., Tenconi L. T., Armas-Merino R., Raia S., Billing B. H. Does deconjugation of bilirubin glucuronide occur in obstructive jaundice? Lancet. 1968 Jan 13;1(7533):68–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. B., Anderson M. C. Changing concepts in the surgical management of pancreatic pseudocysts. Am Surg. 1992 Mar;58(3):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahearne P. M., Baillie J. M., Cotton P. B., Baker M. E., Meyers W. C., Pappas T. N. An endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)-based algorithm for the management of pancreatic pseudocysts. Am J Surg. 1992 Jan;163(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(92)90262-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aranha G. V., Prinz R. A., Freeark R. J., Kruss D. M., Greenlee H. B. Evaluation of therapeutic options for pancreatic pseudocysts. Arch Surg. 1982 May;117(5):717–721. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1982.01380290163029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley E. L., Clements J. L., Jr, Gonzalez A. C. The natural history of pancreatic pseudocysts: a unified concept of management. Am J Surg. 1979 Jan;137(1):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephgrave K., Hunt J. L. Presentation of pancreatic pseudocysts: implications for timing of surgical intervention. Am J Surg. 1986 Jun;151(6):749–753. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey C. F. Pancreatic pseudocyst--operative strategy. Ann Surg. 1978 Nov;188(5):652–662. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197811000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan G. L., Jr Pancreatic fistula. Am J Surg. 1970 Feb;119(2):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(70)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlson K. B., Martin E. C., Fankuchen E. I., Mattern R. F., Schultz R. W., Casarella W. J. Percutaneous drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts and abscesses. Radiology. 1982 Mar;142(3):619–624. doi: 10.1148/radiology.142.3.7063675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiviluoto T., Kivisaari L., Kivilaakso E., Lempinen M. Pseudocysts in chronic pancreatitis. Surgical results in 102 consecutive patients. Arch Surg. 1989 Feb;124(2):240–243. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1989.01410020114019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansden F. T., Adams D. B., Anderson M. C. Treatment of external pancreatic fistulas with somatostatin. Second place winner: Conrad Jobst award. Am Surg. 1989 Dec;55(12):695–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell D. B., Gregory J. R., Sasaki T. M., Vetto R. M. Pancreatic pseudocyst. Am J Surg. 1982 May;143(5):599–601. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins R. J., Malangoni M. A., Bergamini T. M., Casey J. M., Richardson J. D. Controversies in the management of pancreatic pseudocysts. Am J Surg. 1988 Jan;155(1):165–172. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn J. S., Aranha G. V., Greenlee H. B., Prinz R. A. Simultaneous treatment of chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic pseudocyst. Arch Surg. 1987 Jun;122(6):662–667. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400180044008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell K. A., Liu T., Aranha G. V., Prinz R. A. Are cystgastrostomy and cystjejunostomy equivalent operations for pancreatic pseudocysts? Surgery. 1990 Oct;108(4):635–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley V. P., Cannon J. P., Postier R. G. Pancreatic pseudocysts: cause, therapy, and results. Am J Surg. 1985 Dec;150(6):680–682. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(85)90407-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinz R. A., Pickleman J., Hoffman J. P. Treatment of pancreatic cutaneous fistulas with a somatostatin analog. Am J Surg. 1988 Jan;155(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80255-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandy J. T., Taylor R. H., Christensen R. M., Scudamore C., Leckie P. Pancreatic pseudocyst. Changing concepts in management. Am J Surg. 1981 May;141(5):574–576. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaran S., Walt A. J. The natural and unnatural history of pancreatic pseudocysts. Br J Surg. 1975 Jan;62(1):37–44. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatney C. H., Lillehei R. C. Surgical treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Analysis of 119 cases. Ann Surg. 1979 Apr;189(4):386–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres W. E., Evert M. B., Baumgartner B. R., Bernardino M. E. Percutaneous aspiration and drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986 Nov;147(5):1007–1009. doi: 10.2214/ajr.147.5.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw A. L., Compton C. C., Lewandrowski K., Cardenosa G., Mueller P. R. Cystic tumors of the pancreas. New clinical, radiologic, and pathologic observations in 67 patients. Ann Surg. 1990 Oct;212(4):432–445. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199010000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw A. L., Rattner D. W. Timing of surgical drainage for pancreatic pseudocyst. Clinical and chemical criteria. Ann Surg. 1985 Dec;202(6):720–724. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198512000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. T., Woltering E. A., O'Dorisio T. M., Fletcher W. S. Effect of octreotide acetate on pancreatic exocrine function. Am J Surg. 1989 May;157(5):459–462. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(89)90634-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeo C. J., Bastidas J. A., Lynch-Nyhan A., Fishman E. K., Zinner M. J., Cameron J. L. The natural history of pancreatic pseudocysts documented by computed tomography. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1990 May;170(5):411–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vanSonnenberg E., Wittich G. R., Casola G., Brannigan T. C., Karnel F., Stabile B. E., Varney R. R., Christensen R. R. Percutaneous drainage of infected and noninfected pancreatic pseudocysts: experience in 101 cases. Radiology. 1989 Mar;170(3 Pt 1):757–761. doi: 10.1148/radiology.170.3.2644662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



