Abstract
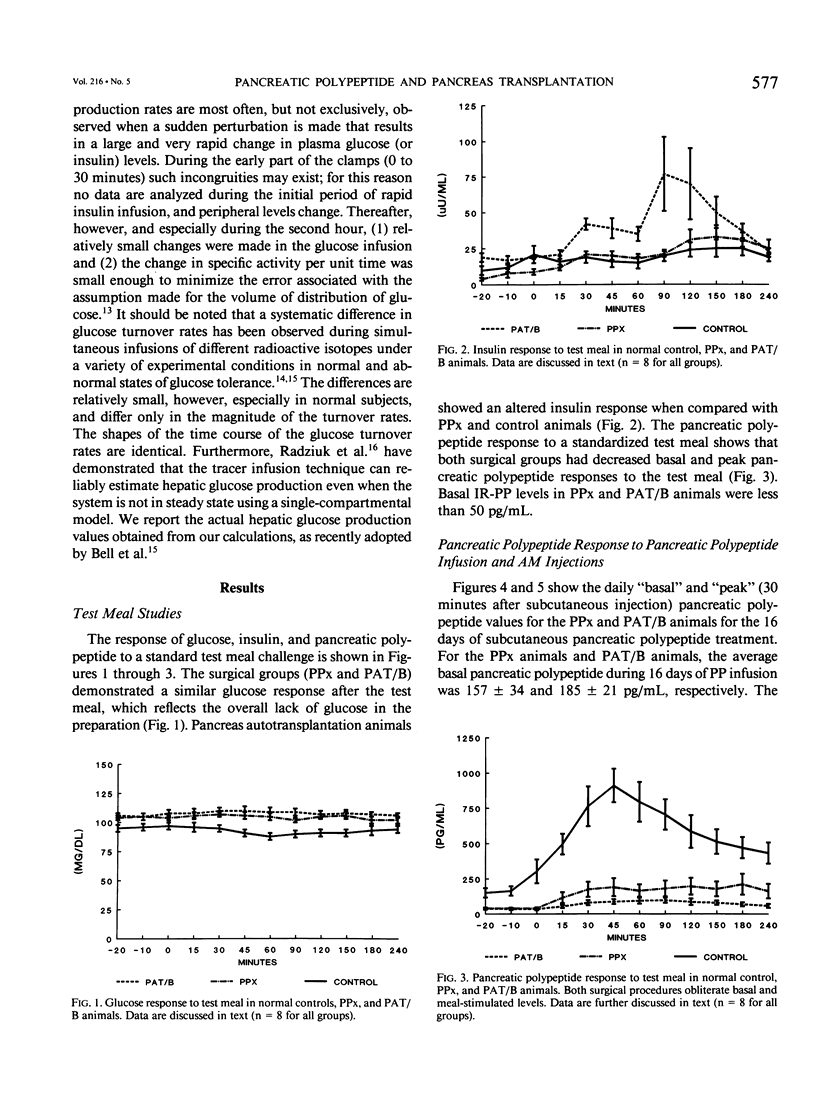
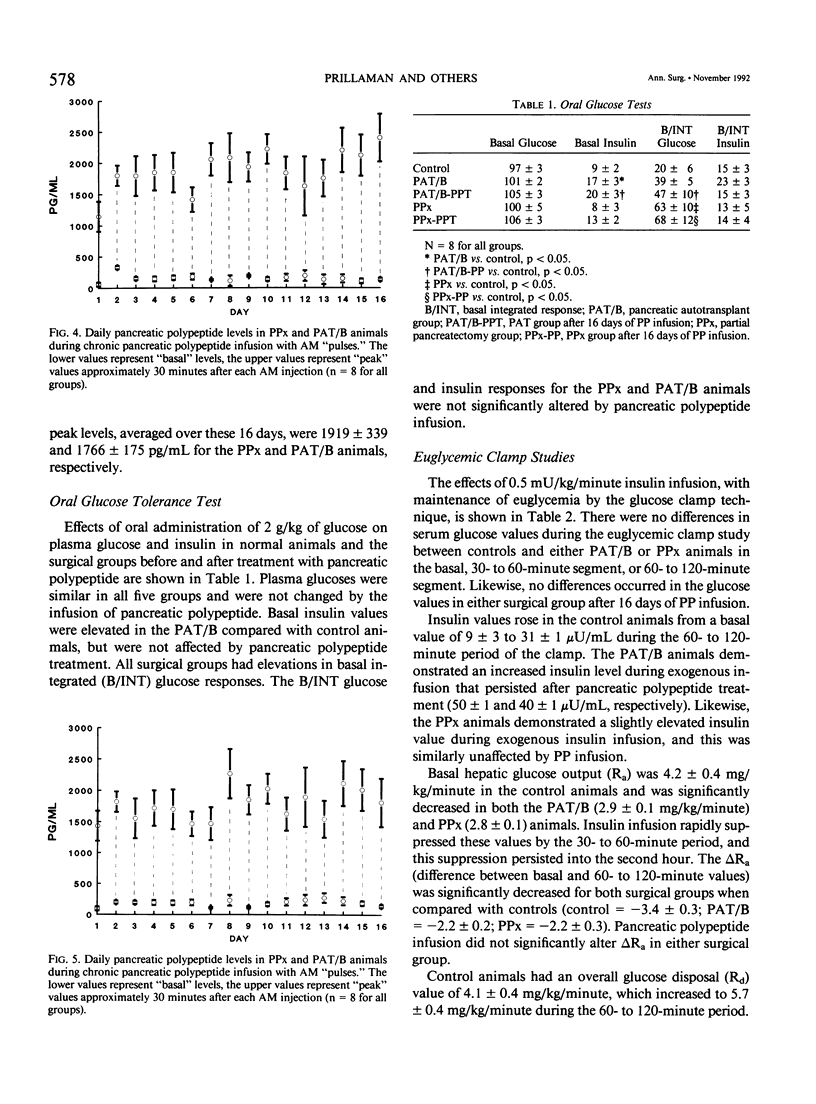
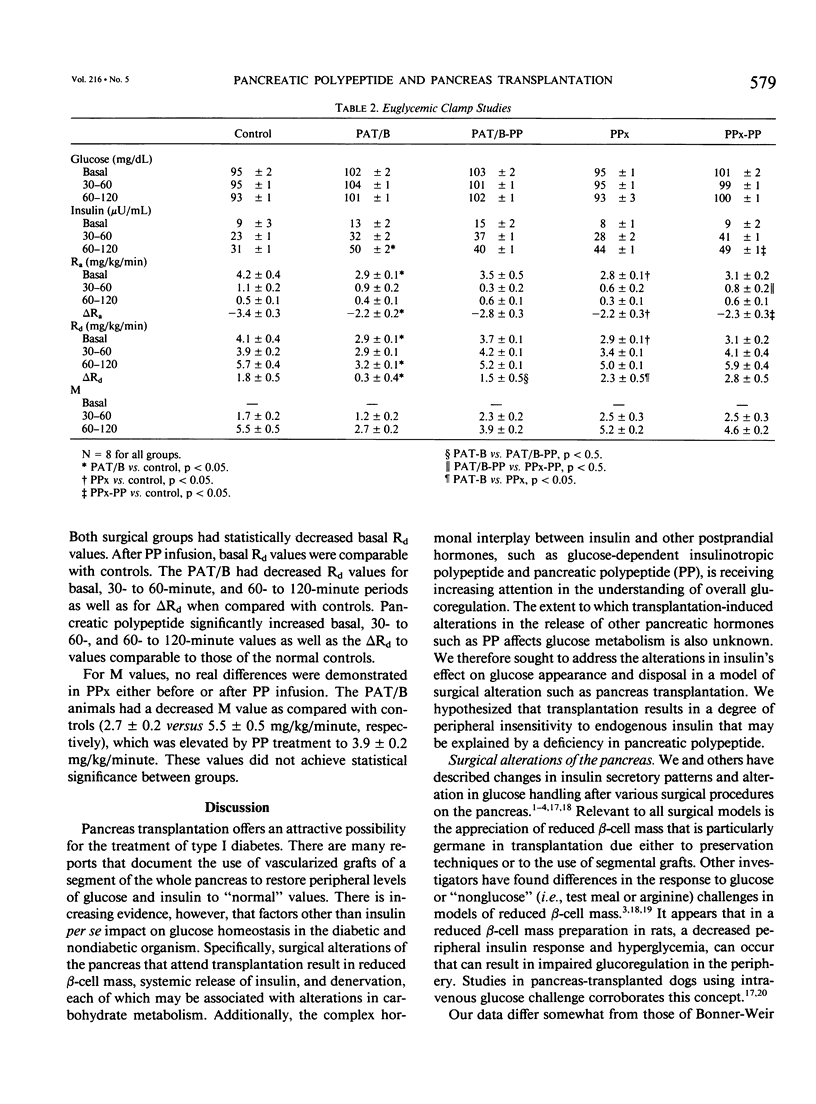
Surgical alterations of the pancreas result in anatomic changes that can affect postoperative glucose metabolism. Pancreas transplantation results in reduction of beta-cell mass, systemic release of insulin, and denervation. The authors hypothesized that such alterations affect peripheral glucose disposal to induce an "insensitivity" to endogenously (systemically) released insulin. Additionally, they hypothesized that surgically induced deficiency of the postprandial hormone, pancreatic polypeptide, might contribute to altered glucose disposal. The authors studied two surgical models in dogs known to be devoid of pancreatic polypeptide--70% proximal pancreatectomy (PPx) and PPx plus distal pancreas autotransplantation (PAT/B). Oral glucose challenge and euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp studies were performed before and after a 16-day "pulsed" infusion of pancreatic polypeptide. Both surgical procedures resulted in elevations in the integrated glucose response after oral glucose, which was not affected by pancreatic polypeptide infusion. Euglycemic clamp studies showed decreased hepatic glucose output (Ra) and overall glucose disposal (Rd) in the fasted state for both surgical groups. The transplant animals demonstrated significant decreases in Rd during the hyperinsulinemic challenge (3.2 +/- 0.01 versus 5.7 +/- 0.01 mg/kg/minute at 60 to 120 minutes for PAT/B versus control). After 16 days of pancreatic polypeptide infusion, however, basal Ra, as well as basal and 60- to 120-minute Rd values, were returned to control values in the transplant group. The authors conclude that pancreas transplantation results in altered glucose disposal, possibly due to an altered effectiveness of systemically released insulin. They conclude that pancreatic polypeptide is an important modulator of peripheral insulin action. Therefore, the role of pancreatic polypeptide must be taken into account when evaluating postoperative glucose metabolism in canine models of pancreas transplantation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argoud G. M., Schade D. S., Eaton R. P. Underestimation of hepatic glucose production by radioactive and stable tracers. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):E606–E615. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.5.E606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone G. W., Flanagan T. L., Cornett G., Pruett T. L., Hanks J. B. Glucose metabolism after pancreas autotransplantation. The effect of open duct versus urinary bladder drainage technique. Ann Surg. 1991 Feb;213(2):159–165. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199102000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastidas J. A., Couse N. F., Yeo C. J., Schmieg R. E., Jr, Andersen D. K., Gingerich R. L., Zinner M. J. The effect of pancreatic polypeptide infusion on glucose tolerance and insulin response in longitudinally studied pancreatitis-induced diabetes. Surgery. 1990 Jun;107(6):661–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell P. M., Firth R. G., Rizza R. A. Effects of hyperglycemia on glucose production and utilization in humans. Measurement with [23H]-, [33H]-, and [614C]glucose. Diabetes. 1986 Jun;35(6):642–648. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.6.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Trent D. F., Weir G. C. Partial pancreatectomy in the rat and subsequent defect in glucose-induced insulin release. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1544–1553. doi: 10.1172/JCI110910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobelli C., Mari A., Ferrannini E. Non-steady state: error analysis of Steele's model and developments for glucose kinetics. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):E679–E689. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.5.E679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diem P., Redmon J. B., Abid M., Moran A., Sutherland D. E., Halter J. B., Robertson R. P. Glucagon, catecholamine and pancreatic polypeptide secretion in type I diabetic recipients of pancreas allografts. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):2008–2013. doi: 10.1172/JCI114936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gettys T. W., Garcia R., Savage K., Whitcomb D. C., Kanayama S., Taylor I. L. Insulin-sparing effects of pancreatic polypeptide in congenitally obese rodents. Pancreas. 1991 Jan;6(1):46–53. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199101000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingerich R. L., Gersell D. J., Greider M. H., Finke E. H., Lacy P. E. Elevated levels of pancreatic polypeptide in obese-hyperglycemic mice. Metabolism. 1978 Oct;27(10):1526–1532. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingerich R. L., Lacy P. E., Chance R. E., Johnson M. G. Regional pancreatic concentration and in-vitro secretion of canine pancreatic polypeptide, insulin, and glucagon. Diabetes. 1978 Feb;27(2):96–101. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.2.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. A., Chance R. E. Crystallization of bovine pancreatic polypeptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):830–835. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusch D. A., Brown K. B., Calhoun P. C., Freedlender A. E., Kaiser D. L., Elahi D., Hanks J. B. Peripheral insulin release after pancreatic resection: the effect of decreased beta-cell mass with systemic or portal drainage. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):426–432. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Bonner-Weir S., Weir G. C. Abnormal glucose regulation of insulin secretion in models of reduced B-cell mass. Diabetes. 1984 Jul;33(7):667–673. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.7.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Carpentier J. L., Patel Y. C., Malaisse W. J., Orci L. Pancreatic polypeptide: a possible role in the regulation of food intake in the mouse. Hypothesis. Experientia. 1977 Jul 15;33(7):915–917. doi: 10.1007/BF01951279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. A., Fries J. L., Meyers C. A., Coy D. H. Human pancreatic polypeptide inhibits insulin release in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 16;101(1):189–193. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinz R. A., El Sabbagh H., Adrian T. E., Bloom S. R., Gardner I., Polak J. M., Inokuchi H., Bishop A. E., Welbourn R. B. Neural regulation of pancreatic polypeptide release. Surgery. 1983 Dec;94(6):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Experimental validation of measurements of glucose turnover in nonsteady state. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):E84–E93. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.1.E84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Shulman G. I., Zawalich W., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of chronic hyperglycemia on in vivo insulin secretion in partially pancreatectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1037–1044. doi: 10.1172/JCI113157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., BISHOP J. S., DUNN A., ALTSZULER N., RATHBEB I., DEBODO R. C. INHIBITION BY INSULIN OF HEPATIC GLUCOSE PRODUCTION IN THE NORMAL DOG. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:301–306. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. W. Pancreatic polypeptide: a hormone under vagal control. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1411–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour N. E., Brunicardi F. C., Chaiken R. L., Lebovitz H. E., Chance R. E., Gingerich R. L., Elahi D., Andersen D. K. Reversal of abnormal glucose production after pancreatic resection by pancreatic polypeptide administration in man. Surgery. 1988 Aug;104(2):119–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. S., Brunicardi F. C., Druck P., Walfisch S., Berlin S. A., Chance R. E., Gingerich R. L., Elahi D., Andersen D. K. Reversal of abnormal glucose metabolism in chronic pancreatitis by administration of pancreatic polypeptide. Am J Surg. 1986 Jan;151(1):130–140. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasaka Y., Inoue S., Marumo K., Hirata Y. Plasma responses of pancreatic polypeptide, glucagon and insulin in normal and alloxan diabetic dogs, and their regional levels in the pancreas. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Feb;105(2):233–238. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1050233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


