NEUROBIOLOGY. For the article “Sustained stimulation shifts the mechanism of endocytosis from dynamin-1-dependent rapid endocytosis to clathrin- and dynamin-2-mediated slow endocytosis in chromaffin cells,” by Cristina R. Artalejo, Abdeladim Elhamdani, and H. Clive Palfrey, which appeared in number 9, April 30, 2002, of Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (99, 6358–6363; First Published April 16, 2002; 10.1073/pnas.082658499), a label at the top of Fig. 3 was omitted due to a printer's error. The complete figure and its legend appear below.
Figure 3.
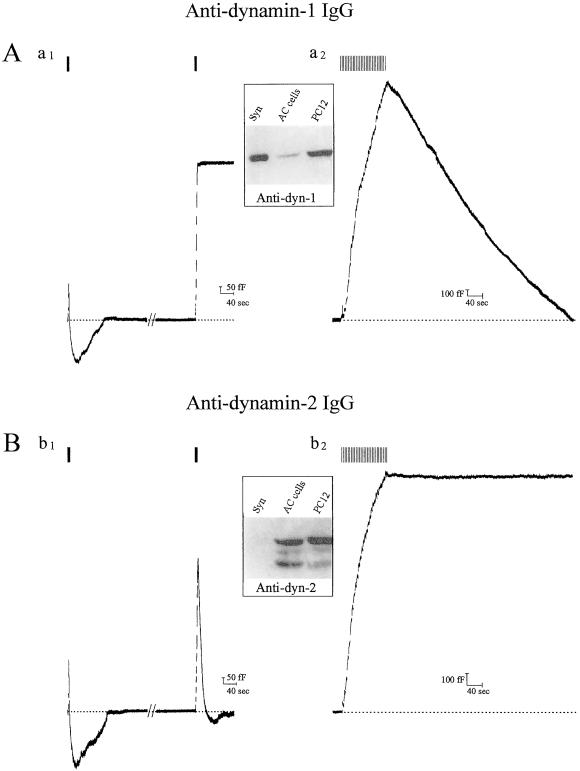
Dynamin-1 mediates RE, whereas dynamin-2 mediates SE. Cm records from cells in which either affinity-purified (A) antidynamin-1-specific IgG or (B) antidynamin-2-specific IgG, both at 1 mg/ml, were introduced into calf chromaffin cells followed by transient or sustained stimulation. In A, note that antidynamin-1 IgG inhibits RE (a1) but has no effect on SE (a2). In B, antidynamin-2 IgG has no effect on RE (b1) but blocks SE (b2). Note in Bb1 that two rounds of exocytosis/RE occur, whereas in Aa1 the second round of RE is blocked after the antibody has diffused into the cell (in the first round, RE is normal because insufficient antibody has diffused into the cell; the extent of the first exocytosis in Aa1 and Bb1 appears smaller because of simultaneous endocytosis that is largely absent in the second round). (Insets) Reactivity of antidynamin-1 (c1)- and -2 (c2)-specific antibodies with lysates from rat brain synaptosomes (Syn; 10 μg of protein); calf chromaffin (AC) cells (100 μg), and PC12 cells (100 μg); immunoblots were performed as described (9) and developed by using enhanced chemiluminescence.