Abstract
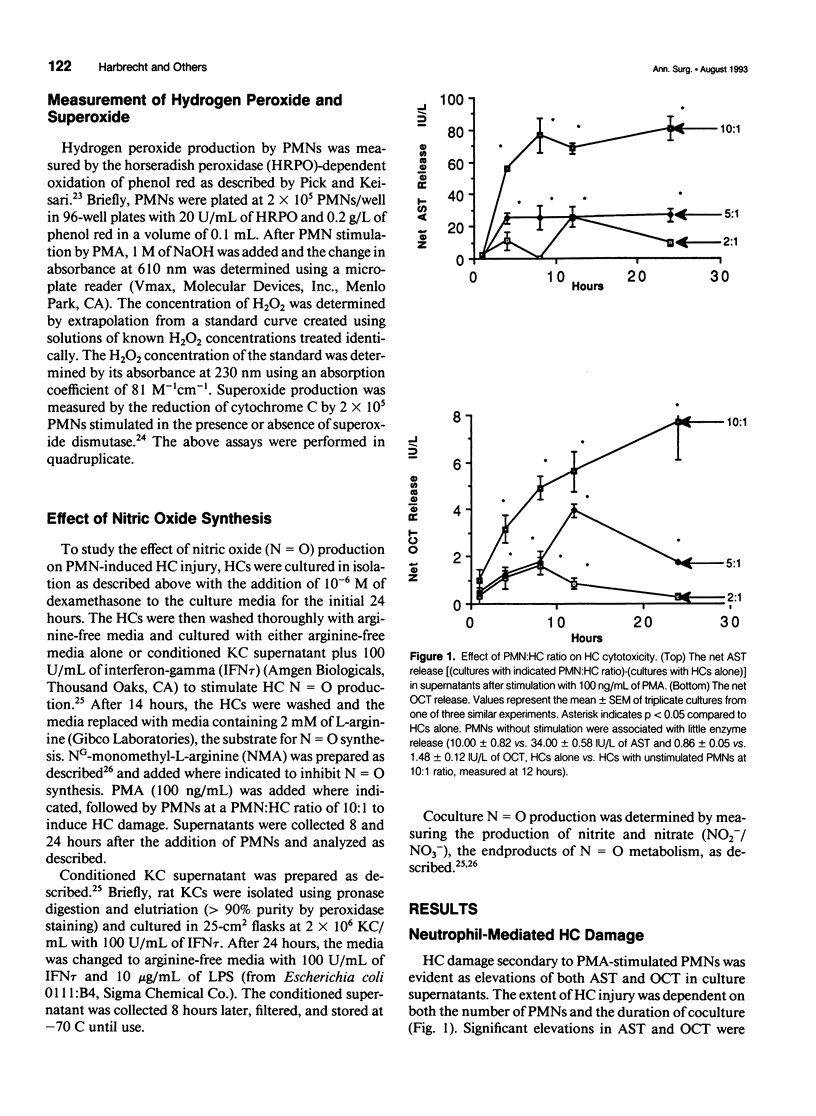
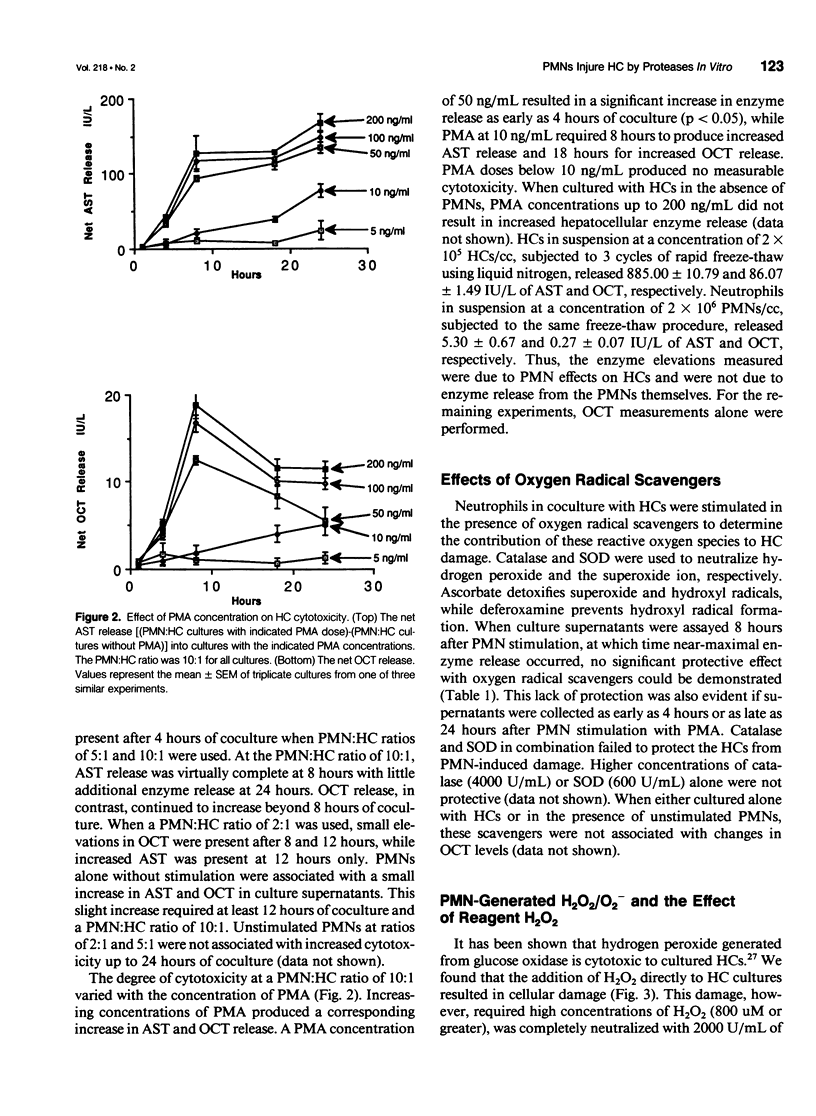
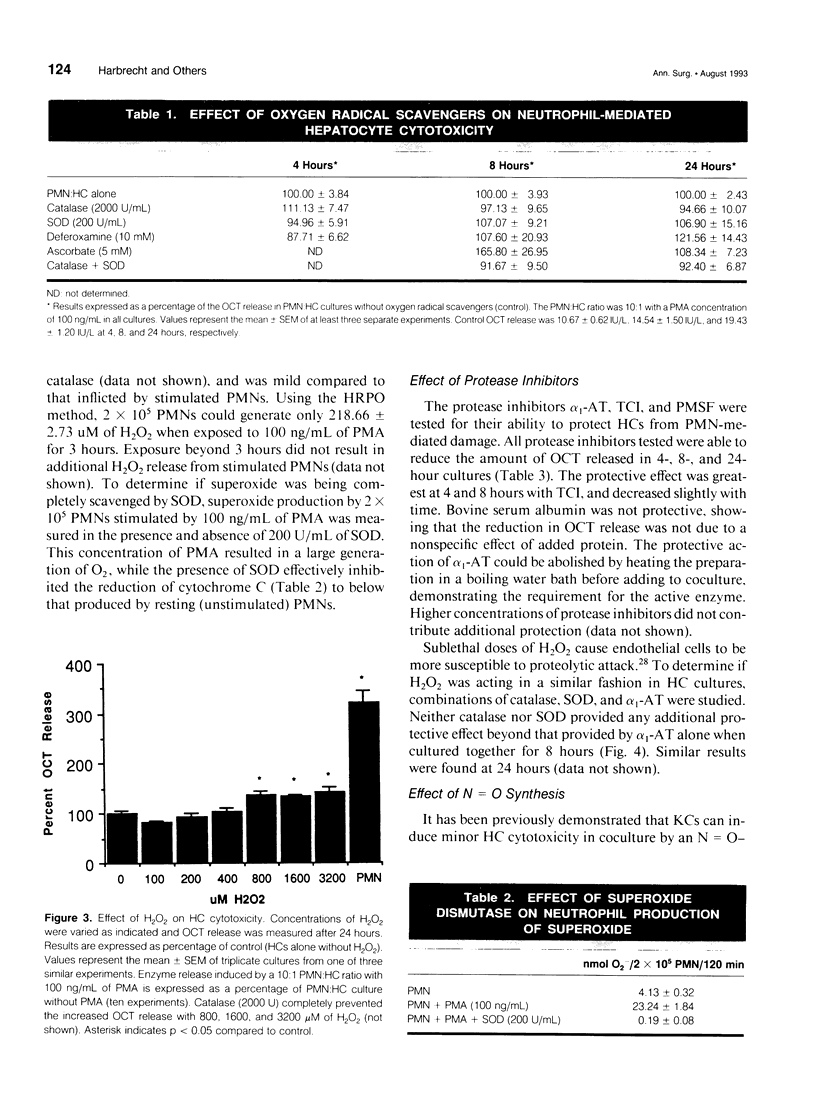
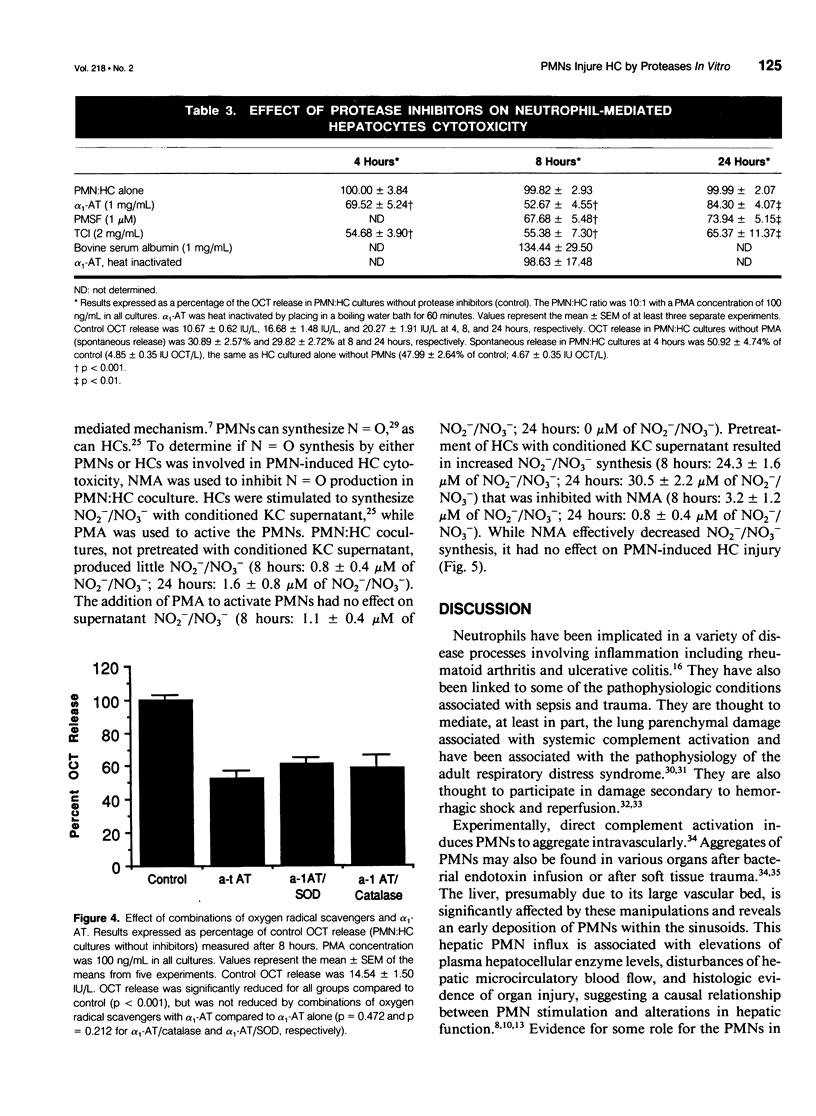
OBJECTIVE: This study determined the mechanism used by neutrophils (PMNs) to induce hepatocellular injury. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Neutrophils have been shown to be potent mediators of cell and tissue injury and have been hypothesized to contribute to the hepatic injury that occurs after trauma and infection. Oxygen radical scavengers protect the liver in vivo from inflammatory injury and it has been suggested that PMNs are the source of these toxic oxygen radicals. The specific mechanism used by PMNs to produce hepatocellular damage, however, has not been determined. METHODS: Neutrophils were cultured in vitro with hepatocytes (HCs) and stimulated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) to induce HC injury in the presence of oxygen radical scavengers and protease inhibitors. RESULTS: PMA induced a PMN-mediated HC injury that was dependent on the number of PMNs present and the concentration of PMA. Protease inhibitors reduced the extent of HC injury, while oxygen radical scavengers had no effect. Hydrogen peroxide, directly applied, was able to injure HCs, but only at concentrations greater than those that could be produced by PMA-stimulated PMNs. CONCLUSIONS: PMNs are cytotoxic to cultured HCs, predominantly due to the release of proteolytic enzymes, while HCs appear relatively resistant to oxidative injury. Involvement of neutrophil toxic oxygen radicals in hepatic damage in vivo may require impairment of HC antioxidant defenses or may involve injury to nonparenchymal liver cells with secondary effects on HCs.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur M. J., Bentley I. S., Tanner A. R., Saunders P. K., Millward-Sadler G. H., Wright R. Oxygen-derived free radicals promote hepatic injury in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1114–1122. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M. J. Reactive oxygen intermediates and liver injury. J Hepatol. 1988 Feb;6(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(88)80472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asher E. F., Rowe R. L., Garrison R. N., Fry D. E. Experimental bacteremia and hepatic nutrient blood flow. Circ Shock. 1986;20(1):43–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautista A. P., Mészáros K., Bojta J., Spitzer J. J. Superoxide anion generation in the liver during the early stage of endotoxemia in rats. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Aug;48(2):123–128. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.2.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman J. S., Beckman T. W., Chen J., Marshall P. A., Freeman B. A. Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1620–1624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., Harbrecht B. G., Stuehr D. J., Demetris A. J., Simmons R. L. Modulation of nitrogen oxide synthesis in vivo: NG-monomethyl-L-arginine inhibits endotoxin-induced nitrate/nitrate biosynthesis while promoting hepatic damage. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Dec;48(6):565–569. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.6.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., West M. A., Hofmann K., Simmons R. L. Kupffer cell cytotoxicity to hepatocytes in coculture requires L-arginine. Arch Surg. 1989 Dec;124(12):1416–1421. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1989.01410120062013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerra F. B., Siegel J. H., Border J. R., Wiles J., McMenamy R. R. The hepatic failure of sepsis: cellular versus substrate. Surgery. 1979 Sep;86(3):409–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran R. D., Billiar T. R., Stuehr D. J., Hofmann K., Simmons R. L. Hepatocytes produce nitrogen oxides from L-arginine in response to inflammatory products of Kupffer cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1769–1774. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran R. D., Billiar T. R., Stuehr D. J., Ochoa J. B., Harbrecht B. G., Flint S. G., Simmons R. L. Multiple cytokines are required to induce hepatocyte nitric oxide production and inhibit total protein synthesis. Ann Surg. 1990 Oct;212(4):462–471. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199010000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantone J. C., Ward P. A. Role of oxygen-derived free radicals and metabolites in leukocyte-dependent inflammatory reactions. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jun;107(3):395–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. L., Kyle M. E., Coleman J. B. Mechanisms of cell injury by activated oxygen species. Lab Invest. 1990 Jun;62(6):670–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feutren G., Lacour B., Bach J. F. Immune lysis of hepatocytes in culture: accurate detection by aspartate aminotransferase release measurement. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Dec 14;75(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90227-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. E., Pearlstein L., Fulton R. L., Polk H. C., Jr Multiple system organ failure. The role of uncontrolled infection. Arch Surg. 1980 Feb;115(2):136–140. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380020006003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham M. B., Hernandez L. A., Granger D. N. Xanthine oxidase and neutrophil infiltration in intestinal ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):G567–G574. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.4.G567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., Harris P. D., Wayland J. H., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Complement-induced granulocyte aggregation in vivo. Am J Pathol. 1981 Feb;102(2):146–150. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman J. M., Jr, Saba T. M. Hepatocyte injury during post-operative sepsis: activated neutrophils as potential mediators. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Mar;43(3):193–203. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.3.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. S., Billiar T., Curran R. D., Zdziarski U. E., Simmons R. L., Basford R. E. Inhibition of chemotaxis Ng-monomethyl-L-arginine: a role for cyclic GMP. Blood. 1989 Nov 1;74(6):1885–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. A., Barke R., Harty J. T., Humphrey E., Simmons R. L. Decreased hepatic glutathione levels in septic shock. Predisposition of hepatocytes to oxidative stress: an experimental approach. Arch Surg. 1985 Aug;120(8):941–945. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390320065013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein A., Seelig M., Berek J., Zighelboim J. Human neutrophil-mediated lysis of ovarian cancer cells. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):805–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallick A. A., Ishizaka A., Stephens K. E., Hatherill J. R., Tazelaar H. D., Raffin T. A. Multiple organ damage caused by tumor necrosis factor and prevented by prior neutrophil depletion. Chest. 1989 May;95(5):1114–1120. doi: 10.1378/chest.95.5.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall T. B., Boughton-Smith N. K., Palmer R. M., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. Synthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine by neutrophils. Release and interaction with superoxide anion. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):293–296. doi: 10.1042/bj2610293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G., Margaretten W., Csavossy I. An electron microscope study of the effects of bacterial endotoxin on the blood-vascular system. Lab Invest. 1966 Dec;15(12):1815–1829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. P. Endotoxin, reticuloendothelial function, and liver injury. Hepatology. 1981 Sep-Oct;1(5):458–465. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshita M., Takeda H., Kamiyama Y., Ozawa K., Honjo I. A direct method for the estimation of ornithine carbamoyltransferase activity in serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Mar 1;67(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90253-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Keisari Y. A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Mizel D. Rapid microassays for the measurement of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production by macrophages in culture using an automatic enzyme immunoassay reader. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(2):211–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R., Farber J. L. Mechanisms of the killing of cultured hepatocytes by hydrogen peroxide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 1;228(2):450–459. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Tanaka J., Kono Y., Jones R. T., Cowley R. A., Trump B. F. Hepatic cellular injury following lethal Escherichia coli bacteremia in rats. Lab Invest. 1982 Sep;47(3):304–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer W. J., Schirmer J. M., Naff G. B., Fry D. E. Contribution of toxic oxygen intermediates to complement-induced reductions in effective hepatic blood flow. J Trauma. 1988 Sep;28(9):1295–1300. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198809000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29–83. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedly L. A., Tonnesen M. G., Sandhaus R. A., Haslett C., Guthrie L. A., Johnston R. B., Jr, Henson P. M., Worthen G. S. Neutrophil-mediated injury to endothelial cells. Enhancement by endotoxin and essential role of neutrophil elastase. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1233–1243. doi: 10.1172/JCI112426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thörne J., Blomquist S., Elmér O., Grafström G., Mårtensson L. Polymorphonuclear leucocyte sequestration in the lungs and liver following soft-tissue trauma: an in vivo study. J Trauma. 1989 Apr;29(4):451–456. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198904000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G. O., Johnson K. J., Kunkel R., Ward P. A. Intravascular activation of complement and acute lung injury. Dependency on neutrophils and toxic oxygen metabolites. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1126–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI110548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Ginsburg I., Schuger L., Gibbs D. F., Bromberg J., Johnson K. J., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Endothelial cell killing by neutrophils. Synergistic interaction of oxygen products and proteases. Am J Pathol. 1989 Sep;135(3):435–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedder N. B., Winn R. K., Rice C. L., Chi E. Y., Arfors K. E., Harlan J. M. A monoclonal antibody to the adherence-promoting leukocyte glycoprotein, CD18, reduces organ injury and improves survival from hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):939–944. doi: 10.1172/JCI113407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland J. E., Davis W. B., Holter J. F., Mohammed J. R., Dorinsky P. M., Gadek J. E. Lung neutrophils in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clinical and pathophysiologic significance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):218–225. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., LoBuglio A. F. Phagocyte-generated oxygen metabolites and cellular injury. Lab Invest. 1982 Jul;47(1):5–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Young J., LoBuglio A. F., Slivka A., Nimeh N. F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil-mediated destruction of cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. A., Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., Hyland B. J., Simmons R. L. Evidence that rat Kupffer cells stimulate and inhibit hepatocyte protein synthesis in vitro by different mechanisms. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jun;96(6):1572–1582. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90529-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. A., Keller G. A., Cerra F. B., Simmons R. L. Killed Escherichia coli stimulates macrophage-mediated alterations in hepatocellular function during in vitro coculture: a mechanism of altered liver function in sepsis. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):563–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.563-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


