Abstract
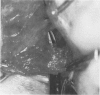
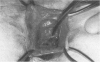
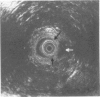
OBJECTIVE: This study was performed to (1) correlate and sphincter defects, identified by endoanal ultrasound with operative findings, and (2) define the appearance of such sphincter defects as seen at operation. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Endoanal ultrasonography is a minimally invasive method of imaging the anal sphincter complex and enables identification of anal sphincter defects. Little is known about the accuracy and limitations of endoanal ultrasound in identifying such defects. Furthermore, there are no data about the appearances of these endosonic sphincter defects as seen at operation. METHODS: Forty-four patients (40 women; age range, 26 to 80 years; mean age, 56 years) with fecal incontinence, undergoing pelvic floor repair, were investigated by endoanal ultrasound before operation. Endosonic findings were correlated with the appearances of external anal sphincter, internal anal sphincter, and intersphincteric space, at operation. Diagnosis of the site and type of defect was made by macroscopic appearances. Uncertainty about the type of sphincter defect was resolved by obtaining muscle biopsies for histology. RESULTS: All external sphincter defects seen by endoanal ultrasound (n = 23) were confirmed at operation. Twenty-one of 22 internal sphincter defects identified by endosonography also were confirmed at operation. In ten patients with a neuropathic anal sphincter complex, the morphology was normal on endosonography, and this was confirmed at operation. (Sensitivity and specificity of 100% for external anal sphincter; 100% and 95.5%, respectively, for internal and sphincter) CONCLUSIONS: These data show that endoanal ultrasound is an accurate method of identifying anal sphincter defects.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnett S. J., Speakman C. T., Kamm M. A., Bartram C. I. Confirmation of endosonographic detection of external anal sphincter defects by simultaneous electromyographic mapping. Br J Surg. 1991 Apr;78(4):448–450. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keighley M. R., Fielding J. W. Management of faecal incontinence and results of surgical treatment. Br J Surg. 1983 Aug;70(8):463–468. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. J., Bartram C. I. Anal endosonography: technique and normal anatomy. Gastrointest Radiol. 1989 Fall;14(4):349–353. doi: 10.1007/BF01889235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. J., Kamm M. A., Bartram C. I. A comparison between electromyography and anal endosonography in mapping external anal sphincter defects. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990 May;33(5):370–373. doi: 10.1007/BF02156260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R., Orrom W. J., Cornes H., Duthie G., Bartolo D. C. Anterior sphincter plication and levatorplasty in the treatment of faecal incontinence. Br J Surg. 1989 Oct;76(10):1058–1060. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800761024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]