Abstract
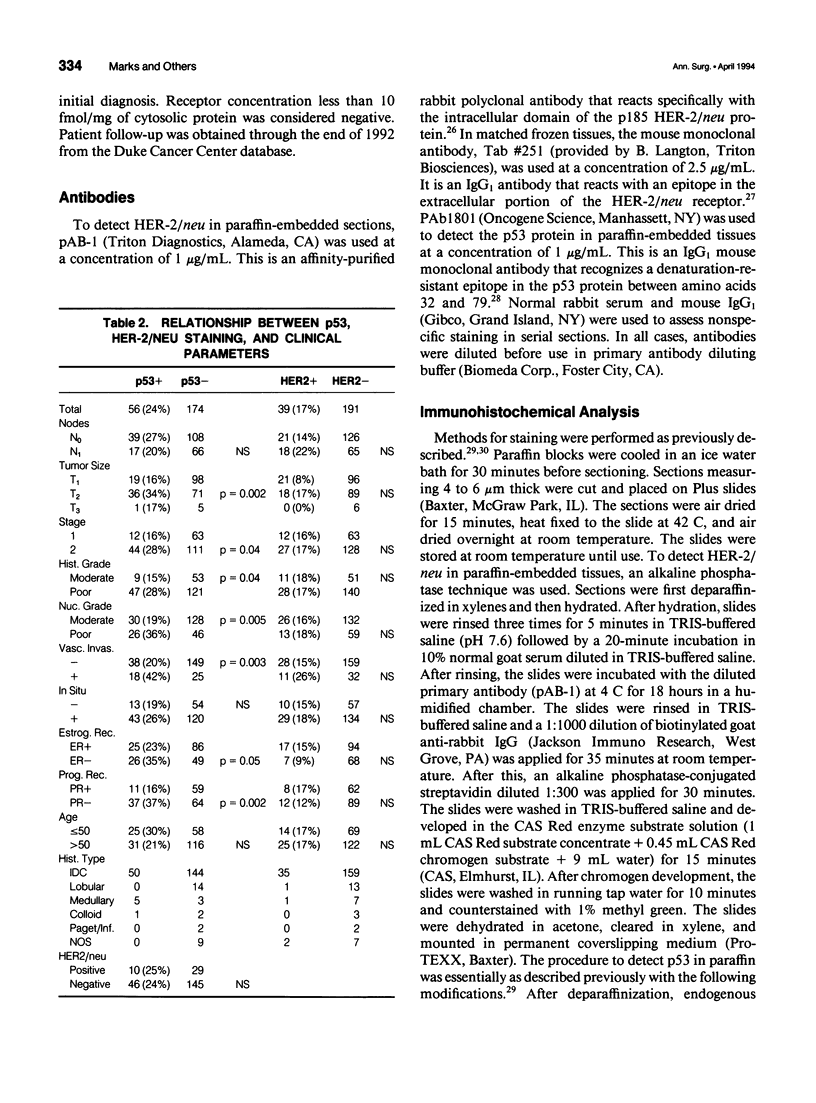
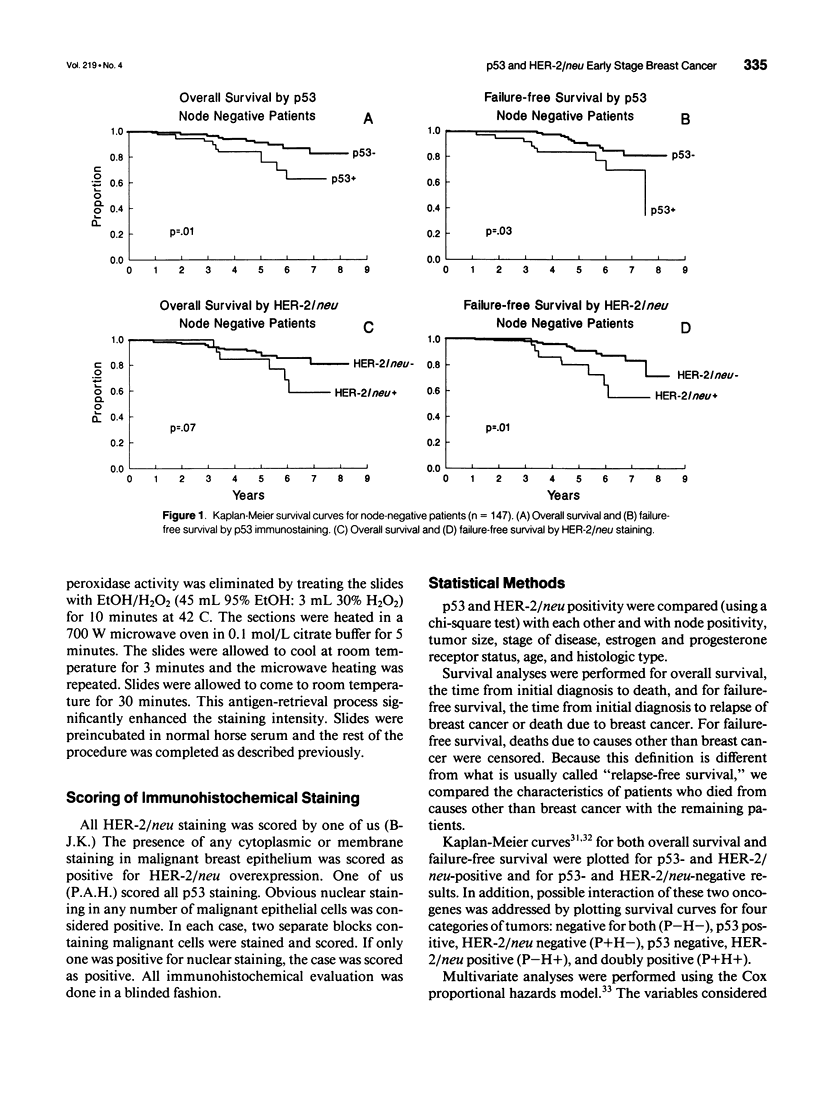
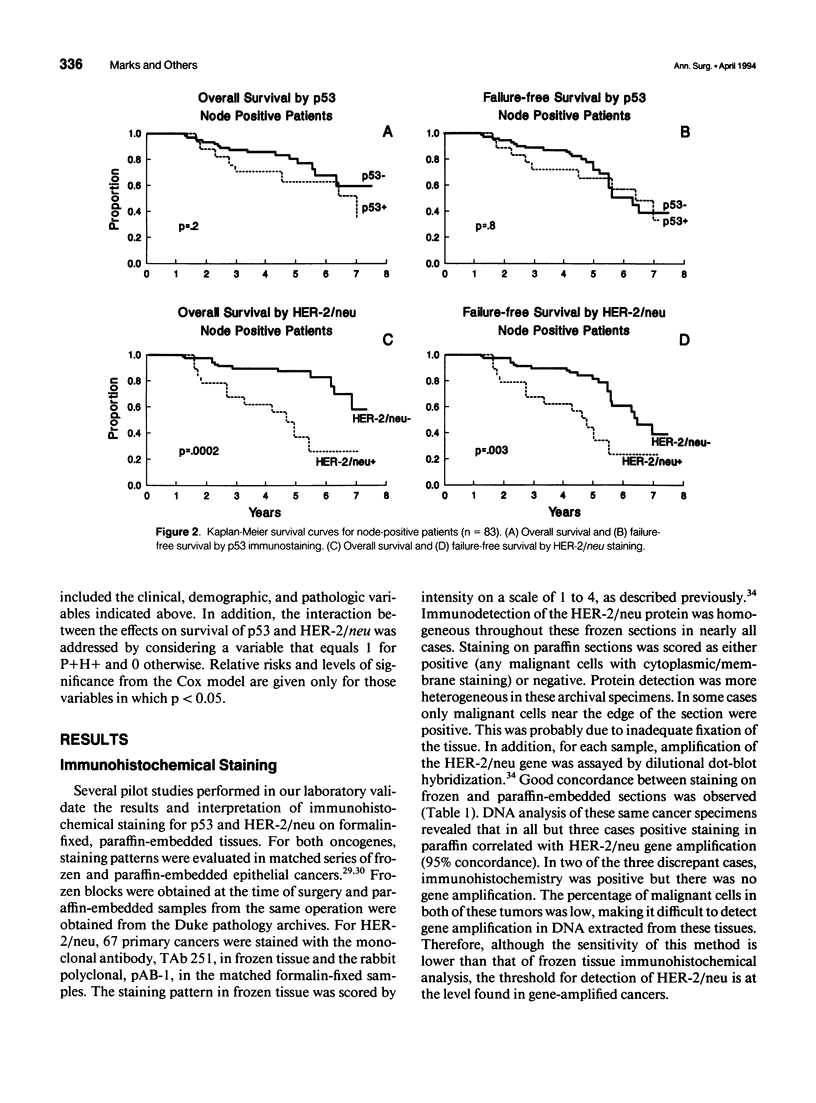
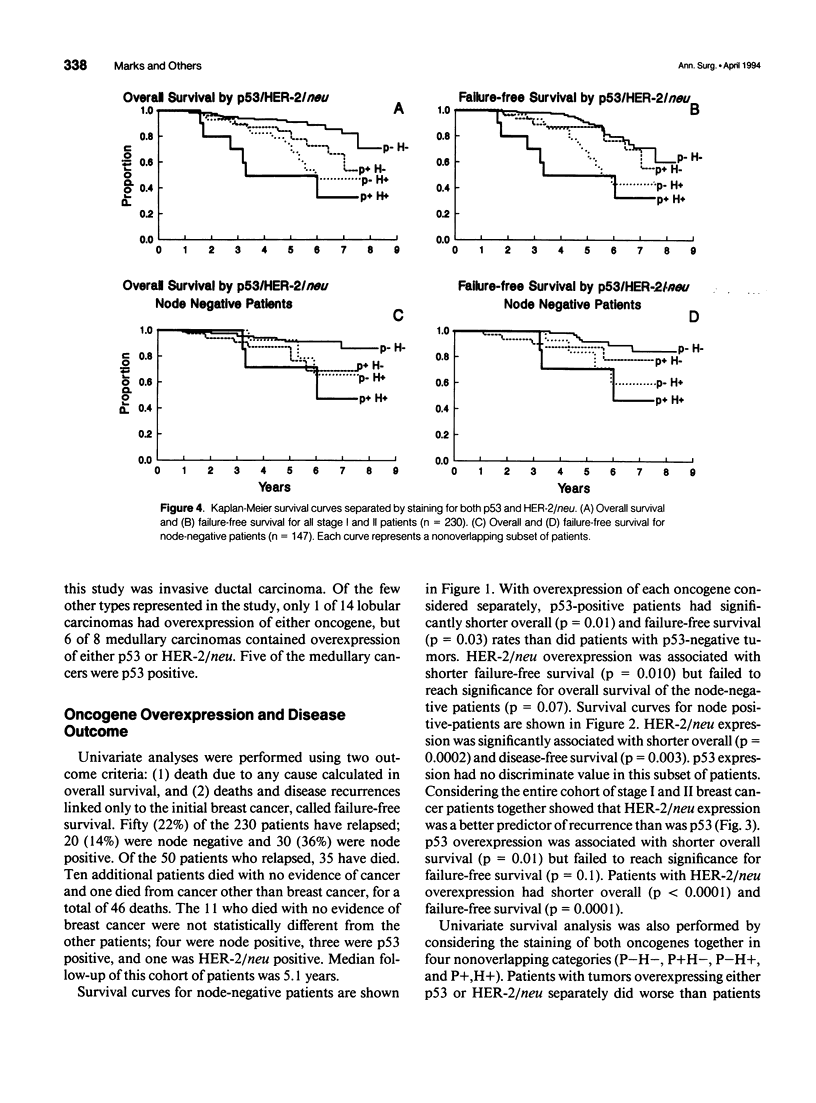
OBJECTIVE: Overexpression of the p53 and HER-2/neu oncogenes are the two most common genetic abnormalities associated with breast cancer. Shorter survival time has been reported in patients with tumors with p53 or HER-2/neu. This report analyzes a retrospective cohort of early stage breast cancers for both oncogenes and relates overexpression to clinicopathologic parameters and survival. METHODS: Immunostaining for p53 and HER-2/neu was performed on 230 paraffin-embedded specimens of stage I and II breast cancers diagnosed and treated at Duke University Medical Center between 1984 and 1987. Positive staining for both p53 and HER-2/neu in paraffin-embedded tissues indicates an underlying genetic abnormality: point mutations in the p53 gene and amplification of the HER-2/neu gene. RESULTS: In this cohort of patients, 24% were positive for p53 and 17% for HER-2/neu. Four per cent were positive for both oncogenes. Significant correlations were found between p53 immunostaining and increasing tumor size, stage, and low estrogen and progesterone receptor contents. Univariate analysis showed that p53 and HER-2/neu were indicators of overall and failure-free survival. An additive effect on survival was observed in patients with both oncogene abnormalities. Nodal status, HER-2/neu, and p53 all attained independent prognostic value in a multivariate analysis. CONCLUSIONS: The p53 and HER-2/neu oncogenes have proven but limited prognostic value. An approach that combines several molecular genetic markers with established pathologic criteria may help physicians to make more accurate predictions of prognosis in patients with early stage breast cancer.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allred D. C., Clark G. M., Elledge R., Fuqua S. A., Brown R. W., Chamness G. C., Osborne C. K., McGuire W. L. Association of p53 protein expression with tumor cell proliferation rate and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Feb 3;85(3):200–206. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.3.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baak J. P., Chin D., van Diest P. J., Ortiz R., Matze-Cok P., Bacus S. S. Comparative long-term prognostic value of quantitative HER-2/neu protein expression, DNA ploidy, and morphometric and clinical features in paraffin-embedded invasive breast cancer. Lab Invest. 1991 Feb;64(2):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. M., Bartkova J., Camplejohn R. S., Gullick W. J., Smith P. J., Millis R. R. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein: why does this occur more frequently in ductal carcinoma in situ than in invasive mammary carcinoma and is this of prognostic significance? Eur J Cancer. 1992;28(2-3):644–648. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(05)80117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. M., Lammie G. A., Millis R. R., Gullick W. L., Allen D. S., Altman D. G. An immunohistochemical evaluation of c-erbB-2 expression in human breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1988 Oct;58(4):448–452. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosari S., Lee A. K., Viale G., Heatley G. J., Coggi G. Abnormal p53 immunoreactivity and prognosis in node-negative breast carcinomas with long-term follow-up. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1992;421(4):291–295. doi: 10.1007/BF01660975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron de Fromentel C., Soussi T. TP53 tumor suppressor gene: a model for investigating human mutagenesis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Jan;4(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Rilke F., Andreola S., D'Amato L., Delia D. P53 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1988 Feb 15;41(2):178–183. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciocca D. R., Fujimura F. K., Tandon A. K., Clark G. M., Mark C., Lee-Chen G. J., Pounds G. W., Vendely P., Owens M. A., Pandian M. R. Correlation of HER-2/neu amplification with expression and with other prognostic factors in 1103 breast cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Aug 19;84(16):1279–1282. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.16.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. M., McGuire W. L. Follow-up study of HER-2/neu amplification in primary breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 1;51(3):944–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff A. M., Herndon J. E., 2nd, Glover N. S., Kerns B. J., Pence J. C., Iglehart J. D., Marks J. R. Relation between p53 overexpression and established prognostic factors in breast cancer. Surgery. 1991 Aug;110(2):259–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff A. M., Humphrey P. A., Iglehart J. D., Marks J. R. Genetic basis for p53 overexpression in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5006–5010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Kraus M. H., Segatto O., King C. R., Aaronson S. A. erbB-2 is a potent oncogene when overexpressed in NIH/3T3 cells. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):178–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2885917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L. Mutant p53--the commonest genetic abnormality in human cancer? J Pathol. 1990 Sep;162(1):5–6. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglehart J. D., Kraus M. H., Langton B. C., Huper G., Kerns B. J., Marks J. R. Increased erbB-2 gene copies and expression in multiple stages of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 15;50(20):6701–6707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isola J., Visakorpi T., Holli K., Kallioniemi O. P. Association of overexpression of tumor suppressor protein p53 with rapid cell proliferation and poor prognosis in node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jul 15;84(14):1109–1114. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.14.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaya K., Tsuda H., Hiraide H., Tamaki K., Tamakuma S., Fukutomi T., Mukai K., Hirohashi S. Nuclear p53 immunoreaction associated with poor prognosis of breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Jul;82(7):835–840. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb02710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerns B. J., Jordan P. A., Huper G., Marks J. R., Iglehart J. D., Layfied L. J. Assessment of c-erbB-2 amplification by immunohistochemistry in paraffin-embedded breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 1993 Nov;6(6):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerns B. J., Jordan P. A., Moore M. B., Humphrey P. A., Berchuck A., Kohler M. F., Bast R. C., Jr, Iglehart J. D., Marks J. R. p53 overexpression in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue detected by immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Jul;40(7):1047–1051. doi: 10.1177/40.7.1607637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuerbitz S. J., Plunkett B. S., Walsh W. V., Kastan M. B. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu E., Thor A., He M., Barcos M., Ljung B. M., Benz C. The HER2 (c-erbB-2) oncogene is frequently amplified in in situ carcinomas of the breast. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):1027–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. R., Davidoff A. M., Kerns B. J., Humphrey P. A., Pence J. C., Dodge R. K., Clarke-Pearson D. L., Iglehart J. D., Bast R. C., Jr, Berchuck A. Overexpression and mutation of p53 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Jun 1;51(11):2979–2984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll U. M., Riou G., Levine A. J. Two distinct mechanisms alter p53 in breast cancer: mutation and nuclear exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7262–7266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski J. L., Sawan A., Henry L., Wright C., Henry J. A., Hennessy C., Lennard T. J., Angus B., Horne C. H. p53 expression in human breast cancer related to survival and prognostic factors: an immunohistochemical study. J Pathol. 1991 May;164(1):75–81. doi: 10.1002/path.1711640113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik S., Hazan R., Fisher E. R., Sass R. E., Fisher B., Redmond C., Schlessinger J., Lippman M. E., King C. R. Pathologic findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project: prognostic significance of erbB-2 protein overexpression in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1990 Jan;8(1):103–112. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1990.8.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Pike M. C., Armitage P., Breslow N. E., Cox D. R., Howard S. V., Mantel N., McPherson K., Peto J., Smith P. G. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. I. Introduction and design. Br J Cancer. 1976 Dec;34(6):585–612. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Pike M. C., Armitage P., Breslow N. E., Cox D. R., Howard S. V., Mantel N., McPherson K., Peto J., Smith P. G. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. analysis and examples. Br J Cancer. 1977 Jan;35(1):1–39. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M. F., Jones L. A., Godolphin W., Edwards C. L., Slamon D. J. HER-2/neu oncogene amplification and expression in breast and ovarian cancers. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;354A:209–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilke F., Colnaghi M. I., Cascinelli N., Andreola S., Baldini M. T., Bufalino R., Della Porta G., Ménard S., Pierotti M. A., Testori A. Prognostic significance of HER-2/neu expression in breast cancer and its relationship to other prognostic factors. Int J Cancer. 1991 Aug 19;49(1):44–49. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Godolphin W., Jones L. A., Holt J. A., Wong S. G., Keith D. E., Levin W. J., Stuart S. G., Udove J., Ullrich A. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):707–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2470152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor A. D., Moore DH I. I., Edgerton S. M., Kawasaki E. S., Reihsaus E., Lynch H. T., Marcus J. N., Schwartz L., Chen L. C., Mayall B. H. Accumulation of p53 tumor suppressor gene protein: an independent marker of prognosis in breast cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jun 3;84(11):845–855. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.11.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Brammar W. J., Lane D. P., Swallow J. E., Dolan C., Walker R. A. Loss of chromosome 17p13 sequences and mutation of p53 in human breast carcinomas. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):413–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin Y., Tainsky M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Strong L. C., Wahl G. M. Wild-type p53 restores cell cycle control and inhibits gene amplification in cells with mutant p53 alleles. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M. J., Peterse J. L., Mooi W. J., Wisman P., Lomans J., Dalesio O., Nusse R. Neu-protein overexpression in breast cancer. Association with comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ and limited prognostic value in stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 10;319(19):1239–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811103191902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


