Abstract
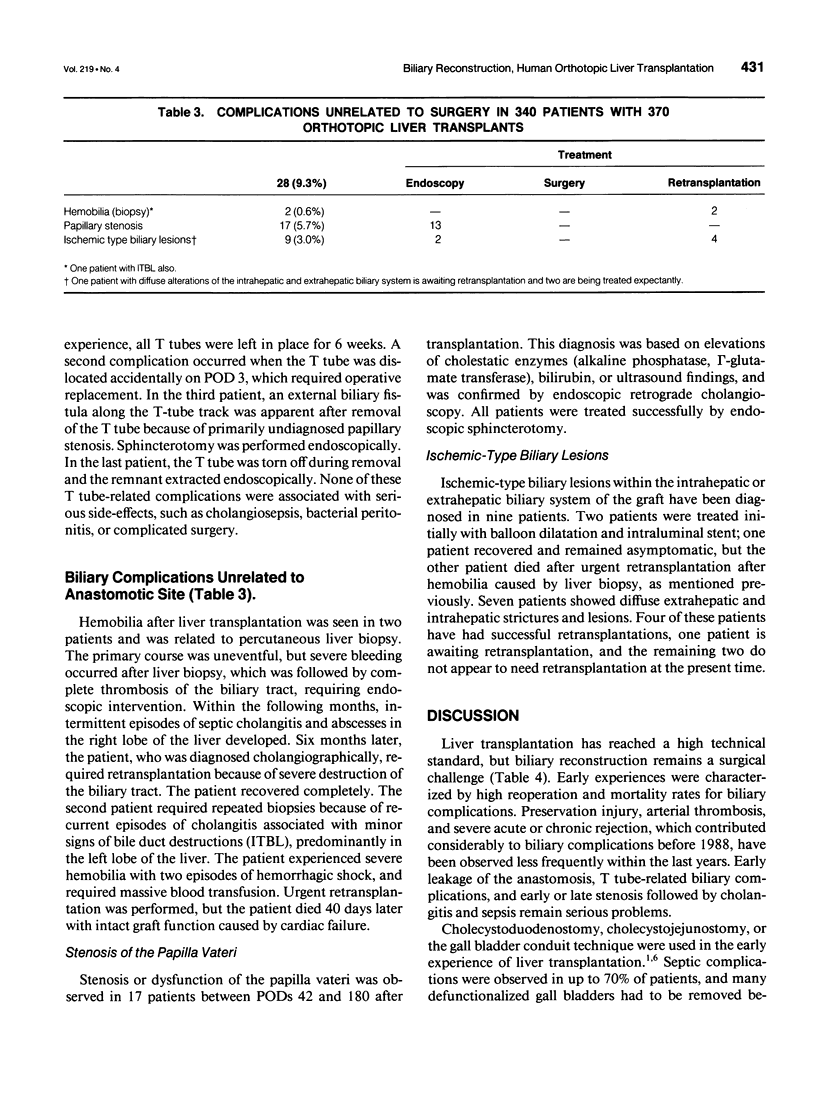
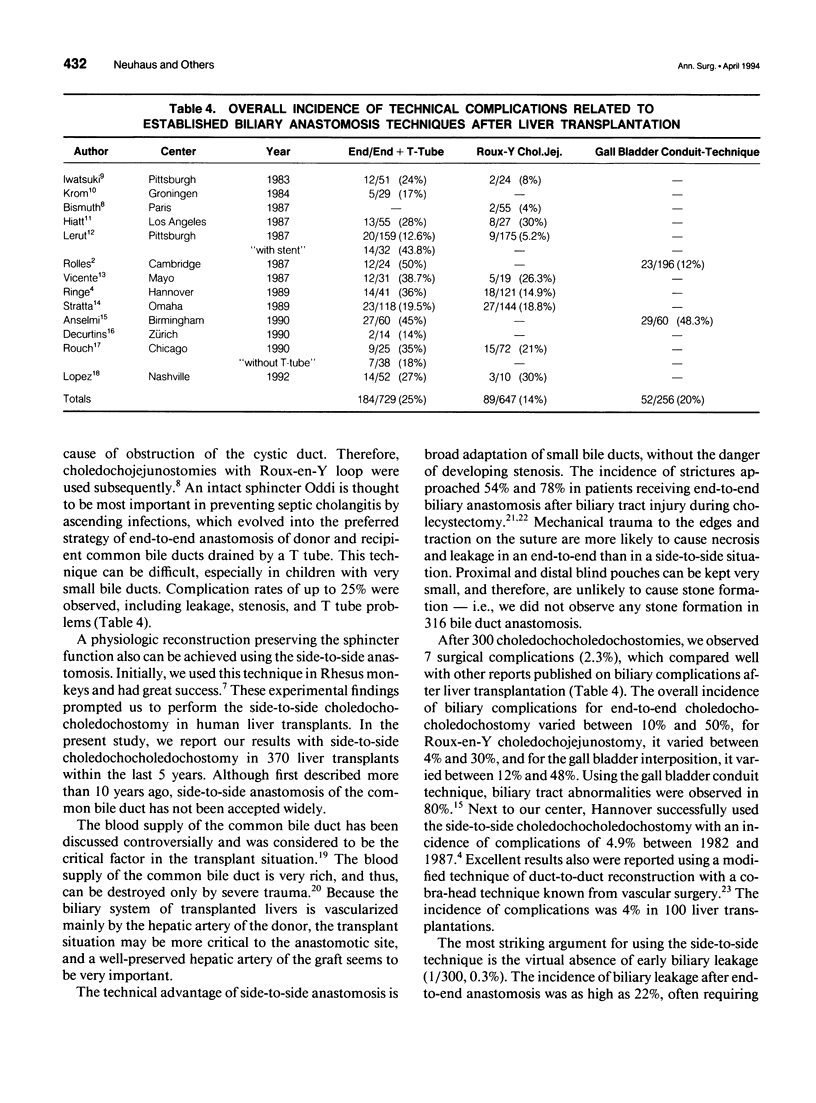
OBJECTIVE: The authors evaluated the complication rate and outcome of side-to-side common bile duct anastomosis after human orthotopic liver transplantation. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Early and late biliary tract complications after orthotopic liver transplantation remain a serious problem, leading to increased morbidity and mortality. Commonly performed techniques are the end-to-end choledochocholedochostomy and the choledochojejunostomy. Both techniques are known to coincide with a high incidence of leakage and stenosis of the bile duct anastomosis. The side-to-side bile duct anastomosis has been shown experimentally to be superior to the end-to-end anastomosis. The authors present the results of 316 human liver transplants, in which a side-to-side choledochocholedochostomy was performed. METHODS: Biliary tract complications of 370 transplants in 340 patients were evaluated. Three hundred patients received primary liver transplants with side-to-side anastomosis of donor and recipient common bile duct. Thirty-two patients with biliary tract pathology received a bilioenteric anastomosis, and in eight patients, side-to-side anastomosis was not performed for various reasons. Clinical and laboratory investigations were carried out at prospectively fixed time points. X-ray cholangiography was performed routinely in all patients on postoperative days (PODs) 5 and 42. In patients with suspected papillary stenosis, endoscopic retrograde cholangioscopy and papillotomy were performed. RESULTS: One biliary leakage (0.3%) was observed within the early postoperative period (PODs 0 through 30) after liver transplantation. No stenosis of the common bile duct anastomosis was observed during this time. Late biliary stenosis occurred in two patients (0.6%). T tube-related complications were observed in 4 of 300 primary transplants (1.3%). Complications unrelated to the surgical technique, including papillary stenosis (5.7%) and ischemic-type biliary lesion (3.0%), which must be considered more serious in nature than complications of the anastomosis or T tube-related complications, were observed. Papillary stenosis led to frequent endoscopic interventions and retransplantations in 1.3%. CONCLUSIONS: Side-to-side common bile duct anastomosis represents a safe technique of bile duct reconstruction and leads to a low technical complication rate after human orthotopic liver transplantation. Ischemic-type biliary lesion evoked by preservation injury, arterial ischemia, cholestasis, and cholangitis may represent a new entity of biliary complication, which markedly increases the morbidity after human liver transplantation. Therefore, this complication should be the subject of further research.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrén-Sandberg A., Johansson S., Bengmark S. Accidental lesions of the common bile duct at cholecystectomy. II. Results of treatment. Ann Surg. 1985 Apr;201(4):452–455. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198504000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anselmi M., Sherlock D., Buist L., Zundel N., Badger I., McMaster P., Buckels J. A. Gallbladder conduit vs end-to-end anastomosis of the common bile duct in orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1990 Oct;22(5):2295–2296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belli L., De Carlis L., Del Favero E., Rondinara G., Meroni A., Zani B., Rimoldi P., Cazzulani A., Brambilla G., Beati C. Biliary complications in orthotopic liver transplantation: experience with a modified technique of duct-to-duct reconstruction. Transpl Int. 1991 Sep;4(3):161–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00335338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismuth H., Castaing D., Gugenheim J., Traynor O., Ciardullo M. Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy: a safe procedure for biliary anastomosis in liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 3):2413–2415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne R. Y. A new technique for biliary drainage in orthotopic liver transplantation utilizing the gall bladder as a pedicle graft conduit between the donor and recipient common bile ducts. Ann Surg. 1976 Nov;184(5):605–609. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197611000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne R. Y., McMaster P., Portmann B., Wall W. J., Williams R. Observations on preservation, bile drainage and rejection in 64 human orthotopic liver allografts. Ann Surg. 1977 Sep;186(3):282–290. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197709000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csendes A., Díaz J. C., Burdiles P., Maluenda F. Late results of immediate primary end to end repair in accidental section of the common bile duct. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1989 Feb;168(2):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decurtins M., Lachat M., Largiadèr F. Die Gallengangsrekonstruktion bei der Lebertransplantation. Helv Chir Acta. 1990 Jun;57(1):83–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiatt J. R., Quinones-Baldrich W. J., Ramming K. P., Brems J., Busuttil R. W. Operations upon the biliary tract during transplantation of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1987 Jul;165(1):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krom R. A., Kingma L. M., Wesenhagen H., Slooff M. J., Haagsma E. B., Gips C. H. Choledochocholedochostomy is successful in orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1984 Oct;16(5):1228–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerut J., Gordon R. D., Iwatsuki S., Esquivel C. O., Todo S., Tzakis A., Starzl T. E. Biliary tract complications in human orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1987 Jan;43(1):47–51. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198701000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez R. R., Benner K. G., Ivancev K., Keeffe E. B., Deveney C. W., Pinson C. W. Management of biliary complications after liver transplantation. Am J Surg. 1992 May;163(5):519–524. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(92)90401-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus P., Brölsch C., Ringe B., Lauchart W., Pichlmayr R. Results of biliary reconstruction after liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1984 Oct;16(5):1225–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus P., Neuhaus R., Pichlmayr R., Vonnahme F. An alternative technique of biliary reconstruction after liver transplantation. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1982;180(3):239–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01852296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northover J., Terblanche J. Bile duct blood supply. Its importance in human liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1978 Jul;26(1):67–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKE W. W., MICHELS N. A., GHOSH G. M. Blood supply of the common bile duct. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963 Jul;117:47–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringe B., Oldhafer K., Bunzendahl H., Bechstein W. O., Kotzerke J., Pichlmayr R. Analysis of biliary complications following orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 2):2472–2476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Urdazpal L., Gores G. J., Ward E. M., Maus T. P., Wahlstrom H. E., Moore S. B., Wiesner R. H., Krom R. A. Ischemic-type biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1992 Jul;16(1):49–53. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Putnam C. W., Hansbrough J. F., Porter K. A., Reid H. A. Biliary complications after liver transplantation: with special reference to the biliary cast syndrome and techniques of secondary duct repair. Surgery. 1977 Feb;81(2):212–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratta R. J., Wood R. P., Langnas A. N., Hollins R. R., Bruder K. J., Donovan J. P., Burnett D. A., Lieberman R. P., Lund G. B., Pillen T. J. Diagnosis and treatment of biliary tract complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. Surgery. 1989 Oct;106(4):675–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]