Abstract
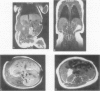
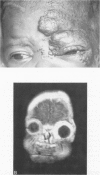
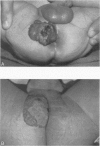
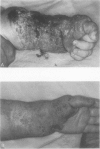
OBJECTIVE: The authors describe the use of interferon-alpha-2a (IFN-alpha-2a) in the treatment of complex hemangiomas and review the role of interferon (IFN) in this example of an angiogenic disease. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Hemangiomas are the most frequent tumors of infants and children. They grow rapidly for 6 to 8 months and then resolve over a period of years. Approximately 5% produce life-, sight-, or limb-threatening complications, with mortality rates between 20% and 50%. Aggressive therapy with steroids, arterial ligation or embolization, or surgery has been used in these situations with variable results and high morbidity. Recently, IFN-alpha was found to be effective treatment in these complex hemangiomas. METHODS: Four infants and one child were treated with IFN-alpha-2a at an initial subcutaneous dose of 1 million units/m2/day and a sustained dose of 3 million units/m2/day for 5 to 11 months. Appropriate laboratory values were monitored and adverse reactions and ultimate response to therapy were recorded. RESULTS: Two patients experienced minor complications that were managed easily. Three patients had total or near-total regression of the hemangioma, one had partial (50%) regression, and one had stabilization but no regression after an average of 7.1 months of IFN therapy. CONCLUSION: Interferon-alpha inhibits angiogenesis and endothelial cell migration and proliferation in vitro. The patients in this study add to the growing number who have benefited from IFN therapy. As such, IFN-alpha should be considered as a first-line agent in treating complex hemangiomas of infants and children.
Full text
PDF

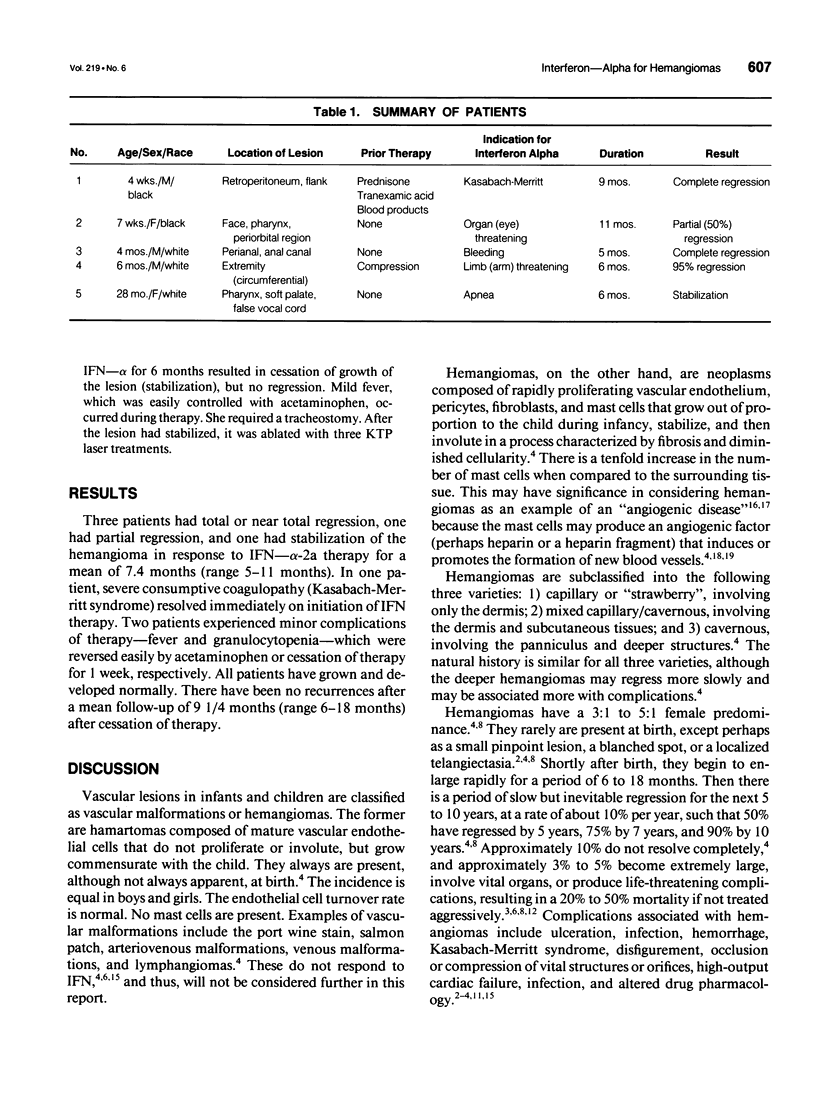
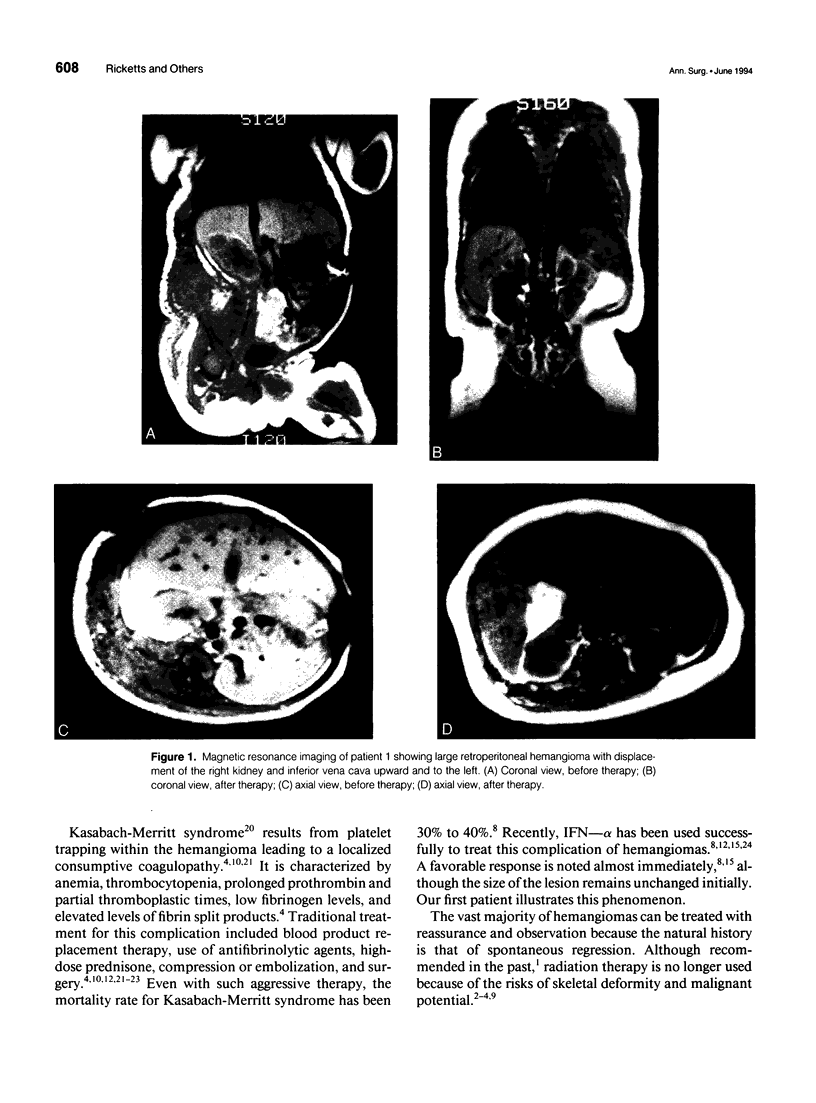
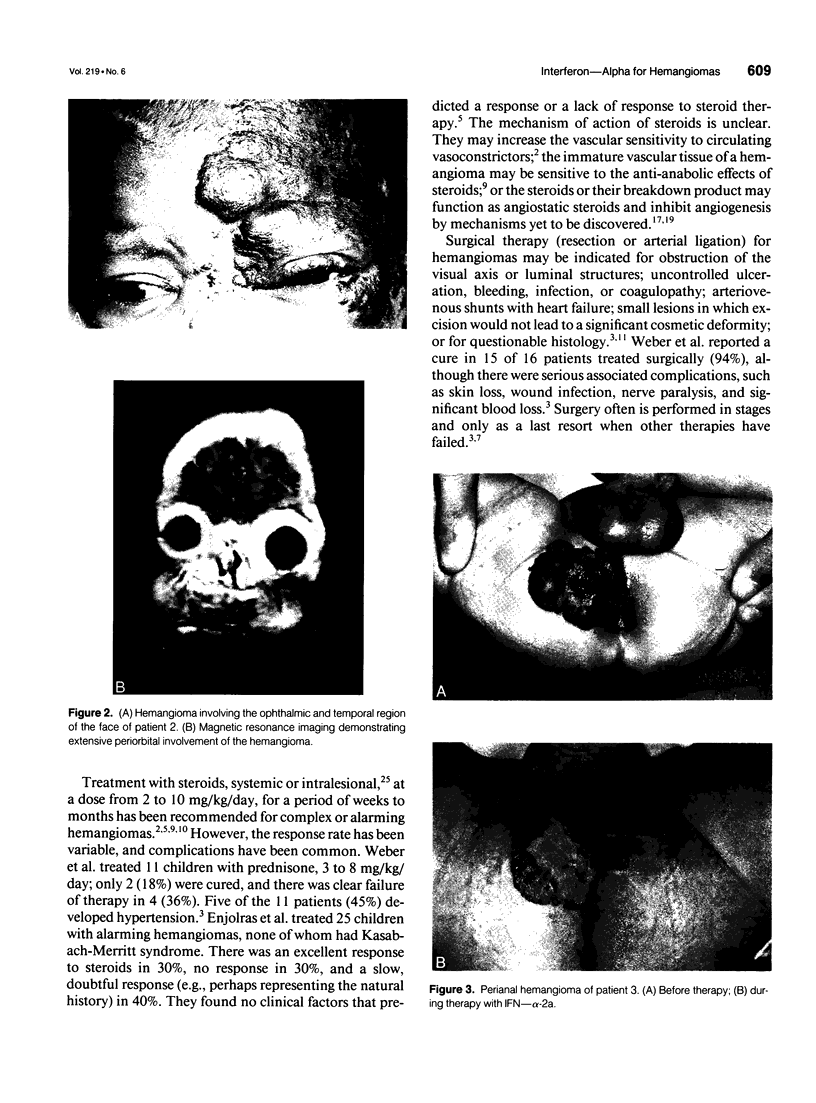



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron S., Tyring S. K., Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Coppenhaver D. H., Niesel D. W., Klimpel G. R., Stanton G. J., Hughes T. K. The interferons. Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. JAMA. 1991 Sep 11;266(10):1375–1383. doi: 10.1001/jama.266.10.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouty-Boyé D., Zetter B. R. Inhibition of cell motility by interferon. Science. 1980 May 2;208(4443):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.6154315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresse M. F., David M., Hume H., Blanchard H., Russo P., Van Doesberg N., Rivard G. E. Successful treatment of Kasabach-Merritt syndrome with prednisone and epsilon-aminocaproic acid. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1991 Oct-Dec;8(4):329–334. doi: 10.3109/08880019109028806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton M. T. The treatment of hemangiomas: with special reference to the role of steroid therapy. Ann Surg. 1976 May;183(5):517–532. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197605000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjolras O., Riche M. C., Merland J. J., Escande J. P. Management of alarming hemangiomas in infancy: a review of 25 cases. Pediatrics. 1990 Apr;85(4):491–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz A., Mulliken J., Folkman J. Interferon alpha therapy of haemangiomas in newborns and infants. Br J Haematol. 1991 Oct;79 (Suppl 1):67–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb08123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Mulliken J. B., Folkman J. Interferon alfa-2a therapy for life-threatening hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 28;326(22):1456–1463. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199205283262203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Ingber D. E. Angiostatic steroids. Method of discovery and mechanism of action. Ann Surg. 1987 Sep;206(3):374–383. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198709000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Successful treatment of an angiogenic disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 4;320(18):1211–1212. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905043201811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov 18;285(21):1182–1186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111182852108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesel R., Komoriya A., Maciag T. Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by gamma-interferon. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):689–696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatley R. M., Sabio H., Howell C. G., Flickinger F., Parrish R. A. Successful management of an infant with a giant hemangioma of the retroperitoneum and Kasabach-Merritt syndrome with alpha-interferon. J Pediatr Surg. 1993 Oct;28(10):1356–1359. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(05)80327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN L. W., MACCOLLUM D. W. Hemangiomas in infants and children. Am J Surg. 1961 May;101:571–580. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(61)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchard P. J., Smith C. M., 3rd, Woods W. G., Day D. L., Dehner L. P., Shapiro R. Treatment of haemangioendotheliomas with alpha interferon. Lancet. 1989 Sep 2;2(8662):565–567. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90694-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozsoylu S., Irken G., Gürgey A. High dose intravenous methylprednisolone for Kassabach-Merritt syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1989 Feb;148(5):403–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00595897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricketts R. R., Stryker S., Raffensperger J. G. Ventral fasciotomy in the management of hepatic hemangioendothelioma. J Pediatr Surg. 1982 Apr;17(2):187–188. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(82)80210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Frey E. E., Wicklund B., Kisker C. T., Smith W. L. Embolization therapy in the management of infantile hemangioma with Kasabach Merritt syndrome. Pediatr Radiol. 1987;17(6):503–504. doi: 10.1007/BF02388292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidky Y. A., Borden E. C. Inhibition of angiogenesis by interferons: effects on tumor- and lymphocyte-induced vascular responses. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 1;47(19):5155–5161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman R. A. Hemangiomas and vascular malformations. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1991 Aug;38(4):811–834. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)38155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan G. M., Reinisch J. F., Nichter L. S., Saber W. L., Lew K., Morwood D. T. Intralesional corticosteroid therapy for infantile hemangiomas. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1989 Mar;83(3):459–467. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198903000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller J. C., Sharma V., Woods G. M., Hall J. C., Seidel F. G. Diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis treated successfully with interferon alfa-2a. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Jul;27(1):102–104. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80815-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl R. L., Henderson J. M., Hooks M. A., Martin L. G., Duncan A. Therapy of the Kasabach-Merritt syndrome with cryoprecipitate plus intra-arterial thrombin and aminocaproic acid. Am J Hematol. 1991 Apr;36(4):272–274. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830360409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Geer G. D., Miller J. H., Gilsanz V., Landing B. H., Boechat I. M. Infantile hepatic hemangiomas. Clinical features, radiologic investigations, and treatment of 20 patients. Cancer. 1989 Aug 15;64(4):936–949. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890815)64:4<936::aid-cncr2820640429>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolaymat A., Leventhal B., Sakarcan A., Kashima H., Monteiro C. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a child receiving long-term interferon therapy. J Pediatr. 1992 Mar;120(3):429–432. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80913-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber T. R., Connors R. H., Tracy T. F., Jr, Bailey P. V. Complex hemangiomas of infants and children. Individualized management in 22 cases. Arch Surg. 1990 Aug;125(8):1017–1021. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1990.01410200081012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. W., Sondheimer H. M., Crouch E. C., Wilson H., Fan L. L. Treatment of pulmonary hemangiomatosis with recombinant interferon alfa-2a. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 4;320(18):1197–1200. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905043201807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. W. Treatment of hemangiomatosis with recombinant interferon alfa. Semin Hematol. 1990 Jul;27(3 Suppl 4):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. W., Wolf S. J., Korones D. N., Sondheimer H. M., Tosi M. F., Yu A. Treatment of childhood angiomatous diseases with recombinant interferon alfa-2a. J Pediatr. 1991 Jan;118(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81844-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarem H. A., Edgerton M. T. Induced resolution of cavernous hemangiomas following prednisolone therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1967 Jan;39(1):76–83. doi: 10.1097/00006534-196701000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]