Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
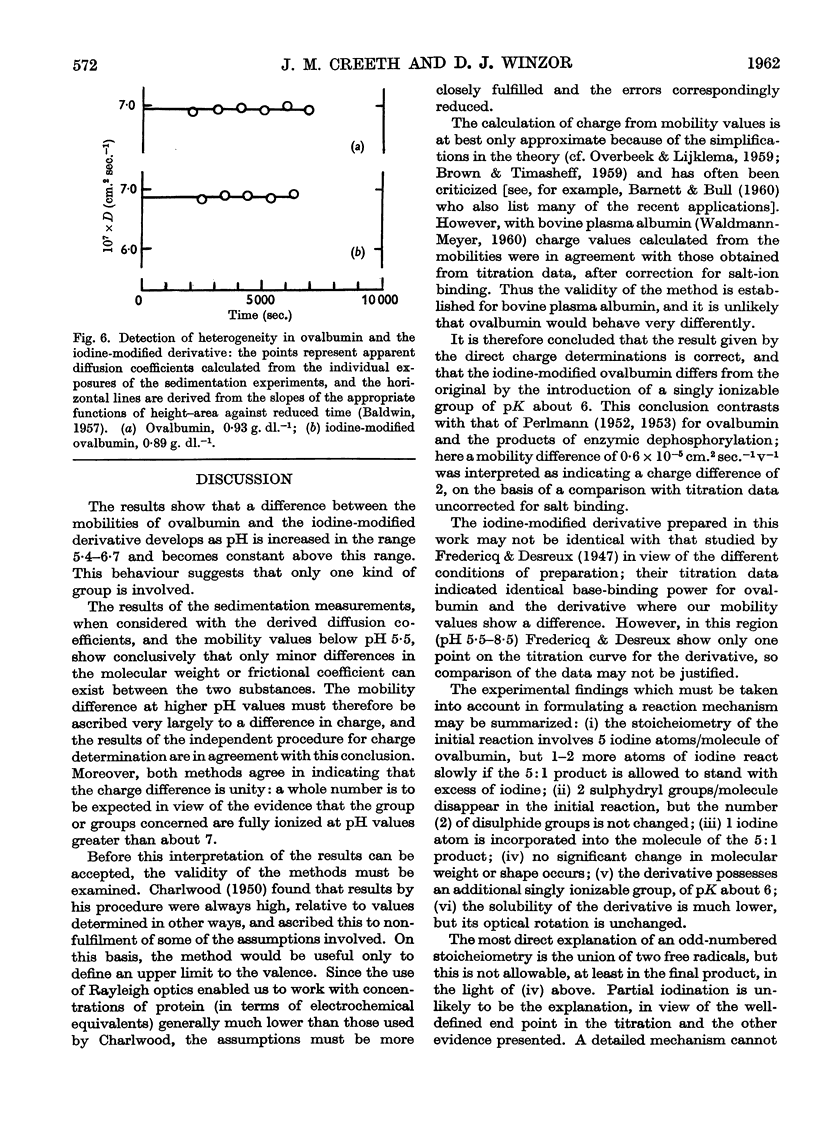
- BALDWIN R. L. Boundary spreading in sedimentation-velocity experiments. V. Measurement of the diffusion coefficient of bovine albumin by Fujita's equation. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):503–512. doi: 10.1042/bj0650503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNETT L. B., BULL H. B. Electrophoresis of ribonuclease and of beta-lactoglobulin: isoelectric points of proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:167–172. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREETH J. M., NICHOL L. W. Evidence for the chemical interaction of urease in solution. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:230–239. doi: 10.1042/bj0770230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUNNINGHAM L. W., NUENKE B. J. Analysis of modified beta-lactoglobulins and ovalbumins prepared from the sulfenyl iodine intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1711–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUNNINGHAM L. W., NUENKE B. J. Physical and chemical studies of a limited reaction of iodine with proteins. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1447–1451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood P. A. The valences of protein ions from electrophoretic and membrane potential measurements. Biochem J. 1950 Mar;46(3):312–319. doi: 10.1042/bj0460312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER J. F., RHEES R. C. An investigation by light scattering of aggregation in the heat denaturation of ovalbumin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):437–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H. The reaction of tobacco mosaic virus with iodine. J Biol Chem. 1955 Nov;217(1):373–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLAREN J. A., LEACH S. J., O'DONNELL I. J. The oxidation of disulphide groups in proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Sep;35:280–281. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90371-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER G. L., GOLDER R. H. Sedimentation studies with the Spinco ultracentrifuge. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Apr;36(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMANN G. E. Enzymatic dephosphorylation of ovalbumin and plakalbumin. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;35(5):711–726. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.5.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALDMANN-MEYER H. Thermodynamic proton-, cadmium-, and zinc-binding constants of serum albumin determined by zone electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3337–3345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINZOR D. J., CREETH J. M. Physicochemical studies on ovalbumin. 3. The sulphydryl and disulphide contents of ovalbumin and an iodine-modified derivative. Biochem J. 1962 Jun;83:559–566. doi: 10.1042/bj0830559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]