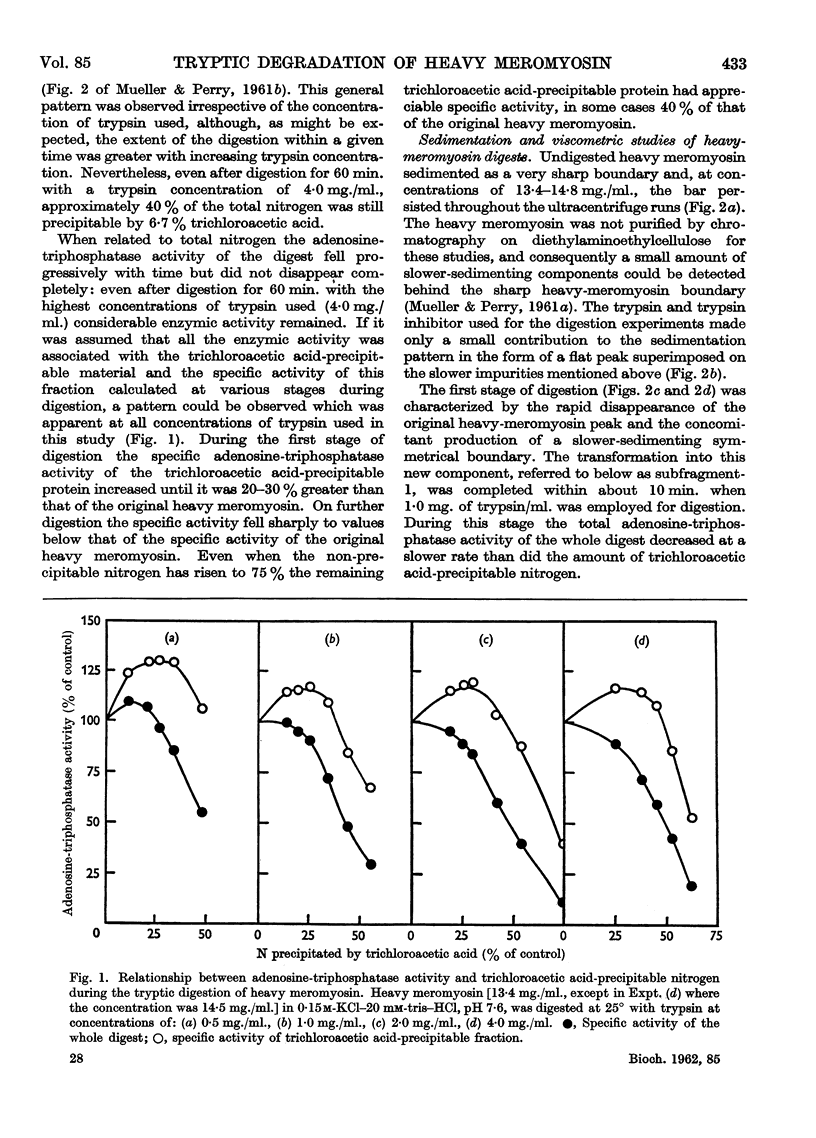
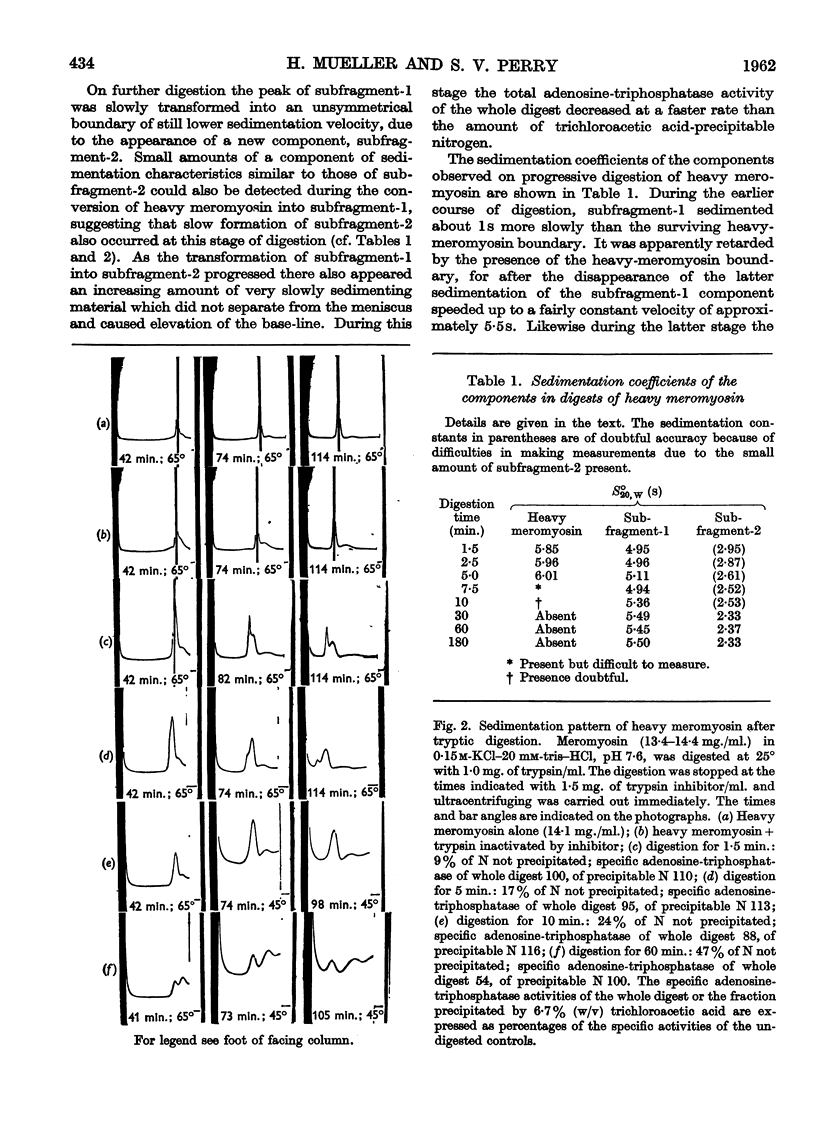
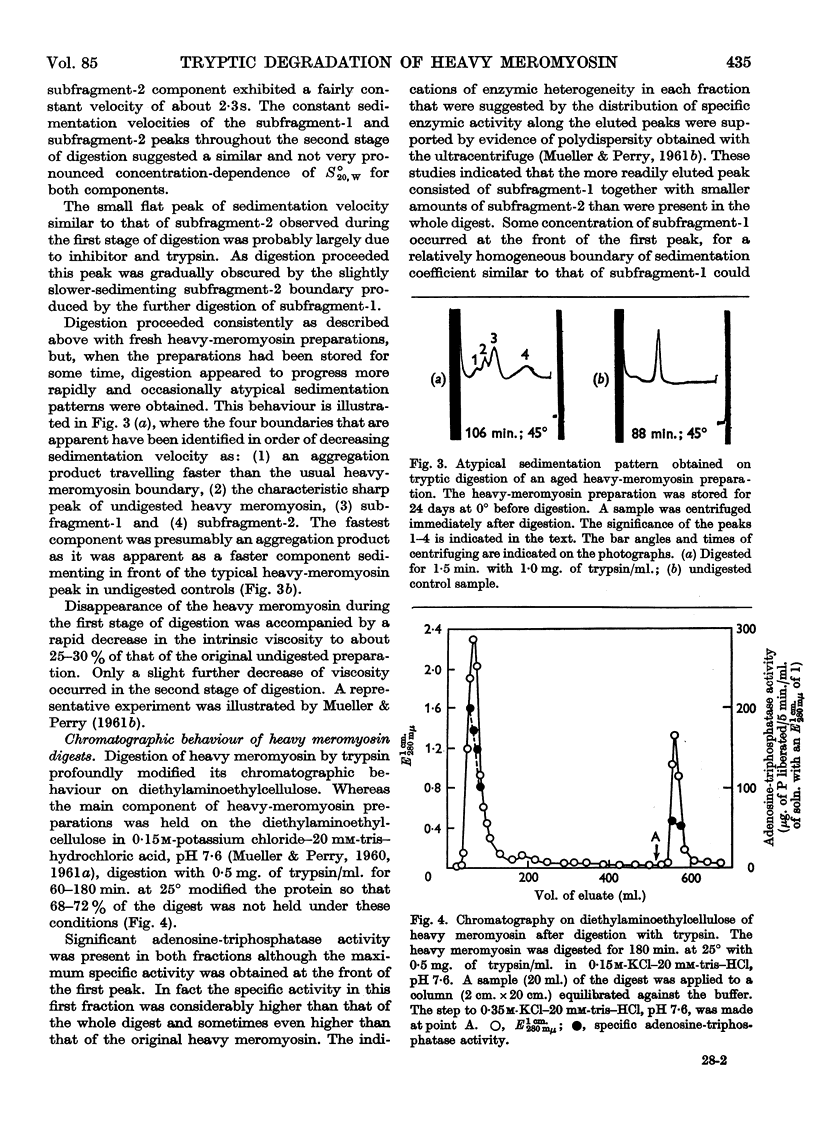
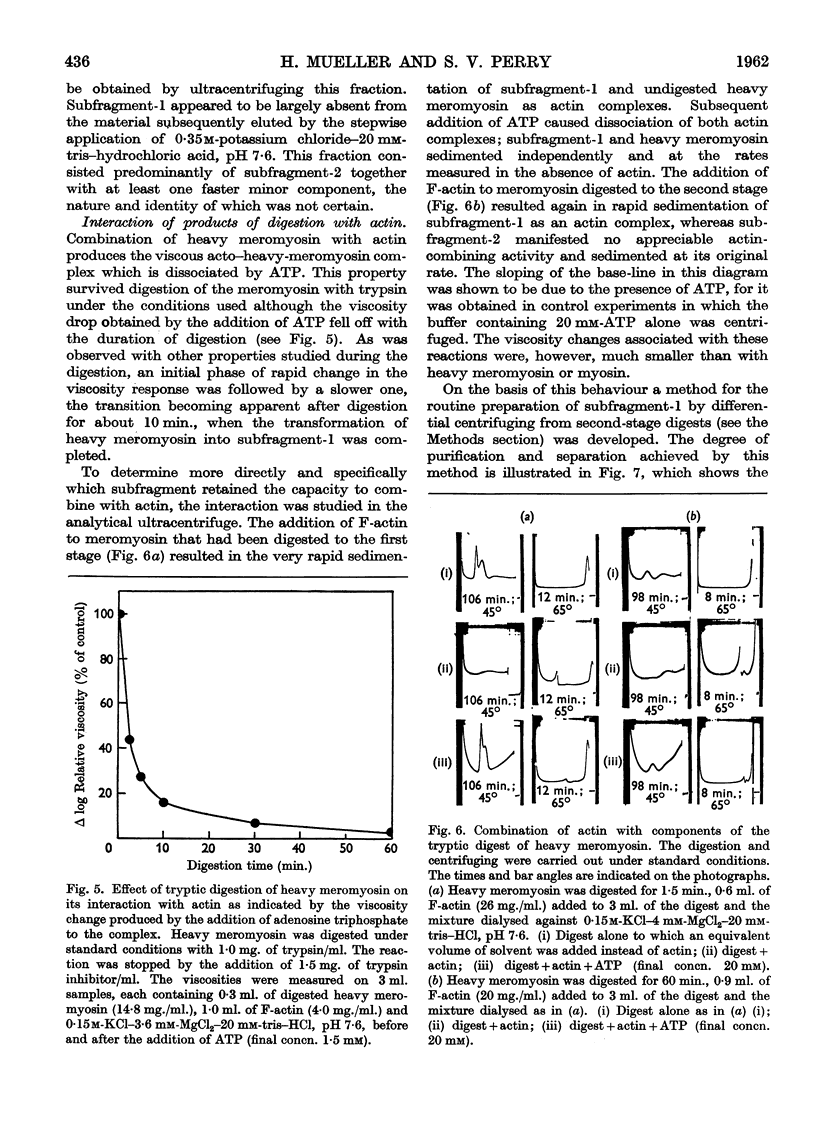
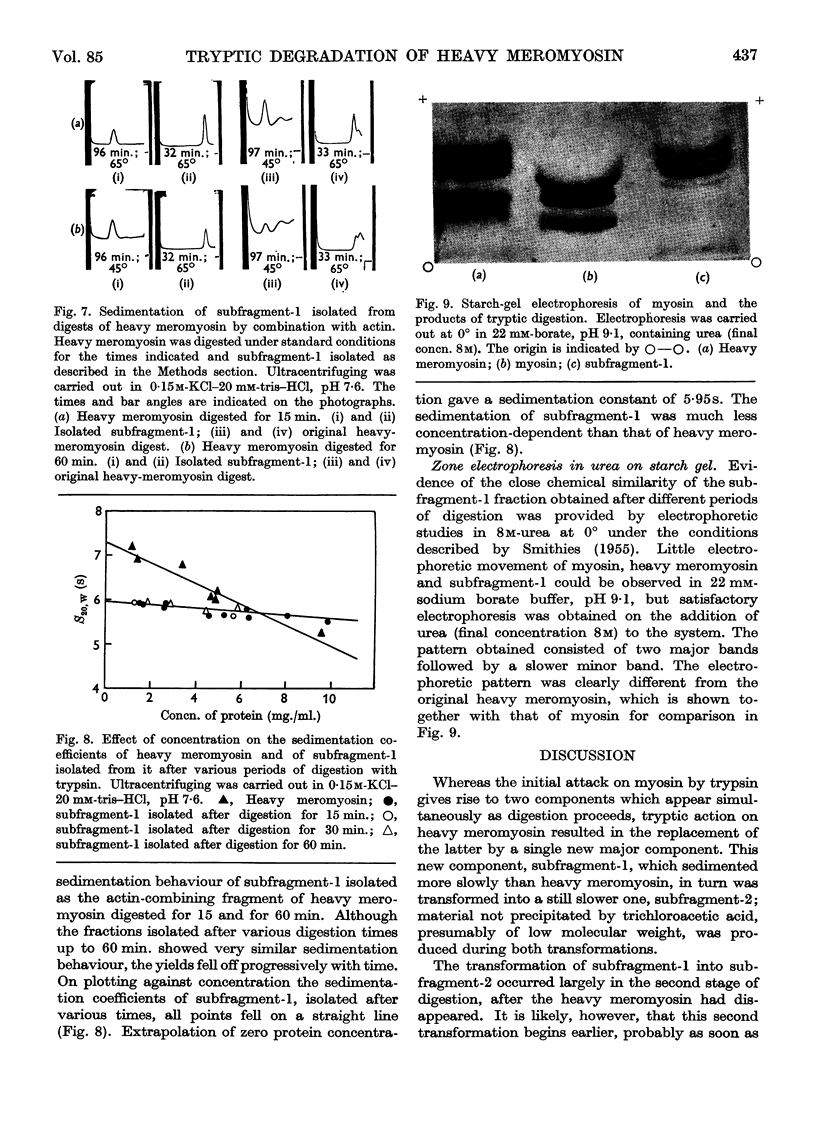
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FRYAR A. J., GIBBS R. J. Bovine muscle proteins. IL. Heterogeneity in H-meromyosin preparations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 May;88:177–178. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERGELY J., GOUVEA M. A., KARIBIAN D. Fragmentation of myosin by chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):165–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERGELY J. Studies on myosin-adenosinetriphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1953 Feb;200(2):543–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOMINZ D. R., HOUGH A., SYMONDS P., LAKI K. The amino acid composition of action, myosin, tropomyosin and the meromyosins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 May;50(1):148–159. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWEY S., HOLTZER A. The homogeneity and molecular weights of the meromyosins and their relative proportions in myosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Aug;34:470–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIHALYI E., SZENT-GYORGYI A. G. Trypsin digestion of muscle proteins. I. Ultracentrifugal analysis of the process. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOMMAERTS W. F. H. M. Reversible polymerization and ultracentrifugal purification of actin. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):559–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER H., PERRY S. V. Studies on the tryptic digestion of heavy meromyosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jul 8;50:599–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER H., PERRY S. V. The chromatography of the meromyosins on diethylaminoethylcellulose. Biochem J. 1961 Jul;80:217–223. doi: 10.1042/bj0800217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V. The ATP-ase activity of isolated myofibrils. Biochem J. 1950 Sep;47(3):xxxviii–xxxviii. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V. The adenosinetriphosphatase activity of myofibrils isolated from skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1951 Mar;48(3):257–265. doi: 10.1042/bj0480257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V. The chromatography of L-myosin on diethylaminoethylcellulose. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:94–101. doi: 10.1042/bj0740094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V., ZYDOWO M. A ribonucleoprotein of skeletal muscle and its relation to the myofibril. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:682–690. doi: 10.1042/bj0720682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZENT-GYORGYI A. G. A new method for the preparation of actin. J Biol Chem. 1951 Sep;192(1):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZENT-GYORGYI A. G. Meromyosins, the subunits of myosin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Feb;42(2):305–320. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90360-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER H. H., PORTZEHL H. Muscle contraction and fibrous muscle proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1952;7:161–252. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]