Abstract
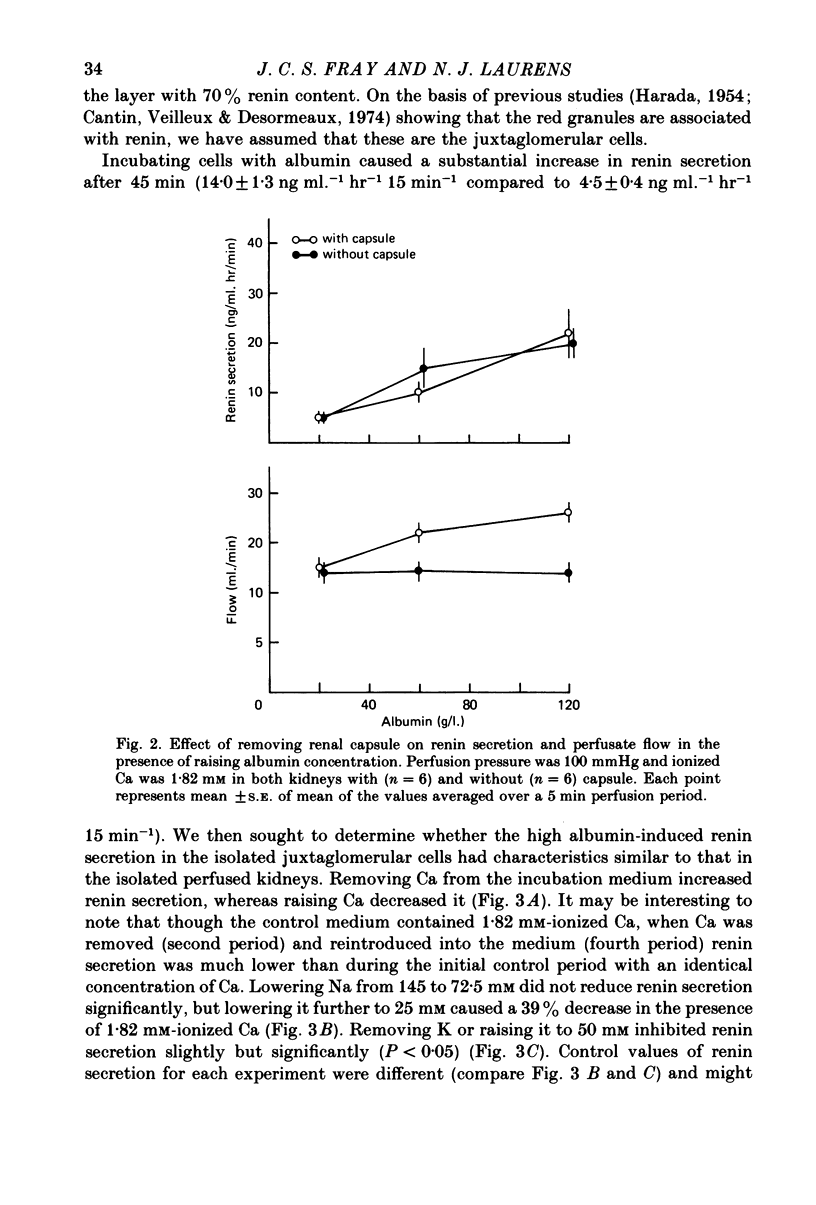
1. Raising albumin concentration stimulates renin secretion in isolated perfused kidneys and isolated juxtaglomerular cells. 2. In isolated perfused kidneys, raising albumin concentration from 20 to 120 g/l. increased renin secretion and perfusate flow when the perfusion medium contained 1.82 mM-total or ionized Ca. Removing the renal capsule abolished the increased flow but not renin secretion. 3. In isolated juxtaglomerular cells, raising albumin concentration from 0 to 60 g/l. increased renin secretion threefold. This was enhanced slightly by removing Ca. Raising Ca, removing or raising K to 50 mM, or lowering Na to 25 mM inhibited renin secretion. 4. Raising pH from 7.36 to 7.64 inhibited renin secretion whether albumin was present or not. Keeping both pH and ionized Ca constant abolished the stimulatory effect of raising albumin. 5. We conclude that raising albumin concentration in plasma may stimulate renin secretion by several mechanisms, two of which are by lowering ionized Ca and lowering pH, and that both effects may be on the juxtaglomerular cells directly. We also conclude that raising pH per se has a powerful inhibitory effect on renin secretion.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S., Jr, Cohen A. J., Fray J. C., Laurens N. J. Role of calcium and albumin in the autoregulation of renal perfusate flow. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:1–9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin M., Veilleux R., Desormeaux Y. Lysosomal function of juxtaglomerular granules. Experientia. 1974 Jul 15;30(7):794–797. doi: 10.1007/BF01924191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C., Karuza A. S. Influence of raising albumin concentration on renin release in isolated perfused rat kidneys. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:45–54. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C. Stimulus-secretion coupling of renin. Role of hemodynamic and other factors. Circ Res. 1980 Oct;47(4):485–492. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.4.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C. Stretch receptor model for renin release with evidence from perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):936–944. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. S. Stimulation of renin release in perfused kidney by low calcium and high magnesium. Am J Physiol. 1977 Apr;232(4):F377–F382. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.4.F377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARADA K. Histochemical studies of the juxta glomerular apparatus. Rev Belg Pathol Med Exp. 1954 Oct;23(5):311–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Guyton A. C. Changes in renal hemodynamics and renin release caused by increased plasma oncotic pressure. Am J Physiol. 1976 Nov;231(5 Pt 1):1550–1556. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.5.1550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz K. D., Zehr J. E. Mechanisms of enhanced renin secretion during CO2 retention in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1978 May;234(5):H573–H581. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1978.234.5.H573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T. Plasma renin activity in acute respiratory acidosis. Jpn Circ J. 1976 Feb;40(2):123–126. doi: 10.1253/jcj.40.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaru Y., Schwartz A. The influence of hydrogen ion concentration on calcium binding and release by skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jan;59(1):22–32. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole-Wilson P. A., Langer G. A. Effects of acidosis on mechanical function and Ca2+ exchange in rabbit myocardium. Am J Physiol. 1979 Apr;236(4):H525–H533. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.4.H525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman S. S. Chymotrypsinogen . inositol phosphatide complexes and the transport of digestive enzyme across membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 18;509(2):374–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickholm A., Wallin B. G., Shrager P. The pH dependency of relative ion permeabilities in the crayfish giant axon. Biophys J. 1969 Jul;9(7):873–883. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86424-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



