Abstract
1. Intracellular recordings were made from neurones in the myenteric plexus of the ileum isolated from adult guinea-pigs.
2. Three synaptic potentials were evoked in different myenteric neurones by focal stimulation of the ganglion surface at a distance of up to 100 μm from the cell body from which the recording was made. These were the fast cholinergic excitatory post-synaptic potential (e.p.s.p.), the slow e.p.s.p. and the slow inhibitory post-synaptic potential (i.p.s.p.).
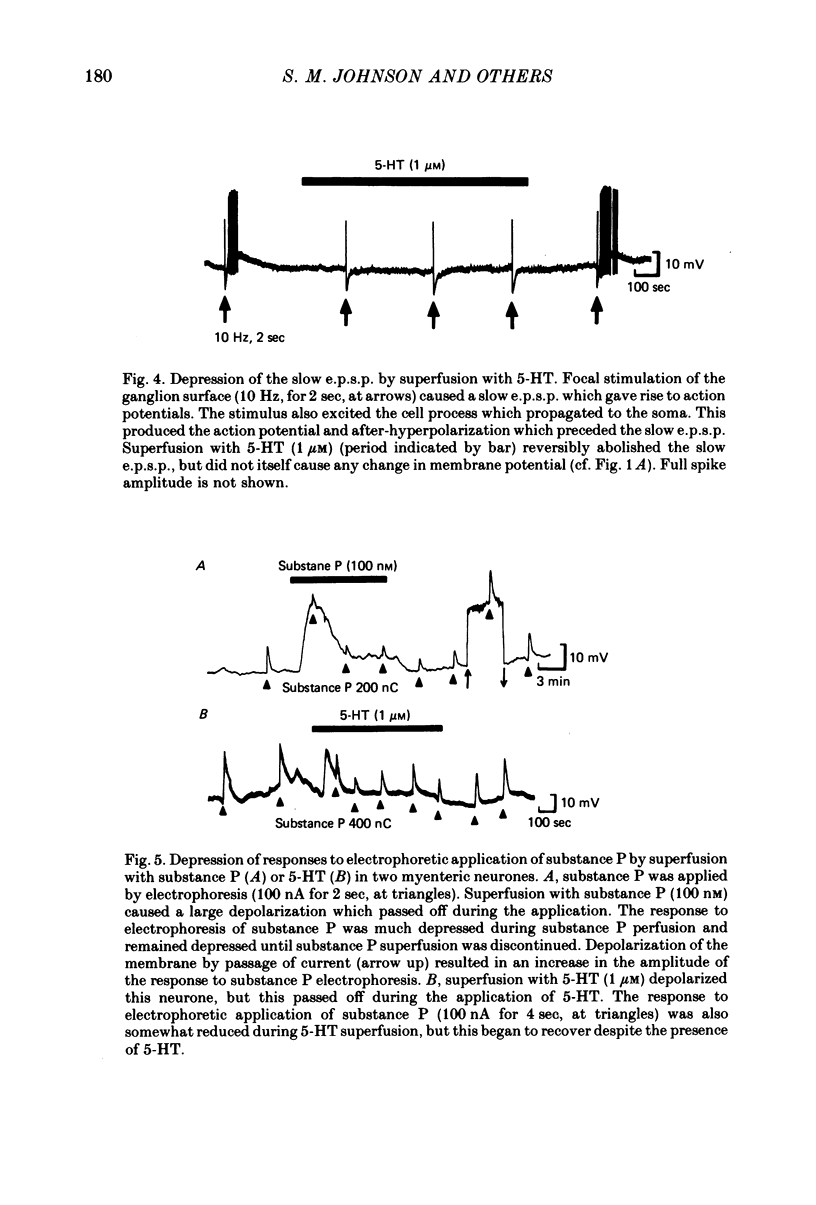
3. 5-hydroxytryptamine and substance P were applied to the neurones by superfusion (10 nm-1 μm) or by electrophoresis within 5 μm of the neurone cell body. 5-HT depolarized, hyperpolarized or had no effect on approximately equal numbers of neurones, whereas substance P depolarized 90% of neurones.
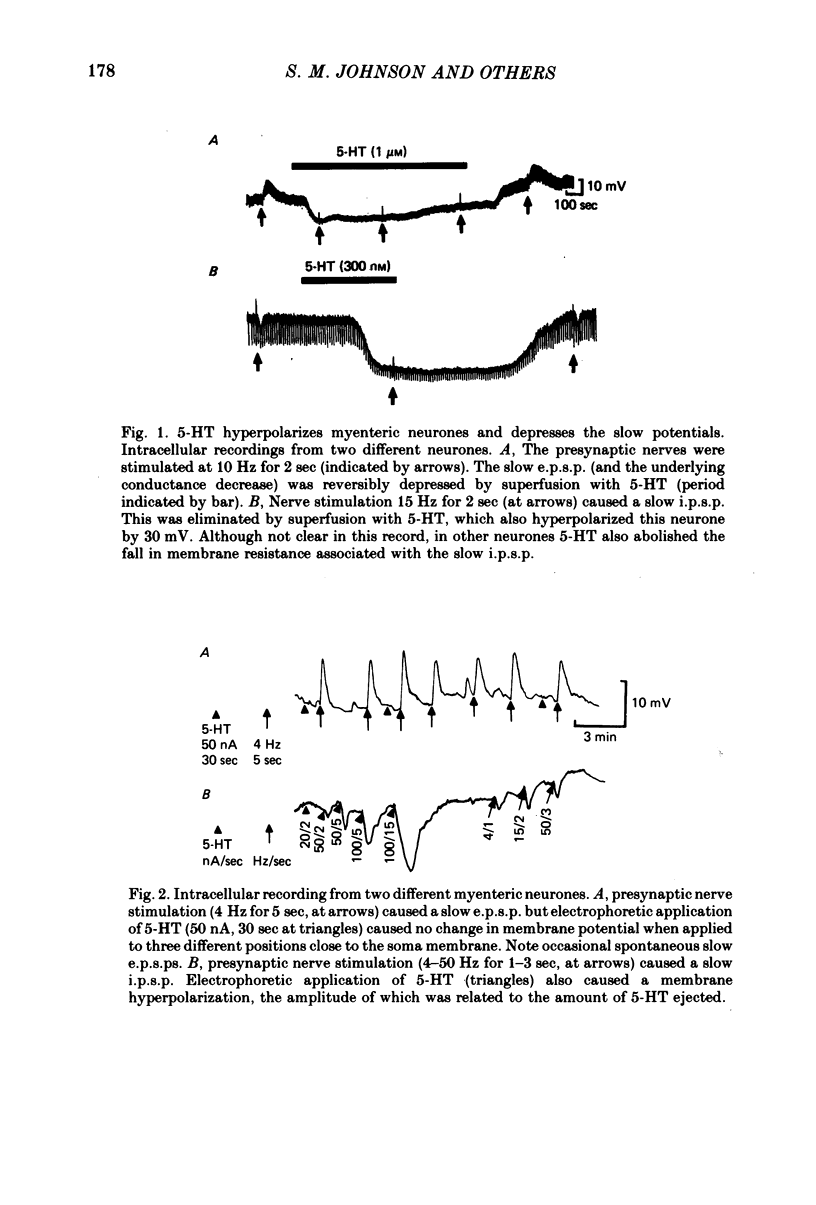
4. Many neurones with a depolarizing slow e.p.s.p. were hyperpolarized by superfusion or electrophoretic application of 5-HT.
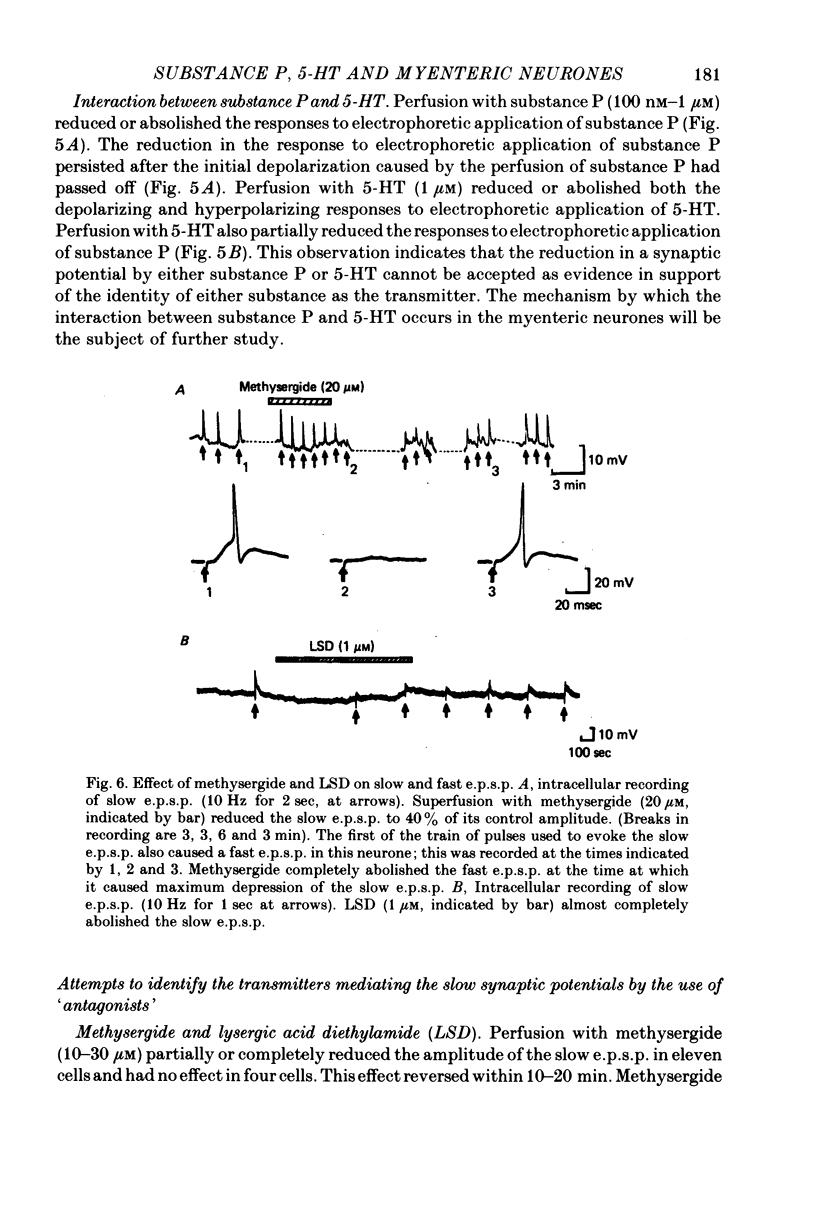
5. Superfusion with 5-HT reversibly depressed the fast e.p.s.p., slow e.p.s.p. and slow i.p.s.p. Superfusion with substance P depressed the slow e.p.s.p.
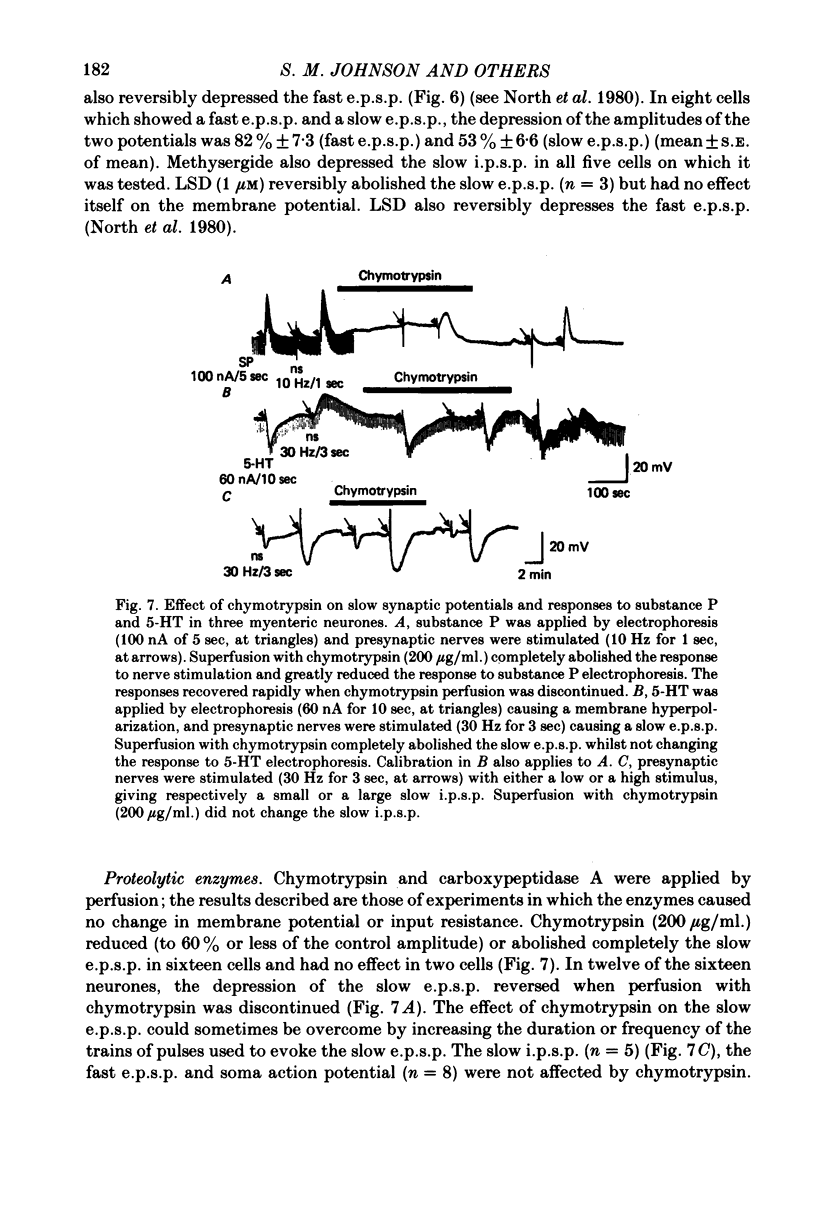
6. Methysergide (10-30 μm) reduced the amplitude of the fast e.p.s.p., the slow e.p.s.p. and the slow i.p.s.p.
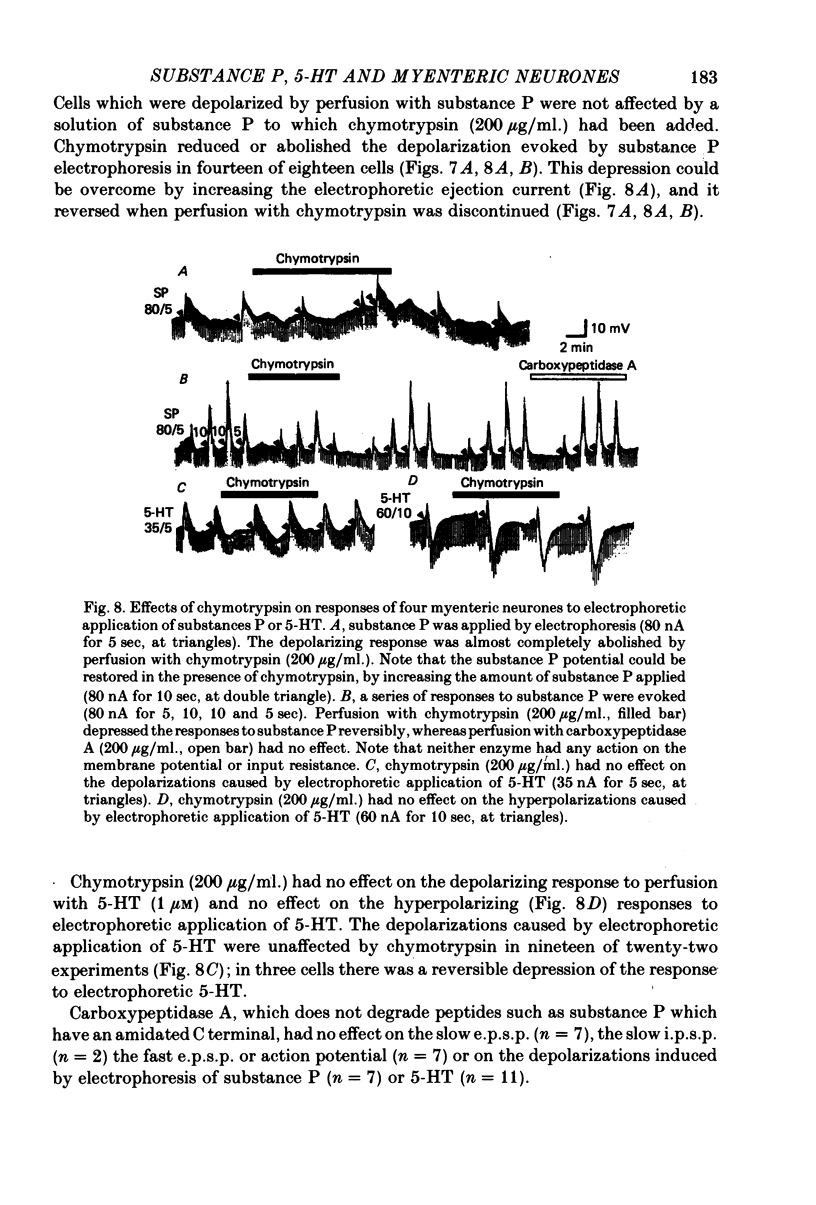
7. Chymotrypsin (200 μg/ml.) reversibly reduced the amplitude of the slow e.p.s.p., but had no effect on membrane potential, the action potential or the fast e.p.s.p. Chymotrypsin reduced or abolished the depolarization caused by electrophoretic application of substance P, but had no effect on the depolarization or hyperpolarization caused by 5HT.
8. The results provide evidence that 5-HT is not the transmitter which mediates the slow e.p.s.p. in myenteric neurones. The slow e.p.s.p. may be caused by substance P or another similar peptide.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Costa M., Cuello A. C., Furness J. B., Franco R. Distribution of enteric neurons showing immunoreactivity for substance P in the guinea-pig ileum. Neuroscience. 1980;5(2):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B. On the possibility that an indoleamine is a neurotransmitter in the gastrointestinal tract. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 1;28(5):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B. The sites of action of 5-hydroxytryptamine in nerve-muscle preparations from the guinea-pig small intestine and colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;65(2):237–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco R., Costa M., Furness J. B. Evidence for the release of endogenous substance P from intestinal nerves. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;306(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00507103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D., Jonakait G. M. Uptake and release of 5-hydroxytryptamine by enteric 5-hydroxytryptaminergic neurones: effects of fluoxetine (Lilly 110140) and chlorimipramine. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 May;66(1):7–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb16089.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Silinsky E. M. Some effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine and noradrenaline on neurones in the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):817–832. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Inhibition of noradrenaline release by lysergic acid diethylamide. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;49(4):706–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Katayama Y., North R. A. Multiple actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine on myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:459–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Katayama Y., North R. A. Slow synaptic potentials in neurones of the myenteric plexus. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:505–516. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A. Does substance P mediate slow synaptic excitation within the myenteric plexus? Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):387–388. doi: 10.1038/274387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A., Williams J. T. The action of substance P on neurons of the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Nov 30;206(1163):191–208. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Katayama Y. Evidence that substance P is a neurotransmitter in the myenteric plexus. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):151–152. doi: 10.1038/287151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Henderson G., Katayama Y., Johnson S. M. Electrophysiological evidence for presynaptic inhibition of acetylcholine release by 5-hydroxytryptamine in the enteric nervous system. Neuroscience. 1980;5(3):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Katayama Y., Williams J. T. On the mechanism and site of action of enkephalin on single myenteric neurons. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 6;165(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Serotonergic activation of tonic-type enteric neurons in guinea pig small bowel. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Mar;42(2):582–593. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.2.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Slow synaptic excitation mediated by serotonin in Auerbach's plexus. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):836–837. doi: 10.1038/276836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



