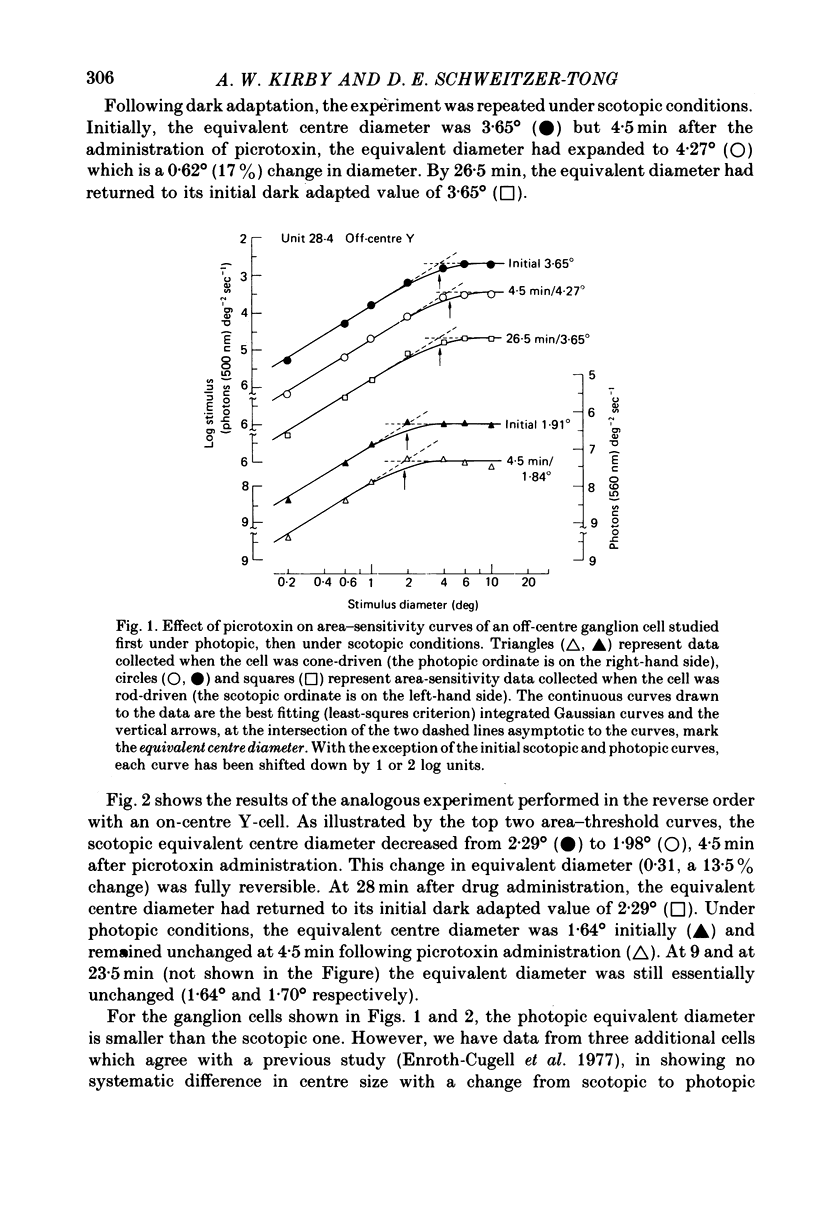
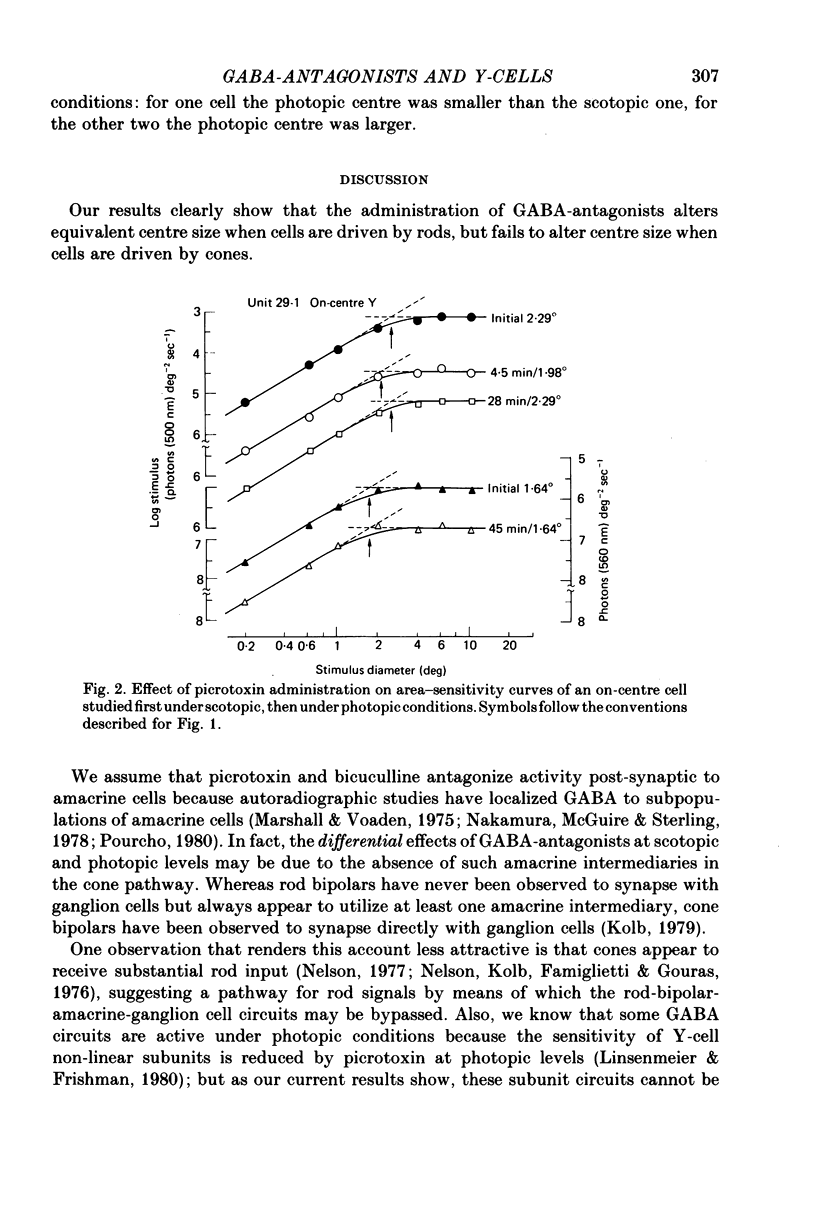
Abstract
1. When Y-type cat retinal ganglion cells were driven by cones, the i.v. administration of the GABA-antagonist picrotoxin failed to alter receptive field centre size. 2. This result is in marked contrast to our previous finding that when Y-cells were driven by rods, GABA-antagonists led to specific and reversible changes in centre size. 3. These results taken together suggest that for centre signals of Y-cells, the rod and cone pathways are pharmacologically distinct.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleland B. G., Enroth-cugell C. Quantitative aspects of sensitivity and summation in the cat retina. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(1):17–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enroth-Cugell C., Hertz G., Lennie P. Cone signals in the cat's retina. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):273–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enroth-Cugell C., Robson J. G. The contrast sensitivity of retinal ganglion cells of the cat. J Physiol. 1966 Dec;187(3):517–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein S., Shapley R. M. Quantitative analysis of retinal ganglion cell classifications. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):237–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby A. W., Enroth-Cugell C. The involvement of gamma-aminobutyric acid in the organization of cat retinal ganglion cell receptive fields. A study with picrotoxin and bicuculline. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Oct;68(4):465–484. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.4.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby A. W., Schweitzer-Tong D. E. GABA-antagonists and spatial summation in Y-type cat retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:335–344. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby A. W. The effect of strychnine, bicuculline, and picrotoxin on X and Y cells in the cat retina. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Jul;74(1):71–84. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. The inner plexiform layer in the retina of the cat: electron microscopic observations. J Neurocytol. 1979 Jun;8(3):295–329. doi: 10.1007/BF01236124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levick W. R. Another tungsten microelectrode. Med Biol Eng. 1972 Jul;10(4):510–515. doi: 10.1007/BF02474199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmeier R. A., Hertz B. G. Eye movements in paralyzed cats induced by drugs and sympathetic stimulation. Vision Res. 1979;19(11):1249–1252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(79)90191-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J., Voaden M. Autoradiographic identification of the cells accumulating 3H gamma-aminobutyric acid in mammalian retinae: a species comparison. Vision Res. 1975 Mar;15(3):459–461. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(75)90102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. Cat cones have rod input: a comparison of the response properties of cones and horizontal cell bodies in the retina of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Mar 1;172(1):109–135. doi: 10.1002/cne.901720106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


