Abstract
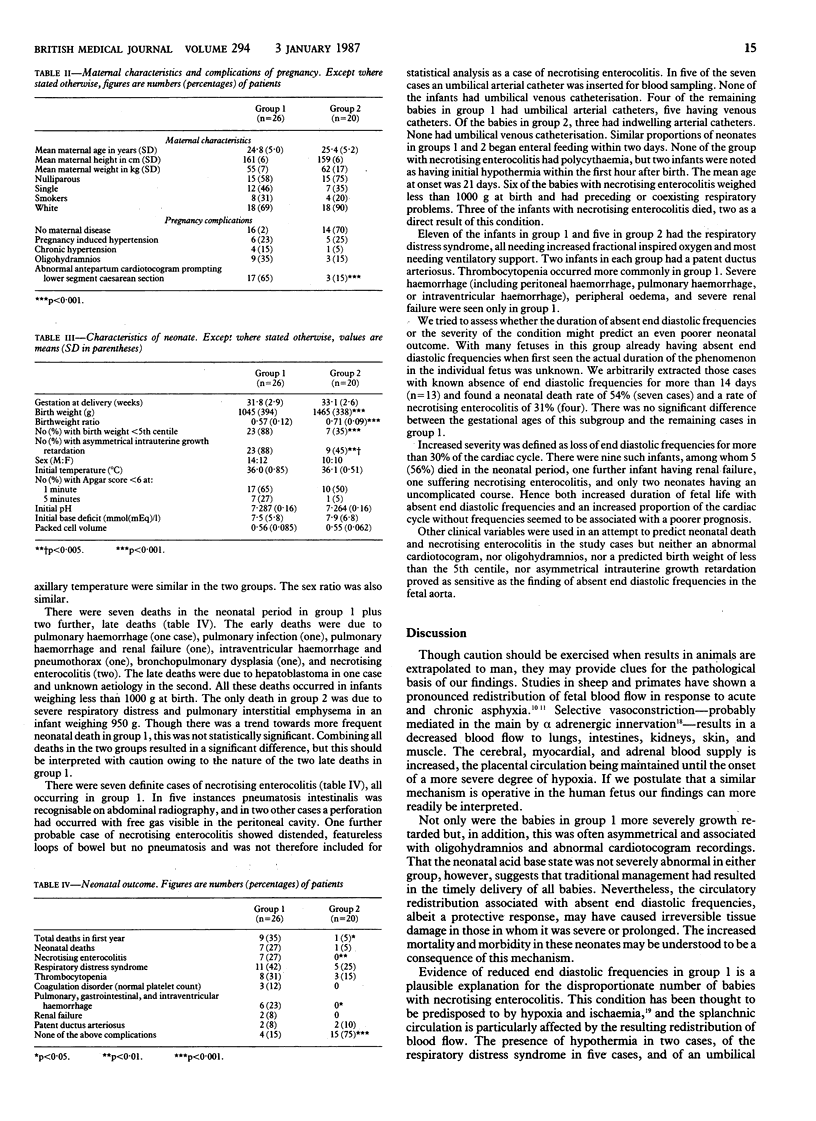
In 82 consecutive cases of intrauterine growth retardation managed by established criteria fetal Doppler studies identified 29 fetuses with absence of end diastolic frequencies in the fetal aorta. These same fetuses were significantly more growth retarded (p less than 0.001) and had an earlier gestational age at delivery (p less than 0.001) than those with end diastolic frequencies present. A subgroup of these cases was analysed in more detail to examine the prognostic value of this phenomenon for the neonate. Two groups of neonates of equivalent gestational age and with a birth weight below 2000 g were compared. There were 26 neonates with absent end diastolic frequencies (group 1) and 20 with end diastolic frequencies (group 2) in the fetal aorta. Those in group 1 were more likely to suffer perinatal death (p less than 0.05), necrotising enterocolitis (p less than 0.01), and haemorrhage (p less than 0.05). Only 4 (15%) of the babies in group 1 had an uncomplicated neonatal period compared with 15 (75%) in group 2 (p less than 0.001). The circulatory changes identified in these cases may provide a more sensitive measure of critical fetal compromise than current techniques and thus allow the clinician to deliver the fetus before irreversible tissue damage has occurred.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behrman R. E., Lees M. H., Peterson E. N., De Lannoy C. W., Seeds A. E. Distribution of the circulation in the normal and asphyxiated fetal primate. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Nov 15;108(6):956–969. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(70)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S., Thoms A. Ultrasound measurement of the fetal head to abdomen circumference ratio in the assessment of growth retardation. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1977 Mar;84(3):165–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1977.tb12550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessells J. M., Wigglesworth J. S. Coagulation studies in severe birth asphyxia. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Jun;46(247):253–256. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.247.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn H. E., Sacks E. J., Heymann M. A., Rudolph A. M. Cardiovascular responses to hypoxemia and acidemia in fetal lambs. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Nov 15;120(6):817–824. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(74)90587-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commey J. O., Fitzhardinge P. M. Handicap in the preterm small-for-gestational age infant. J Pediatr. 1979 May;94(5):779–786. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffos F., Capella-Pavlovsky M., Forestier F. Fetal blood sampling via the umbilical cord using a needle guided by ultrasound. Report of 66 cases. Prenat Diagn. 1983 Oct;3(4):271–277. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson P. C., Abell D. A., Beischer N. A. Mortality and morbidity of fetal growth retardation. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1981 May;21(2):69–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828x.1981.tb00781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D., Bilardo K., Masini L., Diaz-Recasens J., Pearce J. M., Willson K., Campbell S. Doppler blood flow waveforms in the descending thoracic aorta of the human fetus. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1984 Oct;91(10):997–1006. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1984.tb03678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliegman R. M., Fanaroff A. A. Necrotizing enterocolitis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 26;310(17):1093–1103. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404263101707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipper E., Lee K., Gartner L. M., Grellong B. Determinants of neurobehavioral outcome in low-birth-weights infants. Pediatrics. 1981 Apr;67(4):502–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss M. L., Parer J. T., Harris J. L., Krueger T. R. Hemodynamic effects of alpha-adrenergic blockade during hypoxia in fetal sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Feb 15;142(4):410–415. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph A. M., Yuan S. Response of the pulmonary vasculature to hypoxia and H+ ion concentration changes. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):399–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI105355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore R., Woodcock J. P. Physiological interpretation of Doppler-shift waveforms--I. Theoretical considerations. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1980;6(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(80)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. L., Reynolds E. O. Improved prognosis for infants of very low birthweight. Pediatrics. 1974 Dec;54(6):724–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart B., Drumm J., FitzGerald D. E., Duignan N. M. Fetal blood velocity waveforms in normal pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1980 Sep;87(9):780–785. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1980.tb04613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejani N., Mann L. I. Diagnosis and management of the small-for-gestational-age fetus. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Dec;20(4):943–955. doi: 10.1097/00003081-197712000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touloukian R. J., Posch J. N., Spencer R. The pathogenesis of ischemic gastroenterocolitis of the neonate: selective gut mucosal ischemia in asphyxiated neonatal piglets. J Pediatr Surg. 1972 Apr;7(2):194–205. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(72)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudinger B. J., Giles W. B., Cook C. M., Bombardieri J., Collins L. Fetal umbilical artery flow velocity waveforms and placental resistance: clinical significance. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985 Jan;92(1):23–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1985.tb01044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westgren M., Hormquist P., Ingemarsson I., Svenningsen N. Intrapartum fetal acidosis in preterm infants: fetal monitoring and long-term morbidity. Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Mar;63(3):355–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]