Full text
PDF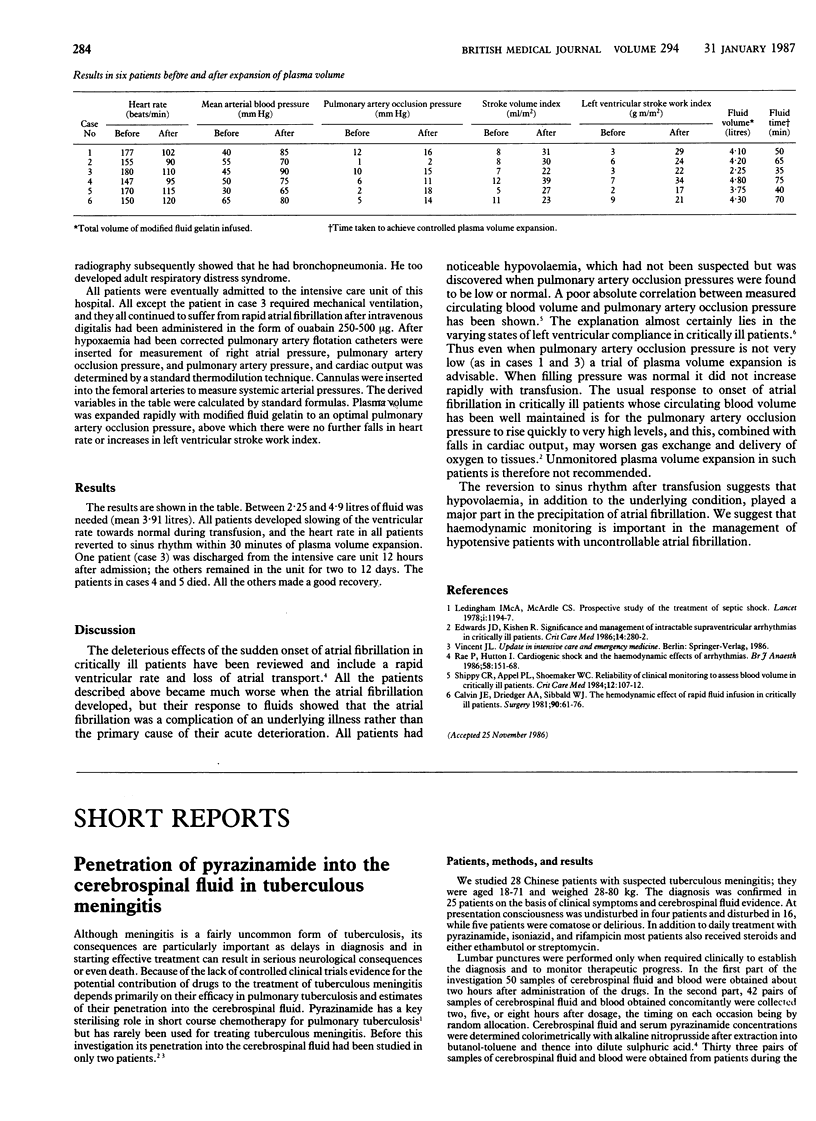

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretton R., Monthaneix C., Coulibaly C., Bretton G., Rey D. Comparaison de l'efficacité thérapeutique des régimes antituberculeux dits "lourd" et "allégé". Bull Int Union Tuberc. 1985 Mar-Jun;60(1-2):34–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellard G. A., Ellard D. R., Allen B. W., Girling D. J., Nunn A. J., Teo S. K., Tan T. H., Ng H. K., Chan S. L. The bioavailability of isoniazid, rifampin, and pyrazinamide in two commercially available combined formulations designed for use in the short-course treatment of tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jun;133(6):1076–1080. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.6.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgan-Smith R., Ellard G. A., Newton D., Mitchison D. A. Pyrazinamide and other drugs in tuberculous meningitis. Lancet. 1973 Aug 18;2(7825):374–374. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiseler P. J., Manis R. D., Jr, Maddux M. S. Dosage of antituberculous drugs in obese patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jun;131(6):944–946. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.6.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girling D. J. The role of pyrazinamide in primary chemotherapy for pulmonary tuberculosis. Tubercle. 1984 Mar;65(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(84)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


