Abstract
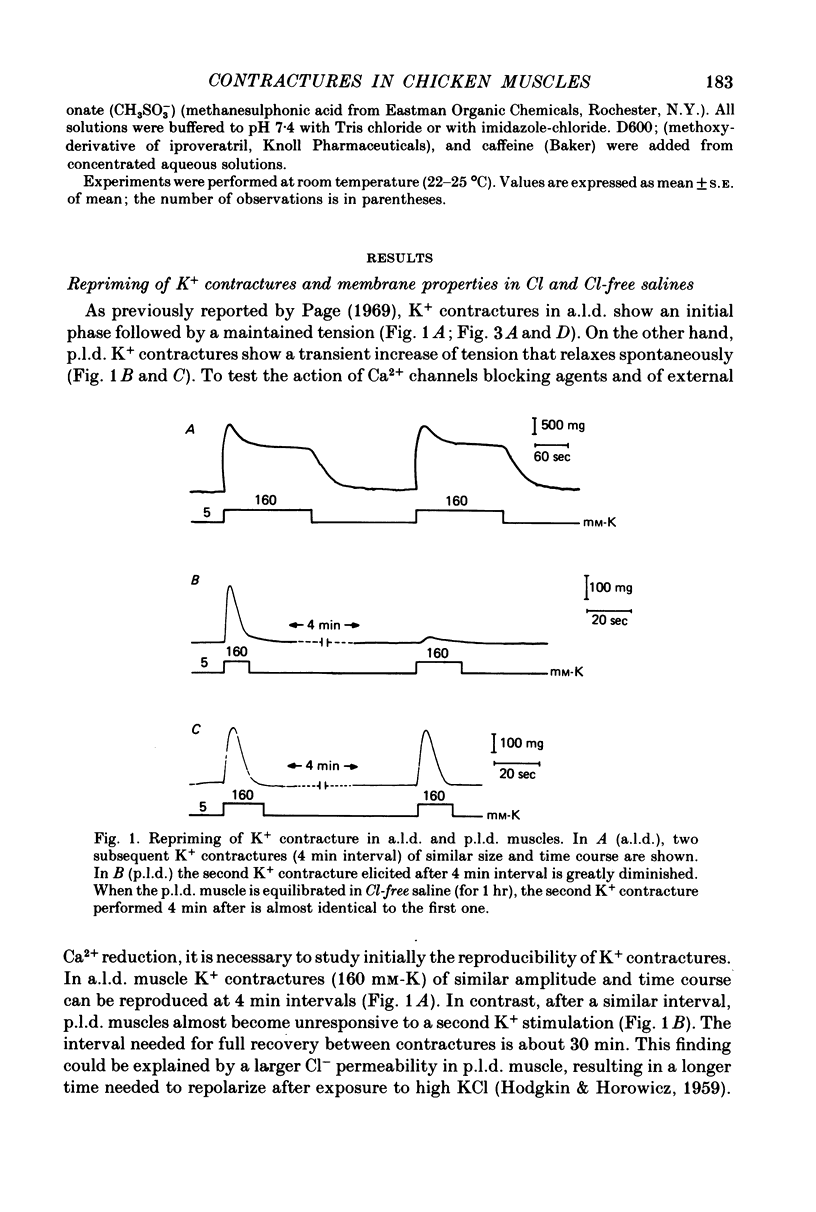
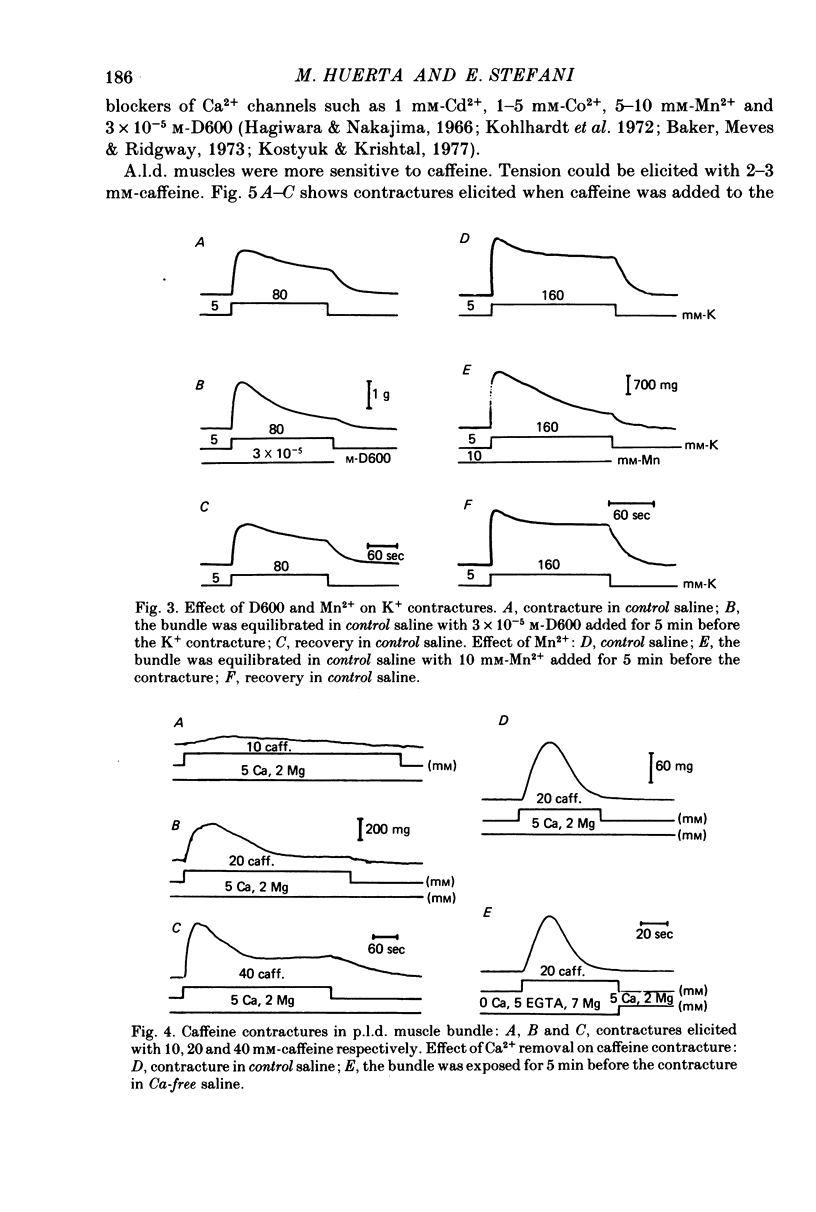
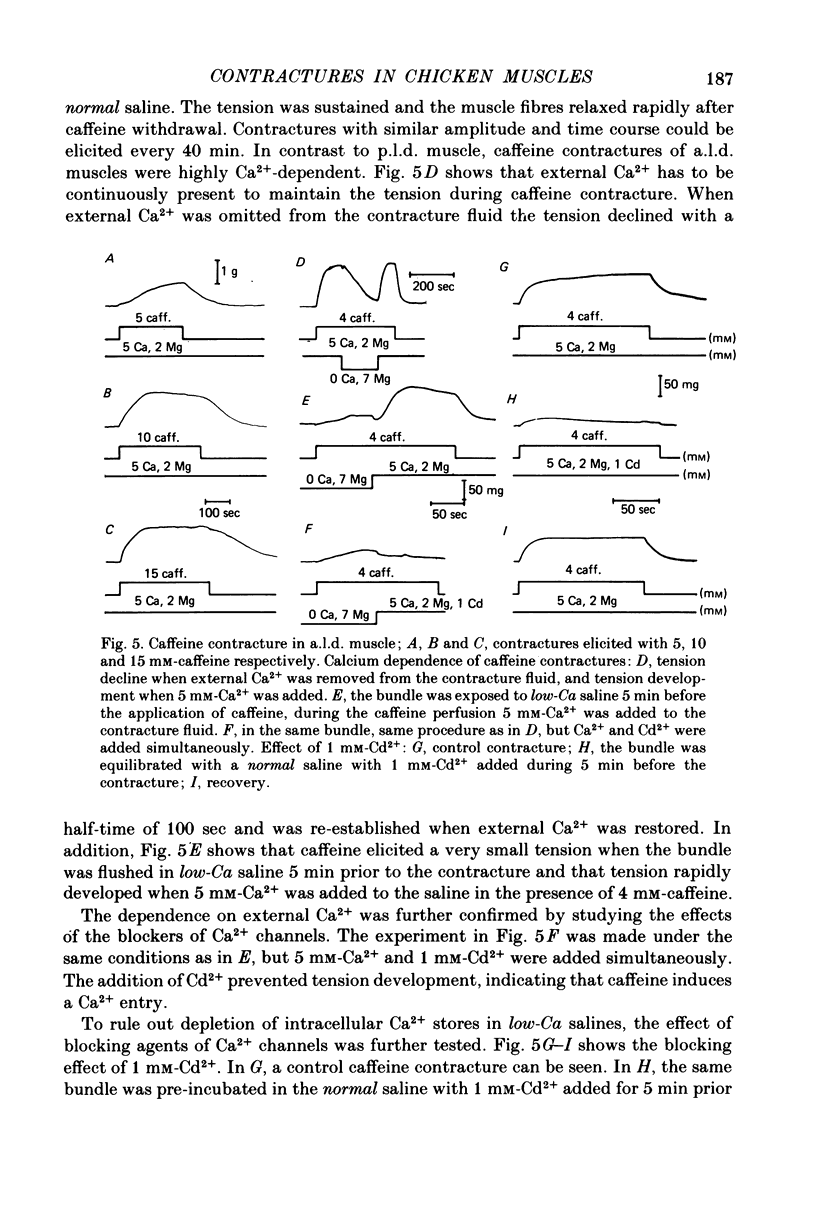
1 K+ contractures, caffeine contractures and electrical properties were studied in slow (posterior latissimus dorsi; p.l.d.) and fast (anterior latissimus dorsi; a.l.d.) chicken muscles. 2. P.l.d. K+ contractures show a transient increase of tension that relaxes spontaneously. Contractures in a.l.d. show an initial component followed by a maintained tension. 3. A.l.d. K+ contractures of similar amplitude and time course were reproduced at 4 min intervals. In p.l.d., the interval needed for full recovery is about 30 min. In Cl-free saline p.l.d. and a.l.d. K+ contractures can be reproduced at 4 min intervals. 4. The time course of repolarization after a short exposure to 160 mM-KCl was much slower in p.l.d. than in a.l.d. In Cl-free saline the time course of repolarization becomes faster in p.l.d. 5. The membrane resistance was not modified in a.l.d. and was increased in p.l.d. by Cl-free saline. The calculated Cl- conductance in p.l.d. was about 70% of the total membrane conductance. 6.In a.l.d., Mn2+, D600 and external Ca2+ reduction greatly diminishes the maintained phase of the K+ contracture leaving the initial phase almost unmodified. Under similar conditions p.l.d. K+ contractures were slightly reduced. 7. P.l.d. caffeine contractures (10-40 mM) were not maintained and they were not modified by Ca-free saline, Cd2+, Co2+, Mn2+ and D600. 8. A.l.d. caffeine contractures (2-15 mM) were maintained and were highly dependent on external Ca2+. In addition they were greatly reduced by Cd2+, Co2+, Mn2 and D600. 9. It is suggested that caffeine contractures of a.l.d. are elicited by a Ca2+ entry into the muscle from the external fluid.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELSSON J., THESLEFF S. Activation of the contractile mechanism in striated muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 28;44(1):55–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Effects of manganese and other agents on the calcium uptake that follows depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):511–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondi A. Y., Chiarandini D. J. Ionic basis for electrical properties of tonic fibres in rat extraocular muscles. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:273–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C. Caffeine- and potassium-induced contractures of frog striated muscle fibers in hypertonic solutions. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Sep;50(1):129–139. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Effect of calcium withdrawal on mechanical threshold in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:153–163. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Stefani E. Electrophysiological identification of two types of fibres in rat extraocular muscles. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):453–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cota G., Stefani E. Effects of external calcium reduction on the kinetics of potassium contractures in frog twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:303–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M. J., Harris J. B., Marshall M. W., Ward M. R. An electrophysiological and morphological study of normal and denervated chicken latissimus dorsi muscles. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):371–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S. Excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:293–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedde M. R. Electrical properties and acetylcholine sensitivity of singly and multiply innervated avian muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 May;53(5):624–637. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.5.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBORG B. L. Spontaneous activity in muscle fibres of the chick. J Physiol. 1960 Mar;150:707–717. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Eisenberg R. S. Capacitance of the surface and transverse tubular membrane of frog sartorius muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):265–278. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Hui C. S. Membrane electrical properties of frog slow muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:157–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Differences in Na and Ca spikes as examined by application of tetrodotoxin, procaine, and manganese ions. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):793–806. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree W., Hill A. V. The Specific Electrical Resistance of Frog's Muscle. Biochem J. 1921;15(3):379–382. doi: 10.1042/bj0150379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. Analysis of the membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):121–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlhardt M., Bauer B., Krause H., Fleckenstein A. New selective inhibitors of the transmembrane Ca conductivity in mammalian myocardial fibres. Studies with the voltage clamp technique. Experientia. 1972 Mar 15;28(3):288–289. doi: 10.1007/BF01928693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebeda F. J., Albuquerque E. X. Membrane cable properties of normal and dystrophic chicken muscle fibers. Exp Neurol. 1975 Jun;47(3):544–557. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Glitsch H. G. Membrane physiology of nerve and muscle fibres. Fortschr Zool. 1976;24(1):1–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Oetliker H. The action of caffeine on the activation of the contractile mechanism in straited muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Spiecker W. The effects of calcium deprivation upon mechanical and electrophysiological parameters in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:411–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page S. G. Structure and some contractile properties of fast and slow muscles of the chicken. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(1):131–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Chiarandini D. J. Skeletal muscle: dependence of potassium contractures on extracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Oct 17;343(2):143–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00585709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Steinbach A. B. Resting potential and electrical properties of frog slow muscle fibres. Effect of different external solutions. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):383–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



