Abstract
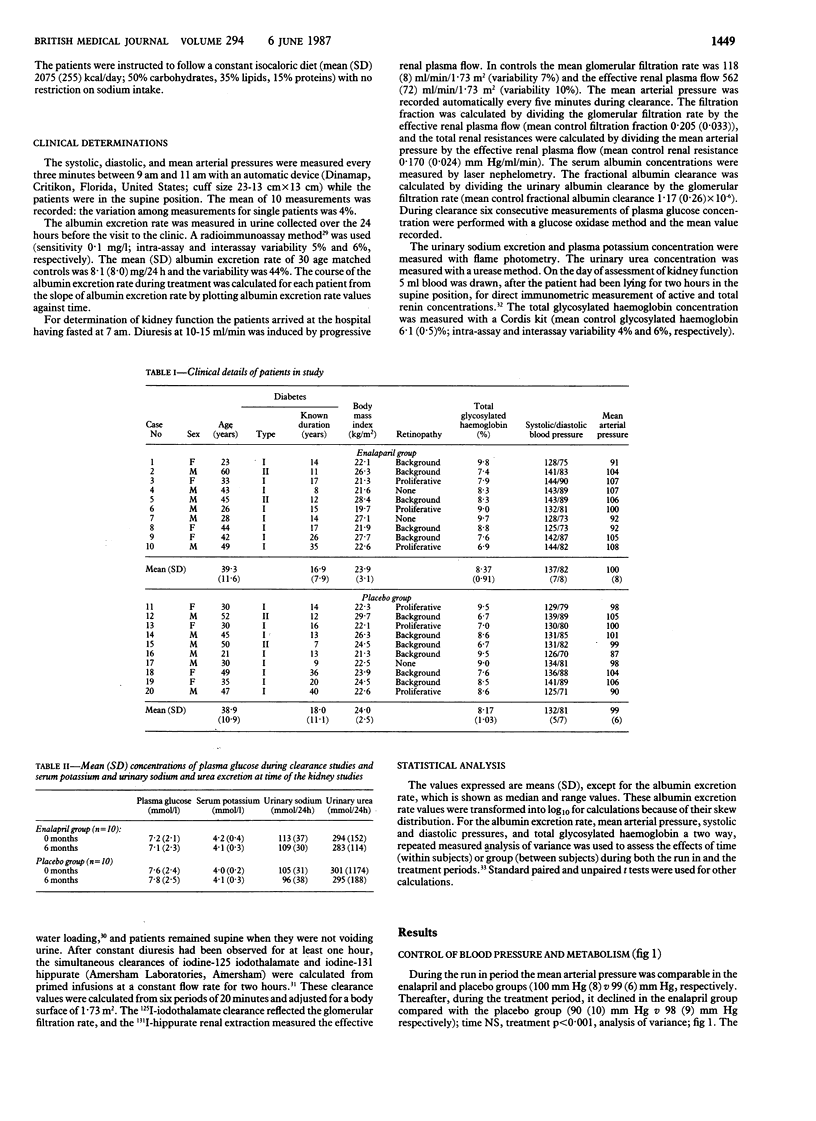
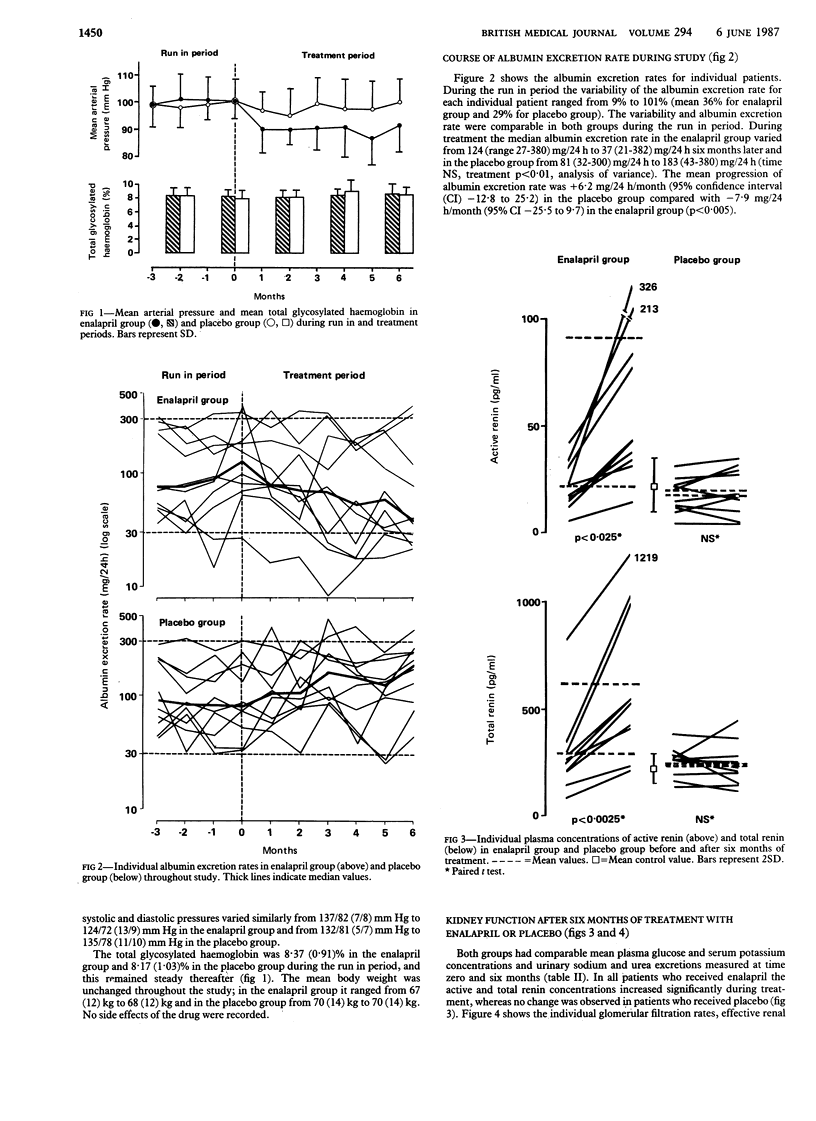
The effects of a long term reduction in blood pressure on the kidney function of normotensive diabetic patients who had persistent microalbuminuria (30-300 mg albumin/24 hours) were studied in two groups of 10 such patients before and during six months of treatment with either 20 mg enalapril or placebo daily. Treatments were assigned randomly in a double blind fashion. Before treatment both groups had similar clinical characteristics, weight, diet, total glycosylated haemoglobin, median albumin excretion rate (enalapril group 124 mg/24 h, placebo group 81 mg/24 h), and mean arterial pressure (enalapril group 100 (SD 8) mm Hg, placebo group 99 (6) mm Hg). During treatment weight, urinary urea excretion, and total glycosylated haemoglobin remained unchanged. The mean arterial pressure decreased in the enalapril group but not in the placebo group (enalapril group 90 (10) mm Hg, placebo group 98 (8) mm Hg). The median albumin excretion rate also fell in the enalapril group but not in the placebo group (enalapril group 37 mg/24 h, placebo group 183 mg/24 h.) The glomerular filtration rate rose in the enalapril group from 130 (23) ml/min/1.73 m2 to 141 (24) ml/min/1.73 m2, and total renal resistances and fractional albumin clearance decreased while fractional albumin clearance increased in the placebo group. These results show that in patients who have diabetes but not hypertension a reduction in blood pressure by inhibition of converting enzyme for six months can reduce persistent microalbuminuria, perhaps by decreasing the intraglomerular pressure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abouna G. M., Al-Adnani M. S., Kremer G. D., Kumar S. A., Daddah S. K., Kusma G. Reversal of diabetic nephropathy in human cadaveric kidneys after transplantation into non-diabetic recipients. Lancet. 1983 Dec 3;2(8362):1274–1276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen A. R., Christiansen J. S., Andersen J. K., Kreiner S., Deckert T. Diabetic nephropathy in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: an epidemiological study. Diabetologia. 1983 Dec;25(6):496–501. doi: 10.1007/BF00284458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck S., Nyberg G., Mulec H., Granerus G., Herlitz H., Aurell M. Beneficial effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition on renal function in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 23;293(6545):471–474. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6545.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blood pressure and salt supplies in West Africa. Lancet. 1986 Jul 5;2(8497):43–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Meyer T. W., Hostetter T. H. Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 9;307(11):652–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209093071104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Cole E., Hanna A. K. Diabetic nephropathy and proliferative retinopathy with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care. 1985 Jul-Aug;8(4):385–390. doi: 10.2337/diacare.8.4.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen C. K. Abnormal albuminuria and blood pressure rise in incipient diabetic nephropathy induced by exercise. Kidney Int. 1984 May;25(5):819–823. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldt-Rasmussen B., Mathiesen E. R., Deckert T. Effect of two years of strict metabolic control on progression of incipient nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1986 Dec 6;2(8519):1300–1304. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldt-Rasmussen B., Mathiesen E. R., Hegedüs L., Deckert T. Kidney function during 12 months of strict metabolic control in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with incipient nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 13;314(11):665–670. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603133141101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Guyton A. C., Jackson T. E., Coleman T. G., Lohmeier T. E., Trippodo N. C. Control of glomerular filtration rate by renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol. 1977 Nov;233(5):F366–F372. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.5.F366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg N. K., Swartz S. L., Passan D. R., Williams G. H. Increased glomerular filtration rate after converting-enzyme inhibition in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):9–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel E., Mathiesen E., Edsberg B., Bahnsen M., Parving H. H. Acute reduction of arterial blood pressure reduces urinary albumin excretion in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with incipient nephropathy. Diabetologia. 1986 Apr;29(4):211–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00454877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel E., Parving H. H., Mathiesen E., Edsberg B., Damkjaer Nielsen M., Giese J. Effect of captopril on kidney function in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 23;293(6545):467–470. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6545.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. The case for intrarenal hypertension in the initiation and progression of diabetic and other glomerulopathies. Am J Med. 1982 Mar;72(3):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90490-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., McGee D. L. Diabetes and glucose tolerance as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: the Framingham study. Diabetes Care. 1979 Mar-Apr;2(2):120–126. doi: 10.2337/diacare.2.2.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen E. R., Oxenbøll B., Johansen K., Svendsen P. A., Deckert T. Incipient nephropathy in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia. 1984 Jun;26(6):406–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00262210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Sutherland D. E., Najarian-S, Michael A. F., Brown D. M. Studies of the rate of regression of the glomerular lesions in diabetic rats treated with pancreatic islet transplantation. Diabetes. 1975 Mar;24(3):280–285. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.3.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Christensen C. K. Predicting diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent patients. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 12;311(2):89–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407123110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Christensen C. K., Vittinghus E. The stages in diabetic renal disease. With emphasis on the stage of incipient diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 1983 May;32 (Suppl 2):64–78. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.s64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Glomerular filtration rate and renal plasma flow in short-term and long-term juvenile diabetes mellitus. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Sep;28(1):91–100. doi: 10.3109/00365517109090667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Long-term antihypertensive treatment inhibiting progression of diabetic nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Sep 11;285(6343):685–688. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6343.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 9;310(6):356–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402093100605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navar L. G., Rosivall L. Contribution of the renin-angiotensin system to the control of intrarenal hemodynamics. Kidney Int. 1984 Jun;25(6):857–868. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Kastrup H., Smidt U. M., Andersen A. R., Feldt-Rasmussen B., Christiansen J. S. Impaired autoregulation of glomerular filtration rate in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with nephropathy. Diabetologia. 1984 Dec;27(6):547–552. doi: 10.1007/BF00276965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Oxenbøll B., Svendsen P. A., Christiansen J. S., Andersen A. R. Early detection of patients at risk of developing diabetic nephropathy. A longitudinal study of urinary albumin excretion. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1982 Aug;100(4):550–555. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1000550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passa P., LeBlanc H., Marre M. Effects of enalapril in insulin-dependent diabetic subjects with mild to moderate uncomplicated hypertension. Diabetes Care. 1987 Mar-Apr;10(2):200–204. doi: 10.2337/diacare.10.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirart J. Diabète et complications dégénératives présentation d'une étude prospective portant sur 4400 cas observés entre 1947 et 1973 (deuxième partie). Diabete Metab. 1977 Sep;3(3):173–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirart J. Diabète et complications dégénératives présentation d'une étude prospective portant sur 4400 cas observés entre 1947 et 1973. (Première partie). Diabete Metab. 1977 Jun;3(2):97–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirart J. Diabète et complications dégénératives. Présentation d'une étude prospective portant sur 4400 cas observés entre 1947 et 1973 (troisième et dernière partie). Diabete Metab. 1977 Dec;3(4):245–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguma Y., Kitamoto Y., Futaki G., Ueda H., Monma H., Ishizaki M., Takahashi H., Sekino H., Sasaki Y. Effect of captopril on heavy proteinuria in azotemic diabetics. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 26;313(26):1617–1620. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512263132601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez B., Flock E. V., Savage P. J., Nagulesparan M., Bennion L. J., Baird H. R., Bennett P. H. Sustained reduction of proteinuria in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes following diet-induced reduction of hyperglycaemia. Diabetologia. 1984 Feb;26(2):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00281119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Bilous R. W., Mackintosh D., Bending J. J., Keen H. Long term correction of hyperglycaemia and progression of renal failure in insulin dependent diabetes. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Feb 19;286(6365):598–602. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6365.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Hill R. D., Jarrett R. J., Argyropoulos A., Mahmud U., Keen H. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1982 Jun 26;1(8287):1430–1432. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92450-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Mogensen C. E., Keen H., Jacobsen F. K., Jarrett R. J., Christensen C. K. Urinary excretion of albumin in normal man: the effect of water loading. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;42(2):147–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Pickup J. C., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Effect of control of blood glucose on urinary excretion of albumin and beta2 microglobulin in insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 22;300(12):638–641. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903223001202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz R., Dunn B. R., Meyer T. W., Anderson S., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Prevention of diabetic glomerulopathy by pharmacological amelioration of glomerular capillary hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1925–1930. doi: 10.1172/JCI112521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


