Abstract
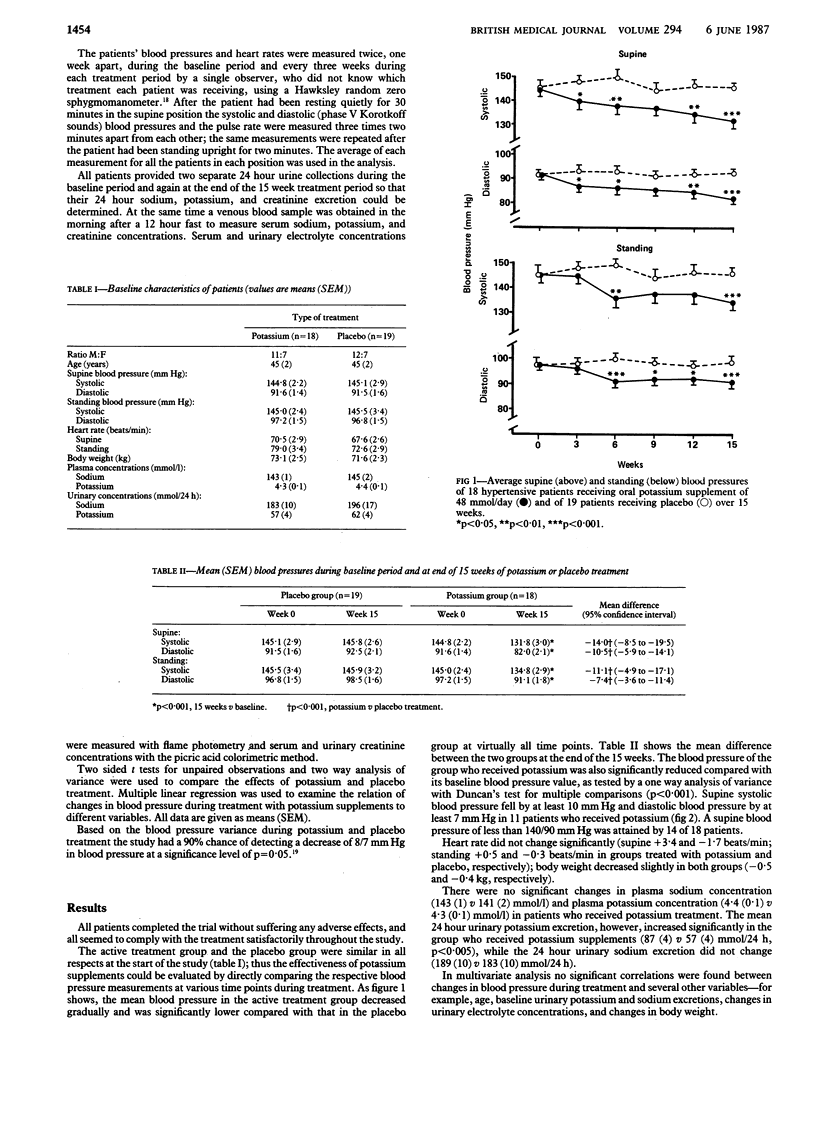
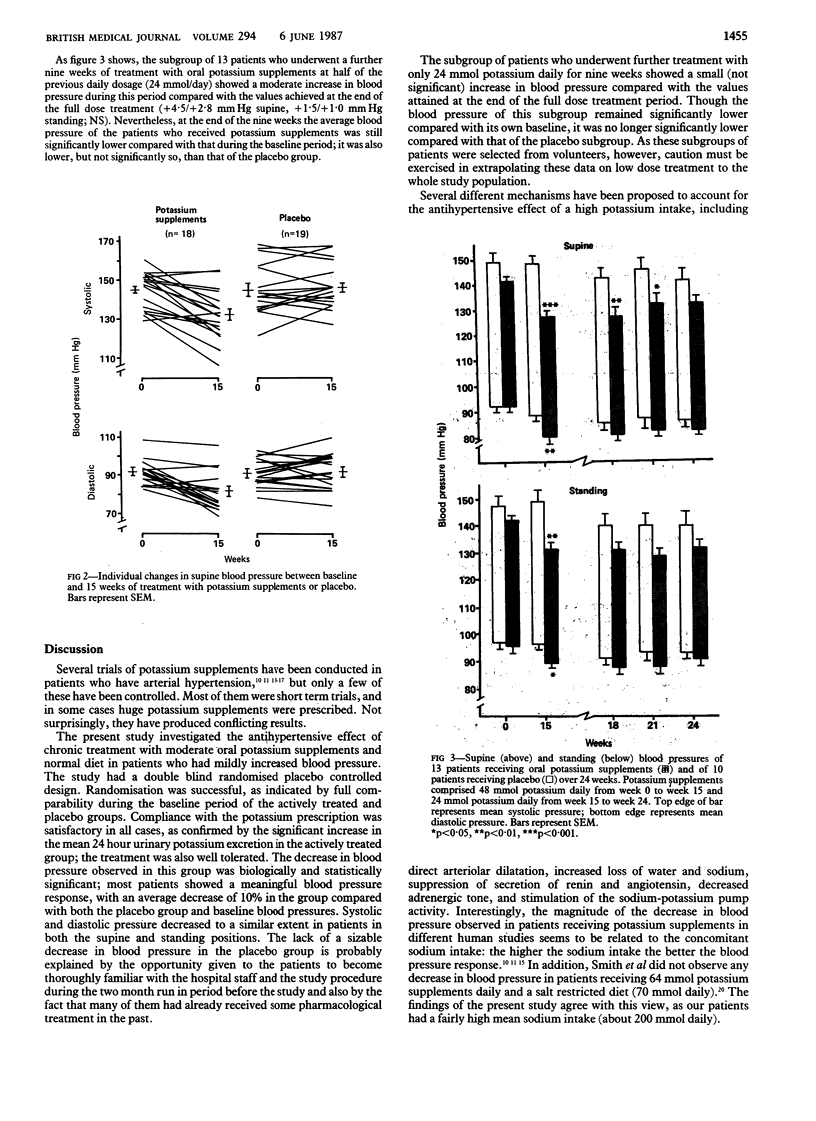
A 15 week randomised double blind placebo controlled trial of oral potassium supplements (48 mmol daily) was conducted in 37 patients who had mildly increased blood pressure and a normal dietary intake of sodium. After a two month run in and a one week baseline period the patients were randomly assigned to receive either potassium supplements (n = 18) or placebo (n = 19). By the third week of treatment blood pressure in the actively treated group had decreased significantly compared with that in the placebo group, though the decrease reached its maximum after 15 weeks. Urinary potassium excretion increased significantly in the group who received potassium supplements, but no significant changes were found in plasma sodium and potassium concentrations or in urinary sodium excretion. In a subgroup of 13 patients who underwent a further nine weeks of treatment with oral potassium supplements at half of the previous dose (24 mmol daily) their blood pressure, at the end of this second study period, was still significantly lower compared with their baseline value but not with that of the placebo group. These results show that moderate oral potassium supplements are associated with a long term reduction in blood pressure in patients who have mild hypertension.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahl L. K., Leitl G., Heine M. Influence of dietary potassium and sodium/potassium molar ratios on the development of salt hypertension. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):318–330. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Ando K. Hemodynamic and endocrine changes associated with potassium supplementation in sodium-loaded hypertensives. Hypertension. 1984 Mar-Apr;6(2 Pt 1):184–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Sato Y. Natriuretic and antihypertensive effects of potassium in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Kidney Int. 1983 Dec;24(6):731–739. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford H. G. Dietary potassium and hypertension: epidemiologic data. Ann Intern Med. 1983 May;98(5 Pt 2):770–772. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-5-770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis W. J., Tabei R., Spector S. Effects of sodium intake on inherited hypertension in the rat. Lancet. 1971 Dec 11;2(7737):1283–1286. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90603-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. A., Smith S. J., Markandu N. D., Banks R. A., Sagnella G. A. Moderate potassium supplementation in essential hypertension. Lancet. 1982 Sep 11;2(8298):567–570. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90657-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlou S. M., Isles C. G., Higgs A., Milne F. J., Murray G. D., Schultz E., Starke I. F. Potassium supplementation in blacks with mild to moderate essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1986 Feb;4(1):61–64. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198602000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. M., Nicholls M. G., Espiner E. A., Ikram H., Maslowski A. H., Hamilton E. J., Wells J. E. Blood-pressure response to moderate sodium restriction and to potassium supplementation in mild essential hypertension. Lancet. 1984 Apr 7;1(8380):757–761. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASAKI N. High blood pressure and the salt intake of the Japanese. Jpn Heart J. 1962 Jul;3:313–324. doi: 10.1536/ihj.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Markandu N. D., Sagnella G. A., MacGregor G. A. Moderate potassium chloride supplementation in essential hypertension: is it additive to moderate sodium restriction? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jan 12;290(6462):110–113. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6462.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kondo K., Saruta T. Effect of potassium chloride on the blood pressure in two-kidney, one clip Goldblatt hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):566–573. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.5.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kondo K., Saruta T. Inhibitory effect of potassium on blood pressure in DOCA salt hypertension in rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Aug;97(4):525–532. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0970525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. M., Dore C. F. A random-zero sphygmomanometer. Lancet. 1970 Feb 14;1(7642):337–338. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90709-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoccali C., Cumming A. M., Hutcheson M. J., Barnett P., Semple P. F. Effects of potassium on sodium balance, renin, noradrenaline and arterial pressure. J Hypertens. 1985 Feb;3(1):67–72. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198502000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


