Abstract
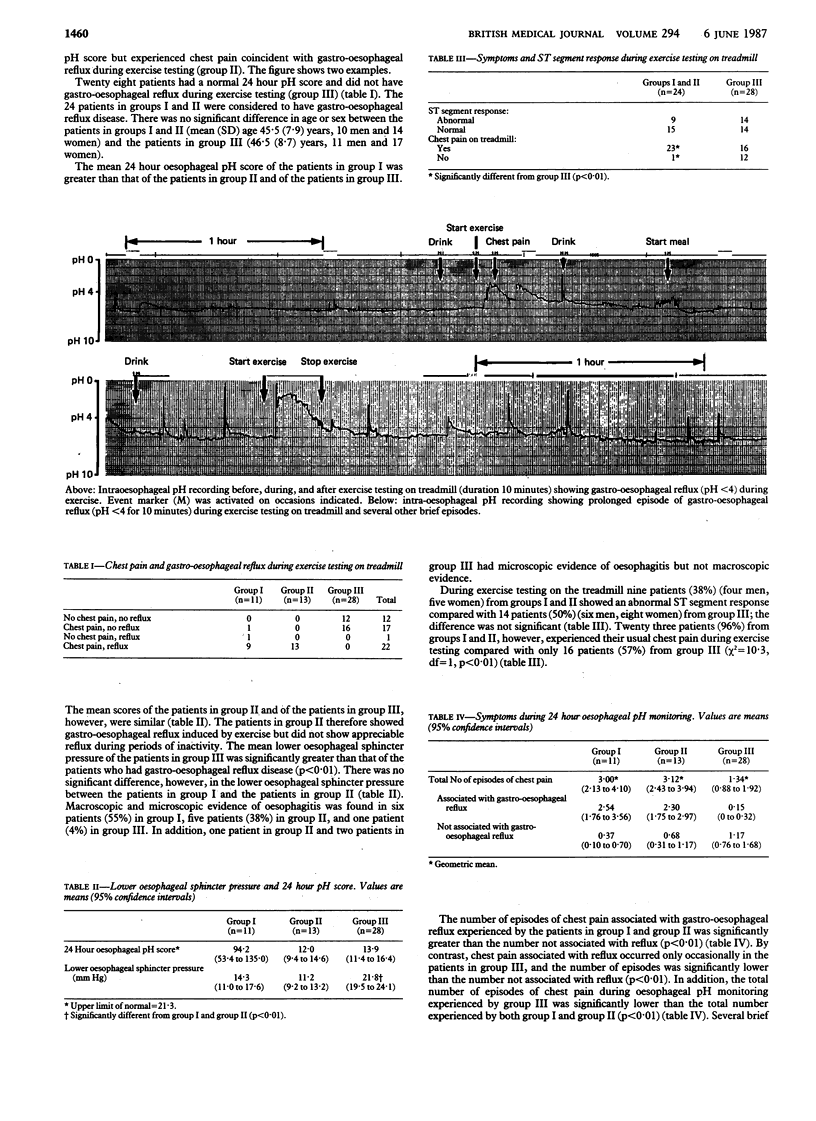
During 24 hour oesophageal pH monitoring 52 patients who had angina pectoris and normal coronary angiograms underwent exercise testing, as far as their symptoms allowed, on a treadmill to determine whether gastro-oesophageal reflux occurred during exertion. In 11 patients the 24 hour oesophageal pH score was abnormally high; 10 of these showed exertional gastro-oesophageal reflux, and in nine this was associated with their usual chest pain. A further 13 patients had a normal 24 hour pH score but had exertional reflux coincident with chest pain during exercise testing. The mean lower oesophageal sphincter pressure in both of these groups of patients was appreciably lower than that in 28 patients who had a normal 24 hour pH score and no exertional reflux. These findings suggest that exertional gastro-oesophageal reflux accounts for the symptoms of a large proportion of patients who have angina pectoris and normal coronary angiograms and that oesophageal pH monitoring during exercise testing on a treadmill enables this group of patients to be identified.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin S. B., Richter J. E., Cordova C. M., Knuff T. E., Castell D. O. Prospective manometric evaluation with pharmacologic provocation of patients with suspected esophageal motility dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 1983 May;84(5 Pt 1):893–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. N., Castell D. O. Oesophageal chest pain: a point of view. Gut. 1984 Jan;25(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand D. L., Martin D., Pope C. E., 2nd Esophageal manometrics in patients with angina-like chest pain. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Apr;22(4):300–304. doi: 10.1007/BF01072186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M., Mannucci P. M., Carnelli V., Savidge G. F., Gazengel C., Schimpf K. Transmission of non-A, non-B hepatitis by heat-treated factor VIII concentrate. Lancet. 1985 Jul 6;2(8445):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dart A. M., Davies H. A., Dalal J., Ruttley M., Henderson A. H. 'Angina' and normal coronary arteriograms: a follow-up study. Eur Heart J. 1980 Apr;1(2):97–100. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a061112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., O'Sullivan G. C., Bermudez G., Midell A. I., Cimochowski G. E., O'Drobinak J. Esophageal function in patients with angina-type chest pain and normal coronary angiograms. Ann Surg. 1982 Oct;196(4):488–498. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198210000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson S. C., Hodges K., Hersh T., Jinich H. Esophageal Manometry in Patients with Chest Pain and Normal Coronary Arteriogram. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981 Feb;75(2):124–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Demeester T. R. Twenty-four-hour pH monitoring of the distal esophagus. A quantitative measure of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 1974 Oct;62(4):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp H. G., Jr, Vokonas P. S., Cohn P. F., Gorlin R. The anginal syndrome associated with normal coronary arteriograms. Report of a six year experience. Am J Med. 1973 Jun;54(6):735–742. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline M., Chesne R., Sturdevant R. A., McCallum R. W. Esophageal disease in patients with angina-like chest pain. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981 Feb;75(2):116–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER A. M. THE SPECTRUM OF ANGINAL AND NONCARDIAC CHEST PAIN. JAMA. 1964 Mar 21;187:894–899. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060250012002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchandise B., Bourassa M. G., Chaitman B. R., Lesperance J. Angiographic evaluation of the natural history of normal coronary arteries and mild coronary atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Feb;41(2):216–220. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meller J., Goldsmith S. J., Rudin A., Pichard A. D., Gorlin R., Teichholz L. E., Herman M. V. Spectrum of exercise thallium-201 myocardial perfusion imaging in patients with chest pain and normal coronary angiograms. Am J Cardiol. 1979 Apr;43(4):717–723. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(79)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellow M. H., Simpson A. G., Watt L., Schoolmeester L., Haye O. L. Esophageal acid perfusion in coronary artery disease. Induction of myocardial ischemia. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):306–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak R. C., Thibault G. E., Savoia M., DeSanctis R. W., Hutter A. M., Jr Chest pain with angiographically insignificant coronary arterial obstruction. Clinical presentation and long-term follow-up. Am J Med. 1980 Jun;68(6):813–817. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90199-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D. R. Diffuse esophageal spasm in patients with undiagnosed chest pain. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1982 Oct;4(5):415–417. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198210000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfit W. L., Shirey E. K., Sones F. M., Jr Selective cine coronary arteriography. Correlation with clinical findings in 1,000 patients. Circulation. 1966 Jun;33(6):901–910. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.33.6.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. M., Brooks N. H., Bennett D. H. Left ventricular dysfunction in patients with angina pectoris and normal coronary angiograms. Br Heart J. 1986 Oct;56(4):327–333. doi: 10.1136/hrt.56.4.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serebro H. A. The prognostic significance of the viscerocardiac reflex phenomenon. S Afr Med J. 1976 May 8;50(20):769–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson O., Stenport G., Tibbling L., Wranne B. Oesophageal function and coronary angiogram in patients with disabling chest pain. Acta Med Scand. 1978;204(3):173–178. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1978.tb08420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



