Abstract
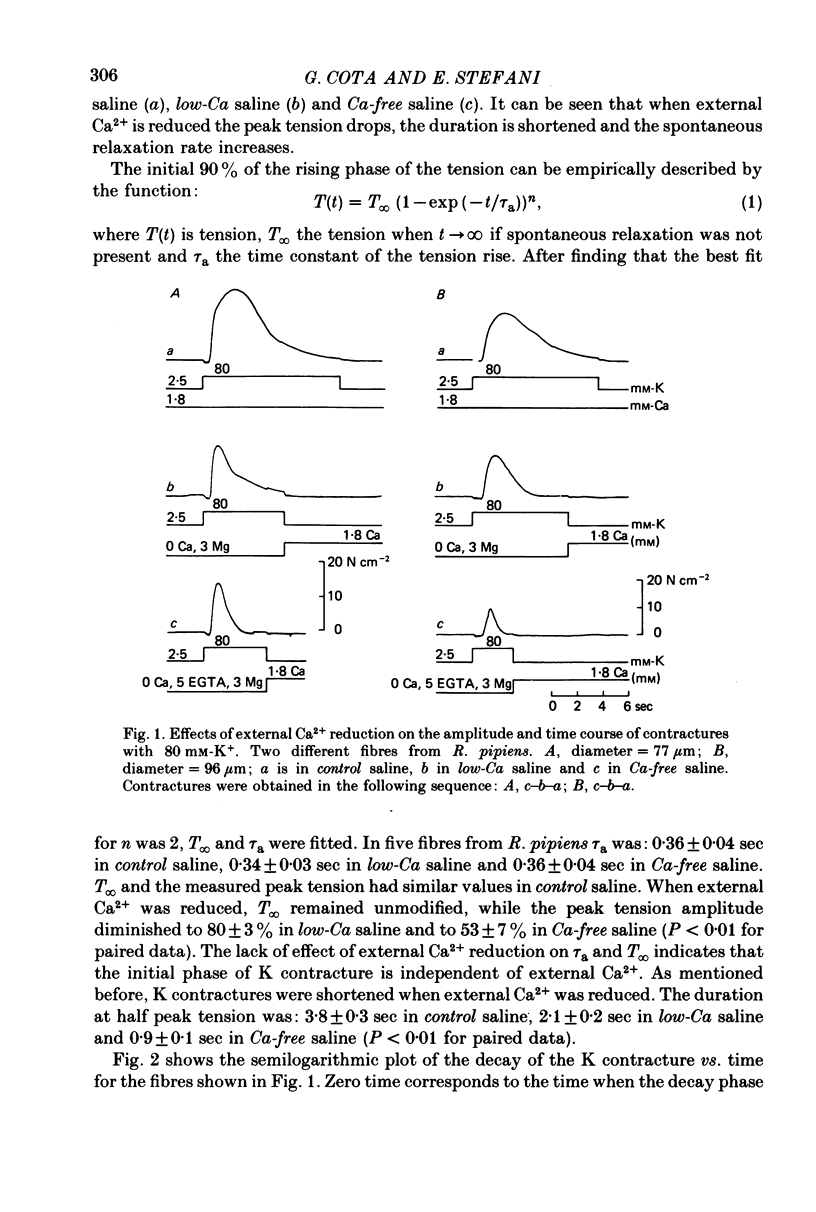
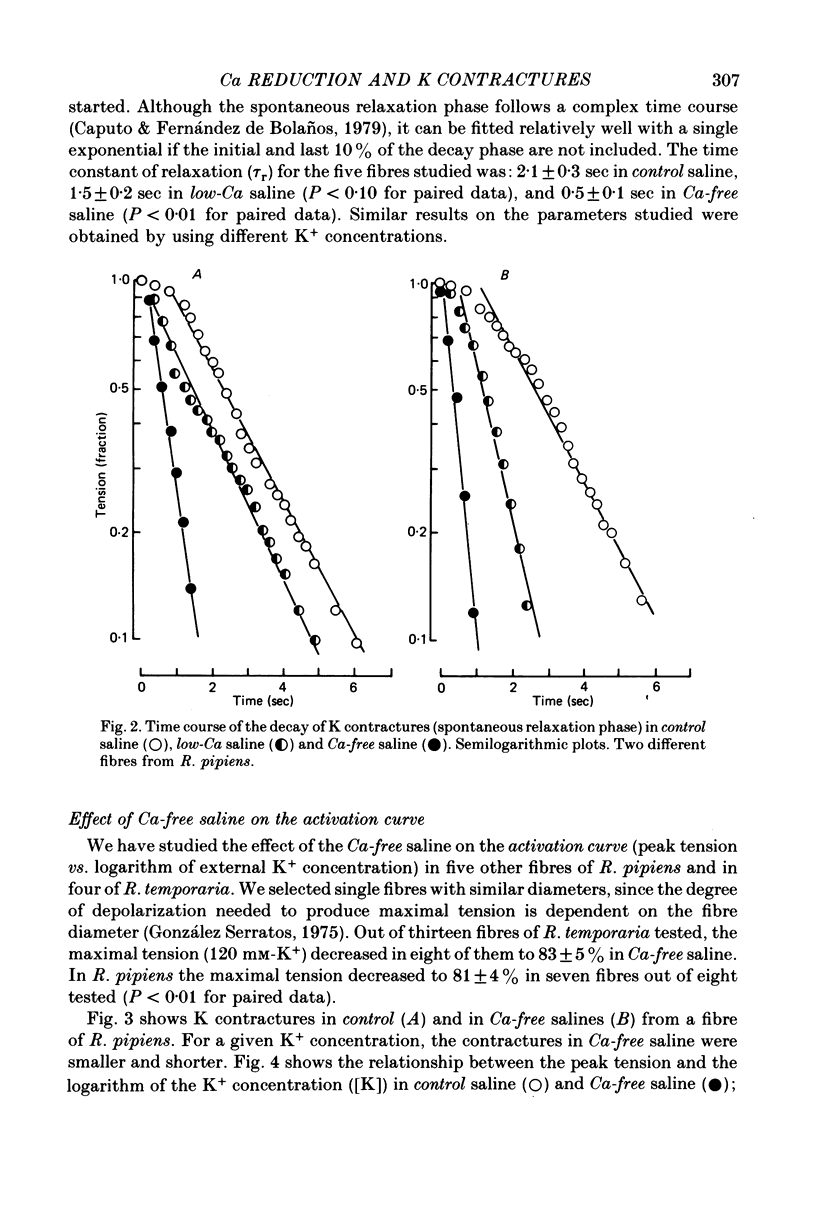
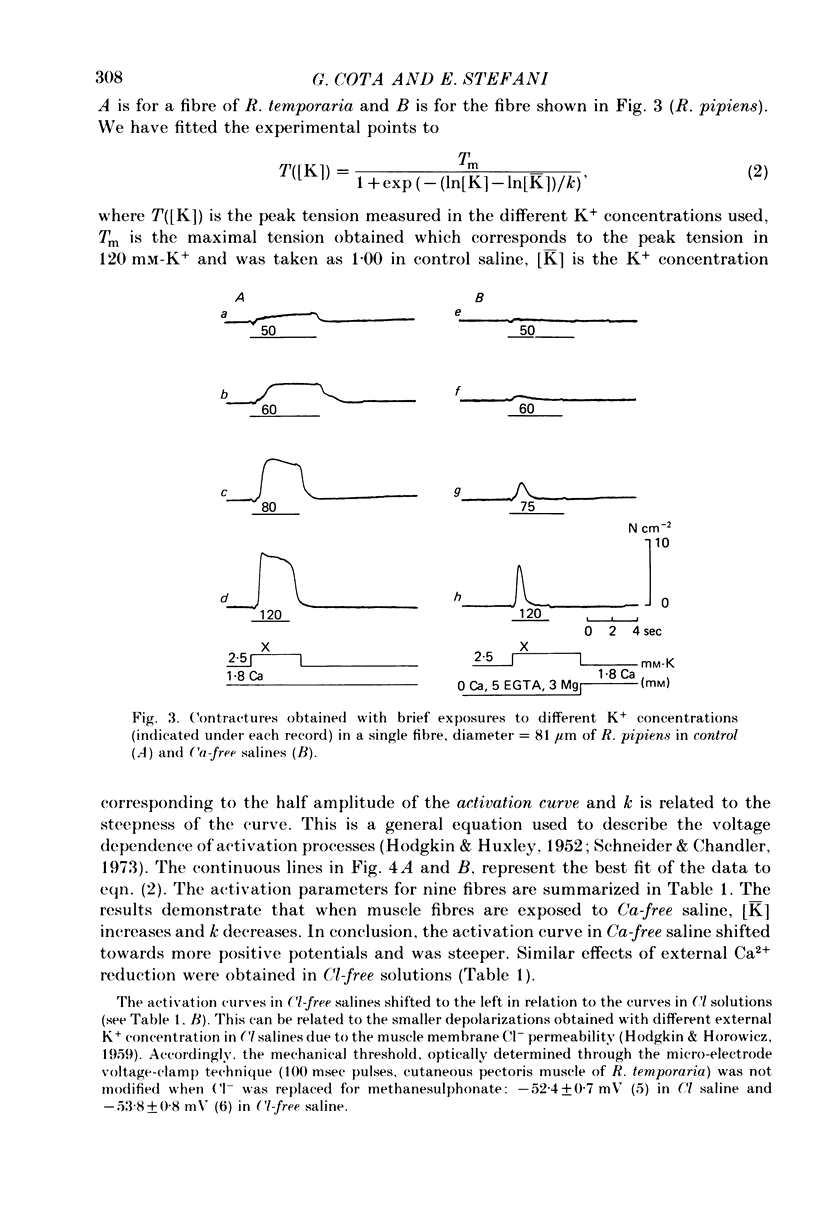
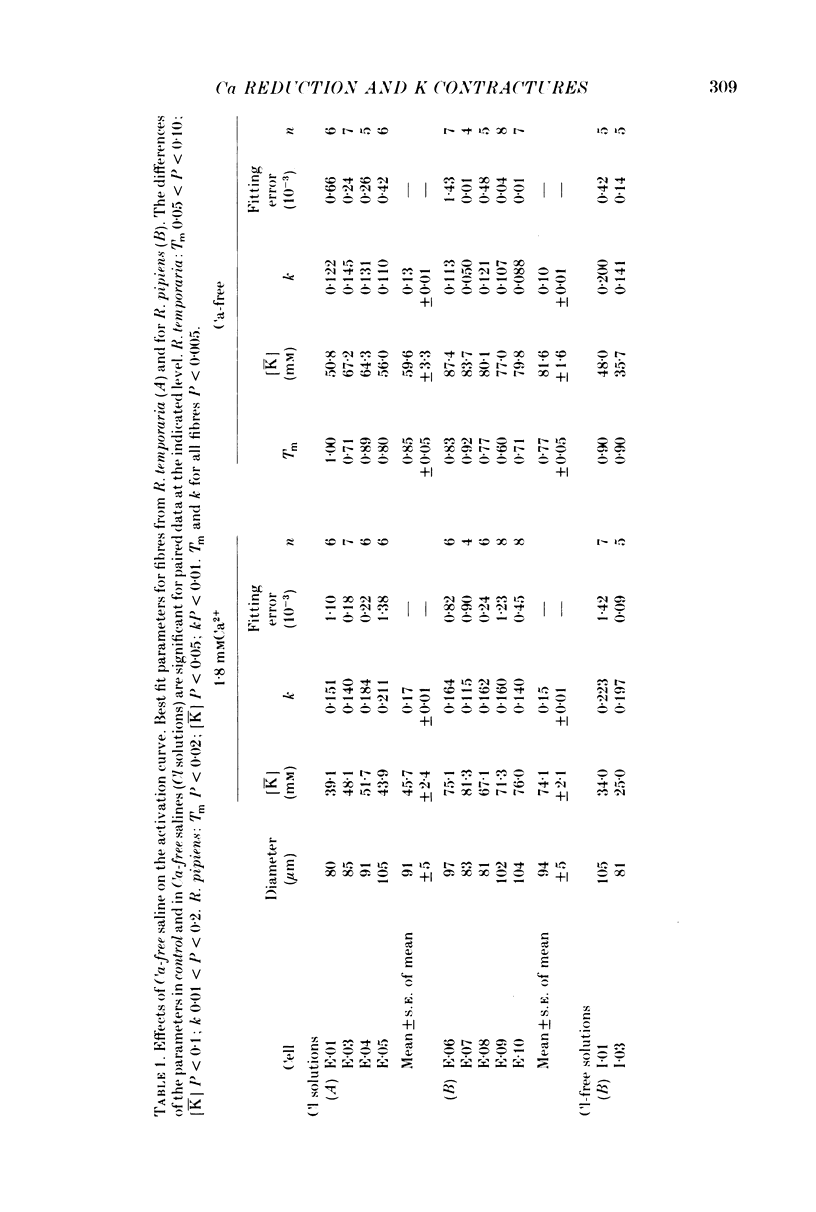
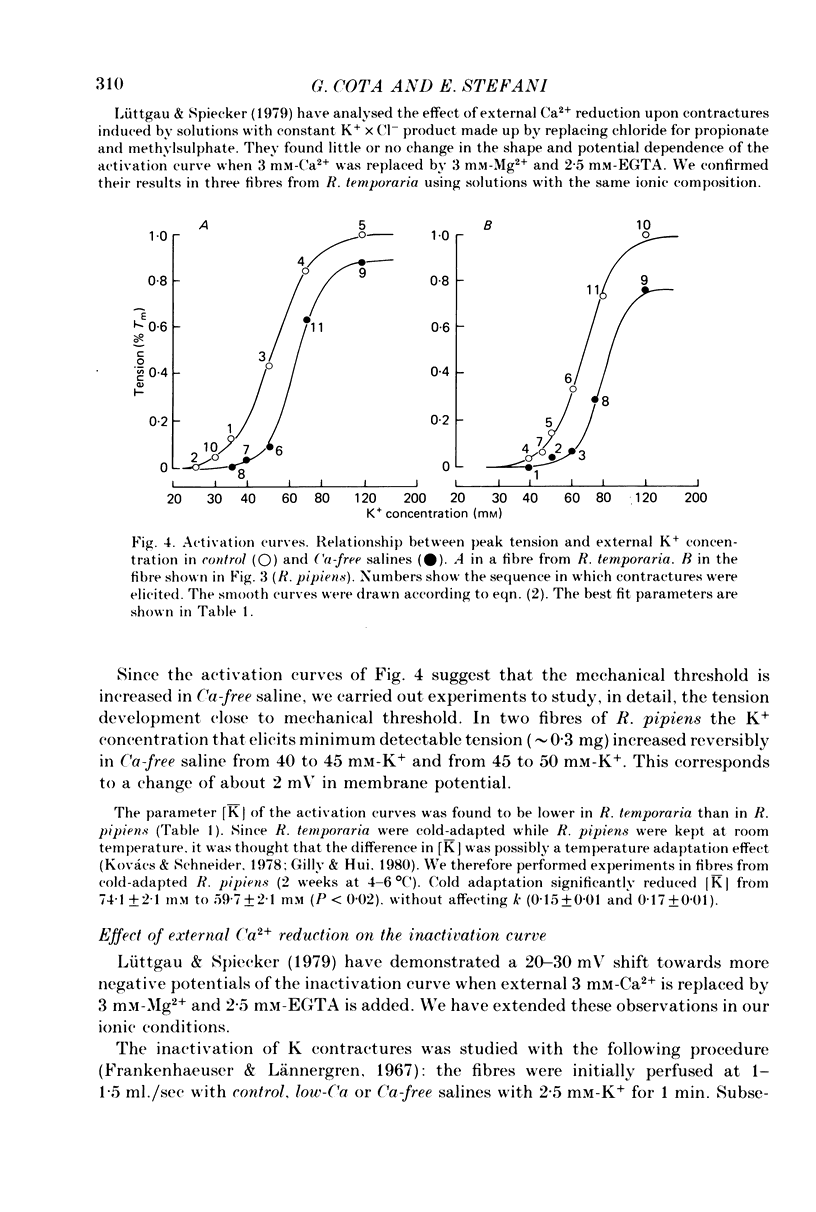
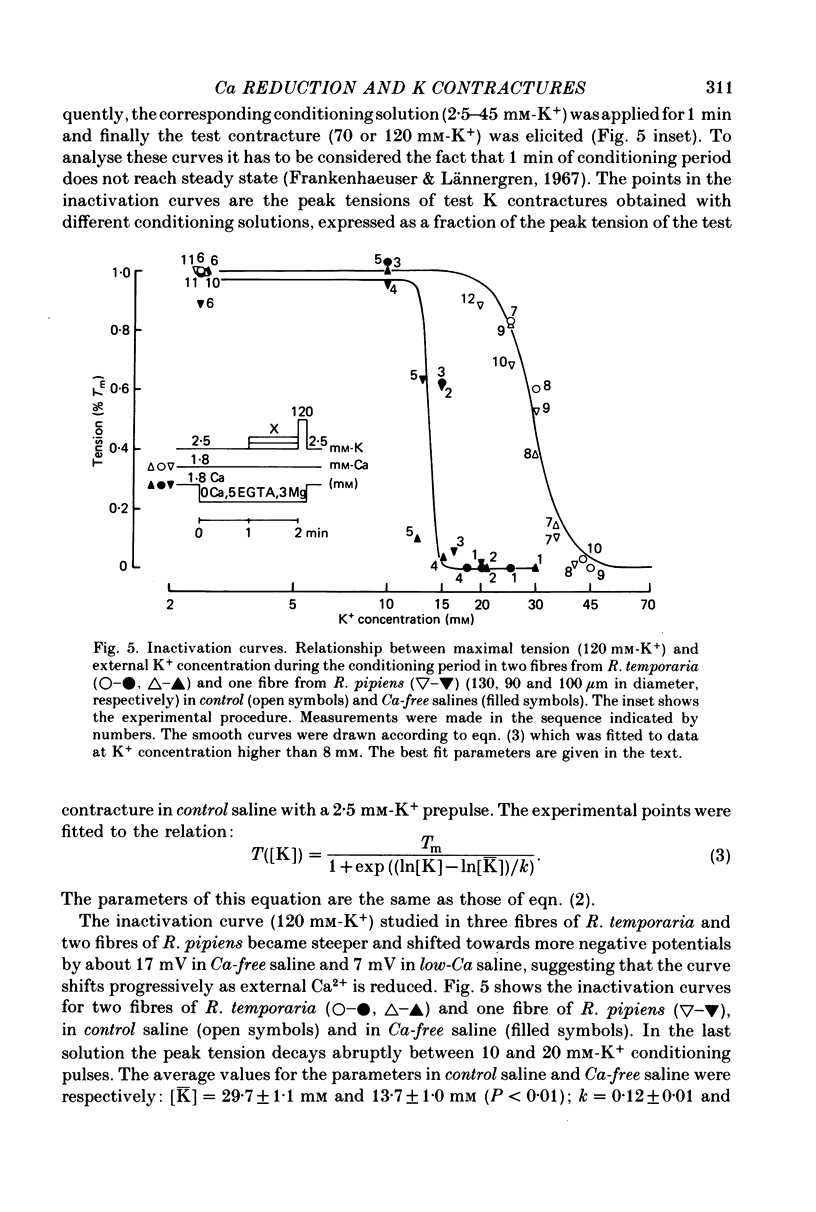
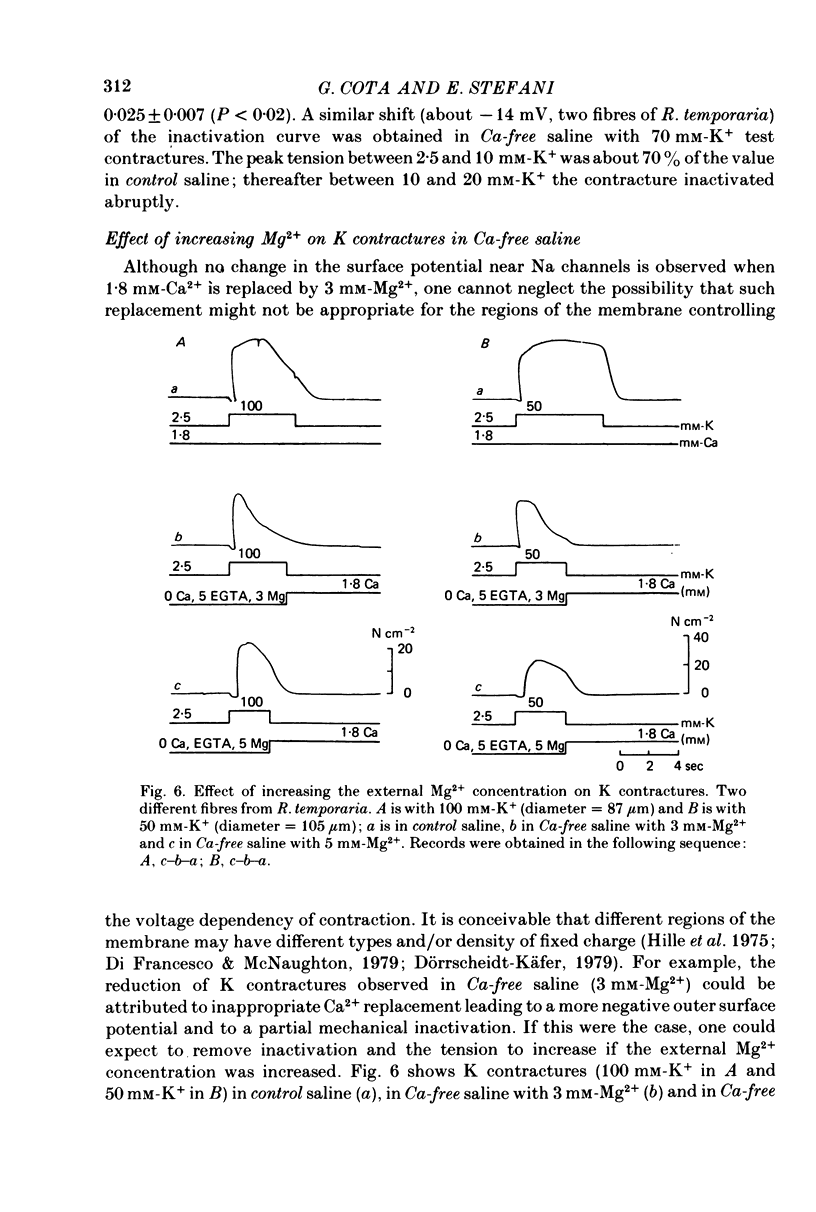
1. The amplitude and time course of K contractures (Cl- constant) of single twitch muscle fibres of the frog have been analysed in three external Ca2+ concentrations. 2. The resting potential, effective resistance, threshold for the Na current and K-induced depolarizations were not modified by replacing 1.8 mM-Ca2+ by 3 mM-Mg2+ in absence (low-Ca saline: 3-6 micro M-Ca2+) or in the presence of 5 mM-EGTA (Ca-free saline: less than or equal to 10(-9) M-Ca2+). 3. The tension development during the initial phase of K contractures was independent of external Ca2+ while the amplitude, the duration and the time constant of spontaneous relaxation decreased progressively as Ca2+ concentration was diminished. 4. When the concentration of Mg2+ was increased to 5 mM in Ca-free saline K contractures were slower and smaller than those in 3 mM-Mg2+. 5. In Ca-free saline the activation curve (peak tension vs. logarithm of external K+ concentration) shifted by 3-5 mV towards more positive potentials while the inactivation curve (peak tension of the test contracture vs. logarithm of external K+ concentration during the conditioning period) shifted by 16-18 mV towards more negative potentials. Both curves became steeper in Ca-free saline. 6. The effects of external Ca2+ reduction were not modified by replacing all chloride for methanesulphonate. 7. Direct effects of external Ca2+ on excitation-contraction coupling during K contractures could involve the inward Ca current and/or specific interactions between external Ca2+ ions and the coupling mechanism.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W. Gating currents and charge movements in excitable membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;82:96–190. doi: 10.1007/BFb0030498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. M., Horowicz P. Twitches in the presence of ethylene glycol bis( -aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetracetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty G. N., Stefani E. Calcium dependent electrical activity in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Aug 27;194(1114):141–150. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaty G. N., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):27P–27P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Calcium transients in isolated amphibian skeletal muscle fibres: detection with aequorin. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:291–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. T., Hille B. Kinetic and pharmacological properties of the sodium channel of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):309–323. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C., Fernandez de Bolaños P. Membrane potential, contractile activation and relaxation rates in voltage clamped short muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:175–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C., Gimenez M. Effects of external calcium deprivation on single muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Oct;50(9):2177–2195. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.9.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C. The time course of potassium contractures of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):483–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. Effects of glycerol treatment and maintained depolarization on charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):285–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Effect of calcium withdrawal on mechanical threshold in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:153–163. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Stefani E. Effects of manganese on the electrical and mechanical properties of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):129–147. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., McNaughton P. A. The effects of calcium on outward membrane currents in the cardiac Purkinje fibre. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:347–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S. Excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:293–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenhaeuser B., Lännergren J. The effect of calcium on the mechanical response of single twitch muscle fibres of Xenopus laevis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Mar;69(3):242–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Hui C. S. Mechanical activation in slow and twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:137–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-serratos H. Graded activation of myofibrils and the effect of diameter on tension development during contractures in isolated skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(2):321–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon J. L., Gibbons W. R. Effects of low-chloride solutions on action potentials of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):635–660. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Schneider M. F. Contractile activation by voltage clamp depolarization of cut skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:483–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUETTGAU H. C. THE ACTION OF CALCIUM IONS ON POTASSIUM CONTRACTURES OF SINGLE MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:679–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Spiecker W. The effects of calcium deprivation upon mechanical and electrophysiological parameters in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:411–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Levis R. A., Eisenberg R. S. Electrical models of excitation-contraction coupling and charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jul;76(1):1–31. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Measurement of calcium transients in frog muscle by the use of arsenazo III. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Aug 22;198(1131):201–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potreau D., Raymond G. Calcium-dependent electrical activity and contraction of voltage-clamped frog single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:9–22. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:197–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A., Krishna M., Pagala D., Sphicas E. C. Excitation-contraction coupling: effects of "zero"-Ca2+ medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 8;404(1):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlevin H. H. Effects of external calcium concentration and pH on charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:129–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siri L. N., Sánchez J. A., Stefani E. Effect of glycerol treatment on the calcium current of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:87–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. A calcium dependent inward current in frog skeletal muscle fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Apr 25;368(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00585206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Chiarandini D. J. Skeletal muscle: dependence of potassium contractures on extracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Oct 17;343(2):143–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00585709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss G. B., Bianchi C. P. The effect of potassium concentration on Ca45 uptake in frog sartorius muscle. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Jun;65(3):385–392. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030650312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



