Abstract
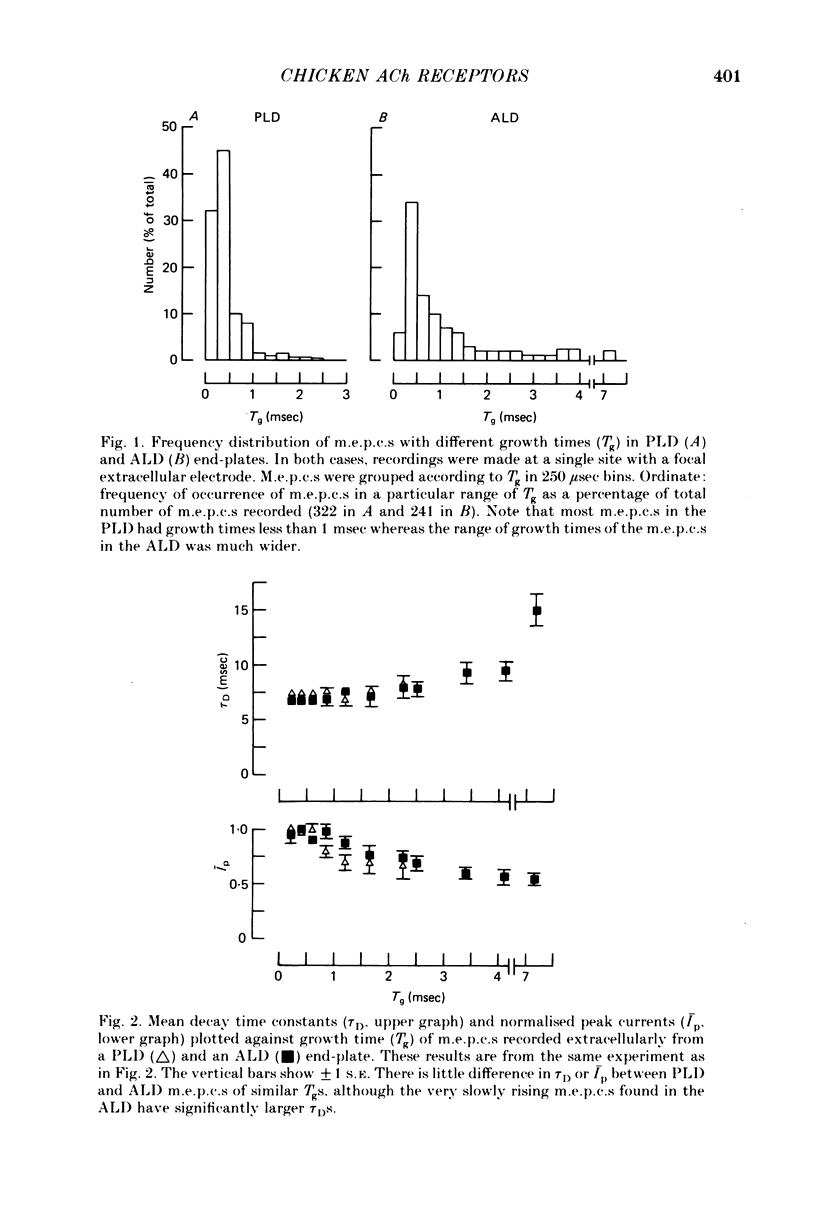
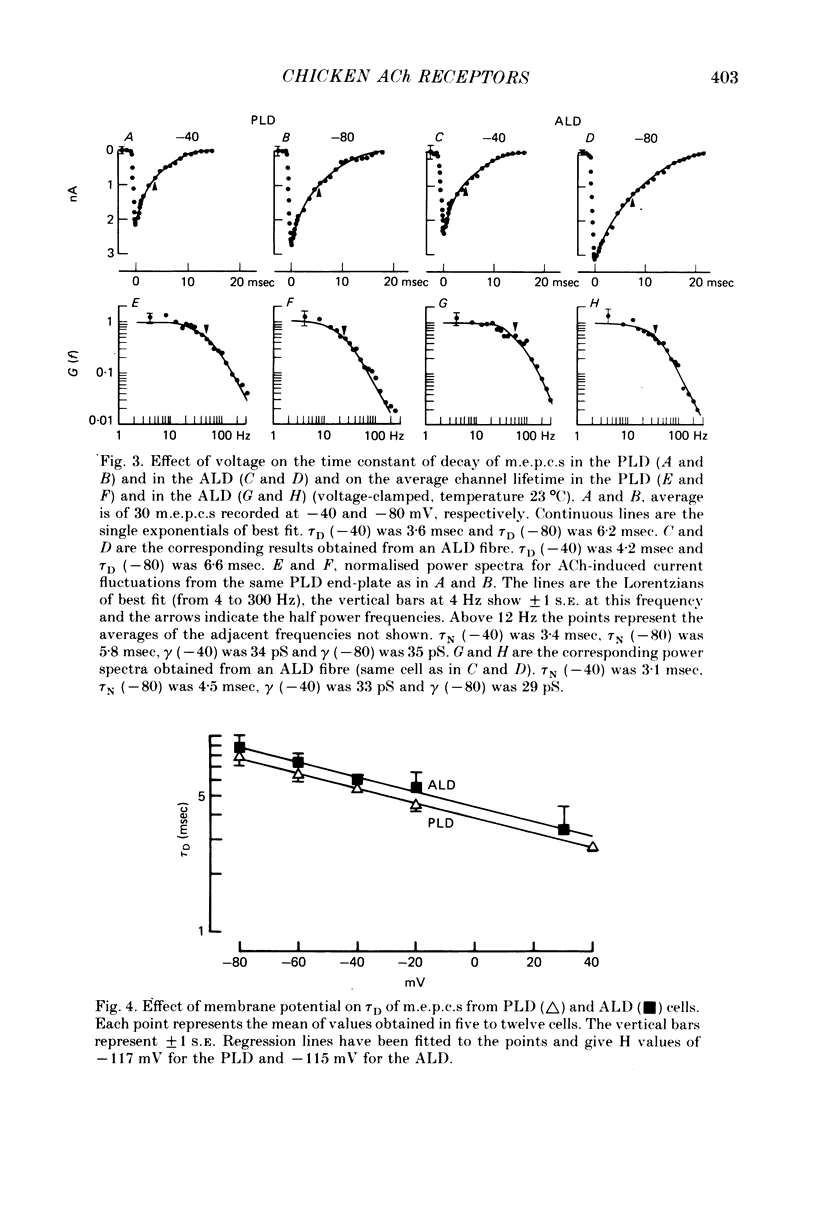
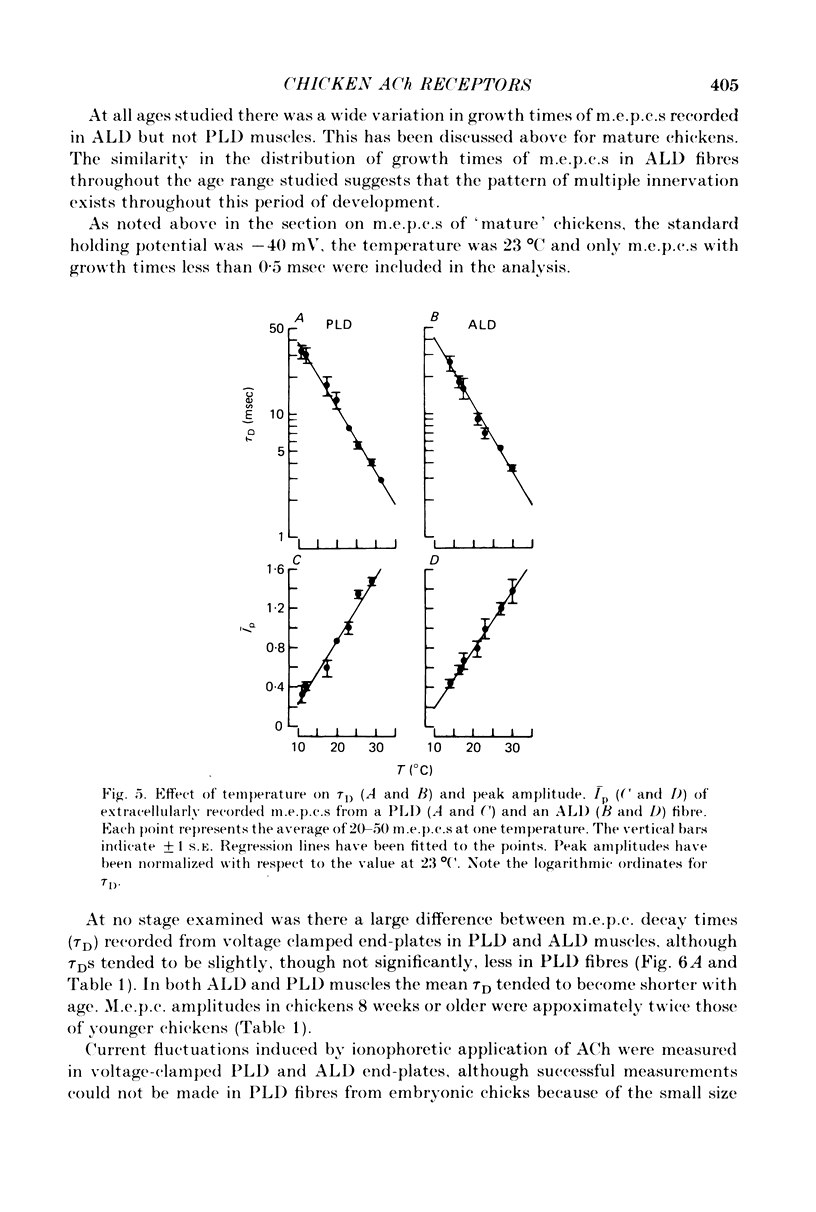
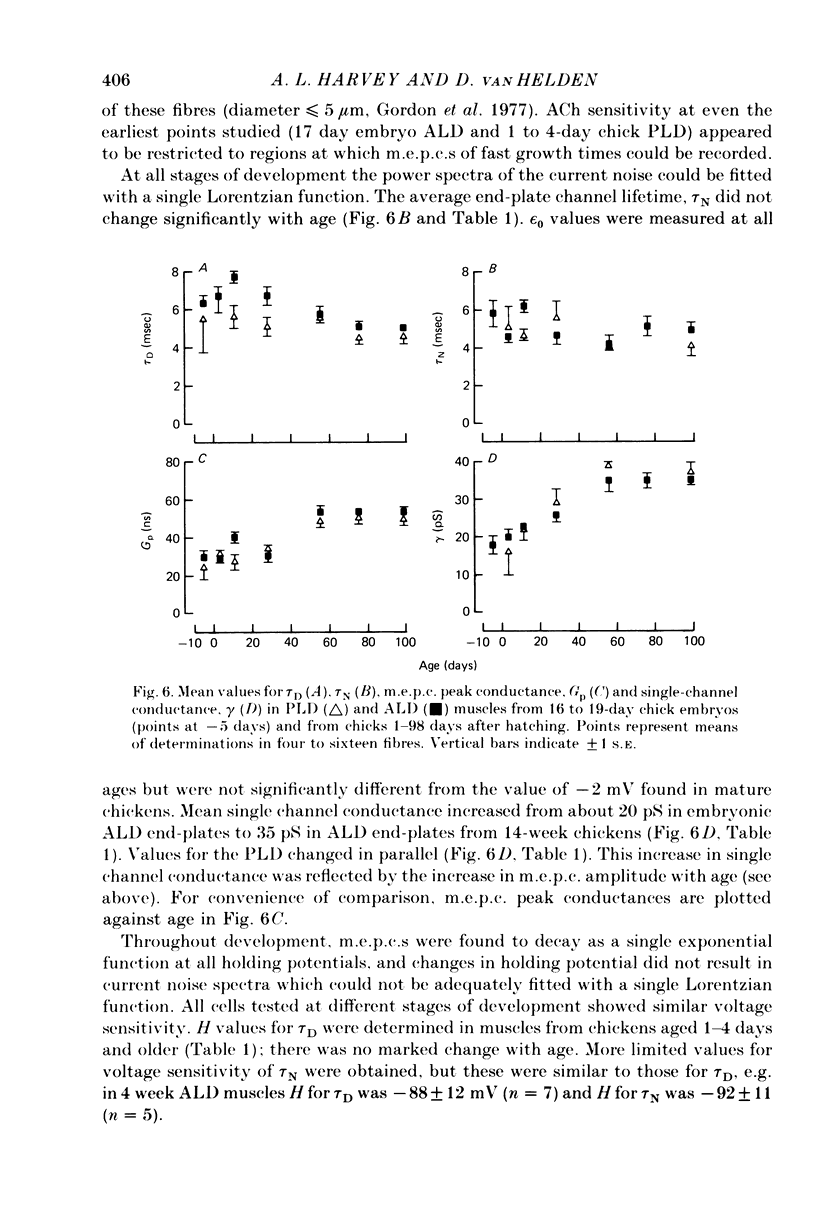
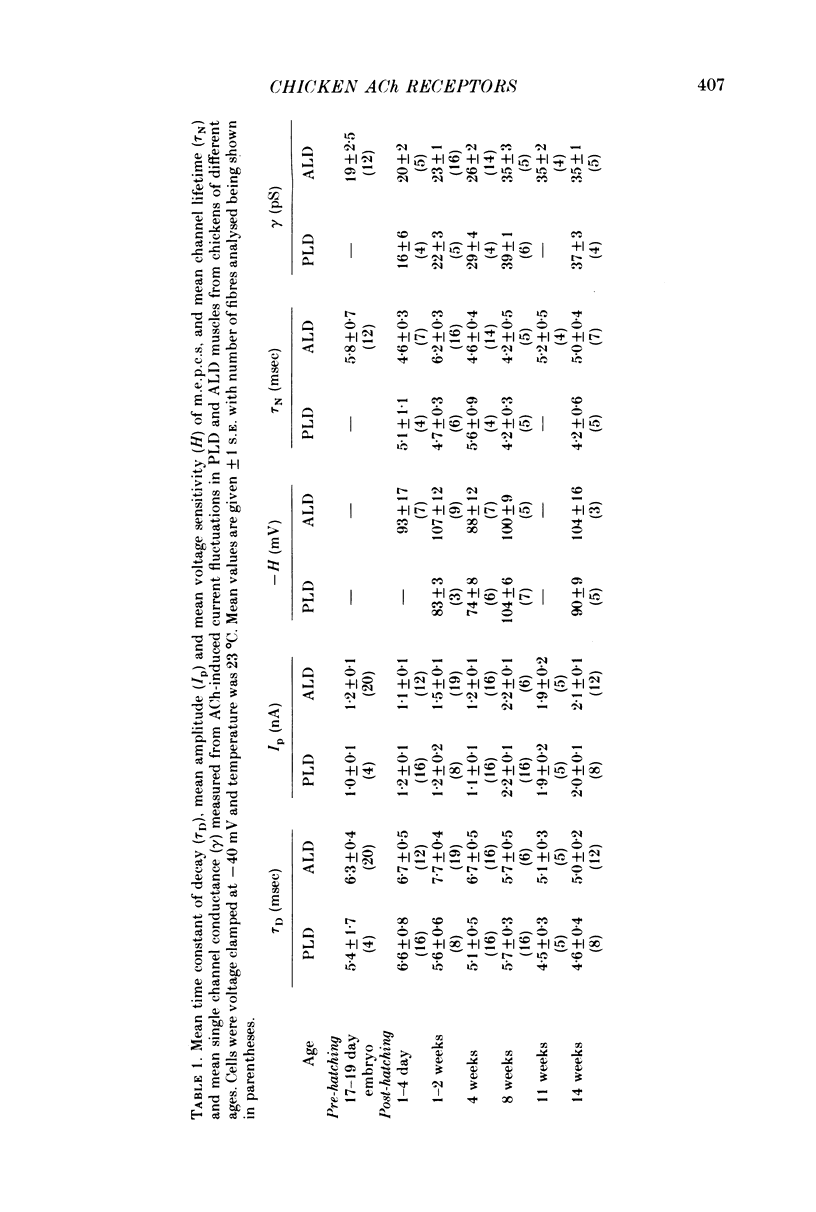
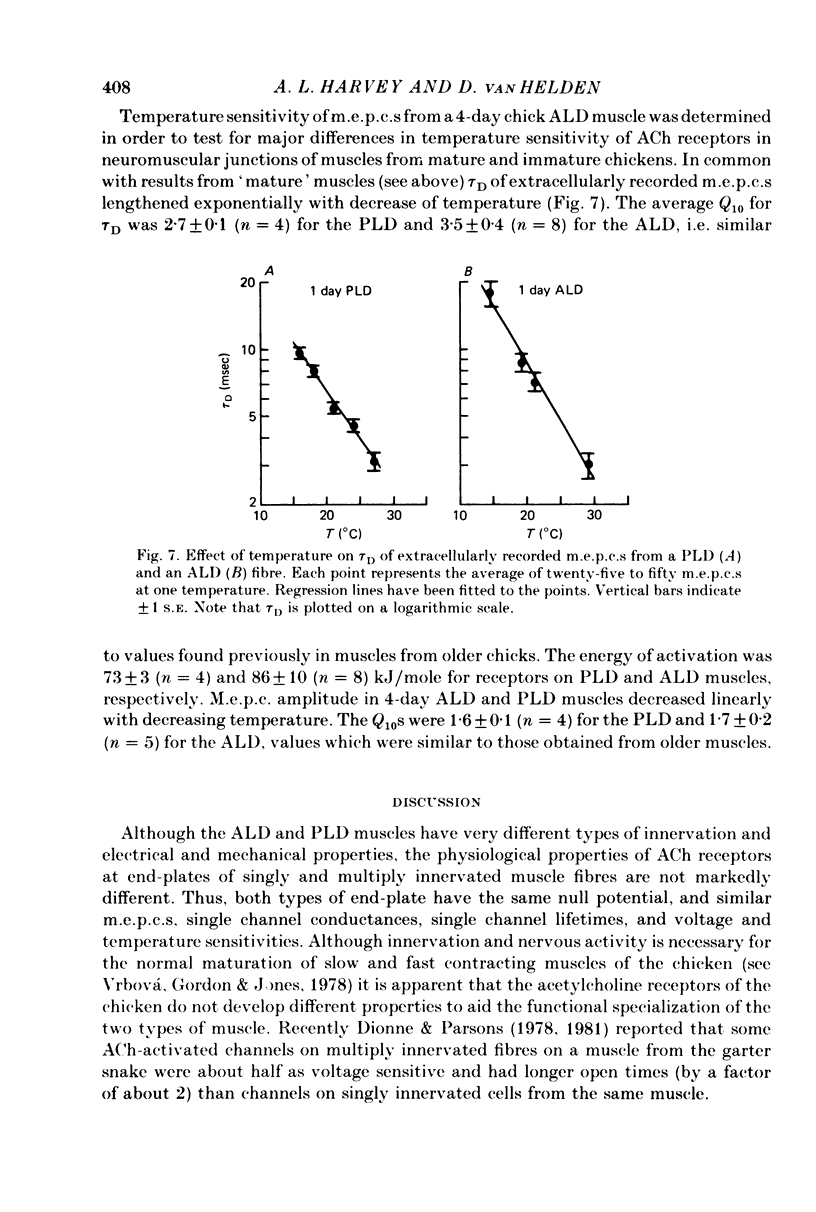
1. The properties of acetylcholine (ACh) receptors of the singly innervated posterior latissimus dorsi (PLD) and the multiply innervated anterior latissimus dorsi (ALD) muscles of the chicken were investigated. Studies were made on chicks from 17 days in ovo to 14 weeks after hatching. Focal extracellular recordings and intracellular recordings in voltage clamped fibres were made. 2. Peak amplitudes of miniature end-plate currents (m.e.p.c.s) of the two muscles were not significantly different. The time constants of decay (tau D) were similar in both muscles, although tau D in the PLD was generally smaller than in the ALD (usually by less than 25%). M.e.p.c. decays in both muscles were well described by a single exponential. 3. The conductance (gamma) and average lifetime (tau N) of end-plate channels activated by ionophoretically applied ACh were calculated from records of current fluctuations. Noise spectra were well fitted by a single Lorentzian function. Values obtained in PLD did not differ significantly from those obtained in the ALD. There was not difference in the ACh null potential. 4. The voltage and temperature sensitivities of the ACh-activated channels in both muscle types were very similar. 5. With age there was a slight decrease in tau D: from about 6 to 5 msec in the PLD and from about 7 to 5 msec in the ALD (at -40 mV). The change in tau N with age was even less marked. However, during development, gamma almost doubled in both muscles, increasing from about 20 to 35 pS. 6. The results provide no evidence for the hypothesis that the different pattern of innervation causes marked differences in the ACh-activated channels of singly and multiply innervated muscles.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz H., Bourgeois J. P., Changeux J. P. Evolution of cholinergic proteins in developing slow and fast skeletal muscles in chick embryo. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:197–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan S., Steinbach J. H. The distribution of alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites of mammalian skeletal muscle developing in vivo. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(1):195–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burden S. Acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction: developmental change in receptor turnover. Dev Biol. 1977 Nov;61(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burden S. Development of the neuromuscular junction in the chick embryo: the number, distribution, and stability of acetylcholine receptors. Dev Biol. 1977 Jun;57(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Large W. A., Rang H. P. An analysis of the action of a false transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(2):361–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Parsons R. L. Characteristics of the acetylcholine-operated channel at twitch and slow fibre neuromuscular junctions of the garter snake. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:145–158. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Parsons R. L. Synaptic channel gating differences at snake twitch and slow neuromuscular junctions. Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):902–904. doi: 10.1038/274902a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Gage P. W. Electrical properties of toad sartorius muscle fibres in summer and winter. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):619–641. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Schuetze S. M. A post-natal decrease in acetylcholine channel open time at rat end-plates. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:125–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N., Van Helden D. Octanol reduces end-plate channel lifetime. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:279–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Van Helden D. Effects of permeant monovalent cations on end-plate channels. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:509–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T., Purves R. D., Vrbová G. Differentiation of electrical and contractile properties of slow and fast muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;269(3):535–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A. Structural differences of fast and slow extrafusal muscle fibres and their nerve endings in chickens. J Physiol. 1961 Jul;157:221–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey A. L. Actions of drugs on developing skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(1):1–41. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. A. Ion-concentration dependence of the reversal potential and the single channel conductance of ion channels at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:417–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVER A. A HISTOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATION OF CHOLINESTERASES AT NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTIONS IN MAMMALIAN AND AVIAN MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:386–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Brenner H. R. Change in synaptic channel gating during neuromuscular development. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):401–402. doi: 10.1038/276401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach J. H., Merlie J., Heinemann S., Bloch R. Degradation of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by developing rat skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3547–3551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



