Abstract
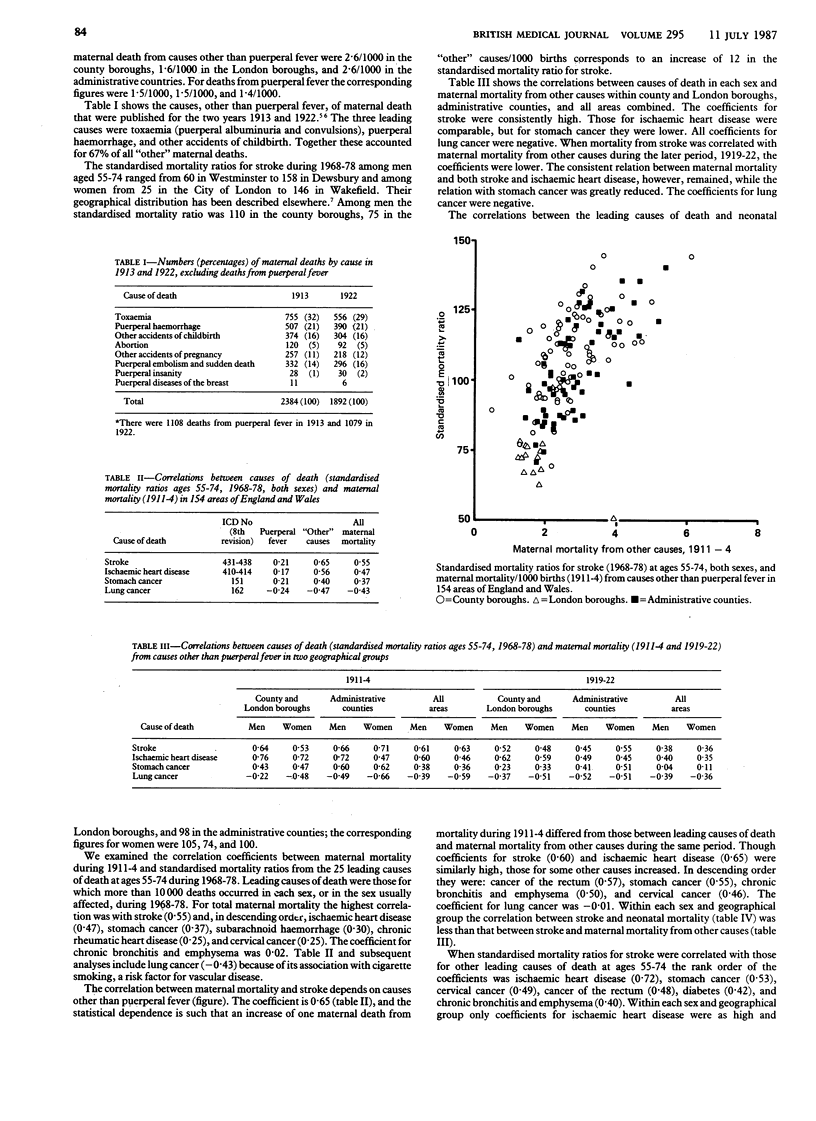
Geographical differences in maternal mortality in England and Wales during 1911-4 correlate closely with death rates from stroke in the generation born around that time. The geographical distribution of stroke is more closely related to past maternal mortality than to any leading cause of death, past or present, except ischaemic heart disease, for which correlation coefficients with stroke are similar. This relation is new evidence that poor health and physique of mothers are important determinants of the risk of stroke among their offspring.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird D. Environment and reproduction. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1980 Dec;87(12):1057–1067. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1980.tb04474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. J., Osmond C. Infant mortality, childhood nutrition, and ischaemic heart disease in England and Wales. Lancet. 1986 May 10;1(8489):1077–1081. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaglehole R., Salmond C. E., Eyles E. F. A longitudianl study of blood pressure in Polynesian children. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Jan;105(1):87–89. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke W. R., Schrott H. G., Leaverton P. E., Connor W. E., Lauer R. M. Tracking of blood lipids and blood pressures in school age children: the Muscatine study. Circulation. 1978 Oct;58(4):626–634. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.58.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. G. The epidemiology of stroke. Age Ageing. 1979;Suppl:50–56. doi: 10.1093/ageing/8.suppl.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON M., PICKERING G. W., ROBERTS J. A. F., SOWRY G. S. The aetiology of essential hypertension. 4. The role of inheritance. Clin Sci. 1954 May;13(2):273–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyden S., Hames C. G., Bartel A., Cassel J. C., Tyroler H. A., Cornoni J. C. Weight and weight history in relation to cerebrovascular and ischemic heart disease. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Dec;128(6):956–960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman A. Blood pressure in childhood: an epidemiological approach to the aetiology of hypertension. J Hypertens. 1984 Aug;2(4):323–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibsen K. K., Grønbaek M. Familial aggregation of blood-pressure in newly born infants and their mothers. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1980 Jan;69(1):109–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1980.tb07040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. H., Rosner B., Gould J. B., Lowe E. W., Kass E. H. Familial aggregation of blood pressures of newborn infants and their mother. Pediatrics. 1976 Nov;58(5):722–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ounsted M. K., Cockburn J. M., Moar V. A., Redman C. W. Factors associated with the blood pressures of children born to women who were hypertensive during pregnancy. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Jul;60(7):631–635. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.7.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paffenbarger R. S., Jr, Wing A. L. Characteristics in youth predisposing to fatal stroke in later years. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):753–754. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler R., Stamler J., Riedlinger W. F., Algera G., Roberts R. H. Family (parental) history and prevalence of hypertension. Results of a nationwide screening program. JAMA. 1979 Jan 5;241(1):43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voors A. W., Webber L. S., Berenson G. S. Time course studies of blood pressure in children--the Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Mar;109(3):320–334. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth M. E., Cripps H. A., Midwinter R. E., Colley J. R. Blood pressure in a national birth cohort at the age of 36 related to social and familial factors, smoking, and body mass. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Nov 30;291(6508):1534–1538. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6508.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner S. H., Rosner B., Oh W., Kass E. H. Significance of blood pressure in infancy. Familial aggregation and predictive effect on later blood pressure. Hypertension. 1985 May-Jun;7(3 Pt 1):411–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Swiet M., Fayers P., Shinebourne E. A. Blood pressure survey in a population of newborn infants. Br Med J. 1976 Jul 3;2(6026):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6026.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


