Abstract
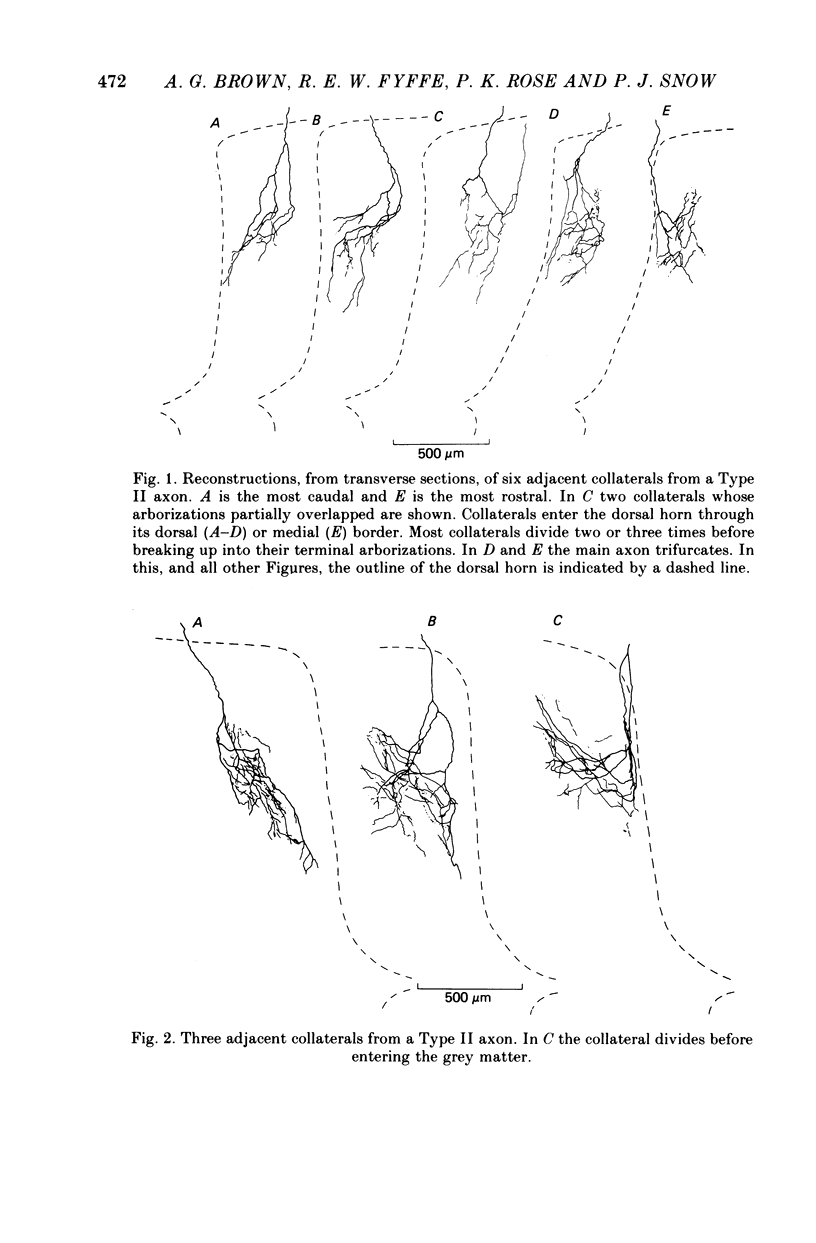
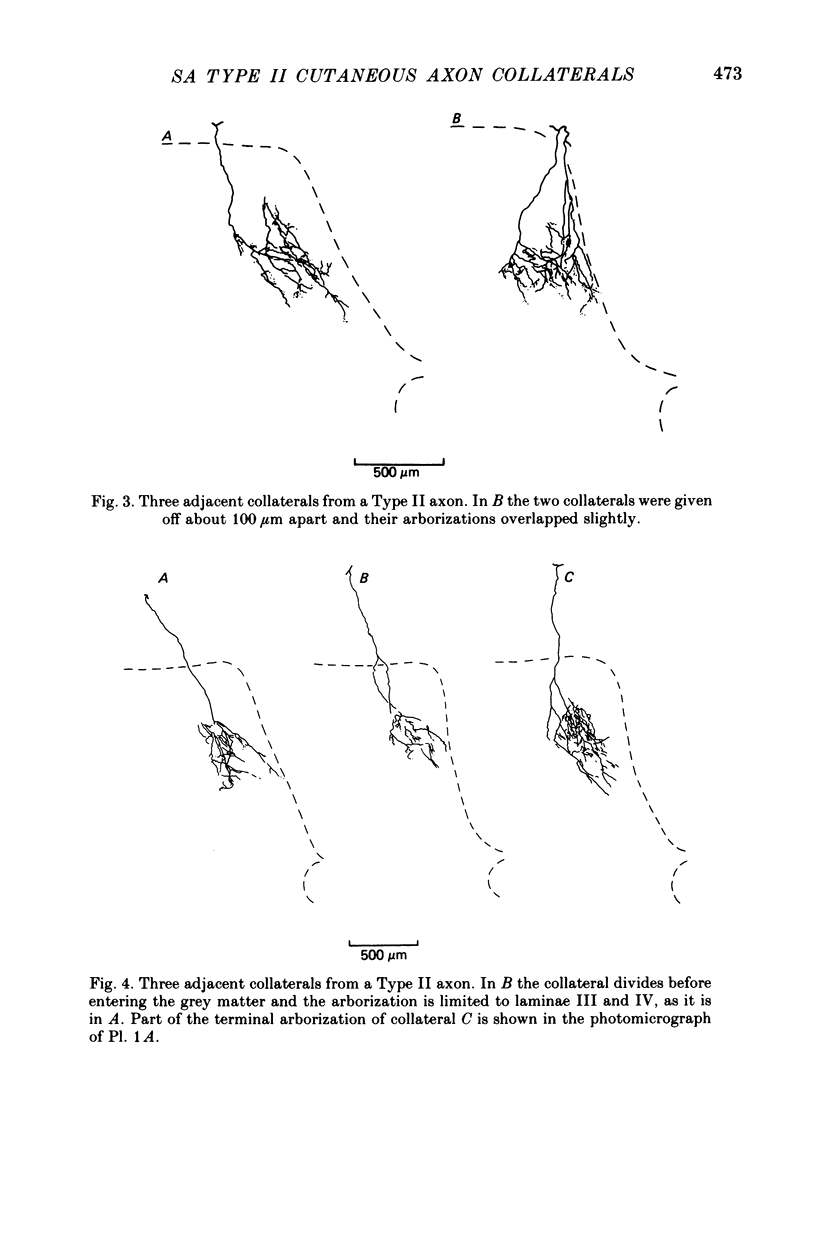
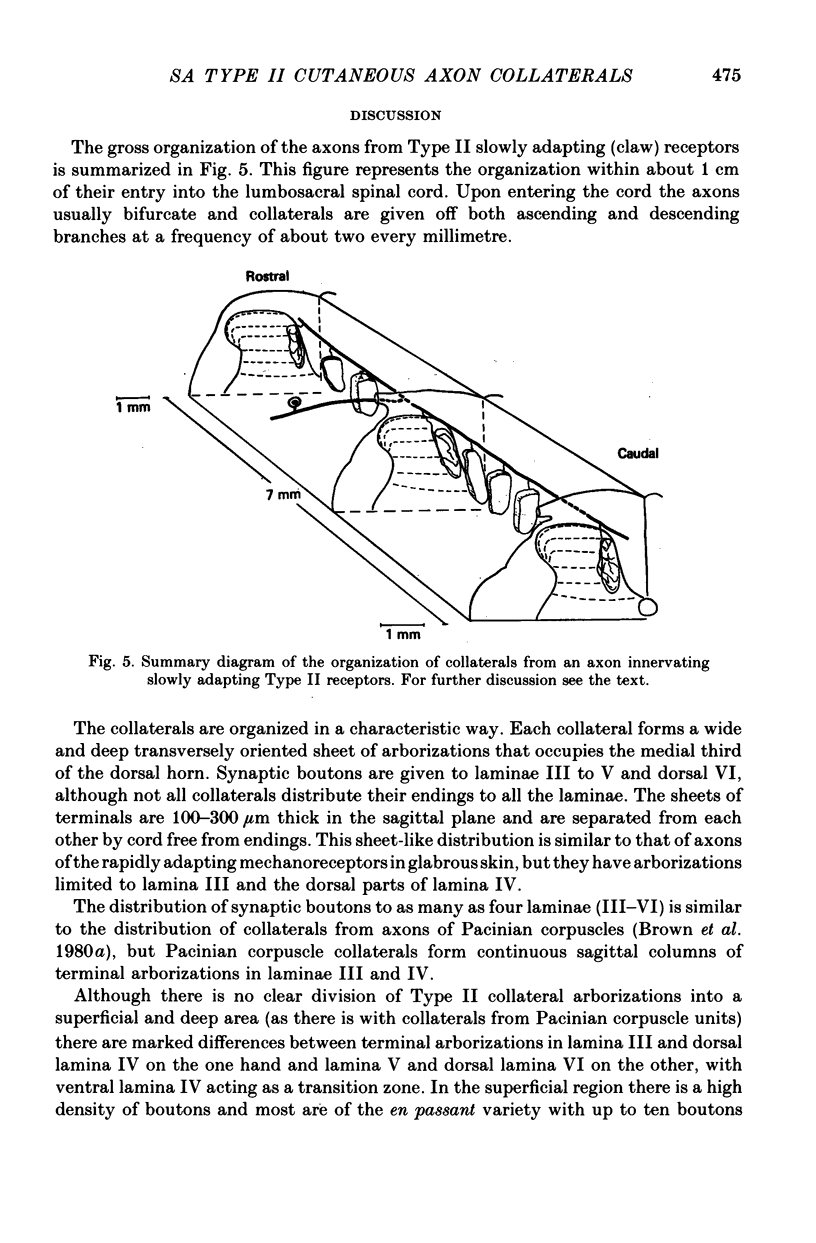
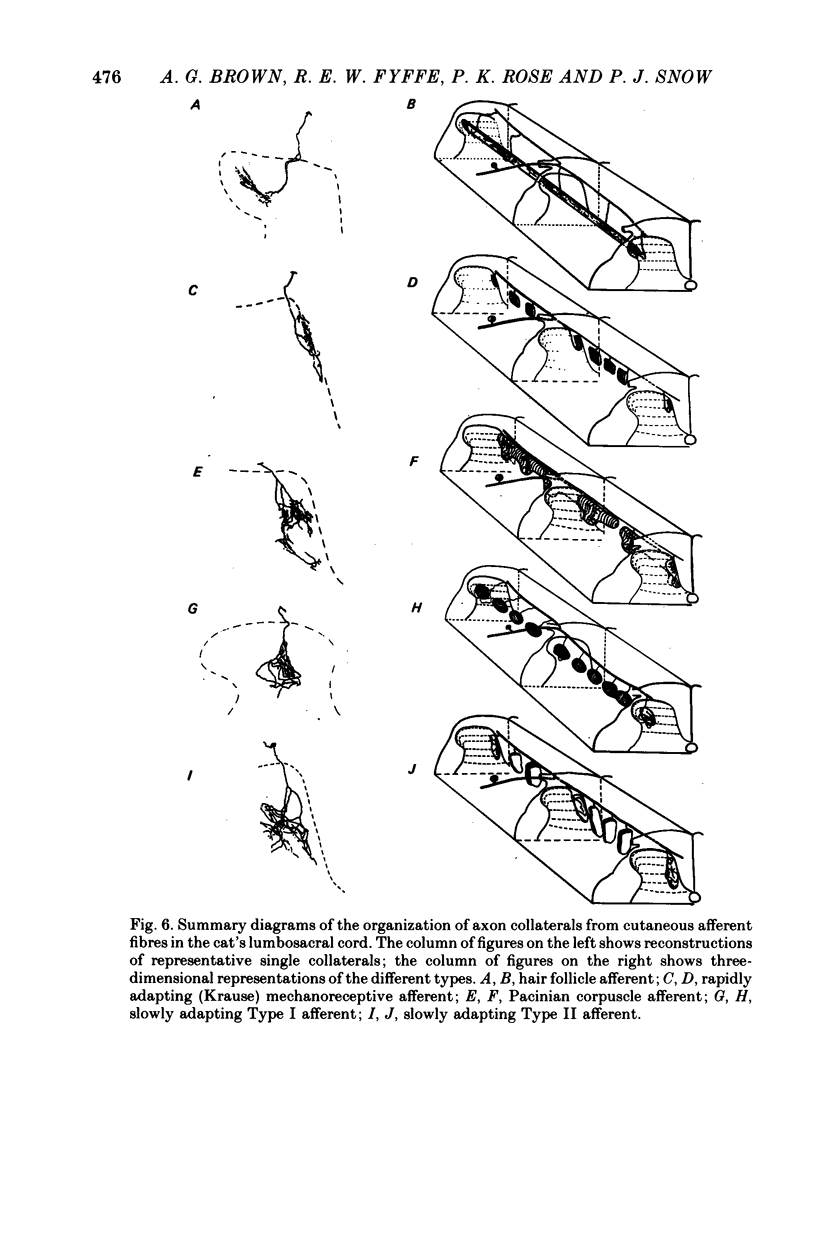
1. The morphology of single axons, and their collaterals, of Type II slowly adapting mechanoreceptors situated at the claw bases was studied. Intra-axonal injections of horseradish peroxidase were made into the axons near their entrance to the lumbosacral spinal cord of anaesthetized cats. The morphology was revealed by subsequent histochemistry. 2. Nine Type II axons were stained. All but one bifurcated into ascending and descending branches upon entering the cord. Eighty-nine collaterals arose from the axons at a mean spacing of about 570 micrometers. 3. The collaterals formed plate-like arborizations usually about 500-600 micrometers wide in the transverse plane but only 100-300 micrometers thick in the longitudinal axis of the cord. The terminal arborizations were in laminae III-VI. 4. Synaptic boutons in laminae III and IV were more numerous than in laminae V and VI. Boutons en passant were common in laminae III and IV and arranged in series of three to six, whereas in deeper laminae only two or three boutons formed a series de passage. 5. The morphology of the slowly adapting Type II collateral is discussed. 6. Some general principles of the organization of cutaneous afferent fibres in the lumbosacral cord are presented.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A. G. Cutaneous axons and sensory neurones in the spinal cord. Br Med Bull. 1977 May;33(2):109–112. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E., Noble R. Projections from Pacinian corpuscles and rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors of glabrous skin to the cat's spinal cord. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:385–400. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E., Noble R., Rose P. K., Snow P. J. The density, distribution and topographical organization of spinocervical tract neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:409–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. The morphology of group Ia afferent fibre collaterals in the spinal cord of the cat. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:111–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. The morphology of group Ib afferent fibre collaterals in the spinal cord of the cat. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:215–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Gordon G., Kay R. H. A study of single axons in the cat's medial lemniscus. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(1):225–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Rose P. K., Snow P. J. Morphology and organization of axon collaterals from afferent fibres of slowly adapting type I units in cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:15–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Rose P. K., Snow P. J. The morphology of hair follicle afferent fibre collaterals in the spinal cord of the cat. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):779–797. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Rose R. K., Snow P. J. The morphology of identified curtaeous afferent fibre collaterals in the spinal cord [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(1):132P–134P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Petit D., Warren R. M. Receptor types in cat hairy skin supplied by myelinated fibers. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Nov;31(6):833–848. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers M. R., Andres K. H., von Duering M., Iggo A. The structure and function of the slowly adapting type II mechanoreceptor in hairy skin. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1972 Oct;57(4):417–445. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1972.sp002177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyffe R. E. The morphology of group II muscle afferent fibre collaterals [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:39P–40P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON G., JUKES M. G. DUAL ORGANIZATION OF THE EXTEROCEPTIVE COMPONENTS OF THE CAT'S GRACILE NUCLEUS. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:263–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Devor M. A microelectrophoretic delivery technique for use with horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 15;68(1):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90541-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanker J. S., Yates P. E., Metz C. B., Rustioni A. A new specific, sensitive and non-carcinogenic reagent for the demonstration of horseradish peroxidase. Histochem J. 1977 Nov;9(6):789–792. doi: 10.1007/BF01003075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo A., Muir A. R. The structure and function of a slowly adapting touch corpuscle in hairy skin. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):763–796. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson R. S. Tactile sensibility in the human hand: receptive field characteristics of mechanoreceptive units in the glabrous skin area. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:101–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light A. R., Perl E. R. Spinal termination of functionally identified primary afferent neurons with slowly conducting myelinated fibers. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jul 15;186(2):133–150. doi: 10.1002/cne.901860203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson J. B., Sypert G. W. Properties of single central Ia afferent fibres projecting to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:315–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel M. E., Scheibel A. B. Terminal axonal patterns in cat spinal cord. II. The dorsal horn. Brain Res. 1968 Jun;9(1):32–58. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow P. J., Rose P. K., Brown A. G. Tracing axons and axon collaterals of spinal neurons using intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase. Science. 1976 Jan 23;191(4224):312–313. doi: 10.1126/science.54936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]