Abstract
1. Inhibitory post-synaptic potentials (i.p.s.p.s) evoked by adequate stimulation of group Ia muscle spindle afferents of triceps surae and plantaris and by near-threshold electrical stimulation of quadriceps and hamstring nerves were recorded in a number of motoneurone species. The aim of the study was to compare the pattern of non-reciprocal Ia inhibitory actions on hind-limb motoneurones with the pattern of inhibition evoked from group Ib tendon organ afferents.
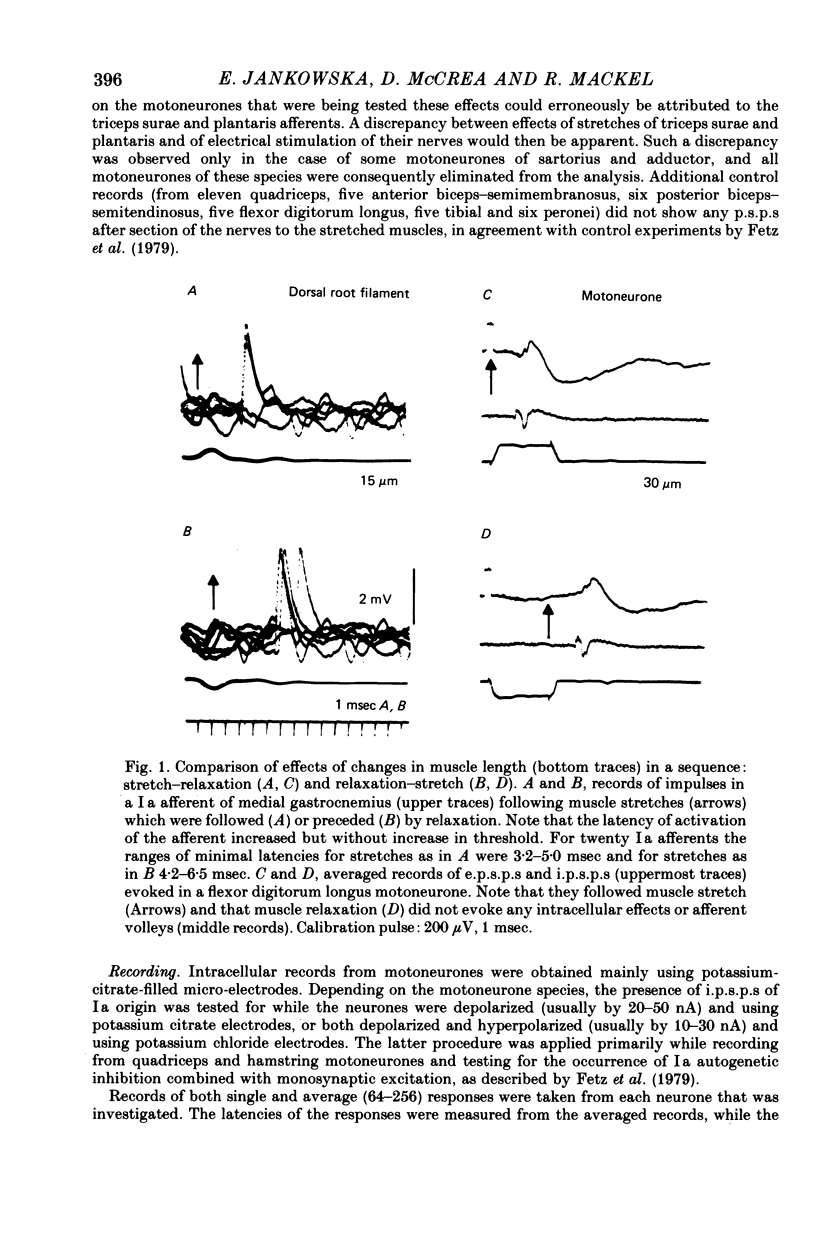
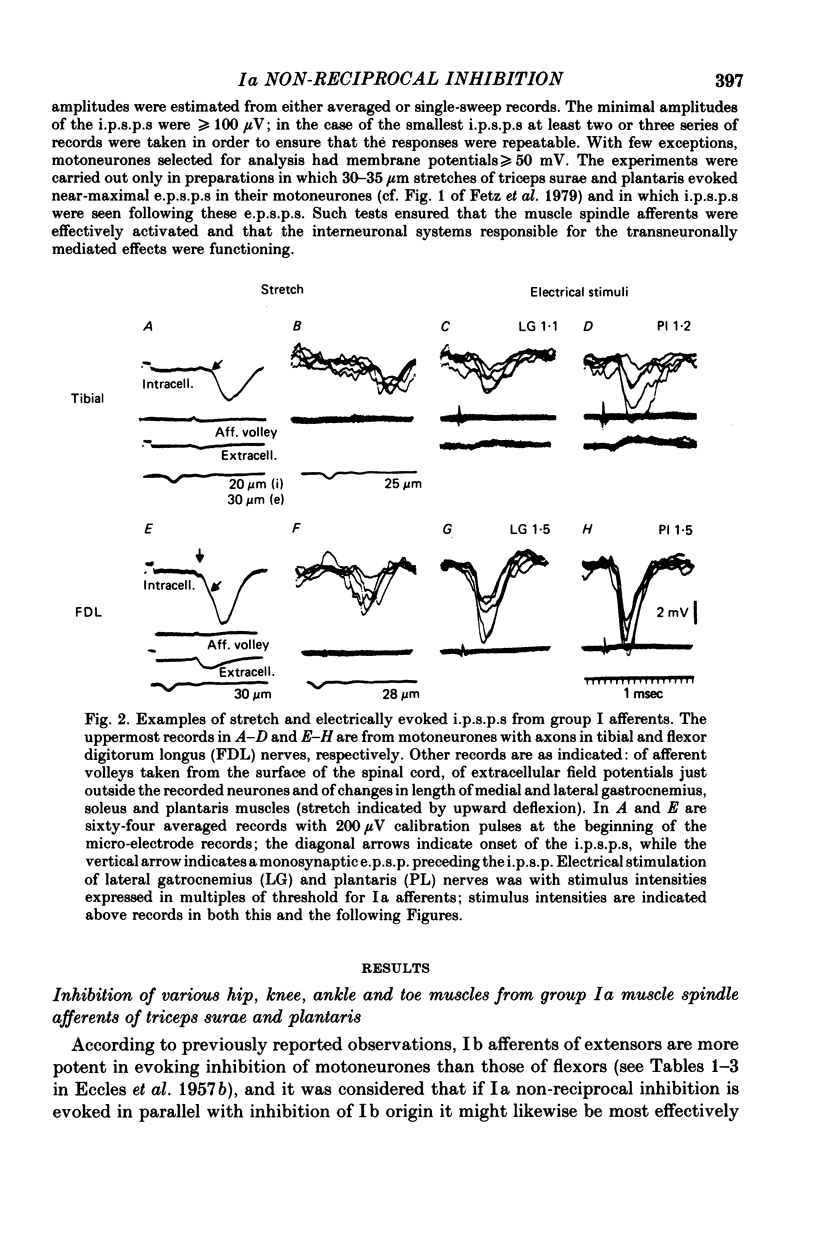
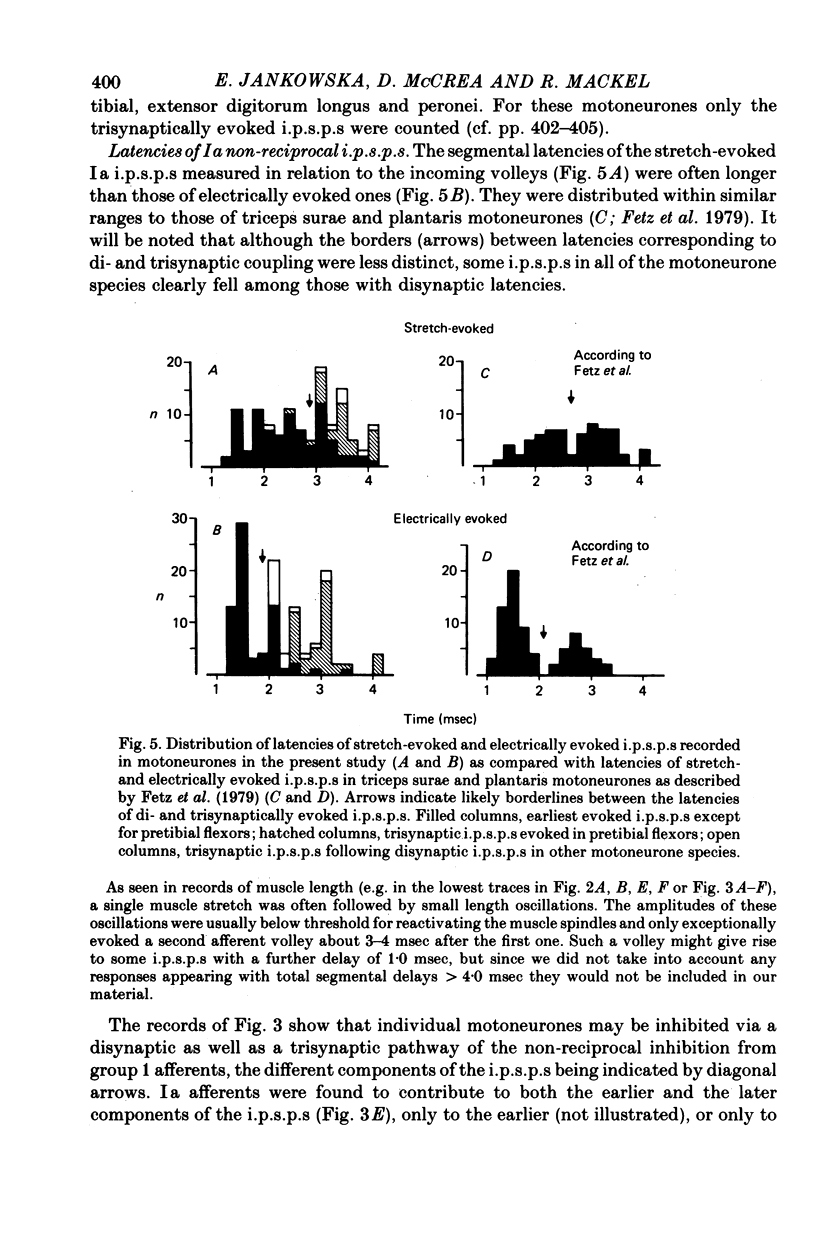
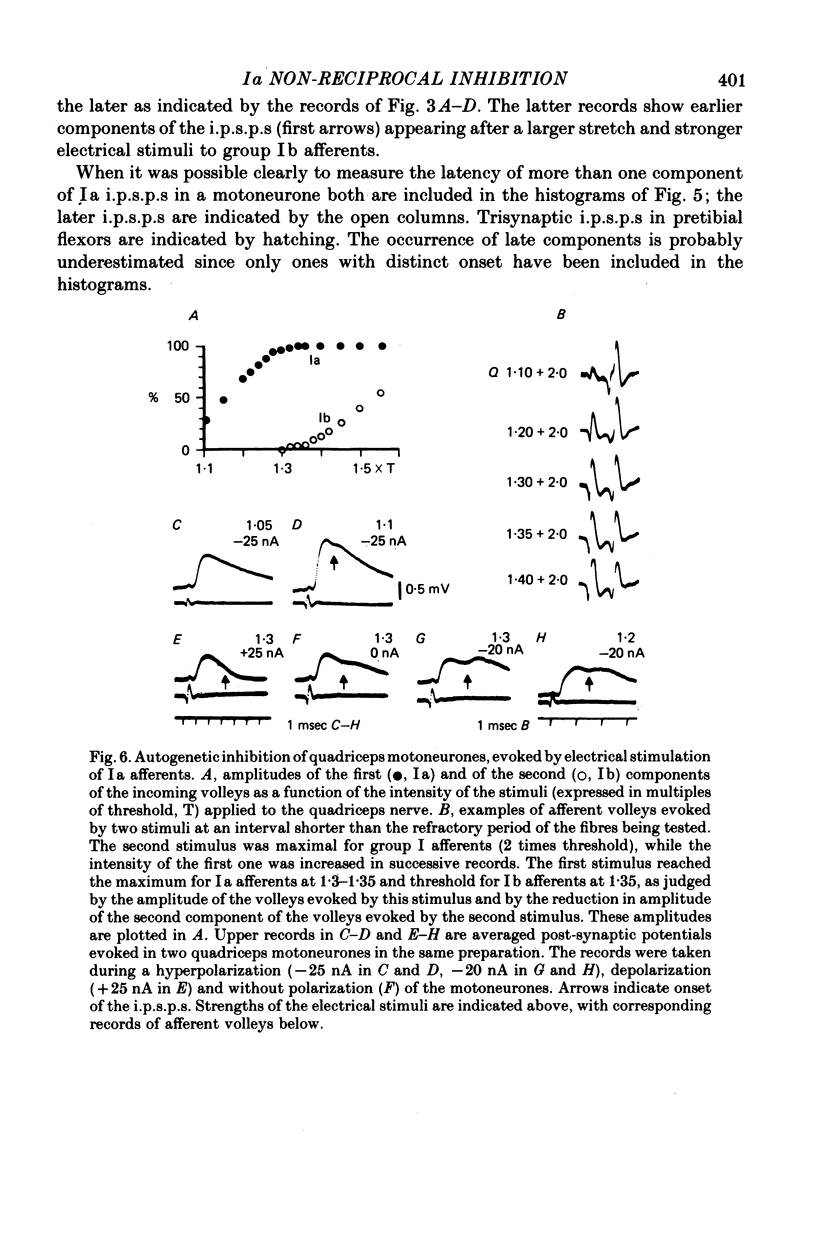
2. In all the motoneurone species analysed in which i.p.s.p.s were evoked by electrical stimulation maximal for both group Ia and Ib afferents of triceps surae and plantaris, they were also evoked when these muscles were stretched and the amplitude of the stretch (10-35 μm) was below threshold for Ib afferents; 70-100% of motoneurones with Ib i.p.s.p.s showed stretch-evoked i.p.s.p.s. The stretch-evoked i.p.s.p.s appeared with latencies compatible with disynaptic and trisynaptic linkage. Since these latencies were too short to allow their mediation by group II afferents the i.p.s.p.s are attributed to a selective action of Ia afferents. The i.p.s.p.s did not appear after the nerves to triceps surae and plantaris had been cut.
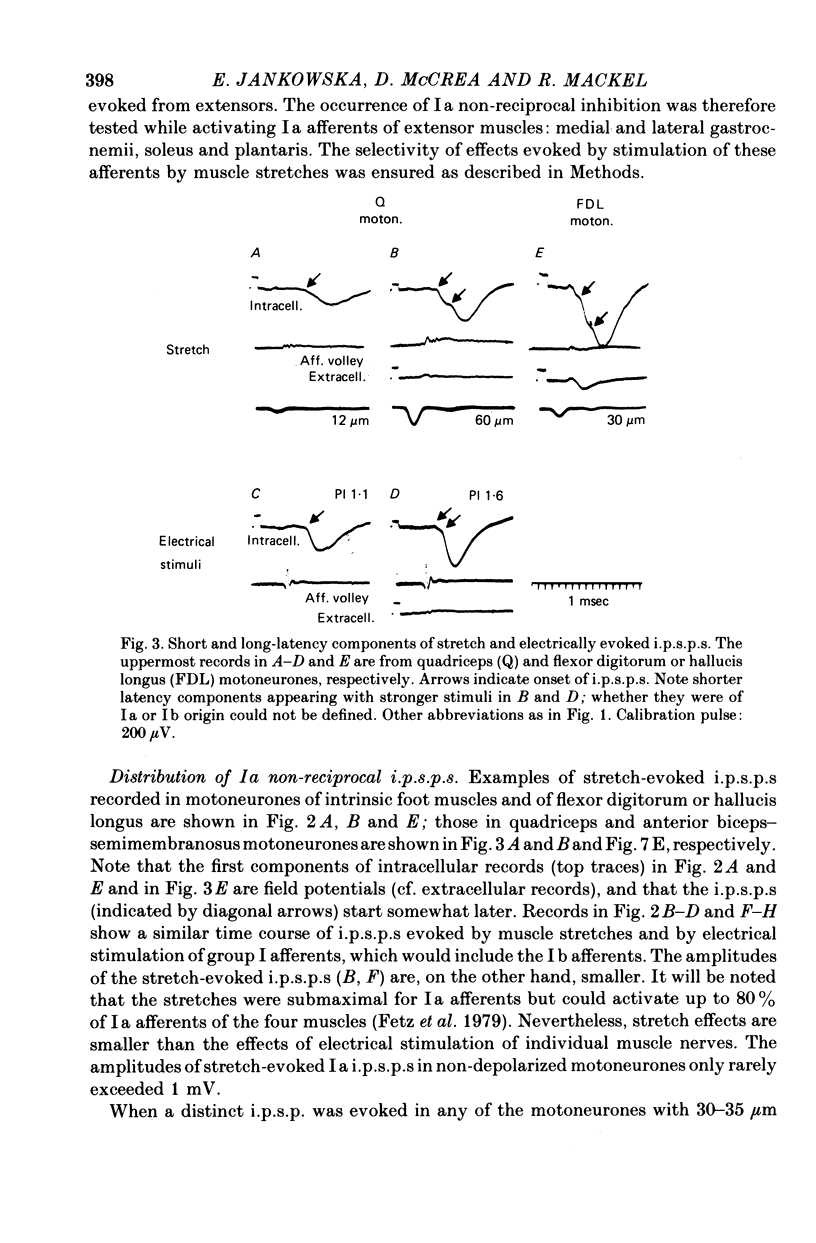
3. Electrical stimulation of quadriceps and hamstring nerves which was near threshold for Ia afferents and well below threshold for either the Ib component of the incoming volley or group II afferents, similarly evoked non-reciprocal i.p.s.p.s. They were found in those motoneurones in which inhibition was evoked by stimulation maximal for group I afferents. Such Ia i.p.s.p.s were evoked both in homonymous motoneurones and in motoneurones of four other hind-limb muscles. Their latencies corresponded to di- and trisynaptic coupling.
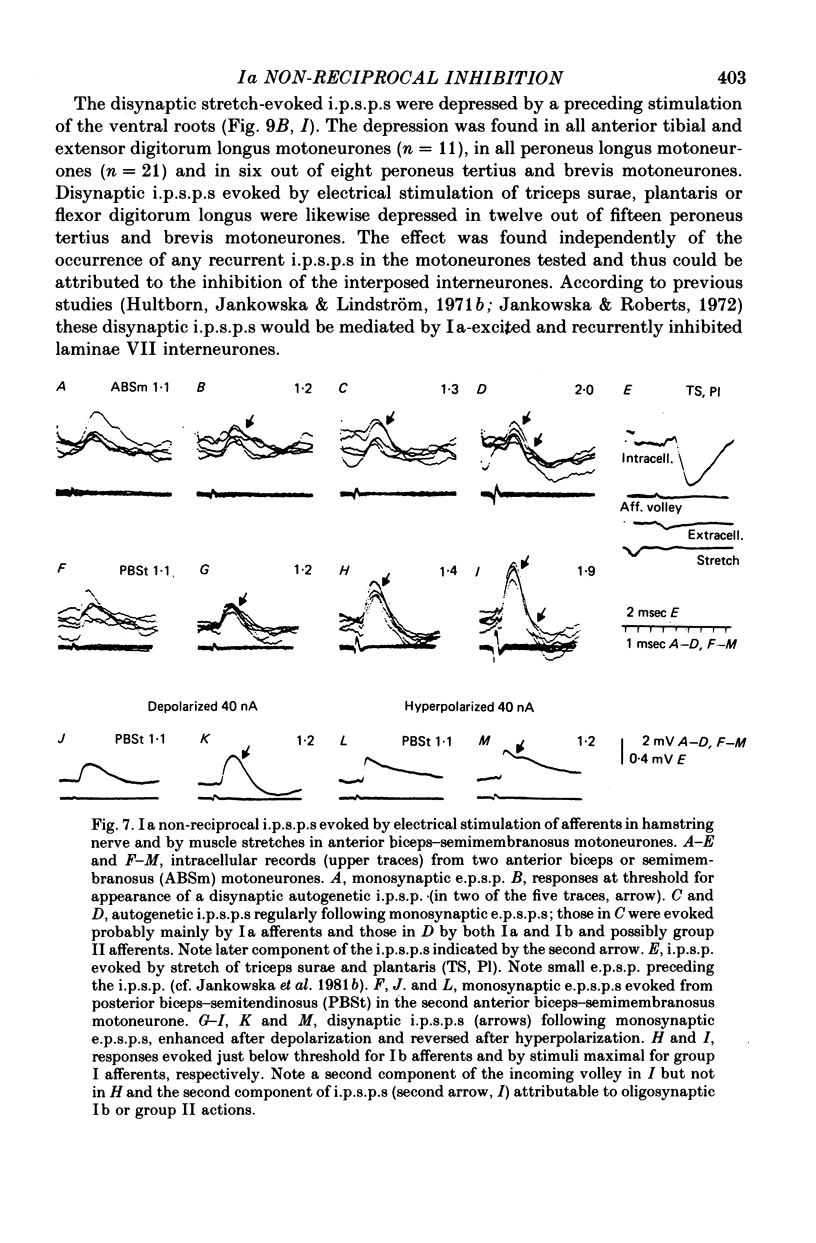
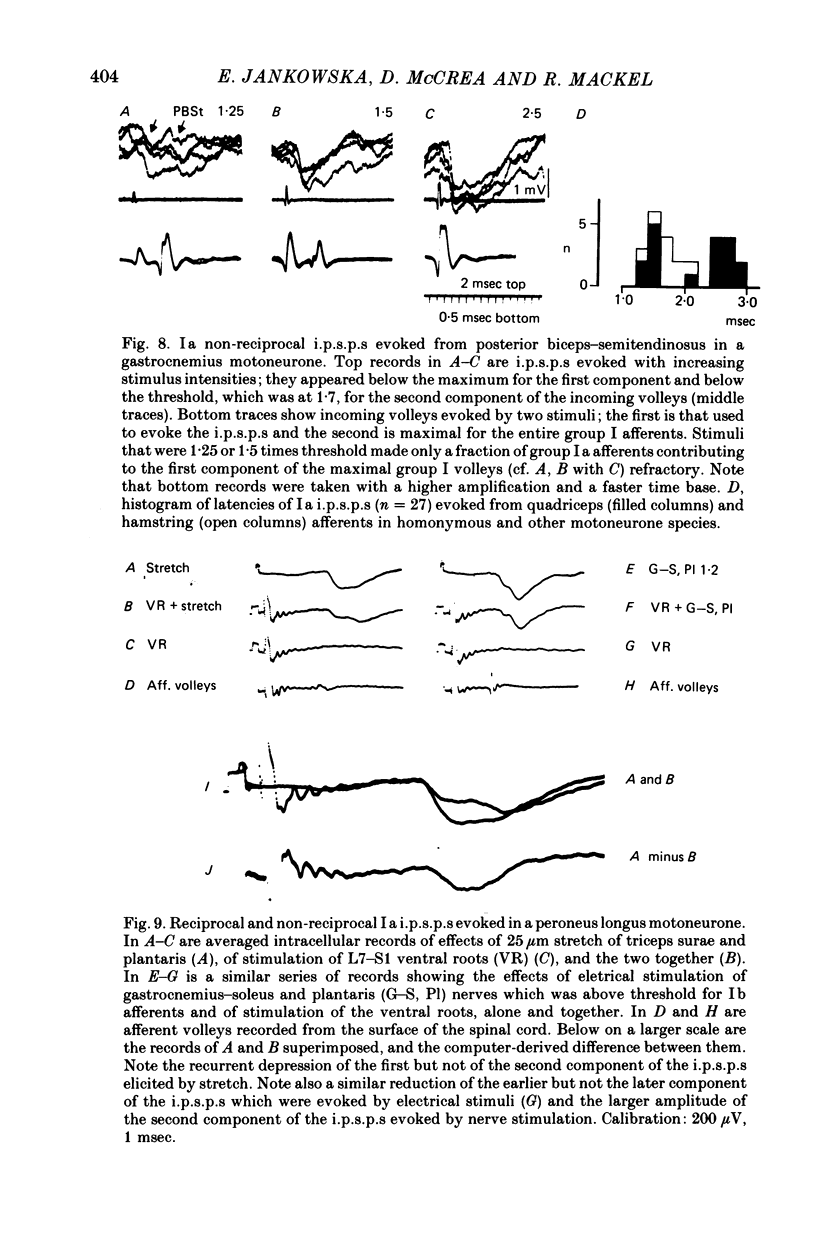
4. In some motoneurones of the pretibial flexors (anterior tibial, extensor digitorum longus and peroneus longus), disynaptic i.p.s.p.s evoked from triceps surae and/or plantaris which were depressed by a conditioning ventral root stimulation (i.e. Ia reciprocal i.p.s.p.s) were followed by trisynaptic i.p.s.p.s which were not depressed in this way (Ia `non-reciprocal' i.p.s.p.s). It thus appears that the same motoneurones may be inhibited by impulses in group Ia afferents via different spinal pathways.
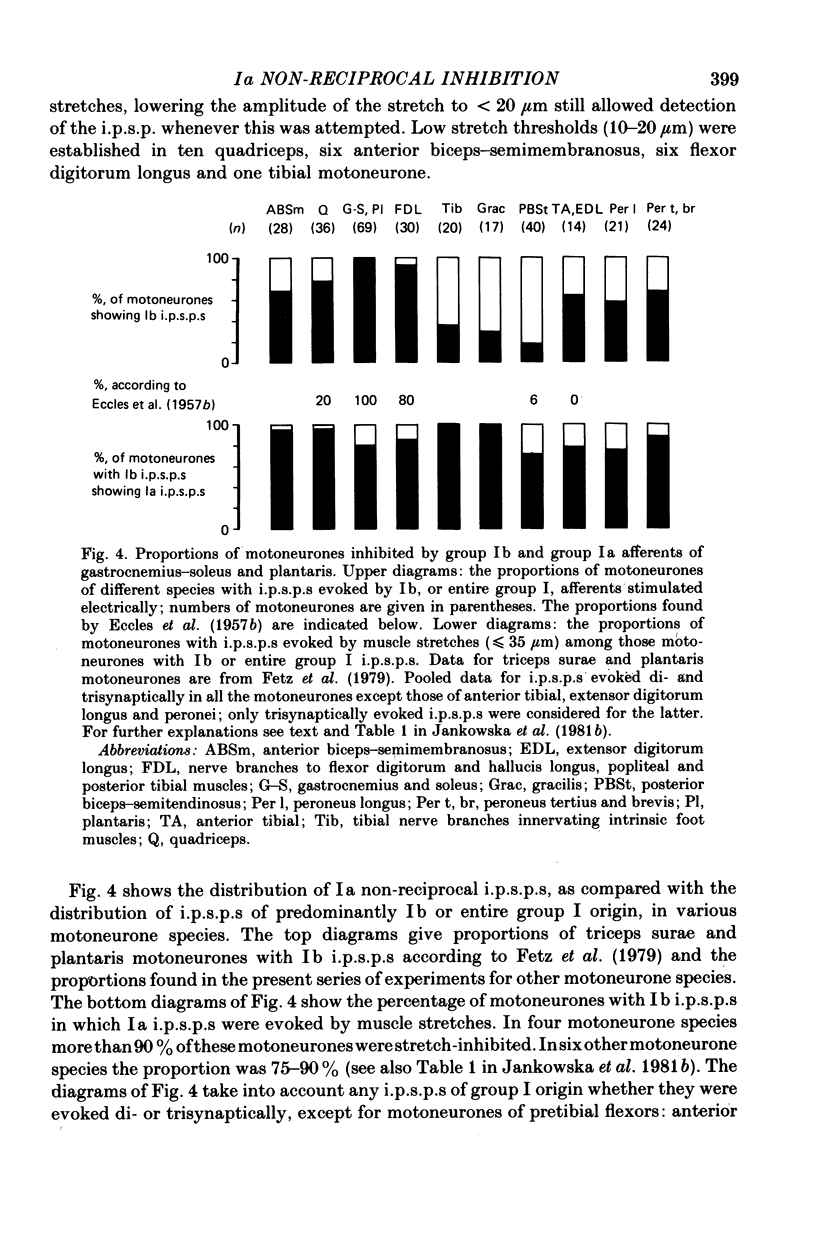
5. The study leads to the conclusion that the non-reciprocal inhibition from group Ia muscle spindle afferents operates in parallel with the inhibition from group Ib tendon organ afferents in all motoneurone species tested.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coppin C. M., Jack J. J., MacLennan C. R. A method for the selective electrical activation of tendon organ afferent fibres from the cat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(1):18P–20P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones in relation to the two components of the group I muscle afferent volley. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):527–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Murphy P. R., Trott J. R. Inhibition of gamma motoneurone discharge by contraction of the homonymous muscle in the decerebrated cat. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:425–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Trott J. R. Autogenetic reflex action on to gamma motoneurones by stretch of triceps surae in the decerebrated cat. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:49–66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Jankowska E., Johannisson T., Lipski J. Autogenetic inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:173–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm C., Noth J. Reflex responses of gamma motoneurones to vibration of the muscle they innervate. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):117–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R. Reflex self-regulation of muscle contraction and autogenetic inhibition. J Neurophysiol. 1950 Sep;13(5):351–372. doi: 10.1152/jn.1950.13.5.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. The effect of stretch receptors from muscle on the discharge of motorneurons. J Physiol. 1952 Jul;117(3):359–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. II. Facilitation of interneuronal transmission in reflex paths to motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(4):365–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00237321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Recurrent inhibition from motor axon collaterals of transmission in the Ia inhibitory pathway to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):591–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Recurrent inhibition of interneurones monosynaptically activated from group Ia afferents. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):613–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Johannisson T., Lipski J. Common interneurones in reflex pathways from group 1a and 1b afferents of ankle extensors in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:381–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lundberg A., Rudomin P., Sykova E. Effects of 4-aminopyridine on transmission in excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the spinal cord. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 11;136(2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90816-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Mackel R. Oligosynaptic excitation of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:411–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E. New observations on neuronal organization of reflexes from tendon organ afferents and their relation to reflexes evoked from muscle spindle afferents. Prog Brain Res. 1979;50:29–36. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60804-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):623–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., WINSBURY G. Selective adequate activation of large afferents from muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Jul 15;49:155–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Characteristics of the excitatory pathway from group II muscle afferents to alpha motoneurones. Brain Res. 1975 May 9;88(3):538–542. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90667-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Comments on reflex actions evoked by electrical stimulation of group II muscle afferents. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90466-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Cutaneous facilitation of transmission in reflex pathways from Ib afferents to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):763–780. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Role of joint afferents in motor control exemplified by effects on reflex pathways from Ib afferents. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:327–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer E. K., Watt D. G., Taylor A., Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 2. Spindle group II afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1393–1402. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. G., Mosher C. G., Gerlach R. L., Reinking R. M. Selective activation of Ia afferents by transient muscle stretch. Exp Brain Res. 1970 Jun 25;10(5):477–487. doi: 10.1007/BF00234264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trott J. R. The effect of low amplitude muscle vibration on the discharge of fusimotor neurones in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):635–649. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



