Abstract
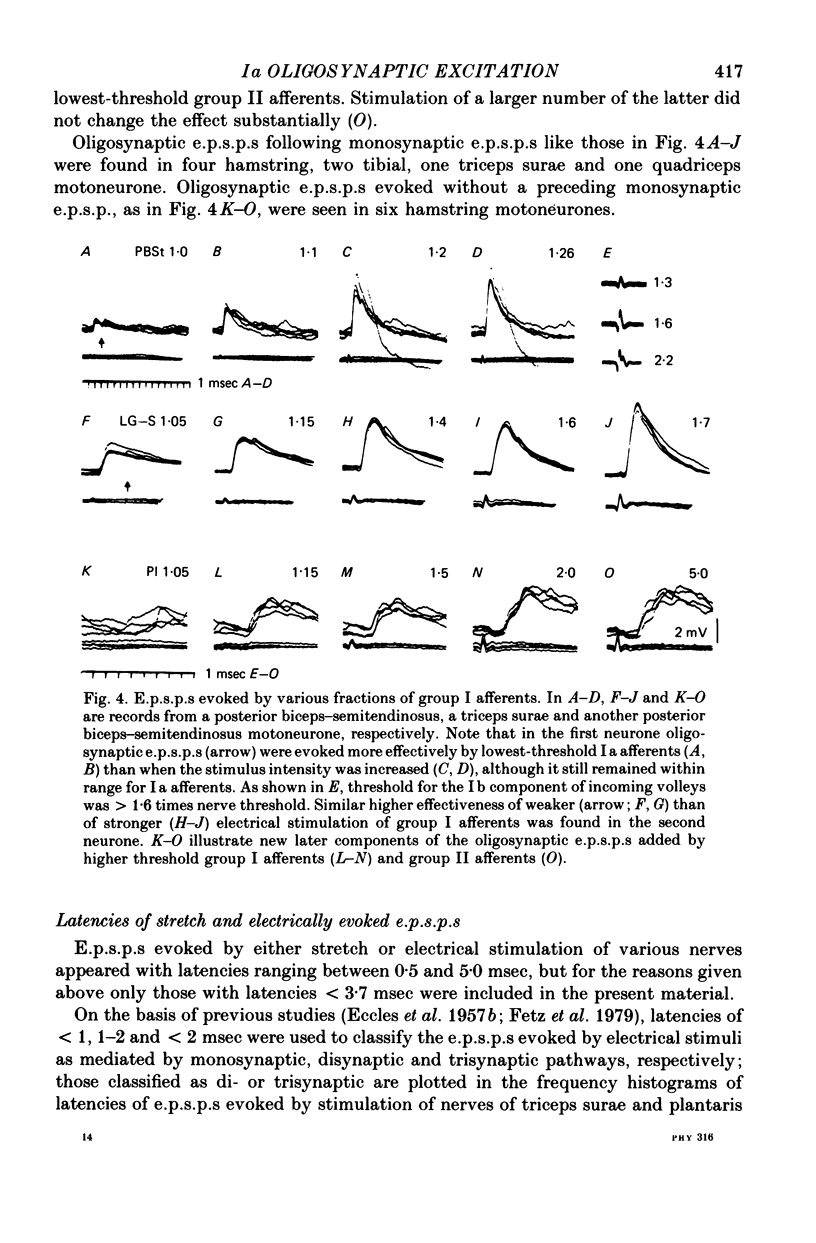
1. Intracellular recording from hind-limb motoneurones was used to investigate whether di- and trisynaptic (oligosynaptic) excitatory post-synaptic potentials (e.p.s.p.s) are evoked from group Ia muscle spindle afferents in those motoneurones in which such potentials are evoked from Ib tendon organ afferents or entire group I afferents. Ia afferents of triceps surae and plantaris were activated either selectively by single brief stretches of these muscles, or together with Ib afferents by electrical stimuli applied to the nerves.
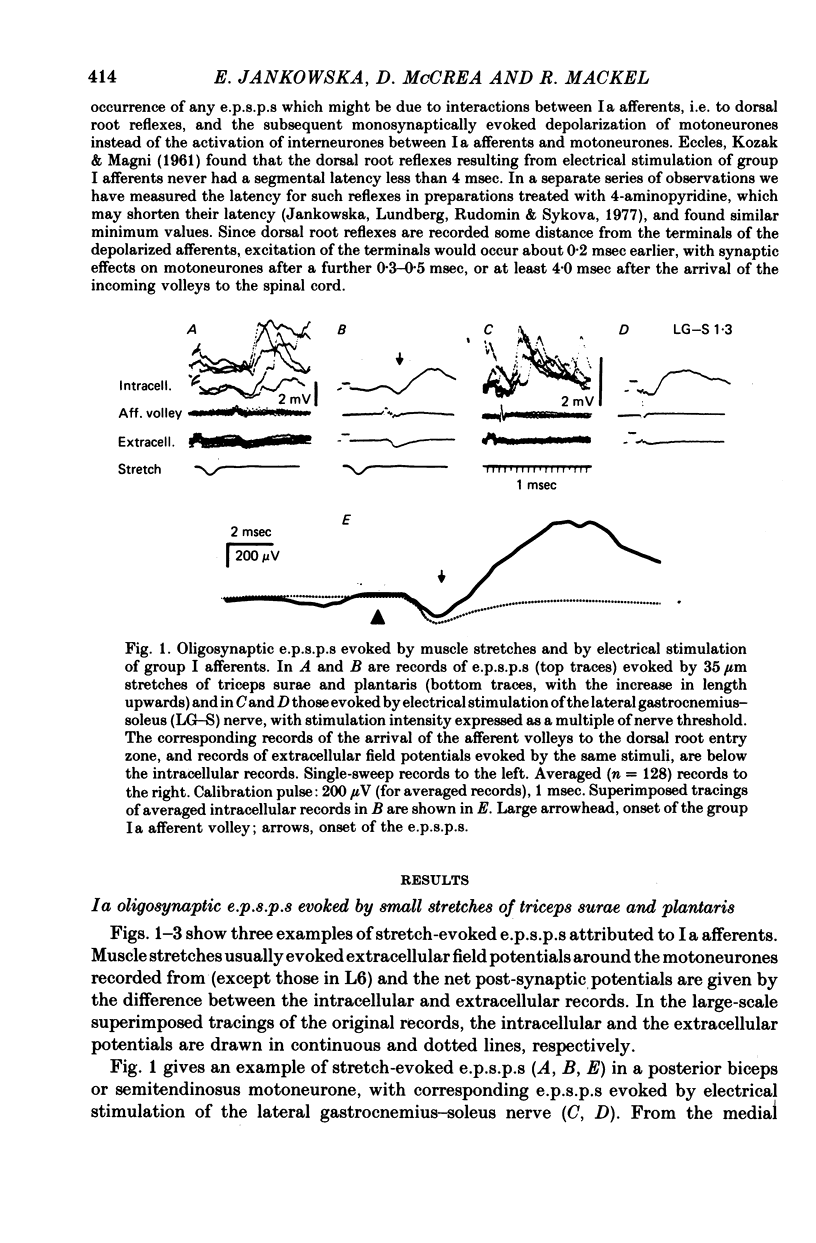
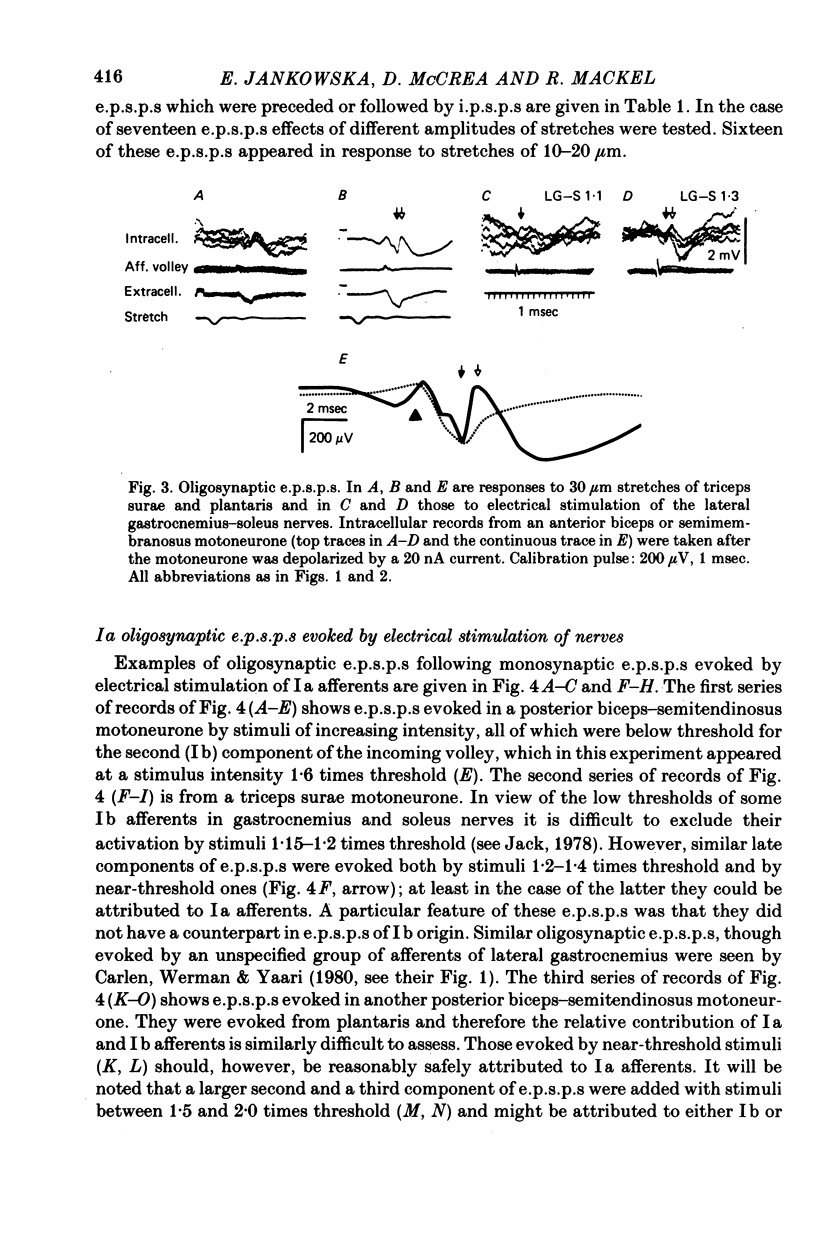
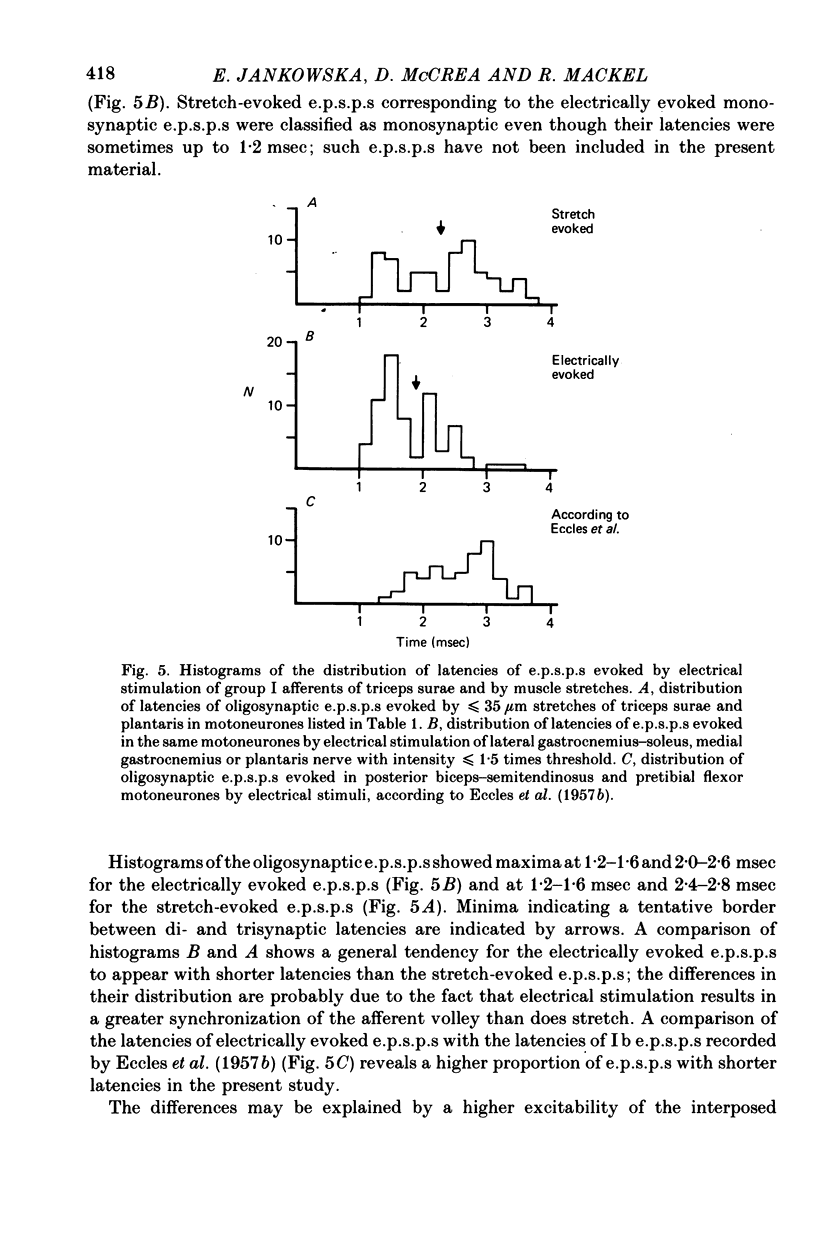
2. Muscle stretches below threshold for Ib afferents (10-35 μm) evoked e.p.s.p.s which appeared with latencies compatible with disynaptic and trisynaptic coupling between the afferents and the motoneurones. The latencies of a majority of these e.p.s.p.s were too short to allow their mediation by group II afferents, if any were activated by the applied stretches. They were also too short to be compatible with effects attributable to dorsal root reflexes. These e.p.s.p.s are thus attributed to oligosynaptic actions of Ia afferents.
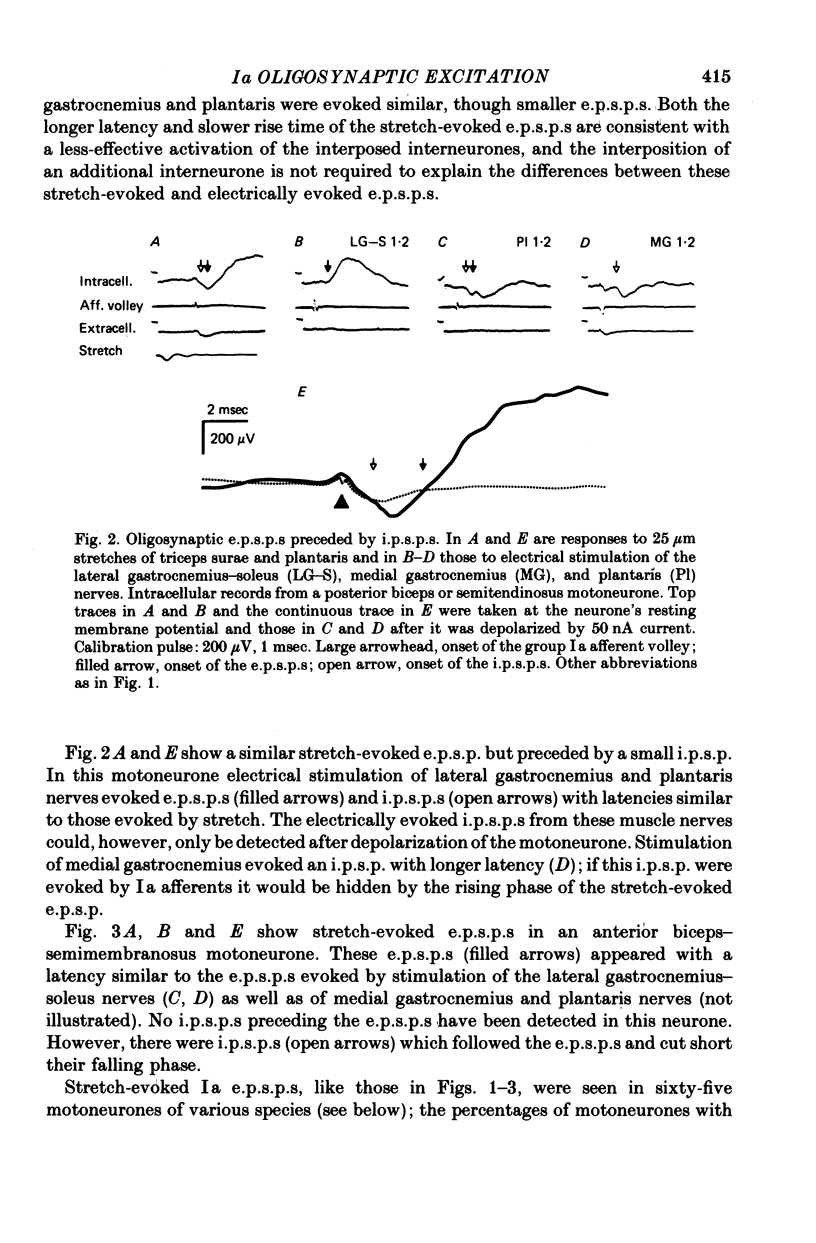
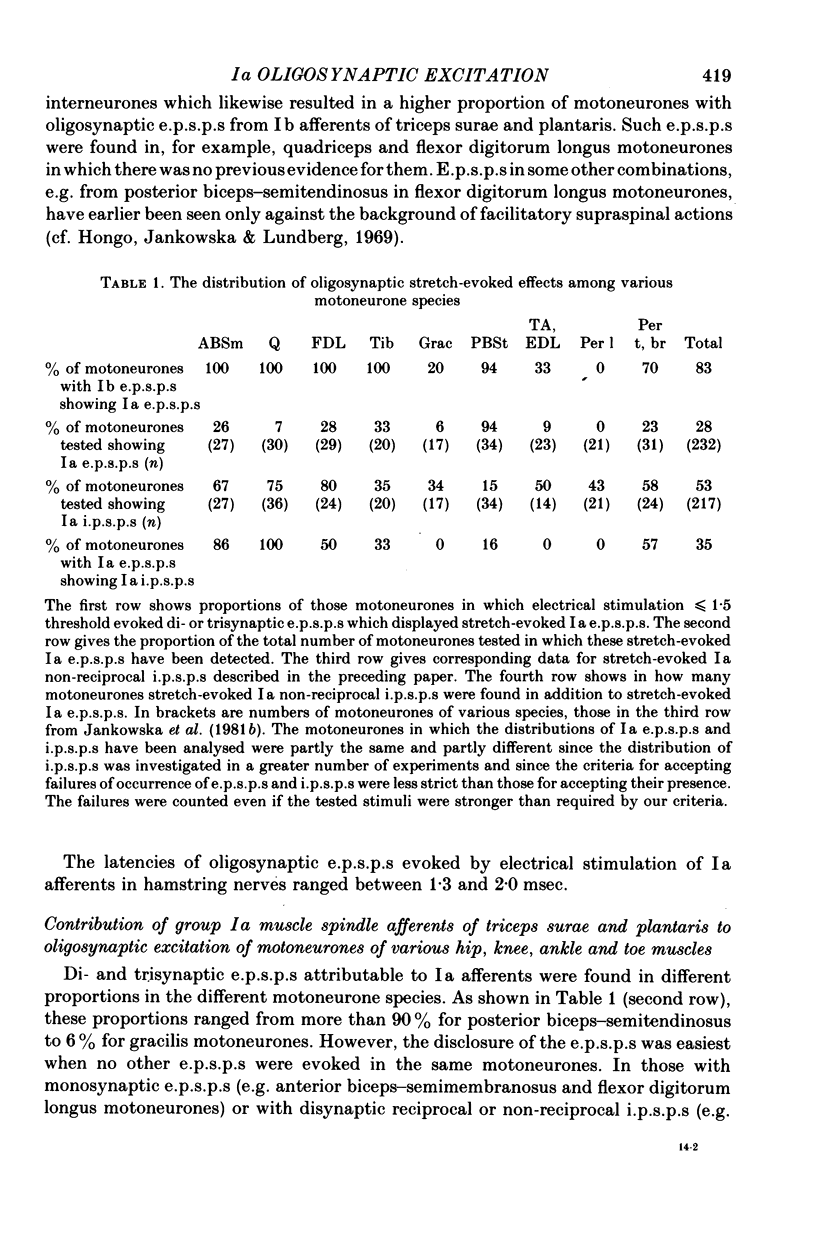
3. Stretch-evoked di- and trisynaptic Ia e.p.s.p.s were found in 83% of motoneurones in which e.p.s.p.s were evoked by stimuli which activated both Ia and Ib afferents; in five motoneurone species they were found in more than 90%. These observations lead to the conclusion that group Ia muscle spindle afferents evoke not only inhibitory but also excitatory actions in parallel with group Ib tendon organ afferents.
4. The distribution of Ia oligosynaptic stretch-evoked excitation from ankle and toe extensor muscles was compared with the distribution of Ia non-reciprocal inhibition as described by Jankowska, McCrea & Mackel (1981b). Excitation pre-dominated in posterior biceps—semitendinosus motoneurones and inhibition in other species of motoneurones investigated, except those of intrinsic foot muscles (tibial motoneurones); similar proportions of the latter showed excitation and inhibition.
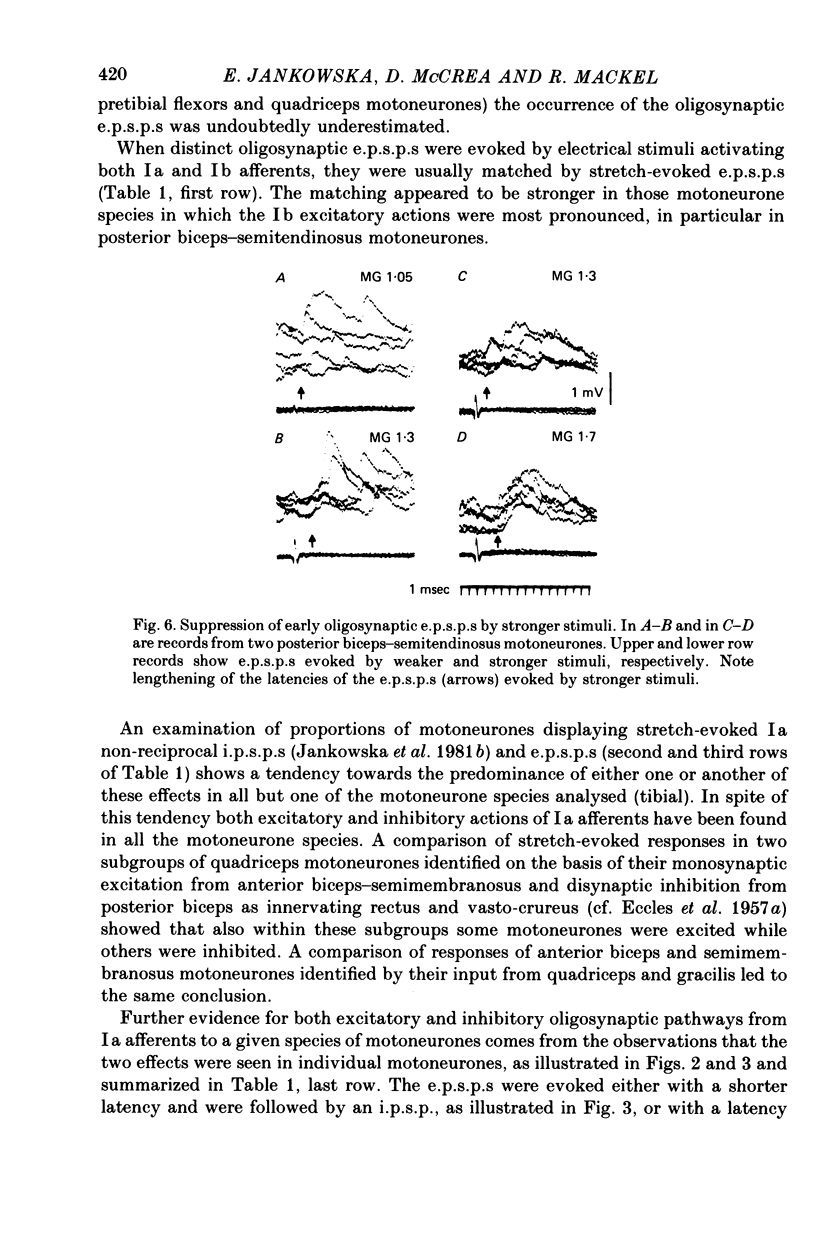
5. Occurrence of oligosynaptic e.p.s.p.s as well as inhibitory post-synaptic potentials (i.p.s.p.s) of Ia origin in some motoneurone species, and in particular in individual motoneurones, is indicative of a number of reflex pathways between group I afferents and these motoneurones. Furthermore, the disappearance of some of the e.p.s.p.s evoked by near-threshold electrical stimulation following stronger stimuli indicates interactions between various functional groups of interneurones mediating group I actions.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke R. E., Fedina L., Lundberg A. Spatial synaptic distribution of recurrent and group Ia inhibitory systems in cat spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(2):305–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlen P. L., Werman R., Yaari Y. Post-synaptic conductance increase associated with presynaptic inhibition in cat lumbar motoneurones. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:539–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppin C. M., Jack J. J., MacLennan C. R. A method for the selective electrical activation of tendon organ afferent fibres from the cat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(1):18P–20P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarkowska J., Jankowska E., Sybirska E. Common interneurones in reflex pathways from group 1a and 1b afferents of knee flexors and extensors in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:367–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The convergence of monosynaptic excitatory afferents on to many different species of alpha motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Jun 18;137(1):22–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Types of neurone in and around the intermediate nucleus of the lumbosacral cord. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:89–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KOZAK W., MAGNI F. Dorsal root reflexes of muscle group I afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:128–146. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Jankowska E., Johannisson T., Lipski J. Autogenetic inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:173–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. II. Facilitation of interneuronal transmission in reflex paths to motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(4):365–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00237321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Johannisson T., Lipski J. Common interneurones in reflex pathways from group 1a and 1b afferents of ankle extensors in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:381–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lundberg A., Rudomin P., Sykova E. Effects of 4-aminopyridine on transmission in excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the spinal cord. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 11;136(2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90816-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Mackel R. Pattern of 'non-reciprocal' inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:393–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. Monosynaptic excitation of motoneurones from muscle spindle secondary endings of intercostal and triceps surae muscles in the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):64P–66P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Comments on reflex actions evoked by electrical stimulation of group II muscle afferents. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90466-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Role of joint afferents in motor control exemplified by effects on reflex pathways from Ib afferents. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:327–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson J. B., Fleshman J. W., Sypert G. W. Properties of single-fiber spindle group II EPSPs in triceps surae motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Oct;44(4):713–725. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.44.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson J. B., Sypert G. W. Properties of single central Ia afferent fibres projecting to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:315–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco P., Guzmán-Flores C. Intracellular recording in extensor motoneurons of spastic cats. Exp Neurol. 1969 Dec;25(4):472–481. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schomburg E. D., Behrends H. B. The possibility of phase-dependent monosynaptic and polysynaptic is excitation to homonymous motoneurones during fictive locomotion. Brain Res. 1978 Mar 31;143(3):533–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer E. K., Watt D. G., Taylor A., Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 2. Spindle group II afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1393–1402. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara N., Ohye C. Polysynaptic activation of extensor motorneurones from group Ia fibres in the cat spinal cord. Experientia. 1964 Nov 15;20(11):628–629. doi: 10.1007/BF02144828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt D. G., Stauffer E. K., Taylor A., Reinking R. M., Stuart D. G. Analysis of muscle receptor connections by spike-triggered averaging. 1. Spindle primary and tendon organ afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1375–1392. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


