Abstract
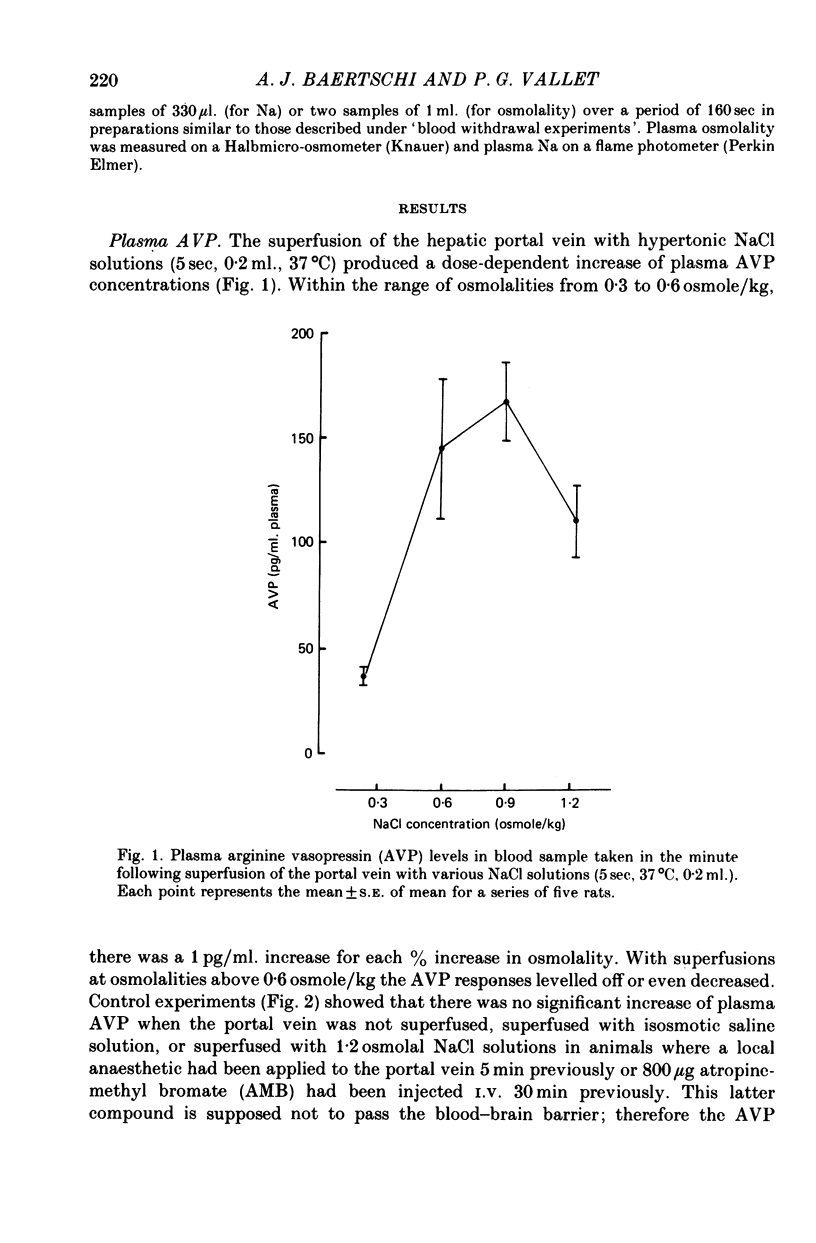
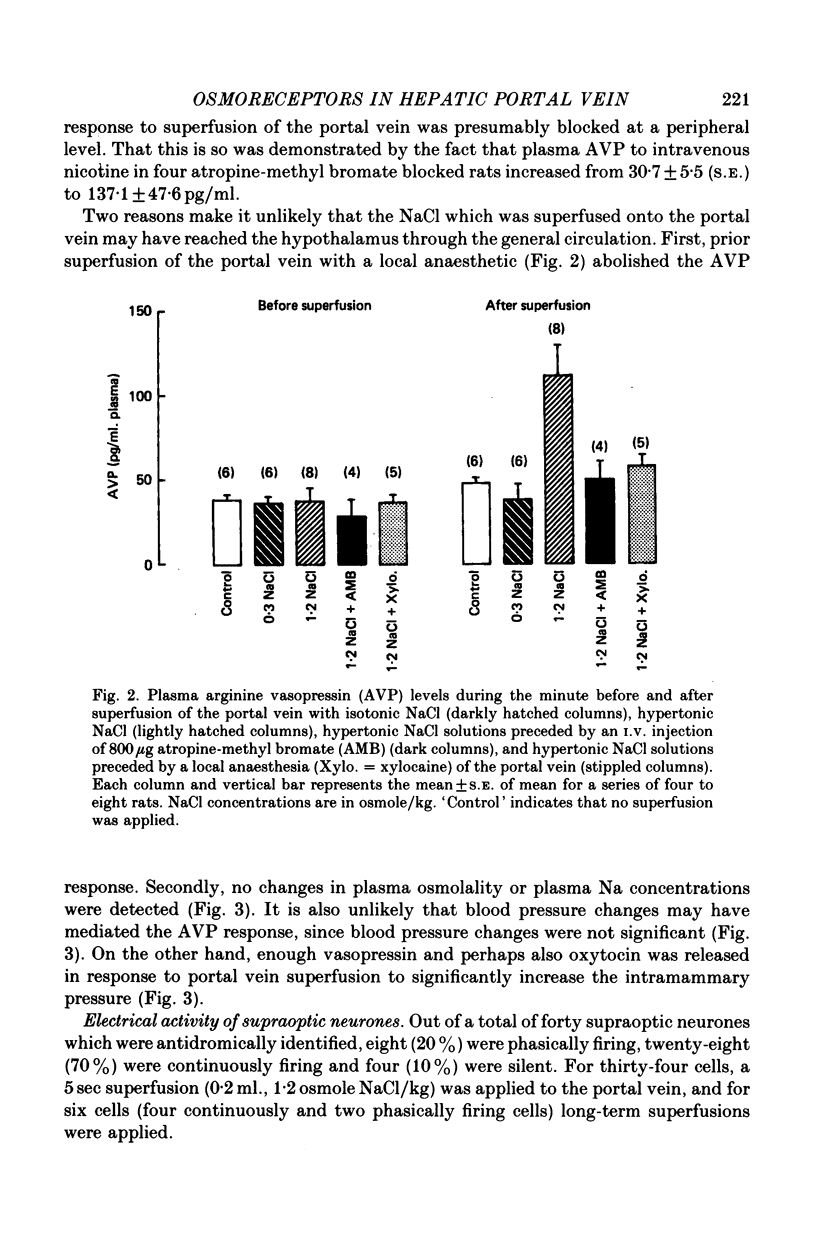
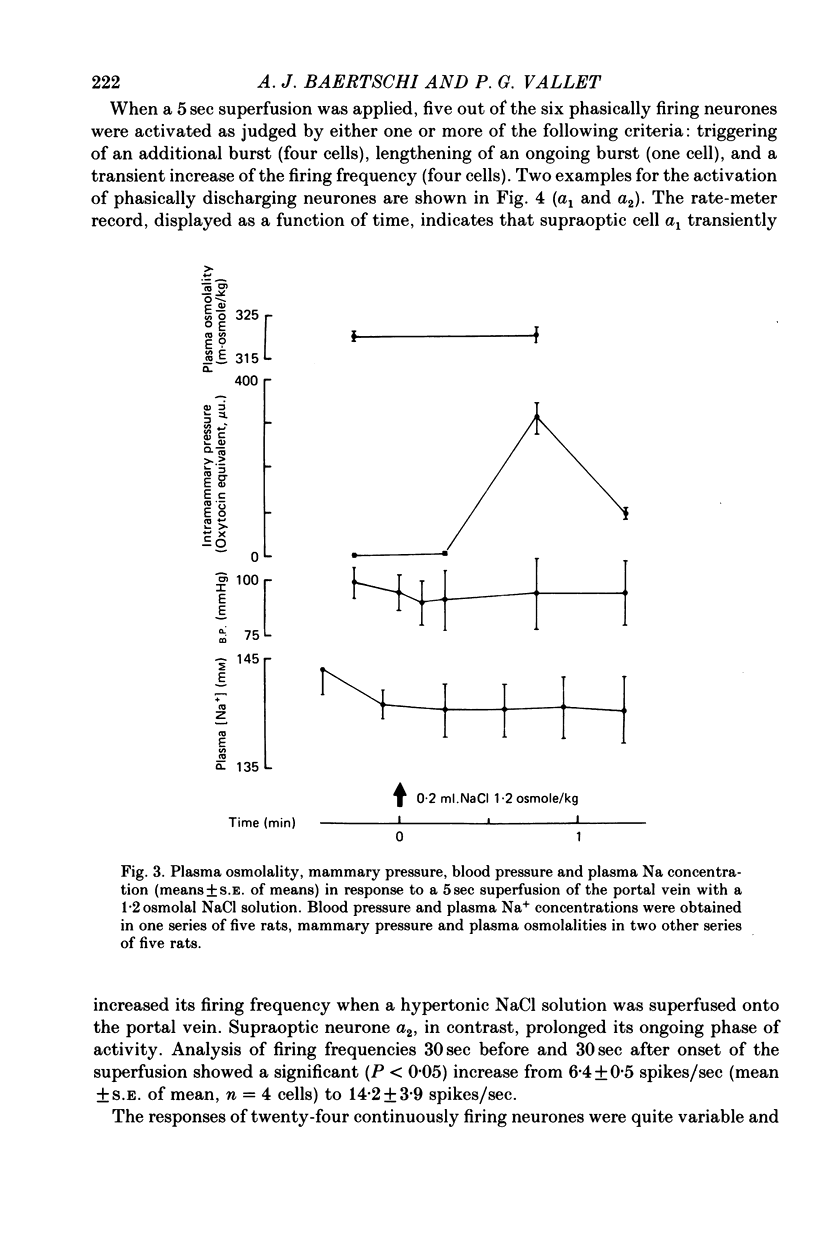
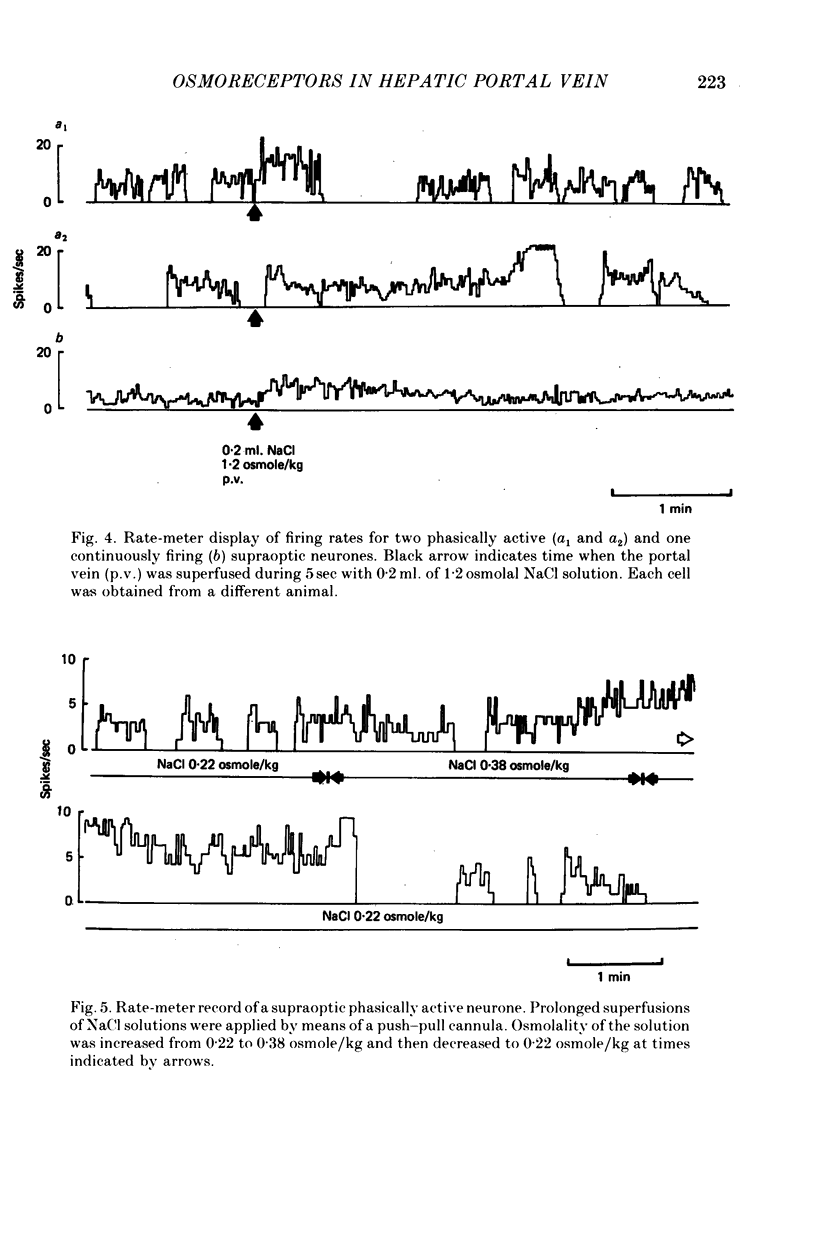
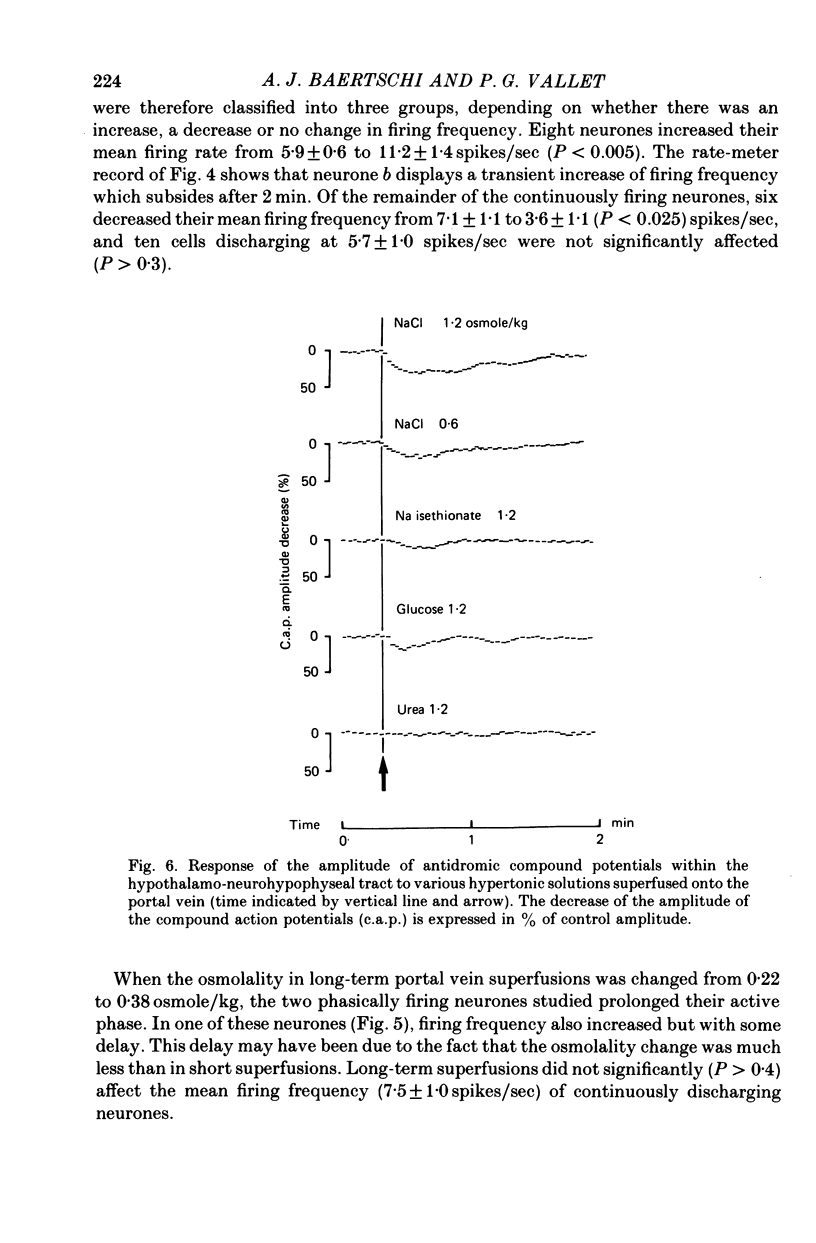
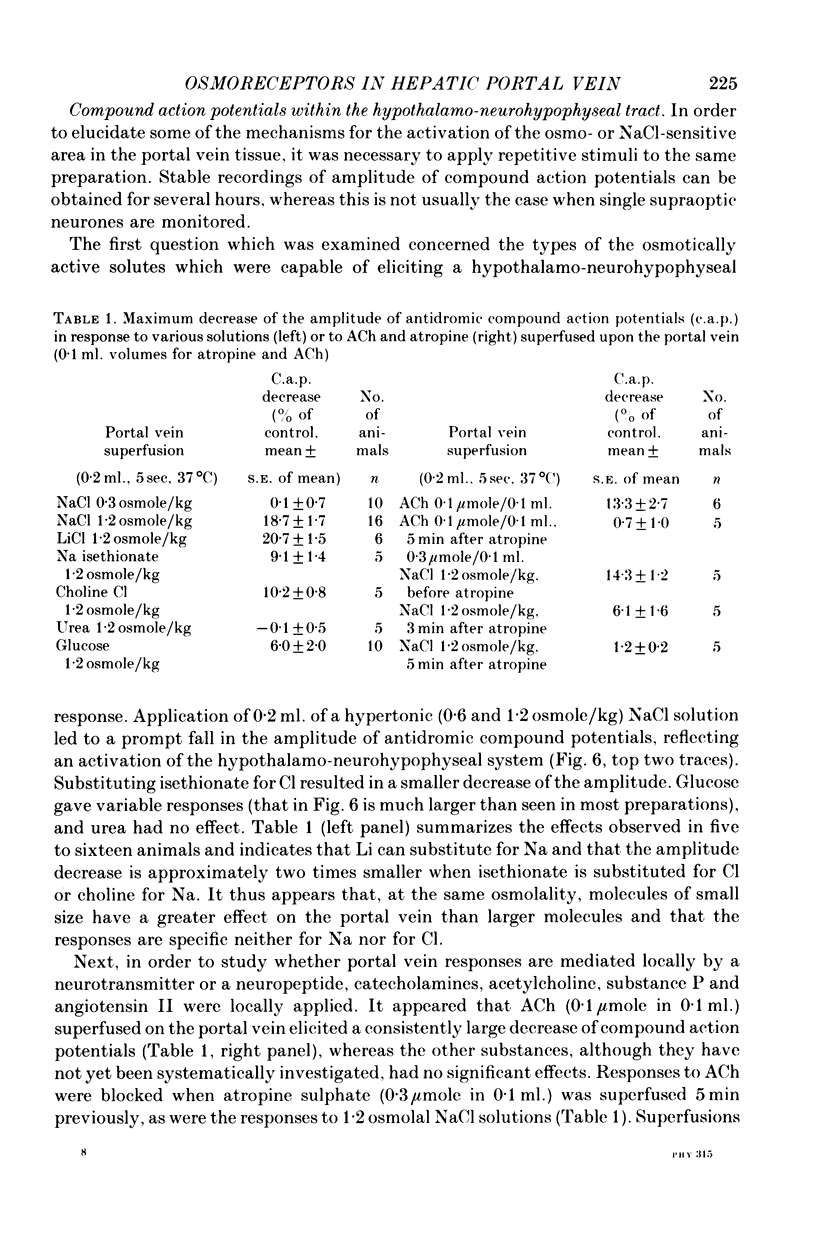
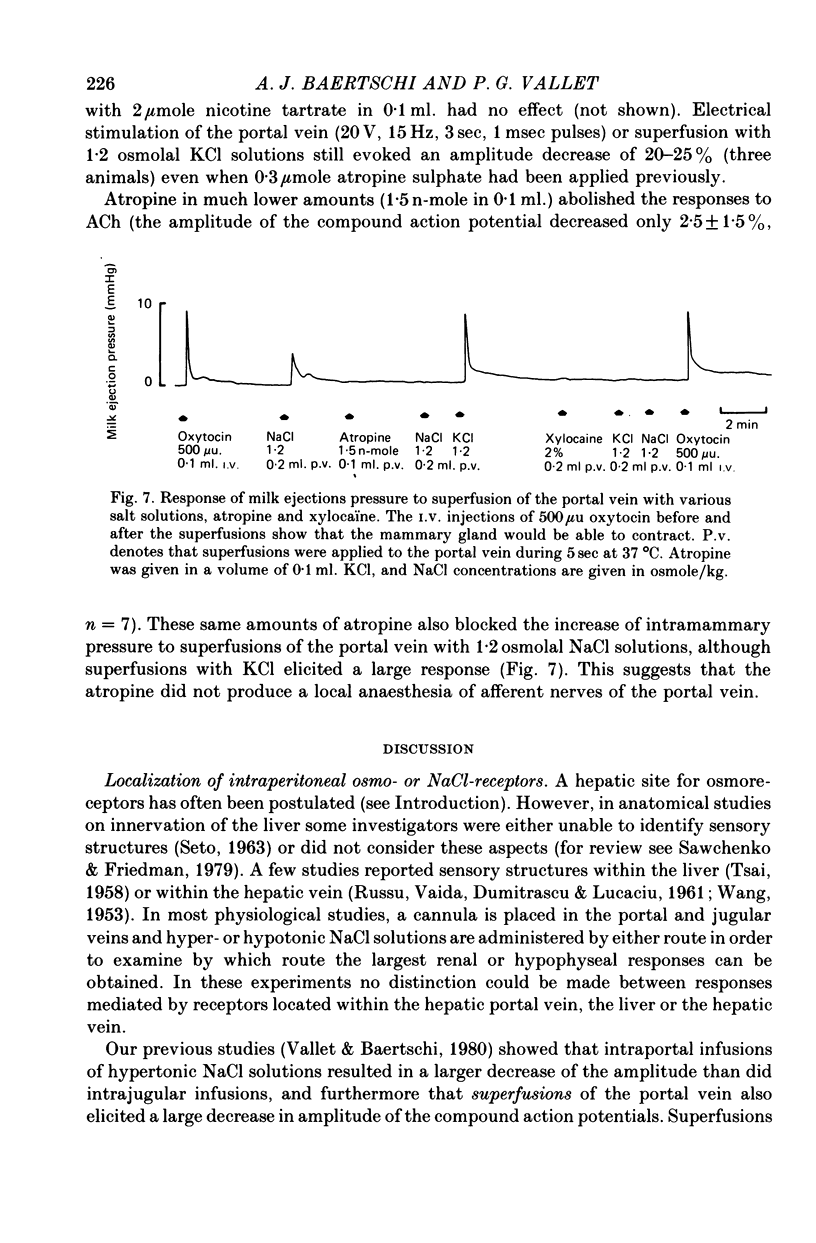
1. The role of intraperitoneal osmoreceptors in hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal control was studied in urethane- or nembutal-anaesthetized rats. Plasma samples were taken for radioimmunoassay of arginine vasopressin, and the electrical activity of single supraoptic endocrine neurones and of the hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal tract were monitored during superfusion of the hepatic portal vein with hypo-, iso- and hypertonic solutions. 2. Plasma arginine vasopressin increased within 1 min following superfusion with 0.3-0.9 osmolal NaCl solutions in a dose-related manner from basal levels of 30 pg/ml, to 170 pg/ml. Prior superfusion with xylocaine or intravenous infusions of 800 micrograms atropine-methyl bromate abolished this response, although vasopressin was still released to nicotine in atropine-blocked rats. 3. Portal vein superfusions had no significant effects on arterial blood pressure, plasma osmolality and plasma Na concentrations. 4. Forty supraoptic neurones were antidromically activated from the neural lobe/stalk region. Superfusions of the portal vein with NaCl solutions (0.33-1.20 osmole/kg, 37 degrees C, 5-120 sec) stimulated seven out of eight phasically firing and eight out of twenty-four continuously firing neurones. One phasically active, ten continuously firing and four silent cells were not affected, and six continuously firing neurones were inhibited by the superfusions. 5. The amplitude decreases of antidromic compound action potentials in the hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal tract, reflecting an increase of the orthodromic nerve impulse traffic, ranged from 17 to 22% for superfusions with 1.2 osmolal NaCl or LiCl solutions, from 8 to 11% for 1.2 osmolal Na isethionate or choline Cl and from 3 to 9% for 1.2 osmolal glucose; there was no effect when 1.2 osmolal urea and isotonic or hypotonic NaCl solutions were applied. 6. Responses of the amplitude of compound action potentials to superfusions with 1.2 osmolal NaCl solutions or with 0.1 mumole ACh, but not to electrical stimulation of the portal vein or its superfusion with 1.2 osmolal KCl, were abolished by prior application of 0.3 mumole atropine sulphate. Prior superfusions with xylocaine abolished the responses to all stimuli above. 7. These results suggest that within the hepatic portal vein area there are osmosensitive receptor cells and/or nerve terminals which activate the hypothalamoneurohypophyseal system through a peripheral cholinergic mechanism.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Niijima A., Jacobs H. L. An hepatic osmoreceptor mechanism in the rat: electrophysiological and behavioral studies. Am J Physiol. 1976 Oct;231(4):1043–1049. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.4.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aizman R. I., Finkinshtein Ia D. Osmo- i ionnye retseptory pecheni. Fiziol Zh SSSR Im I M Sechenova. 1976 Jan;62(1):128–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews W. H., Orbach J. Sensitivity of nerve endings to changes of osmolarity in the perfused rabbit liver. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):115P–116P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews W. H., Orbach J. Sodium receptors activating some nerves of perfused rabbit livers. Am J Physiol. 1974 Dec;227(6):1273–1275. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.6.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews W. H., Palmer J. F. Afferent nervous discharge from the canine liver. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1967 Jul;52(3):269–276. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1967.sp001912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baertschi A. J., Dreifuss J. J. The antidromic compound action potential of the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial tract, a tool for assessing posterior pituitary activity in vivo. Brain Res. 1979 Aug 10;171(3):437–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Keynes R. D., Manil J., Shaw T. I., Steinhardt R. A. The ouabain-sensitive fluxes of sodium and potassium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):459–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisset G. W., Clark B. J., Haldar J., Harris M. C., Lewis G. P., Rocha e Silva R., Jr The assay of milk-ejecting activity in the lactating rat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Nov;31(3):537–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb00418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake W. D., Lin K. K. Hepatic portal vein infusion of glucose and sodium solutions on the control of saline drinking in the rat. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:129–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimble M. J., Dyball R. E. Characterization of the responses of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones in the supraoptic nucleus to osmotic stimulation. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimble M. J., Dyball R. E., Forsling M. L. Oxytocin release following osmotic activation of oxytocin neurones in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:69–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chwalbińska-Moneta J. Role of hepatic portal osmoreception in the control of ADH release. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):E603–E609. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.6.E603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. J., Roe J. W., Horrocks P. A comparison of sodium excretion following the infusion of saline into systemic and portal veins in the dog: evidence for a hepatic role in the control of sodium excretion. Clin Sci. 1967 Dec;33(3):481–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennhardt R., Ohm W. W., Haberich F. J. Die Ausschaltung der Leberäste des N. vagus an der wachen Ratte und ihr Einfluss auf die hepatogene Diurese--indirekter Beweis für die afferente Leitung der Leber-Osmoreceptoren über den N. vagus. Pflugers Arch. 1971;328(1):51–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00587360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dogterom J., Van Wimersma Greidanus T. B., Swabb D. F. Evidence for the release of vasopressin and oxytocin into cerebrospinal fluid: measurements in plasma and CSF of intact and hypophysectomized rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1977;24(2):108–118. doi: 10.1159/000122702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Harris M. C., Tribollet E. Excitation of phasically firing hypothalamic supraoptic neurones by carotid occlusion in rats. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(2):337–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasby M. A., Ramsay D. J. Hepatic osmoreceptors? J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):765–776. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberich F. J., Aziz O., Nowacki P. E. Uber einen osmoreceptorisch tätigen Mechanismus in der Leber. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965 Jul 16;285(1):73–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberich F. J. Osmoreception in the portal circulation. Fed Proc. 1968 Sep-Oct;27(5):1137–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. C., Dreifuss J. J., Legros J. J. Excitation of phasically firing supraoptic neurones during vasopressin release. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):80–82. doi: 10.1038/258080b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward J. N., Jennings D. P. Activity of magnocellular neuroendocrine cells in the hypothalamus of unanaesthetized monkeys. II. Osmosensitivity of functional cell types in the supraoptic nucleus and the internuclear zone. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;232(3):545–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOIZUMI K., ISHIKAWA T., BROOKS C. M. CONTROL OF ACTIVITY OF NEURONS IN THE SUPRAOPTIC NUCLEUS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Sep;27:878–892. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.5.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapteina F. W., Motz W., Schwartz-Porsche D., Gauer O. H. Comparison of renal responses to 5% saline infusions into vena portae and vena cava in conscious dogs. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Apr 25;374(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00585693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski S., Drzewiecki K. The role of osmoreception in portal circulation in control of water intake in dogs. Acta Physiol Pol. 1973;24(2):325–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze D. L., Saum W. R., Brown A. M. Sodium sensitivity of baroreceptors mediates reflex changes of blood pressure and urine flow. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):75–78. doi: 10.1038/267075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS H. P. Pain in acute and chronic diseases of the liver. Ann Intern Med. 1951 Oct;35(4):878–888. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-35-4-878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin K. K., Blake W. D. Hepatic sodium receptor in control of saline drinking behavior. Commun Behav Biol. 1971 Apr;5(6):359–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A. Afferent discharges from osmoreceptors in the liver of the guinea pig. Science. 1969 Dec 19;166(3912):1519–1520. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3912.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijima A. Afferent discharges from venous pressoreceptors in liver. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jan;232(1):C76–C81. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.1.C76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passo S. S., Thornborough J. R., Rothballer A. B. Hepatic receptors in control of sodium excretion in anesthetized cats. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):373–375. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B., Dyball R. E. Electrophysiological differentiation of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr;196(1125):367–384. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSU I. G., VAIDA A., DUMITRASCU D., LUCACIU O. [Contributions to innervation of the liver; nerve pathways of the hepatic vein in man]. Acta Anat (Basel) 1961;44:70–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers R. C., Novin D., Butcher L. L. Electrophysiological and neuroanatomical studies of hepatic portal osmo- and sodium-receptive afferent projections within the brain. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1979 Dec;1(2):183–202. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(79)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. G., Davis J. O., Robb C. A., Baumber J. S., Johnson J. A., Wright F. S. Lack of evidence for a hepatic osmoreceptor mechanism in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jan;218(1):42–45. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandhoy J. W., Williamson H. E. Evidence for an hepatic role in the control of sodium excretion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):419–422. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSAI T. L. [A histological study of sensory nerves in the liver]. Acta Neuroveg (Wien) 1958;17(3-4):354–385. doi: 10.1007/BF01227774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallet P., Baertschi A. J. Sodium-chloride sensitive receptors located in hepatic portal vein of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1980 May 1;17(3):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. D., Arnauld E., Nicolescu-Catargi A. Osmoreceptors and neurosecretory cells in the supraoptic complex of the unanaesthetized monkey. Brain Res. 1972 Oct 13;45(1):278–281. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90238-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakerley J. B., Poulain D. A., Dyball R. E., Cross B. A. Activity of phasic neurosecretory cells during haemorrhage. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):82–84. doi: 10.1038/258082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Azuma T., Matsuda K. Neurosecretory cell: capable of conducting impulse in rats. Science. 1966 Nov 11;154(3750):778–779. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3750.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


