Abstract
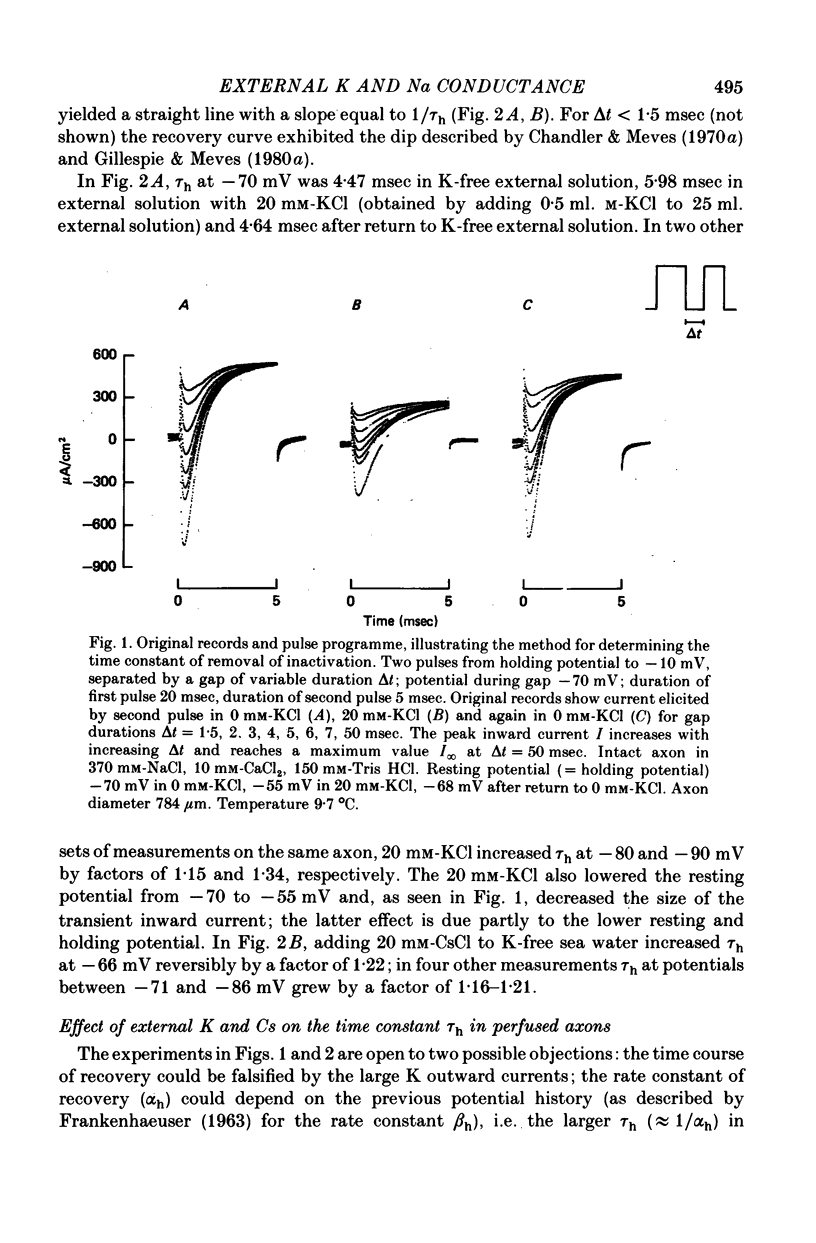
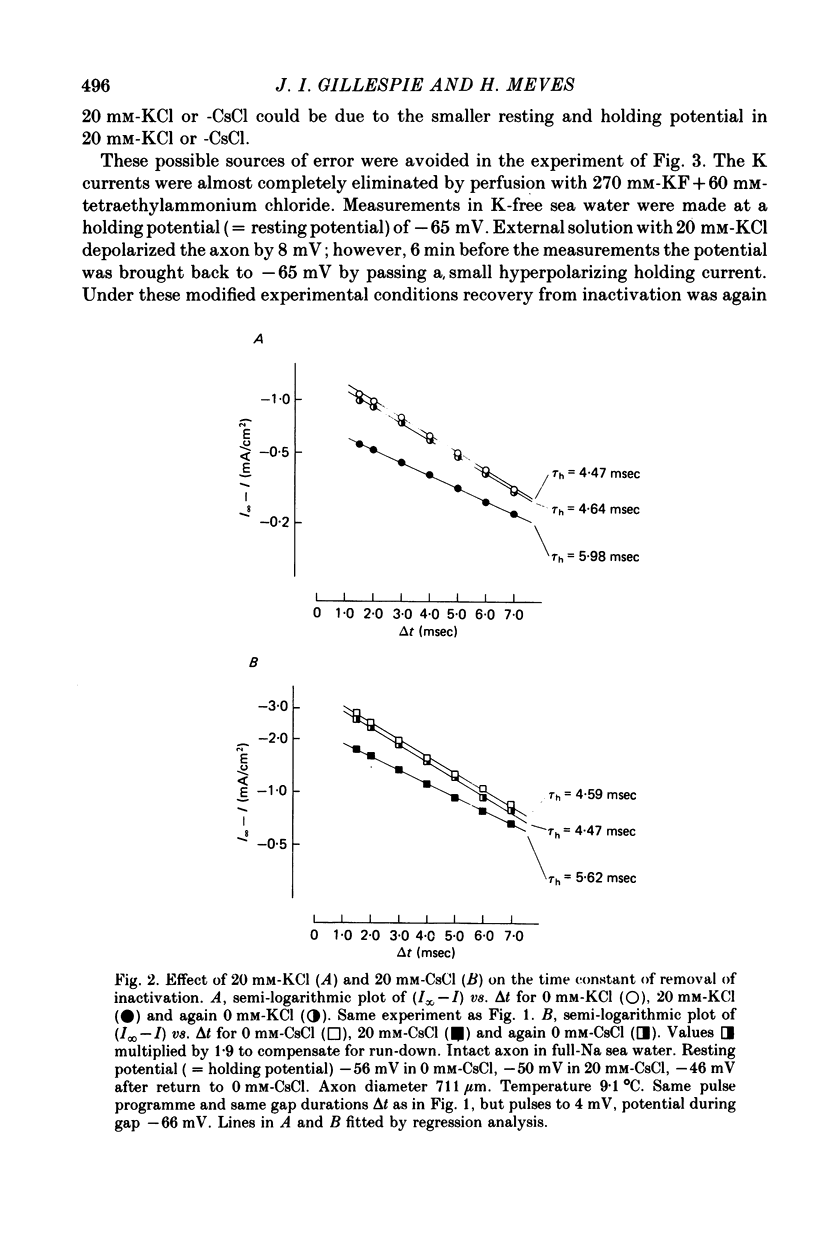
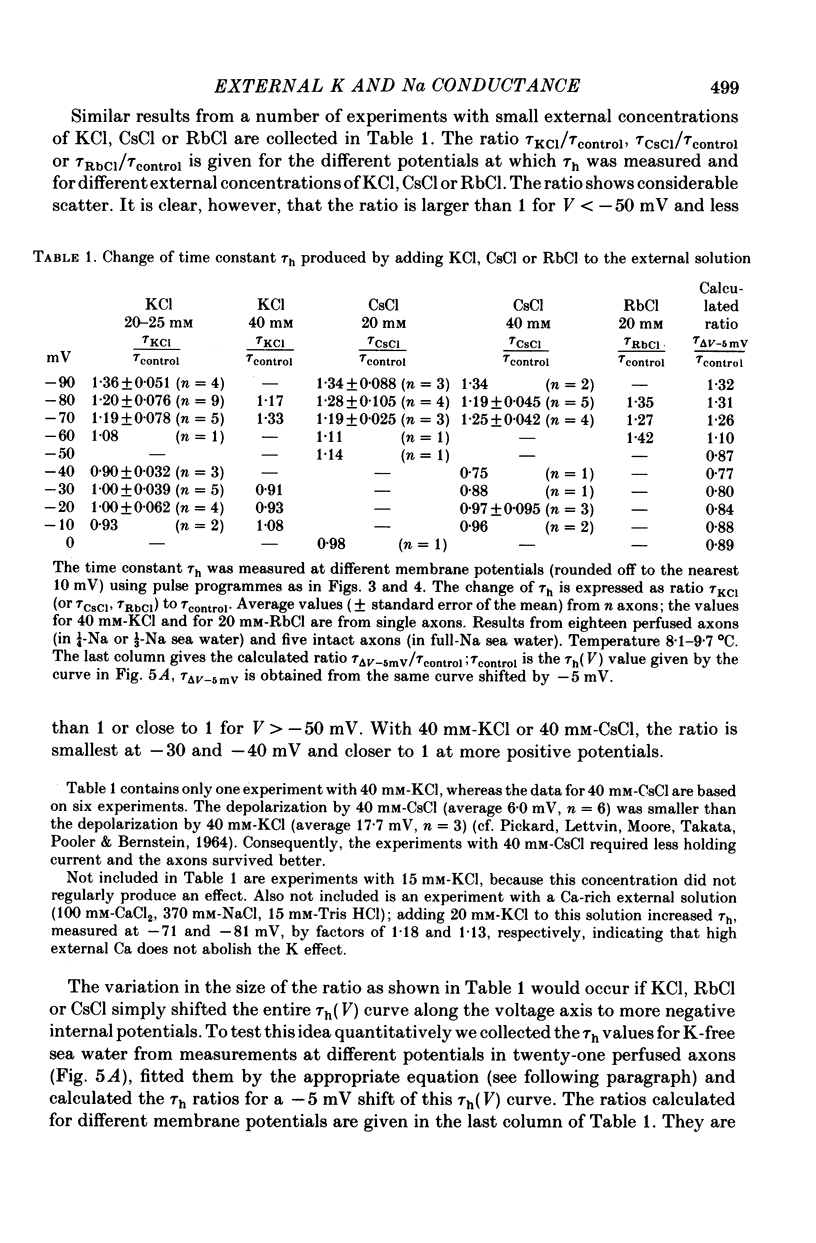
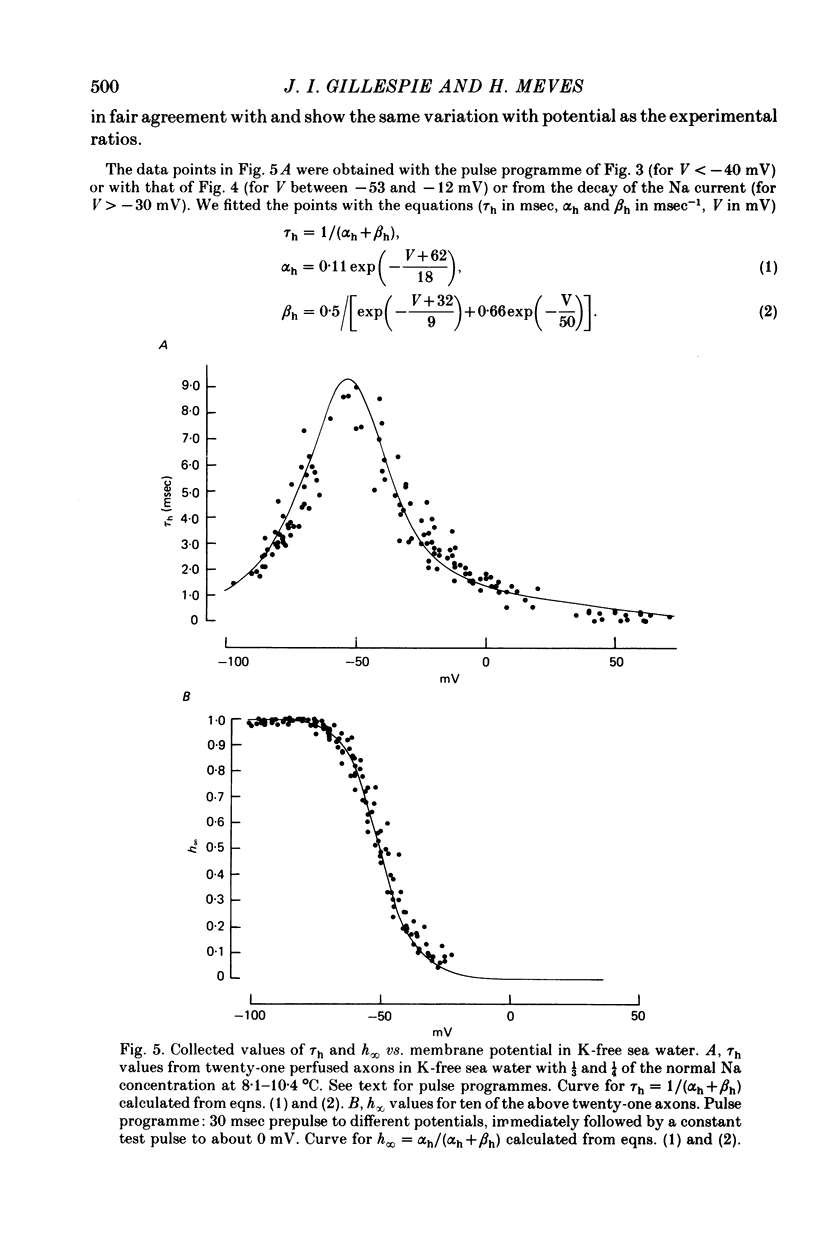
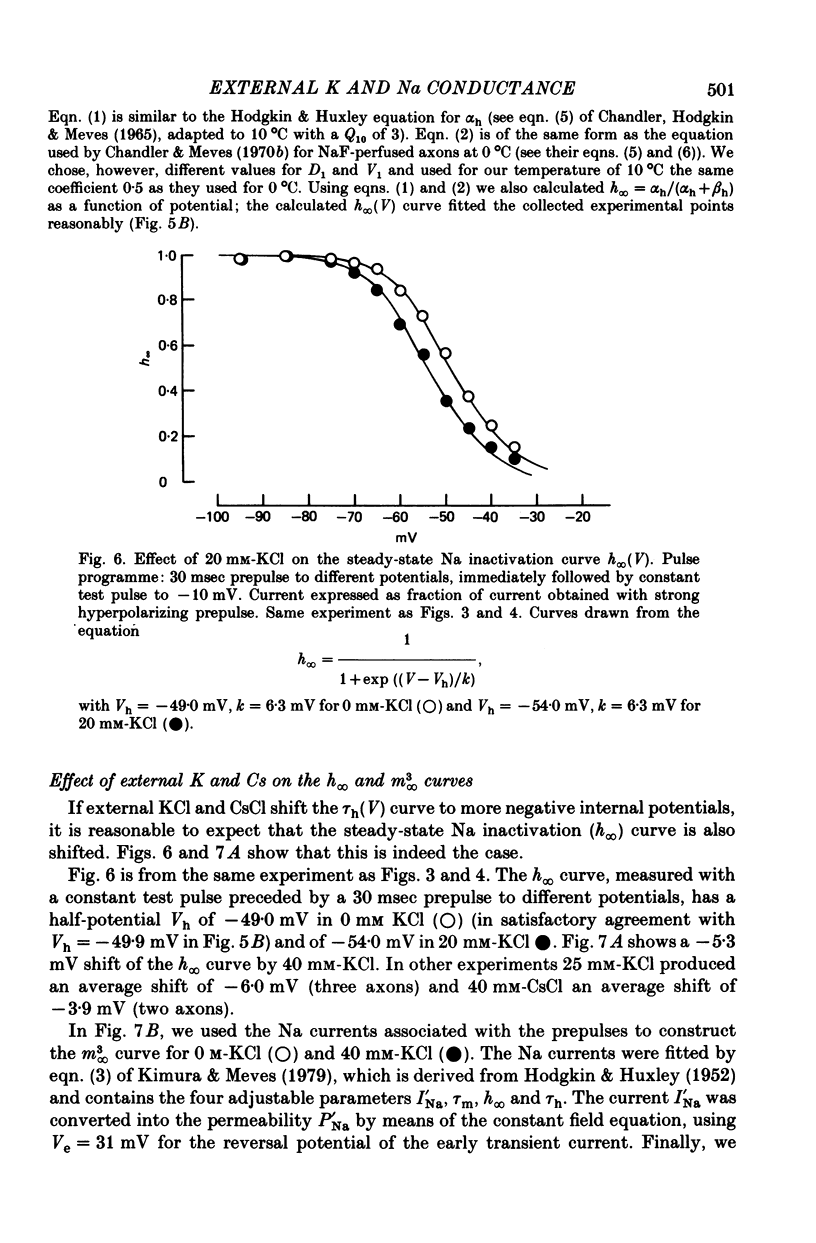
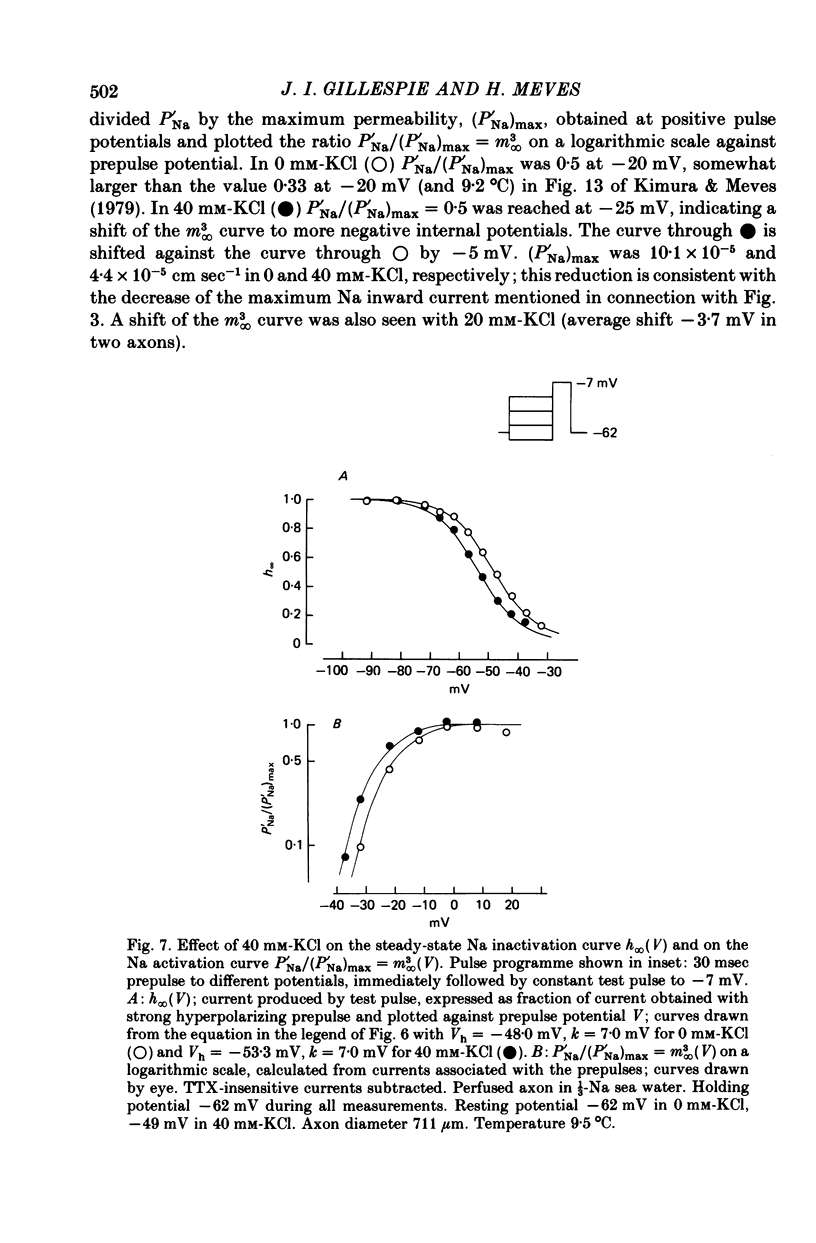
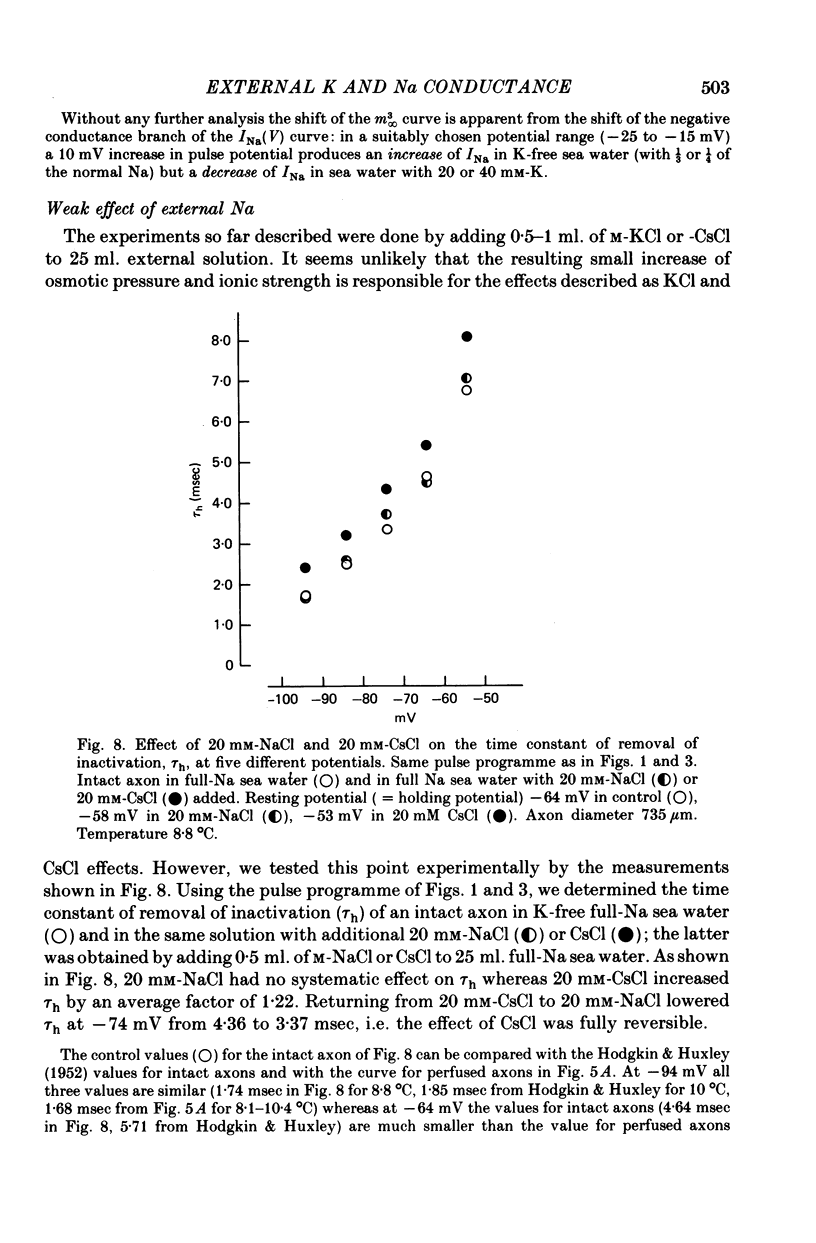
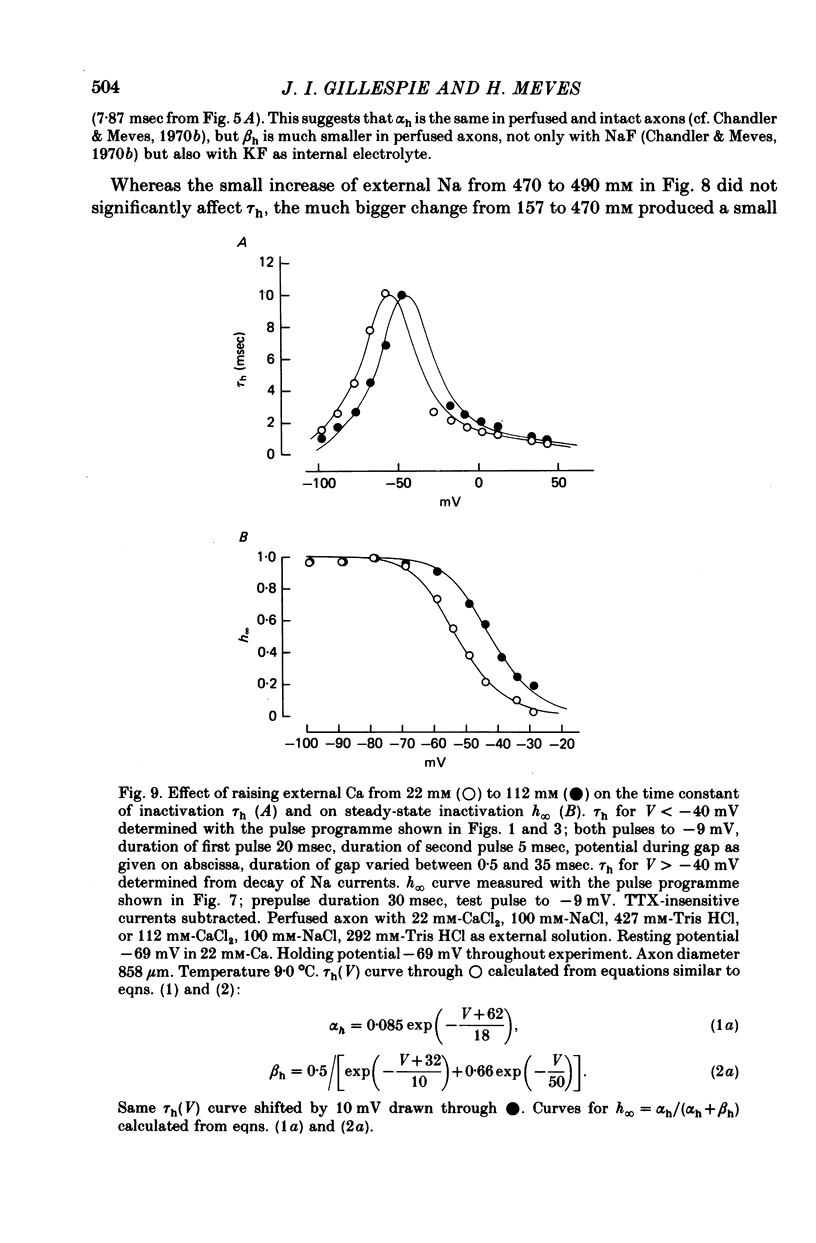
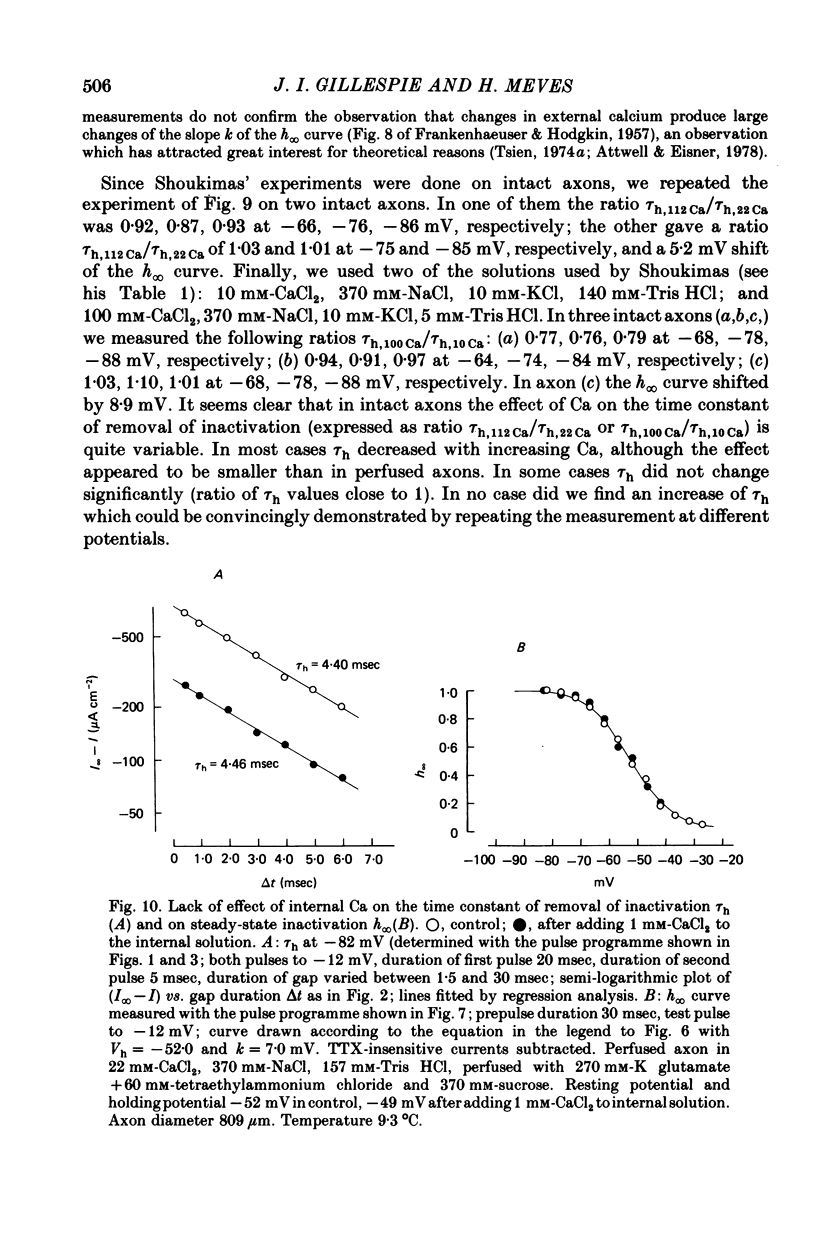
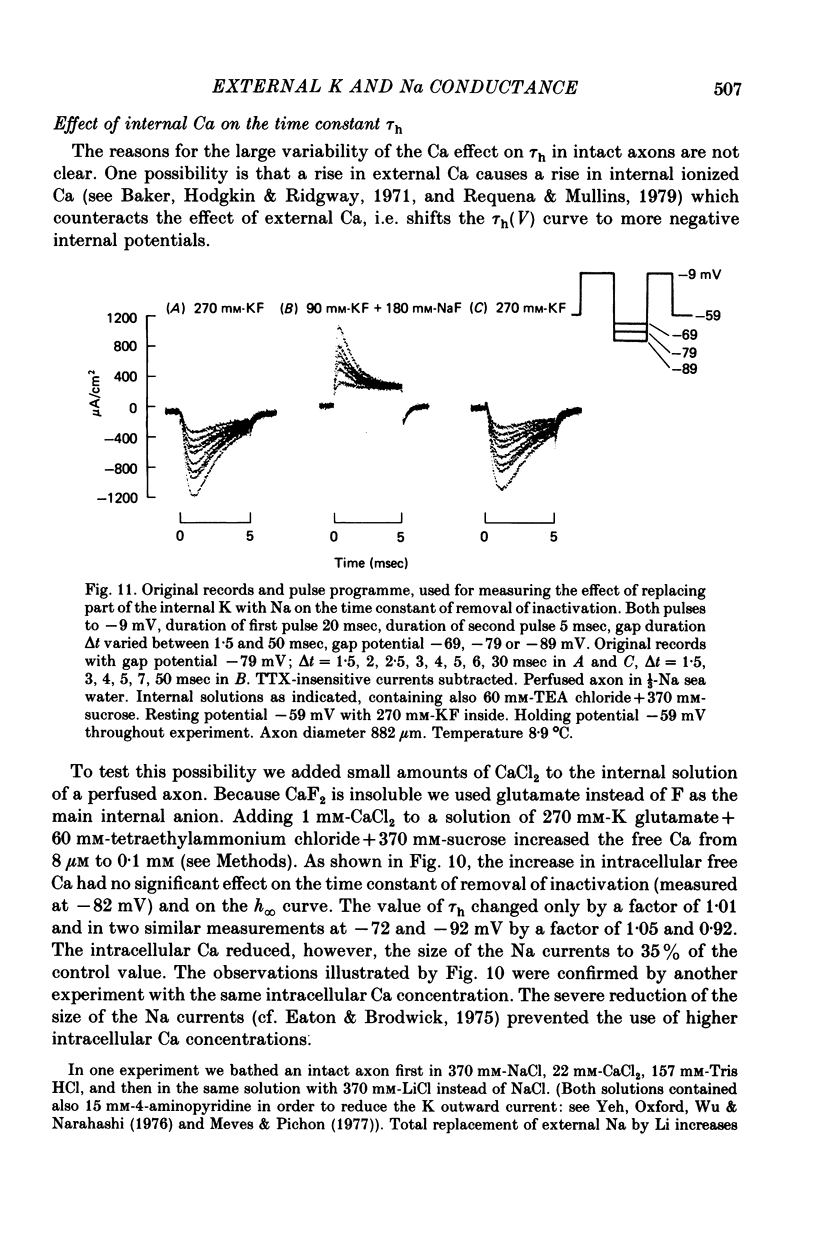
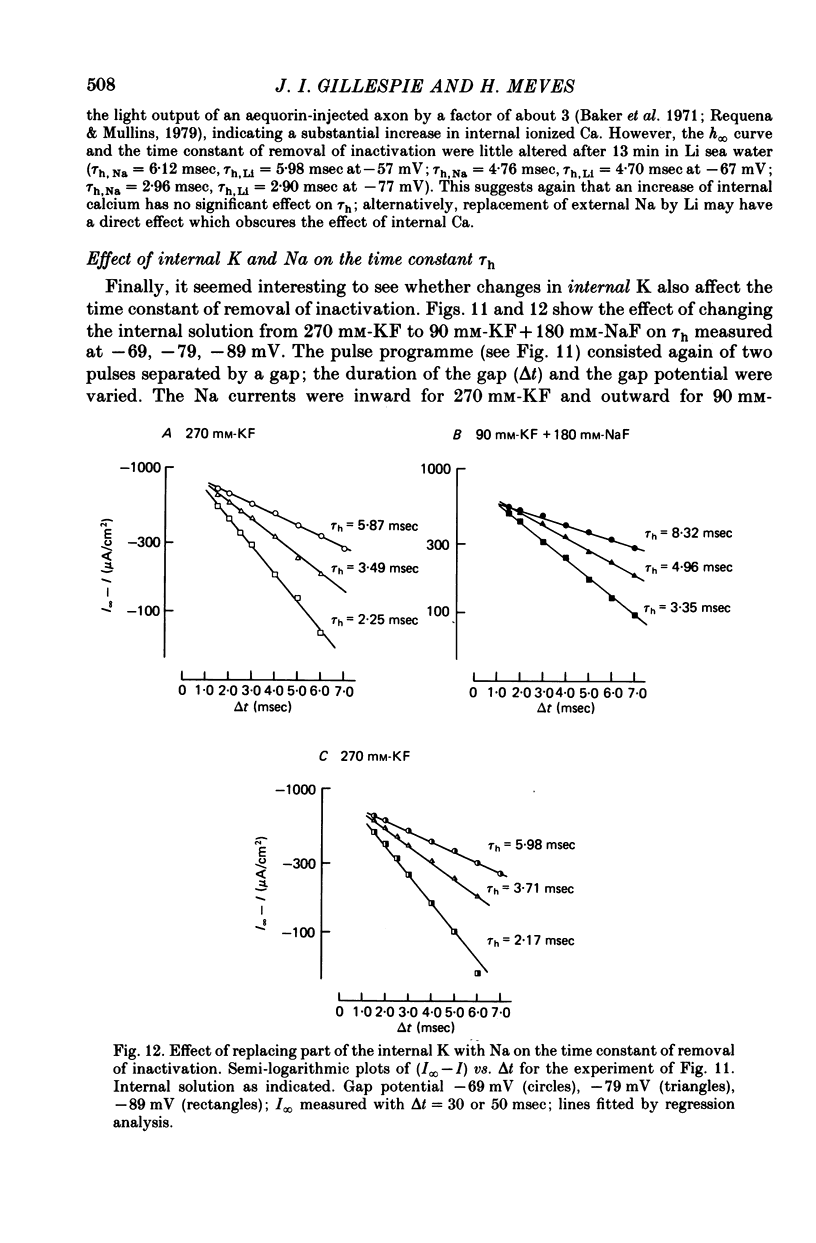
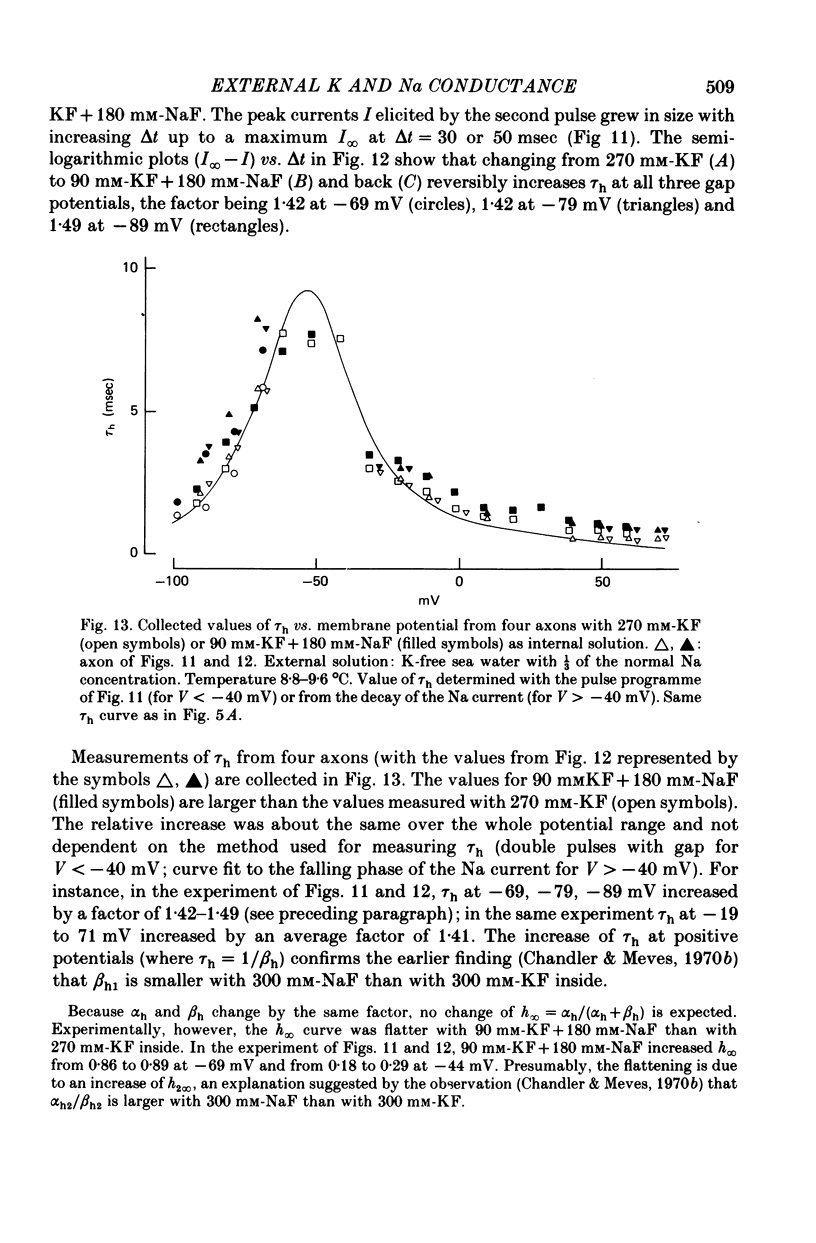
1. The effect of external and internal electrolytes on the parameters of the Na conductance, in particular on the time constant of removal of Na inactivation, was studied in intact and perfused squid giant axons under voltage-clamp conditions. 2. Adding 20-40 mM-KCl, -CsCl or -RbCl to K-free sea water reversibly increased the time constant of removal of inactivation by a factor of about 1.3; adding 20 mM-NaCl had no effect. The time constant of development of inactivation was decreased. The results are consistent with a -5 mV shift of the tau h(V) curve. The sodium activation (m infinity 3) and inactivation (h infinity) curves were shifted by the same amount. 3. Raising external Ca, by contrast, decreased the time constant of removal of inactivation and increased the time constant of development of inactivation, i.e. shifted the tau h(V) curve to more positive internal potentials. A free Ca concentration of 0.1 mM in the internal solution had no effect on Na inactivation. 3. The observations are compatible with the idea that external K, Cs or Rb interfere with the binding of Ca to negative fixed charges at the outer side of the membrane, thereby causing a shift in the opposite direction to the shift produced by raising external Ca. 5. Replacing two thirds of the internal K by Na reversibly increased the time constant of removal of sodium inactivation and moved the tau h(V) curve in the vertical direction.
Full text
PDF

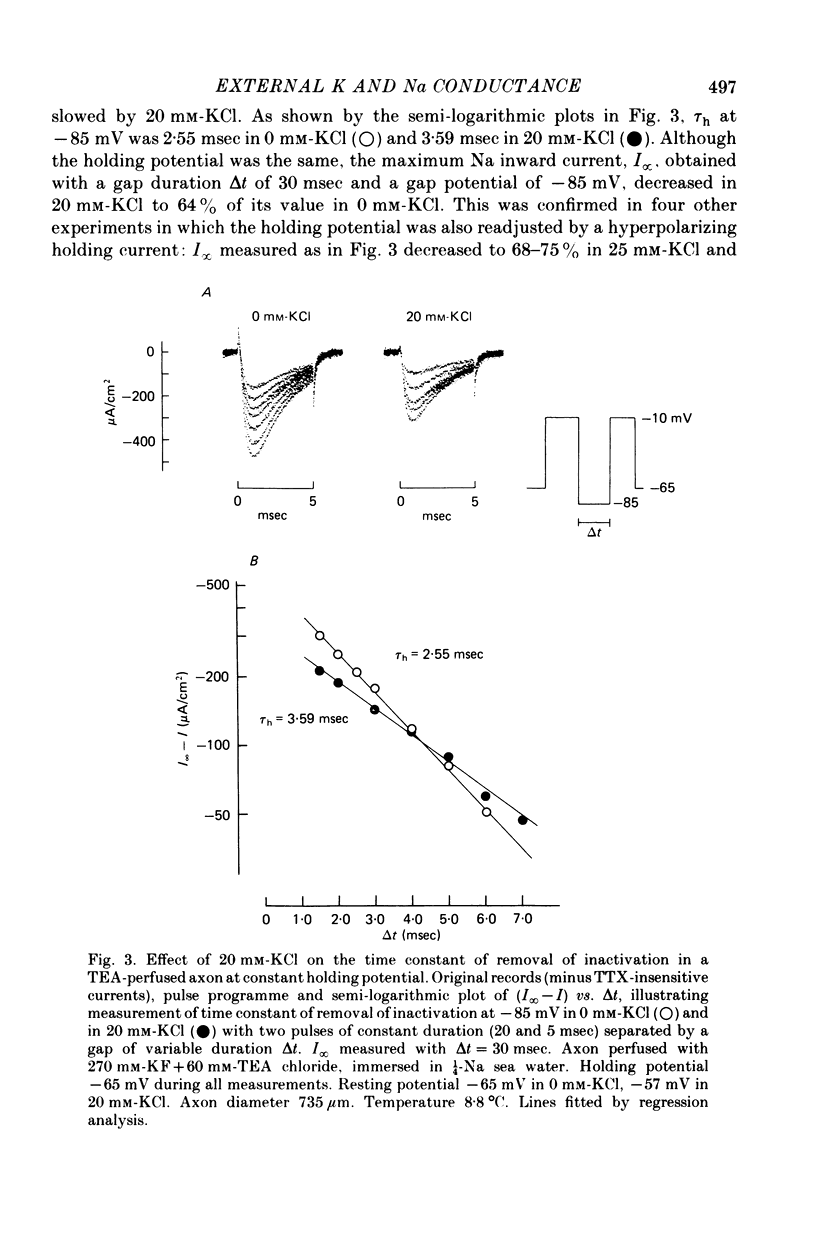






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman W. J., Jr, Palti Y. The effects of external potassium and long duration voltage conditioning on the amplitude of sodium currents in the giant axon of the squid, Loligo pealei. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):589–606. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
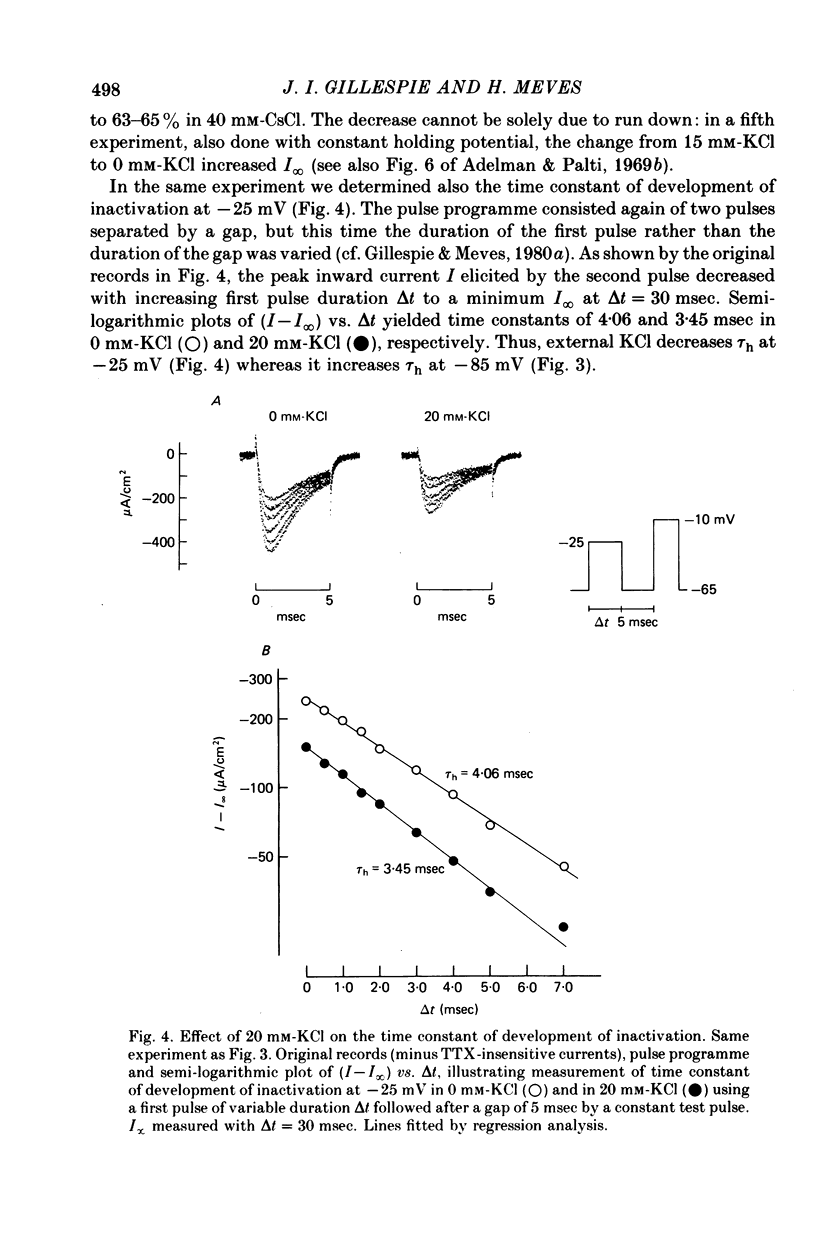
- Adelman W. J., Jr, Palti Y. The influence of external potassium on the inactivation of sodium currents in the giant axon of the squid, Loligo pealei. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Jun;53(6):685–703. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.6.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Eisner D. Discrete membrane surface charge distributions. Effect of fluctuations near individual channels. Biophys J. 1978 Dec;24(3):869–875. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85426-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Calcium entry in response to maintained depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T., Lynch C. Effects of internal divalent cations on voltage-clamped squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jun;63(6):675–689. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.6.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T. Effects of ionic concentration on permeability properties of nodal membrane in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. Potential clamp experiments. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Apr;87(4):474–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T., Frankenhaeuser B. Effects of ionic concentration on sodium permeability properties of myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):549–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Evidence for two types of sodium conductance in axons perfused with sodium fluoride solution. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):653–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Rate constants associated with changes in sodium conductance in axons perfused with sodium fluoride. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):679–705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Slow changes in membrane permeability and long-lasting action potentials in axons perfused with fluoride solutions. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):707–728. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney K. R. Extracellular pH selectively modulates recovery from sodium inactivation in frog myelinated nerve. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85183-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arrigo J. S. Possible screening of surface charges on crayfish axons by polyvalent metal ions. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):117–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The after-effects of impulses in the giant nerve fibres of Loligo. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):341–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. INACTIVATION OF THE SODIUM-CARRYING MECHANISM IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:445–451. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenhaeuser B., Arhem P. Steady state current rectification in potential clamped nodes of Ranvier (Xenopus laevis). Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):515–525. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. L., Ehrenstein G. Effect of divalent cations on potassium conductance of squid axons: determination of surface charge. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):447–463. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86396-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. I., Meves H. The time course of sodium inactivation in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:289–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Schauf C. L. Inactivation of the sodium current in Myxicola giant axons. Evidence for coupling to the activation process. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):659–675. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. E., Meves H. The effect of temperature on the asymmetrical charge movement in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:479–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. G., Szabo G., Eisenman G. Divalent ions and the surface potential of charged phospholipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):667–687. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton P. A., Noble D. Proceedings: The role of intracellular calcium ion concentration in mediating the adrenaline-induced acceleration of the cardiac pacemaker potential. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):53P–54P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Pichon Y. The effect of internal and external 4-aminopyridine on the potassium currents in intracellularly perfused squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):511–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G., Ashley C. C. The effect of physiologically occurring cations upon aequorin light emission. Determination of the binding constants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 11;460(2):189–205. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naitoh Y., Yasumasu I. Binding of Ca ions by Paramecium caudatum. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1303–1310. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble S. J. Potassium accumulation and depletion in frog atrial muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;258(3):579–613. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PICKARD W. F., LETTVIN J. Y., MOORE J. W., TAKATA M., POOLER J., BERNSTEIN T. CAESUM IONS DO NOT PASS THE MEMBRANE OF THE GIANT AXON. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Nov;52:1177–1183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.5.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramón F., Anderson N., Joyner R. W., Moore J. W. Axon voltage-clamp simulations. A multicellular preparation. Biophys J. 1975 Jan;15(1):55–69. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85791-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Requena J., Mullins L. J. Calcium movement in nerve fibres. Q Rev Biophys. 1979 Aug;12(3):371–460. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoukimas J. J. Effect of calcium upon sodium inactivation in the giant axon of Loligo pealei. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jan 18;38(3):271–289. doi: 10.1007/BF01871926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somjen G. G. Extracellular potassium in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:159–177. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Effects of epinephrine on the pacemaker potassium current of cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Sep;64(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Mode of action of chronotropic agents in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Does epinephrine act by directly modifying the external surface charge? J Gen Physiol. 1974 Sep;64(3):320–342. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.3.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Dynamics of aminopyridine block of potassium channels in squid axon membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Nov;68(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


