Abstract
1. The efflux of Na in dialysed axons of the squid has been used to monitor the sidedness of the interactions of the Na pump with Na+ ions, K+ ions and ATP. The axons were under conditions such that most of the Na efflux went through the Na pump by means of a complete cycle of ATP hydrolysis.
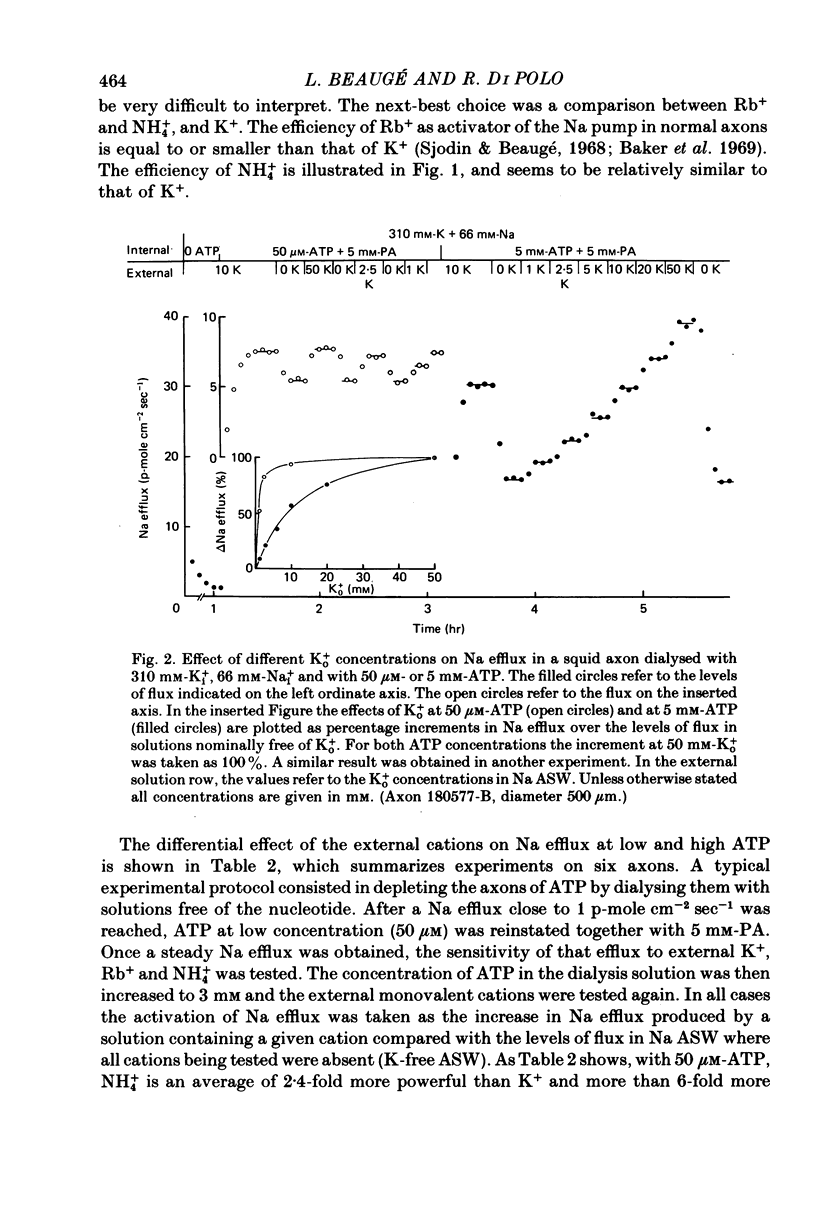
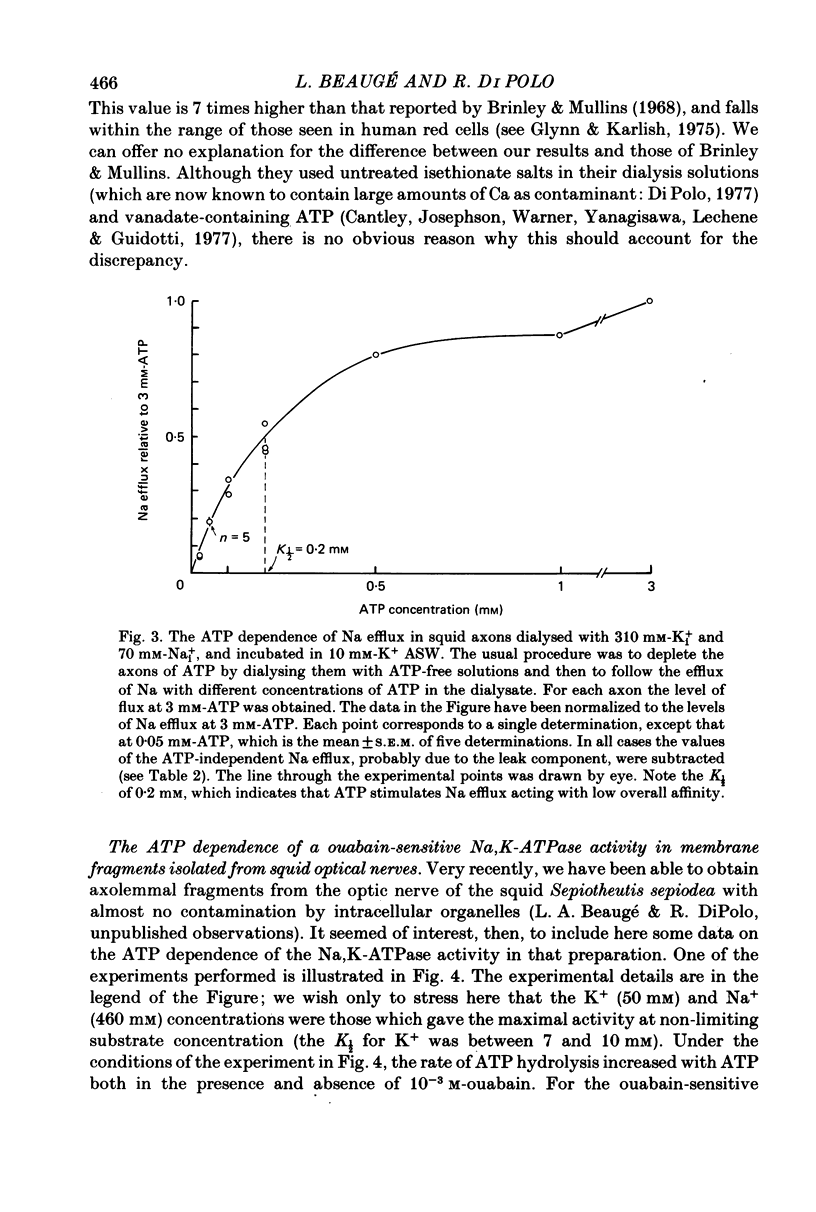
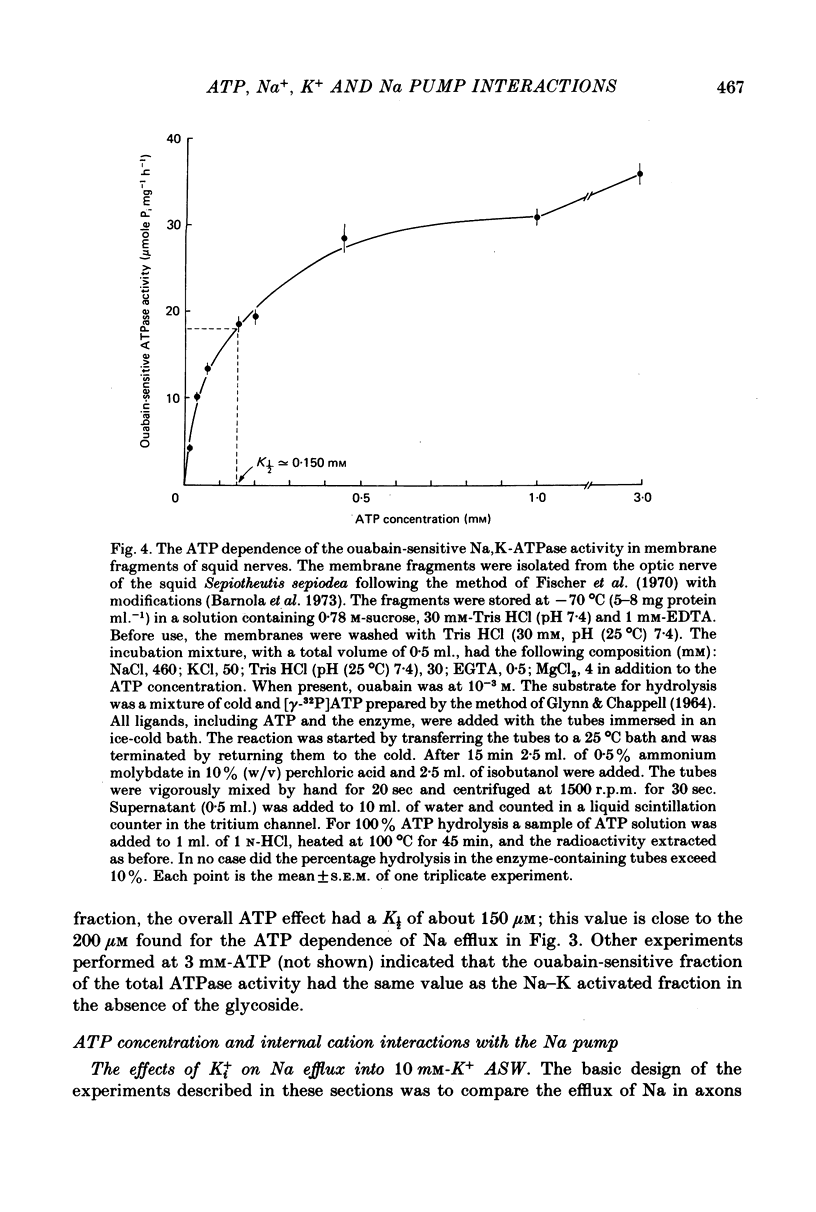
2. With 310 mm-Ki+, 70 mm-Nai+ and 10 mm-K+ artificial sea water (ASW) more than 97% of the Na efflux was abolished by removal of ATP. The efflux of Na was stimulated by ATP with a K½ of about 200 μm. This is similar to the K½ of 150 μm found for the ATP dependence of a ouabain-sensitive Na,K-ATPase activity in membrane fragments isolated from squid optical nerves.
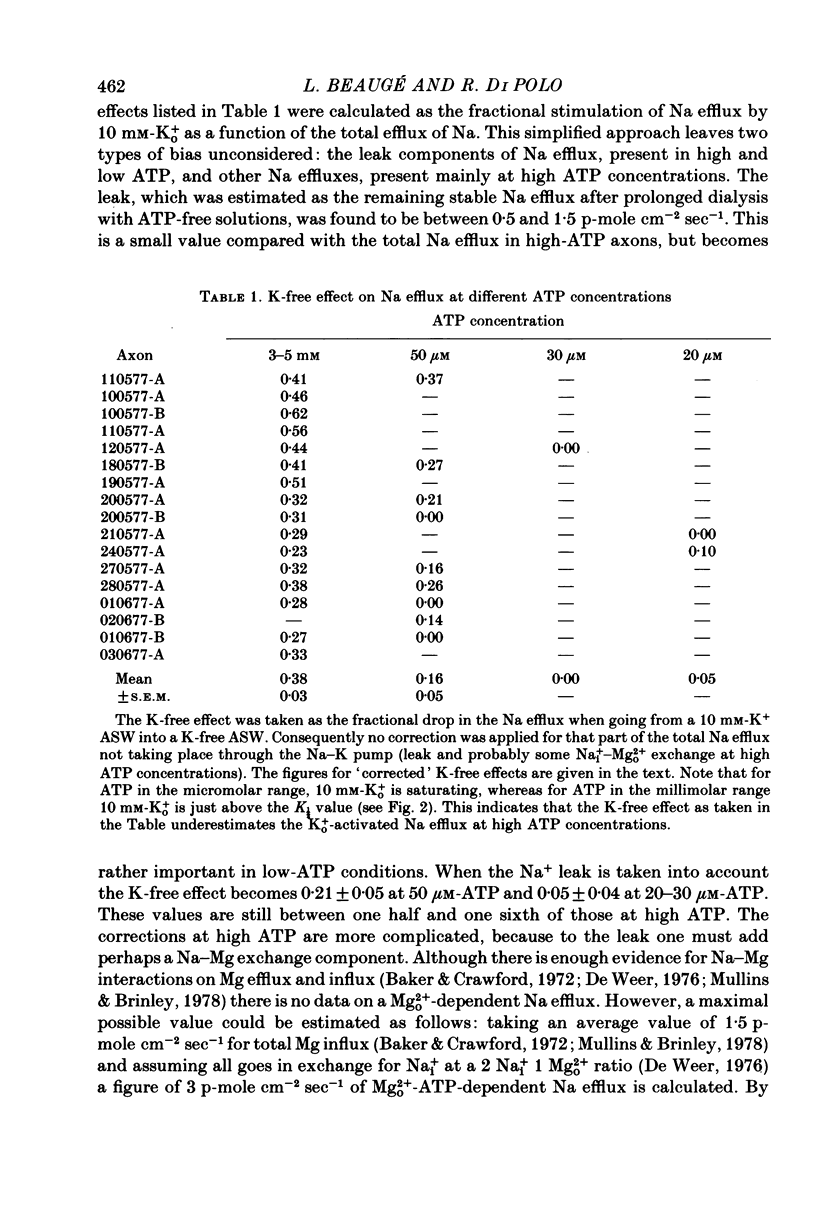
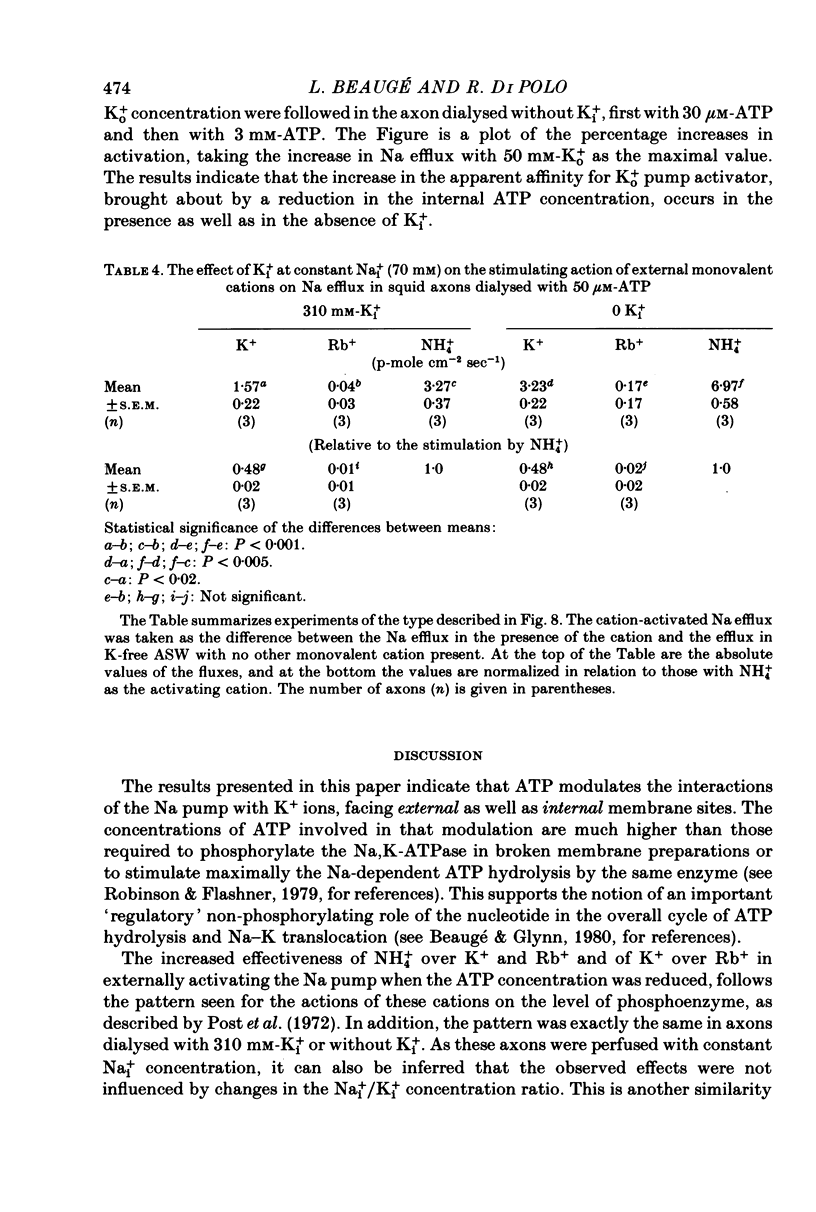
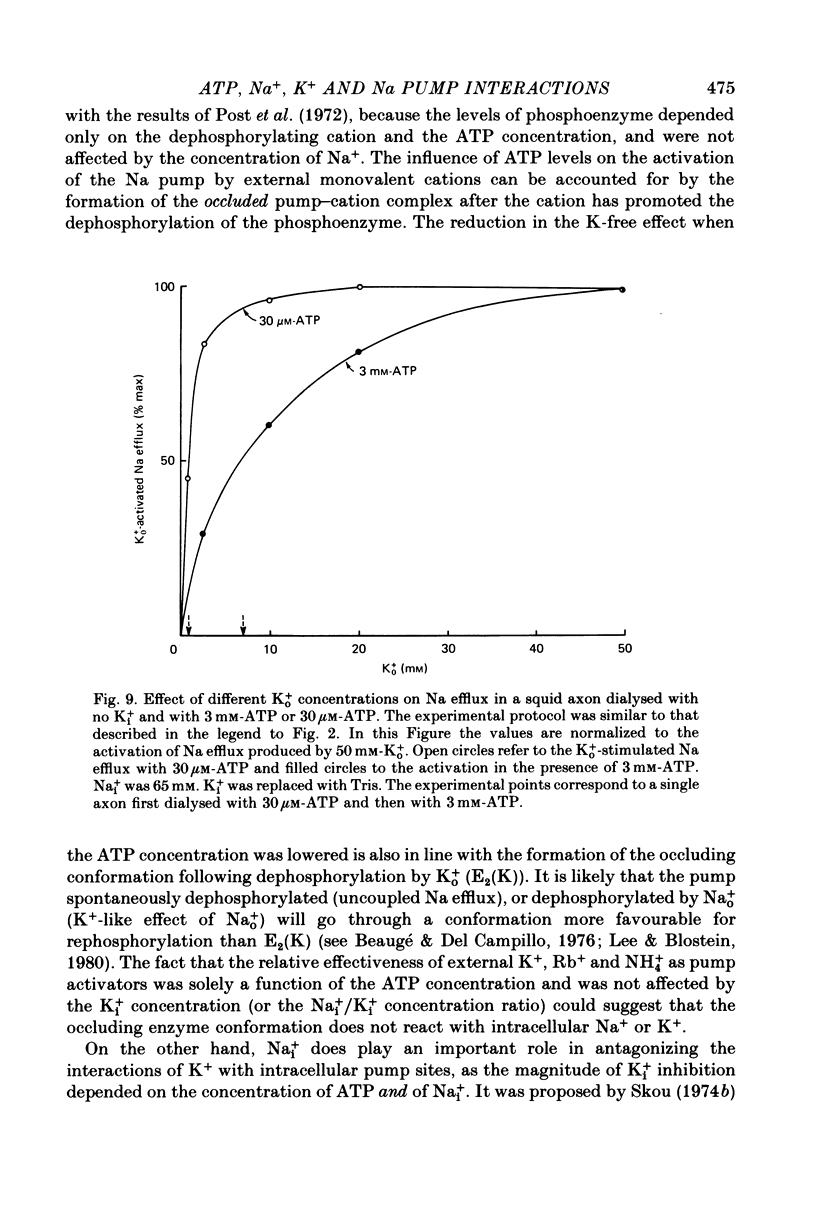
3. A 100-fold reduction in the ATP concentration (from 3-5 mm to 30-50 μm) increased the apparent affinity of the Na pump for Ko+ about 8-fold. In addition, the maximal rate of Ko+-stimulated Na efflux was reduced by a similar factor. Analogous results were seen in axons dialysed with 310 mm-Ki+ or without Ki+.
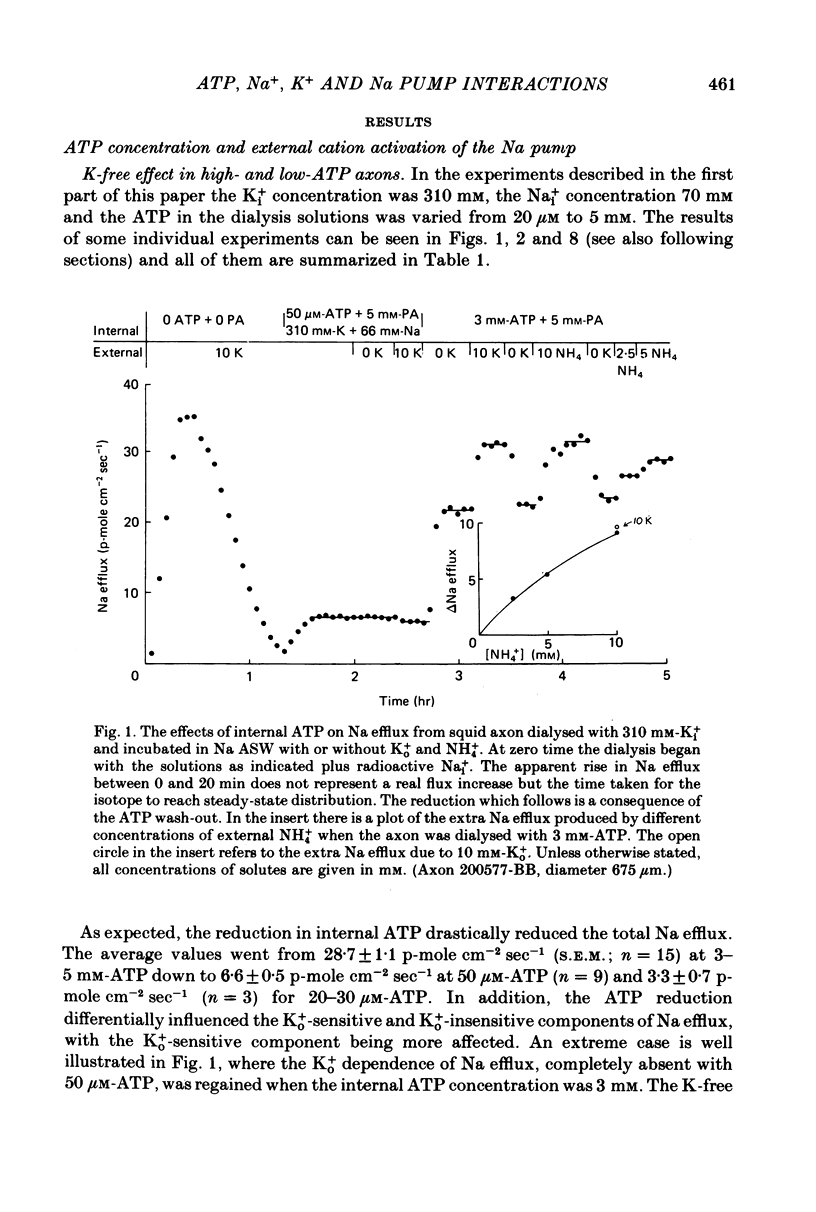
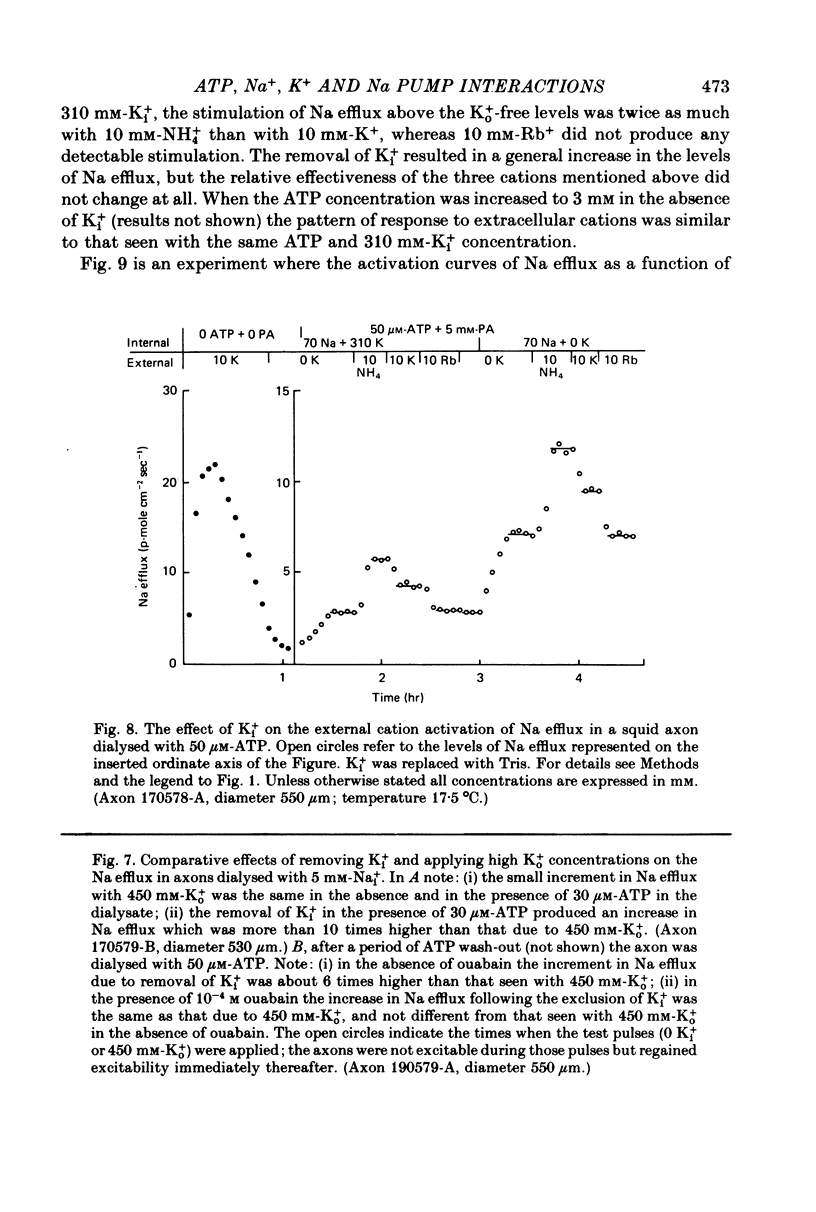
4. The relative effectiveness of external monovalent cations as activators of the Na efflux was a function of the ATP concentration inside the axon. With 3-5 mm-ATP the order of effectiveness was K+ > NH4+ > Rb+. With 30-50 μm-ATP the sequence was NH4+ » K+ » Rb+. These results were not affected by the removal of Ki+.
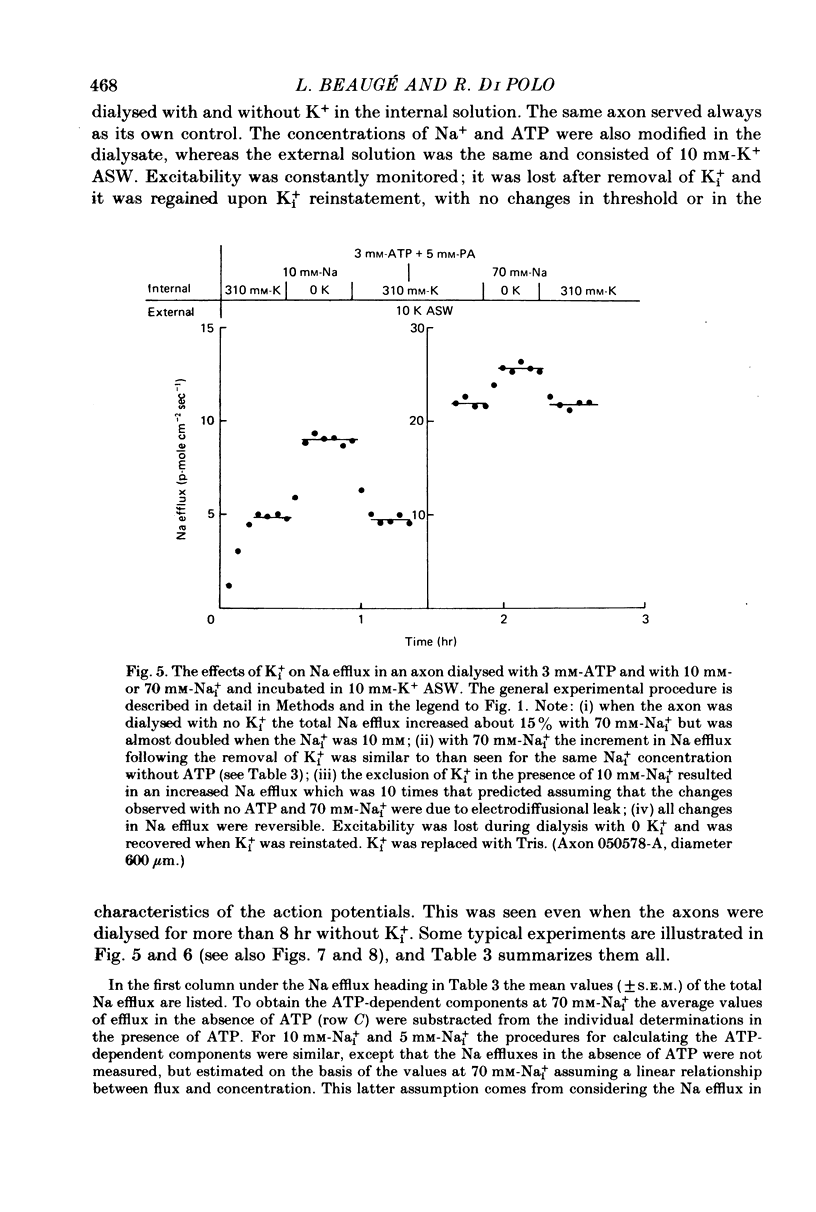
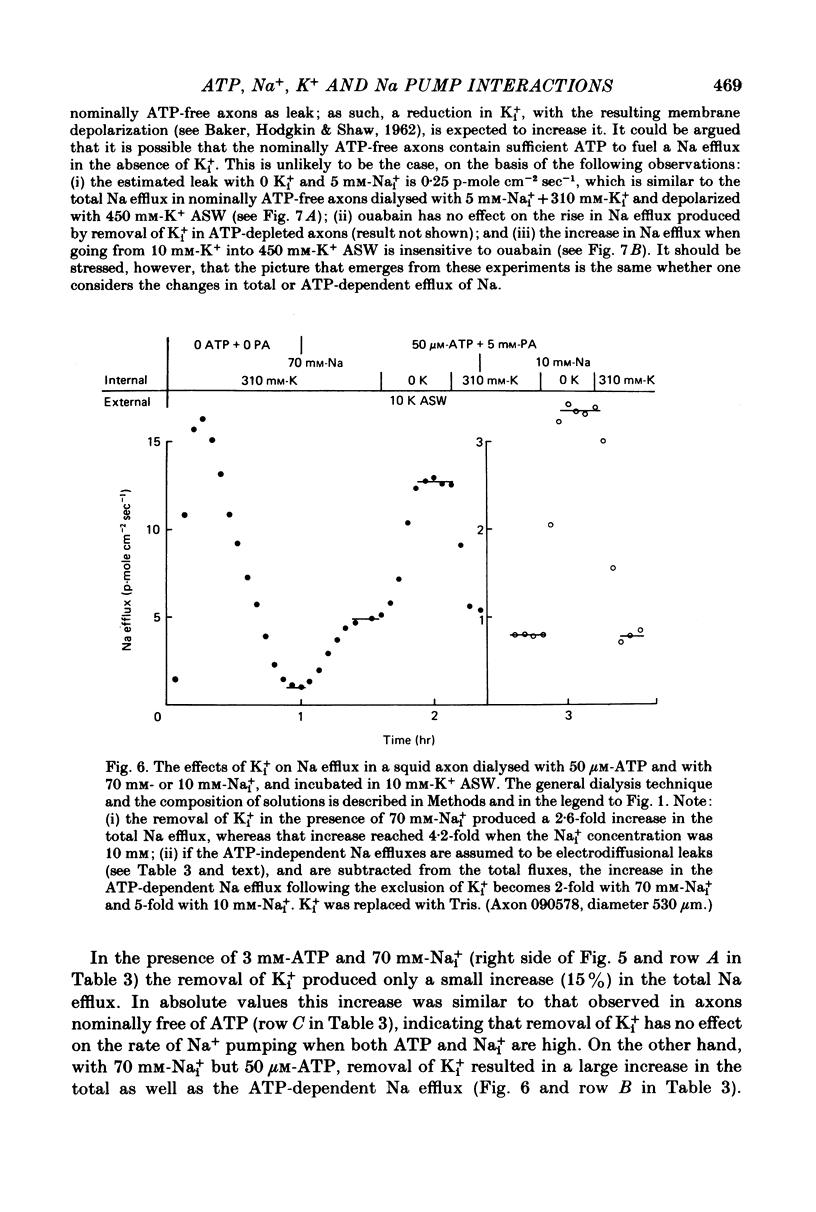
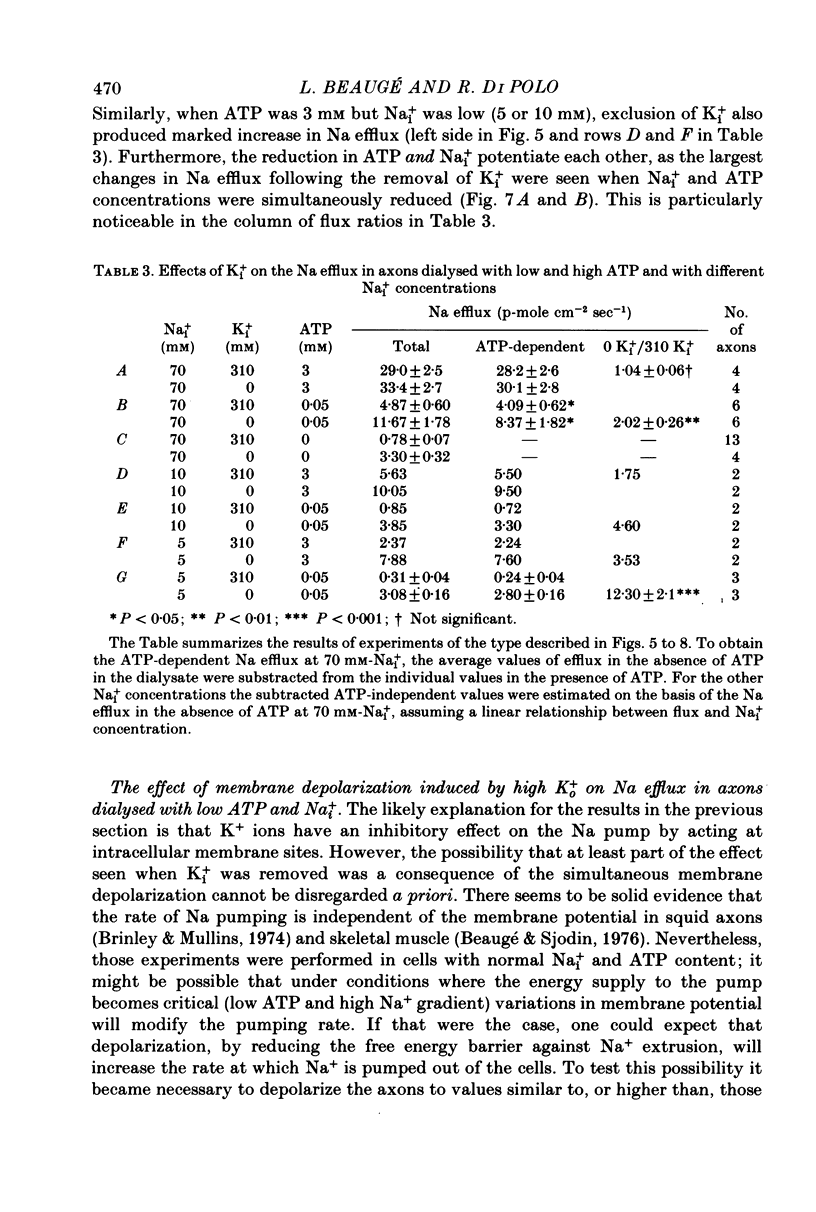
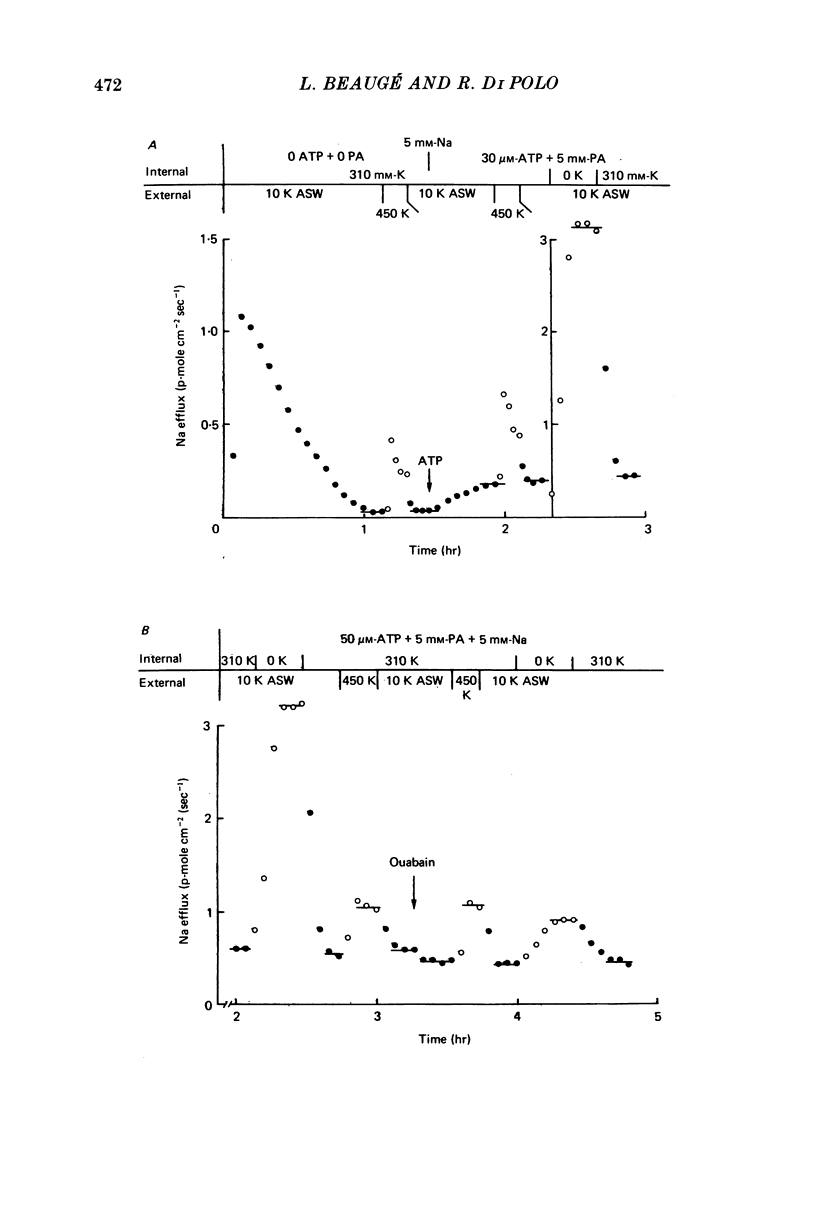
5. When the ATP concentration was 3 mm and the Nai+ concentration 70 mm, the removal of Ki+ produced a slight and reversible increase in the total efflux of Na (15%) and no change in the ATP-dependent Na efflux. When the ATP concentration was reduced to 30-50 μm, or the Nai+ concentration lowered to 5-10 mm, the removal of Ki+ reversibly increased the total and the ATP-dependent efflux of Na. The largest increase in Na efflux was seen when both ATP and Nai+ were simultaneously reduced. The ATP-dependent extra Na efflux resulting from the exclusion of Ki+ was abolished by 10-4 m-ouabain in the sea waters.
6. The increase in the ATP-dependent Na efflux observed in axons dialysed with 0 Ki+ + 10 mm-K+ ASW was not seen in axons perfused with 310 mm-Ki+ + 450 mm-K+ ASW. However, both experimental conditions gave rise to a similar (and small) ATP-independent and ouabain-insensitive efflux of Na. This indicates that the effects on the Na pump of removing Ki+ are not due to the simultaneous membrane depolarization. In addition, it suggests that Ki+ has an inhibitory effect on the Na pump, and that that effect is antagonized by Nai+ and ATP.
7. The present results are consistent with the idea that the same conformation of the Na pump (and Na,K-ATPase) can be reached by interaction with external K+ after phosphorylation and with internal K+ before rephosphorylation. This enzyme conformation produces an enzyme—K complex from which K+ ions are not easily released unless high concentrations of ATP are present. This also stresses a non-phosphorylating regulatory role of ATP.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. The effects of changes in internal ionic concentrations on the electrical properties of perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:355–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Keynes R. D., Manil J., Shaw T. I., Steinhardt R. A. The ouabain-sensitive fluxes of sodium and potassium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):459–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Crawford A. C. Mobility and transport of magnesium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):855–874. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnola F. V., Villegas R., Camejo G. Tetrodotoxin receptors in plasma membranes isolated from lobster nerve fibers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 27;298(1):84–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Del Campillo E. The ATP dependence of a ouabain-sensitive sodium efflux activated by external sodium, potassium and lithium in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):547–554. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., DiPolo R. Sidedness of the ATP-Na+-K+ interactions with the Na+ pump in squid axons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 2;553(3):495–500. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Glynn I. M. The equilibrium between different conformations of the unphosphorylated sodium pump: effects of ATP and of potassium ions, and their relevance to potassium transport. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:367–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Sjodin R. A. An analysis of the influence of membrane potential and metabolic poisoning with azide on the sodium pump in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(3):383–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. The interaction of lithium ions with the sodium-potassium pump in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):397–420. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J. Effects of membrane potential on sodium and potassium fluxes in squid axons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):406–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J. Sodium extrusion by internally dialyzed squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Nov;50(10):2303–2331. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.10.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J. Sodium fluxes in internally dialyzed squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Aug;52(2):181–211. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Josephson L., Warner R., Yanagisawa M., Lechene C., Guidotti G. Vanadate is a potent (Na,K)-ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7421–7423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weer P. Axoplasmic free magnesium levels and magnesium extrusion from squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Aug;68(2):159–178. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weer P. Effects of intracellular adenosine-5'-diphosphate and orthophosphate on the sensitivity of sodium efflux from squid axon to external sodium and potassium. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Nov;56(5):583–620. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.5.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPolo R. Calcium influx in internally dialyzed squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Jan;73(1):91–113. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPolo R. Characterization of the ATP-dependent calcium efflux in dialyzed squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jun;69(6):795–813. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.6.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R. Effect of ATP on the calcium efflux in dialyzed squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Oct;64(4):503–517. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.4.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S., Cellino M., Zambrano F., Zampighi G., Tellez Nagel M., Marcus D., Canessa-Fischer M. The molecular organization of nerve membranesI. Isolation and characterization of plasma membranes from the retinal axons of the squid: an axolemma-rich preparation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 May;138(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Garrahan P. J. The interaction of adenosinetriphosphate and inorganic phosphate with the sodium pump in red cells. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):51–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Garrahan P. J. The interaction of sodium and potassium with the sodium pump in red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):297–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. Facftors affecting the relative magnitudes of the sodium:potassium and sodium:sodium exchanges catalysed by the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):189–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Hoffman J. F. Nucleotide requirements for sodium-sodium exchange catalysed by the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. ATP hydrolysis associated with an uncoupled sodium flux through the sodium pump: evidence for allosteric effects of intracellular ATP and extracellular sodium. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):465–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. The sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1975;37:13–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.37.030175.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwahashi H., Kyogoku Y. Direct proton exchange between complementary nucleic acid bases. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):277–278. doi: 10.1038/271277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+, K+)-ATPase. V. Conformational changes in the enzyme Transitions between the Na-form and the K-form studied with tryptic digestion as a tool. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 2;401(3):399–415. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Beaugé L. A., Glynn I. M. Vanadate inhibits (Na+ + K+)ATPase by blocking a conformational change of the unphosphorylated form. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):333–335. doi: 10.1038/282333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Yates D. W., Glynn I. M. Conformational transitions between Na+-bound and K+-bound forms of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase, studied with formycin nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 7;525(1):252–264. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Yates D. W., Glynn I. M. Elementary steps of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase mechanism, studied with formycin nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 7;525(1):230–251. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Yates D. W. Tryptophan fluorescence of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase as a tool for study of the enzyme mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 10;527(1):115–130. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Blostein R. Red cell sodium fluxes catalysed by the sodium pump in the absence of K+ and ADP. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):338–339. doi: 10.1038/285338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Brinley F. J. Magnesium influx in dialyzed squid axons. J Membr Biol. 1978 Oct 19;43(2-3):243–250. doi: 10.1007/BF01933481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norby J. G., Jensen J. Binding of ATP to brain microsomal ATPase. Determination of the ATP-binding capacity and the dissociation constant of the enzyme-ATP complex as a function of K+ concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):104–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Hegyvary C., Kume S. Activation by adenosine triphosphate in the phosphorylation kinetics of sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6530–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D., Flashner M. S. The (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase. Enzymatic and transport properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 17;549(2):145–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D. Kinetic studies on a brain microsomal adenosine triphosphatase. Evidence suggesting conformational changes. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3250–3258. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjodin R. A., Beauge L. A. The influence of potassium- and sodium-free solutions on sodium efflux from squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):664–674. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skou J. C. Effect of ATP on Na:K affinity and catalytic activity of (Na+ plus K+)-activated enzyme system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):168–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


