Abstract
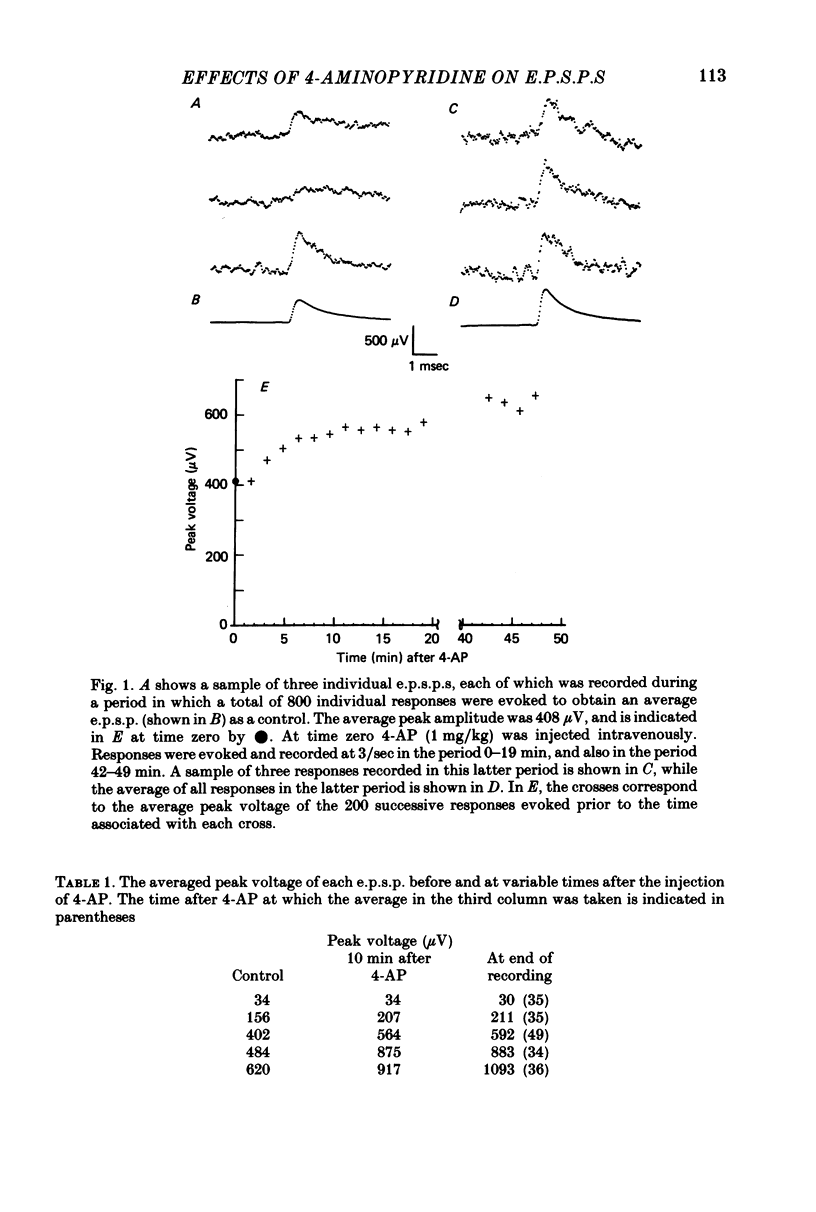
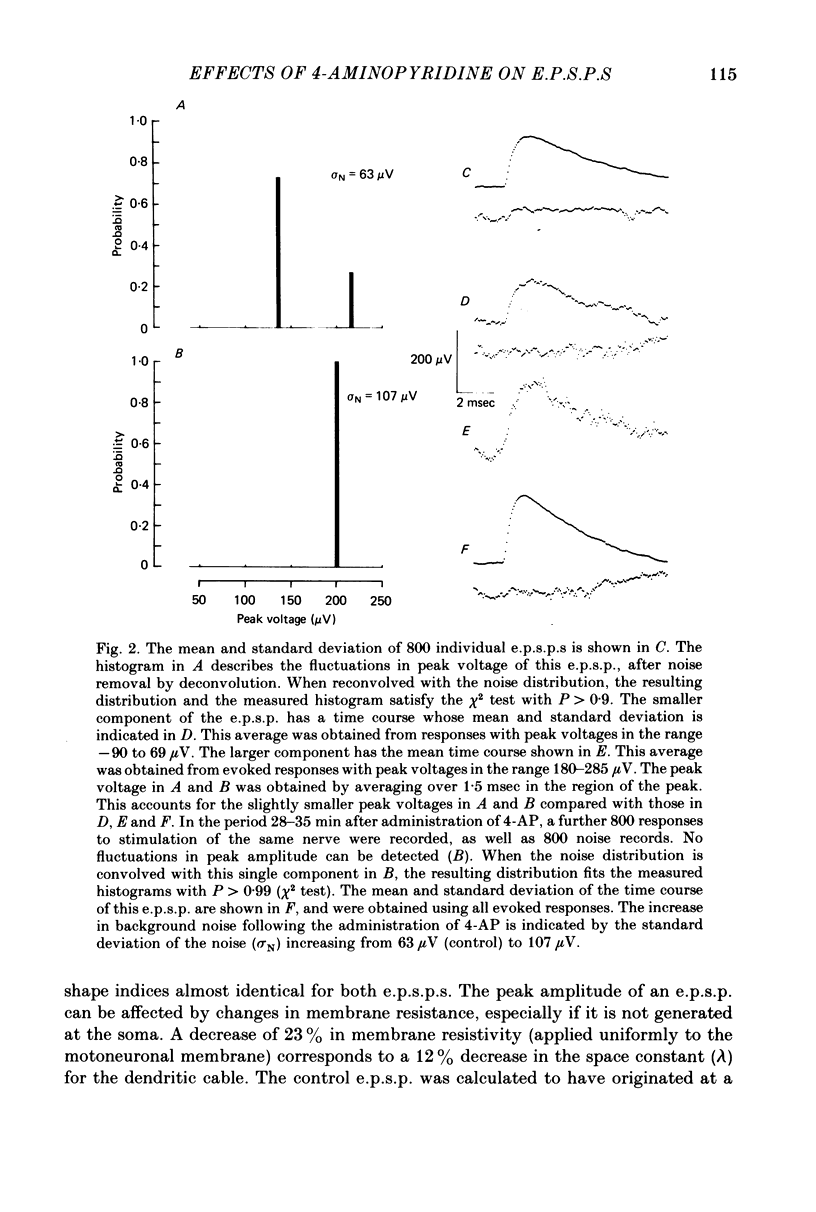
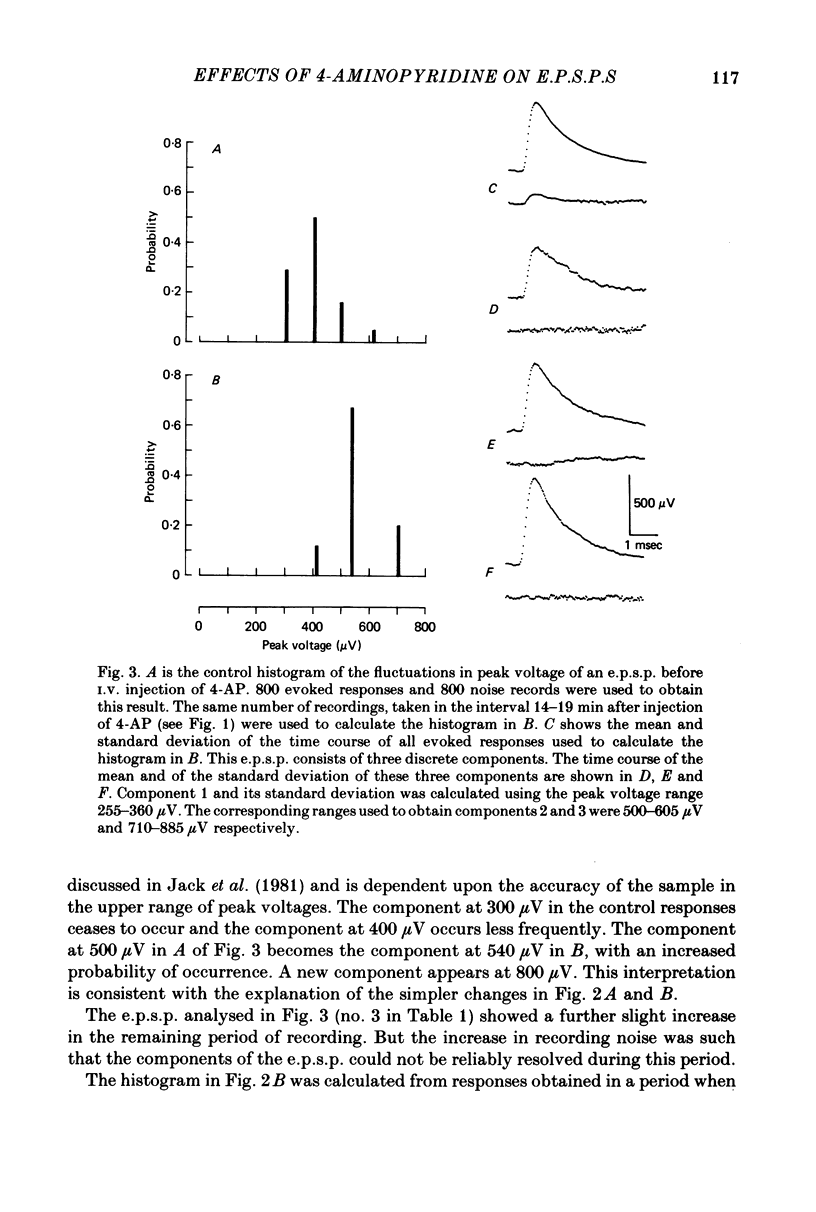
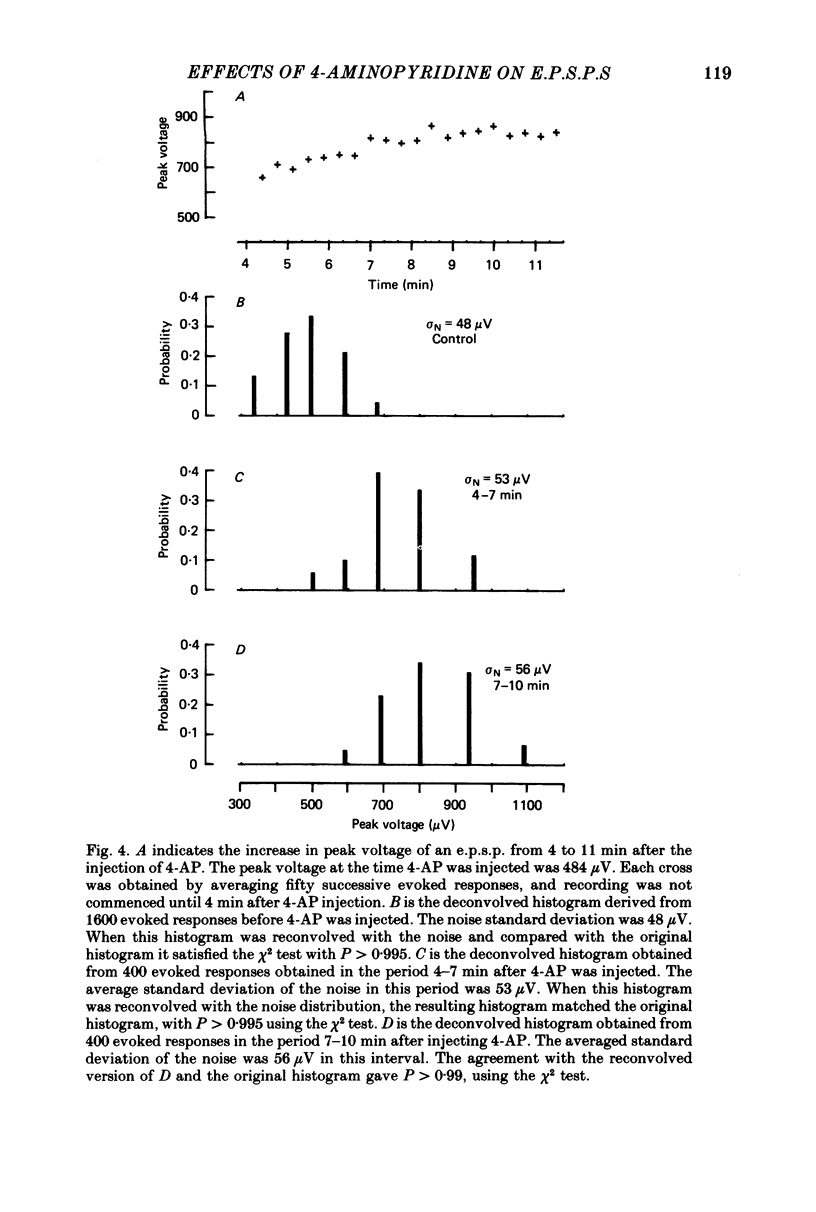
1. The average amplitude of e.p.s.p.s evoked in cat spinal motoneurones by impulses in single group Ia afferents usually increased following the intravenous injection of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP). Most of this increase occurred over the first 30 min following injection of 4-AP. 2. The increase in the average amplitude following 4-AP occurred by a reduction in the probability of occurrence of component e.p.s.p.s with smaller peak amplitudes, and an increase in the probability of occurrence of component e.p.s.p.s with larger peak amplitudes. There was no evidence that the discrete amplitudes of components after 4-AP were a result of graded increases of the discrete amplitudes before 4-AP. 3. The interpretation suggested for these results is that each component e.p.s.p. is generated by transmission at a different combination of boutons. At each of these boutons sufficient transmitter is released to saturate all available receptors. The effect of 4-AP is to decrease the probability of failure to release transmitter at each bouton, including some boutons which, before 4-AP, did not release transmitter.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Silfvenius H., Sundberg S. H., Sveen O. A comparison of distal and proximal dendritic synapses on CAi pyramids in guinea-pig hippocampal slices in vitro. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:273–299. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott E. R., Ballard K. J., Boyd I. A., Kalu K. U. Quantitative study of the non-circularity of myelinated peripheral nerve fibres in the cat. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:99–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. The morphology of group Ia afferent fibre collaterals in the spinal cord of the cat. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:111–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Walmsley B., Hodgson J. A. HRP anatomy of group Ia afferent contacts on alpha motoneurones. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 12;160(2):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90430-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. R., Redman S. J., Walmsley B. Non-quantal fluctuations and transmission failures in charge transfer at Ia synapses on spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Aug;259(3):689–704. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Landis D. M. Preservation of synaptic structure by rapid freezing. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:17–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Redman S. J., Wong K. Post-tetanic potentiation and facilitation of synaptic potentials evoked in cat spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:97–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iansek R., Redman S. J. The amplitude, time course and charge of unitary excitatory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurone dendrites. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):665–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles J. F. Central terminations of muscle afferents on motoneurones in the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):91–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Miller S., Porter R., Redman S. J. The time course of minimal excitory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones by group Ia afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J., Wong K. The components of synaptic potentials evoked in cat spinal motoneurones by impulses in single group Ia afferents. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:65–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lundberg A., Rudomin P., Sykova E. Effects of 4-aminopyridine on transmission in excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the spinal cord. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 11;136(2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90816-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Estimates of quantal content during 'chemical potentiation' of transmitter release. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Aug 31;205(1160):369–378. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Walton K., Bohr V. Synaptic transmission in squid giant synapse after potassium conductance blockage with external 3- and 4-aminopyridine. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):83–86. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85664-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundh H. Effects of 4-aminopyridine on neuromuscular transmission. Brain Res. 1978 Sep 22;153(2):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundh H., Thesleff S. The mode of action of 4-aminopyridine and guanidine on transmitter release from motor nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Apr 21;42(4):411–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher H. R., Ruenzel P., Henneman E. How the size of motoneurones determines their susceptibility to discharge. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):859–861. doi: 10.1038/282859a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Weiner R. Analysis of pairs of individual Ia-E.P.S.P.S in single motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(1):81–104. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman S. J. The attenuation of passively propagating dendritic potentials in a motoneurone cable model. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):637–664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman S. Junctional mechanisms at group Ia synapses. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;12(1):33–83. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov A. I., Shiriaev B. I. Modulation of transmission in different electronic junctions by aminopyridine. Experientia. 1978 Jan 15;34(1):67–68. doi: 10.1007/BF01921906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streit P., Akert K., Sandri C., Livingston R. B., Moor H. Dynamic ultrastructure of presynaptic membranes at nerve terminals in the spinal cord of rats. Anesthetized and unanesthetized preparations compared. Brain Res. 1972 Dec 24;48:11–26. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga A., Sandri C., Akert K. Ultrastructural effects of 4-aminopyridine on the presynaptic membrane in the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 9;163(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K., Redman S. The recovery of a random variable from a noisy record with application to the study of fluctuations in synaptic potentials. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Aug;2(4):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Dynamics of aminopyridine block of potassium channels in squid axon membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Nov;68(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


