Abstract
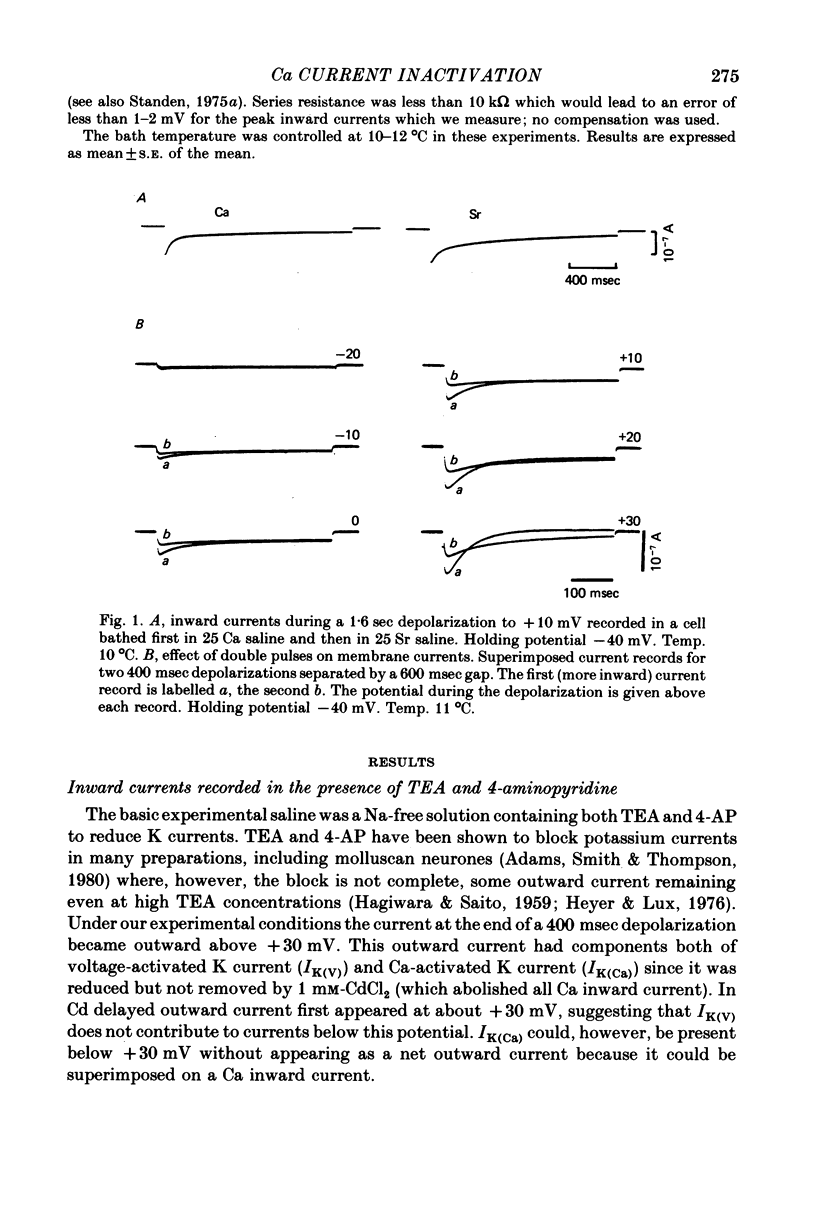
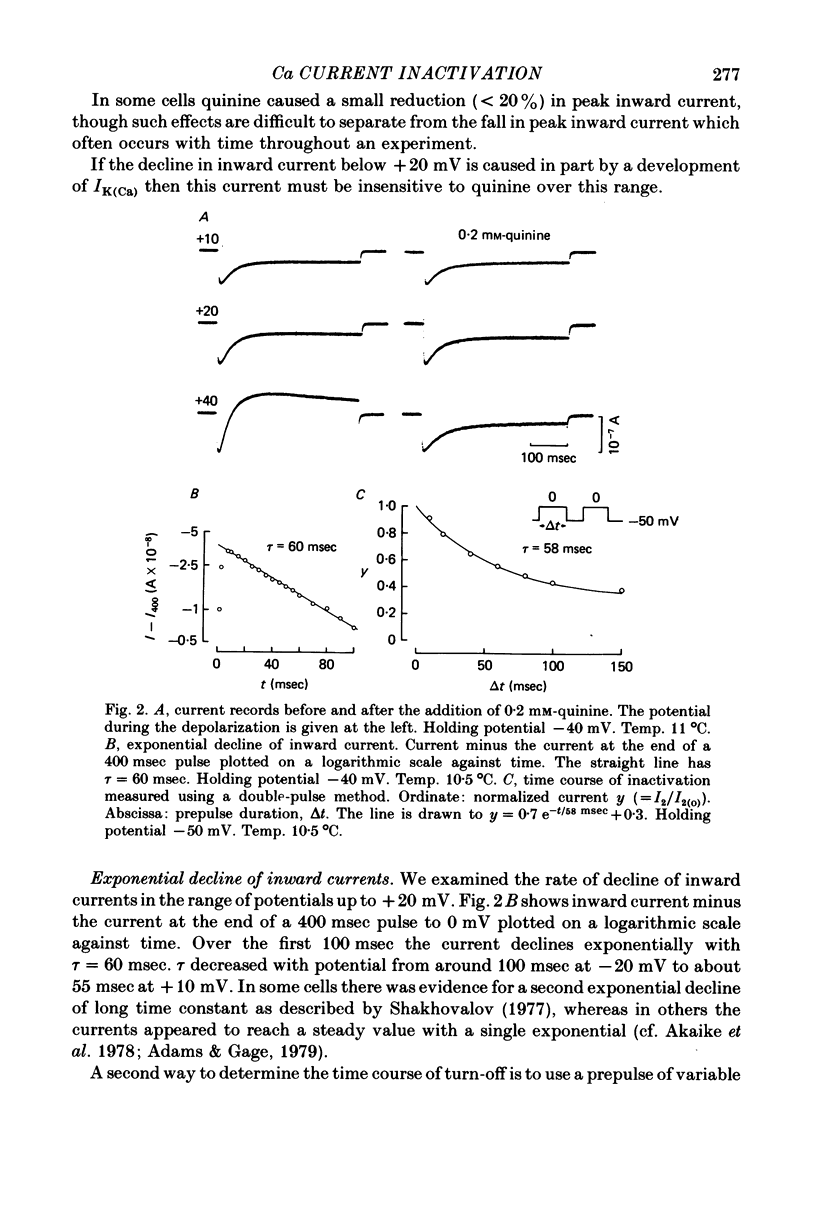
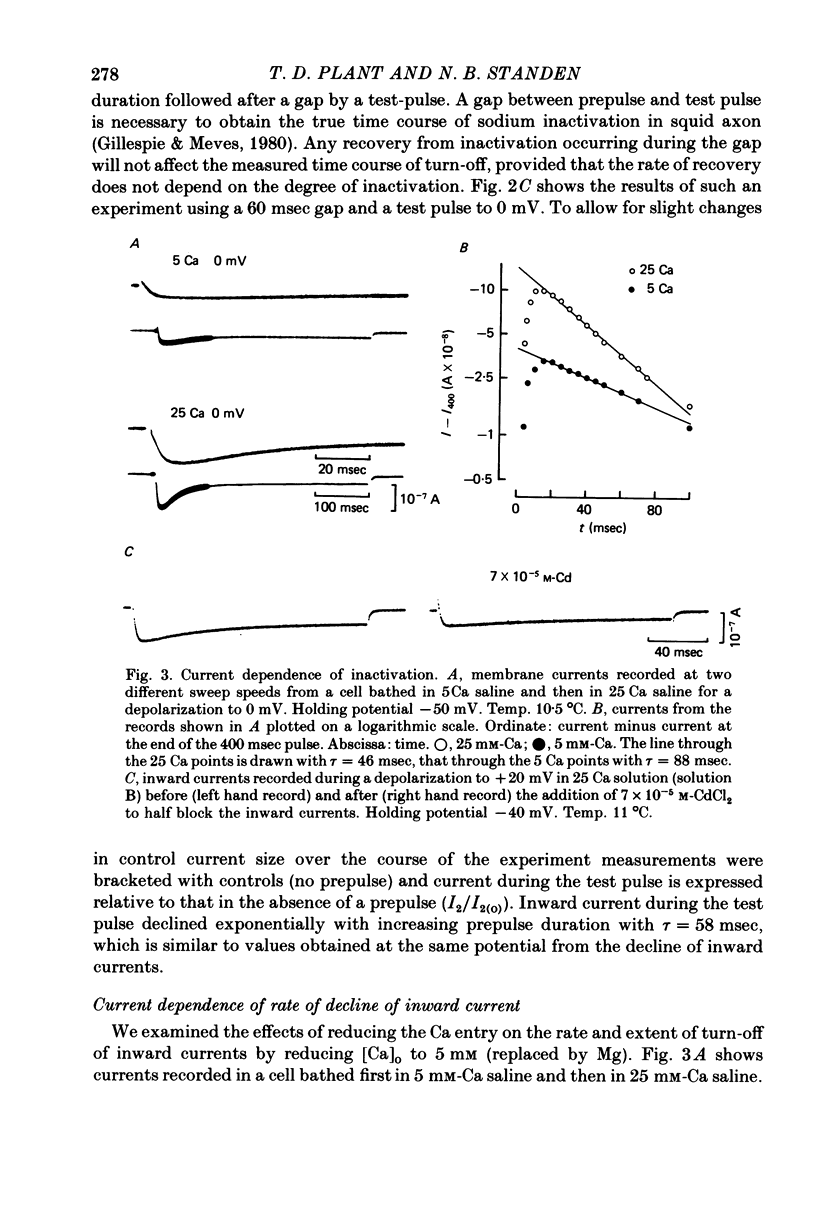
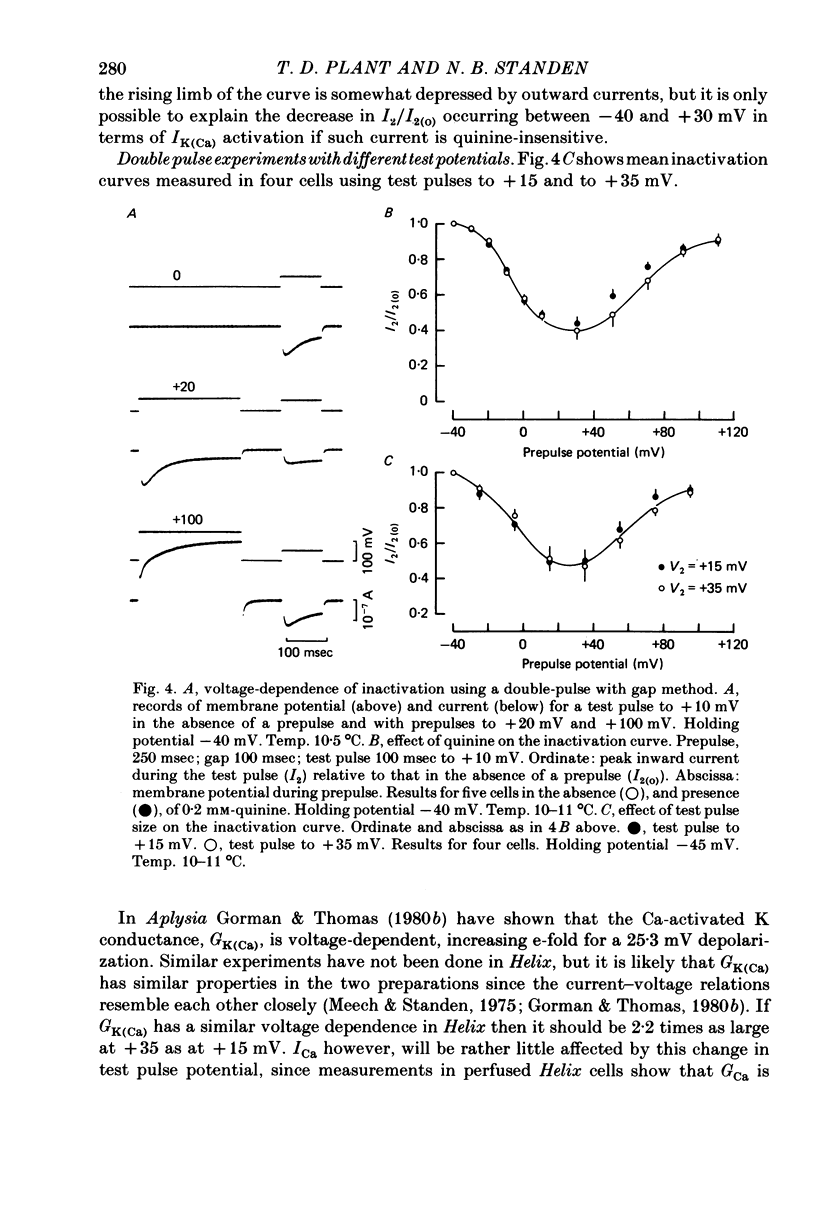
1. A two-electrode voltage clamp method was used to study Ca inward currents in identified Helix aspersa neurones bathed in 25 mM-Ca, Na-free saline with TEA and 4-AP. 2. Inward currents were blocked by CdCl2. In Cd delayed outward currents appeared at +30 mV. When two identical depolarizations were separated by a gap inward current turned off to the same level during the two pulses up to +20 mV; above this potential the records cross over. 3. The turn-off of inward current at potentials up to +20 mV was not affected by 0.2 mM-quinine, which reduced outward currents at more depolarized potentials. Inward currents declined exponentially over the first 100 msec with a time constant around 60 msec at 0 mV. Double-pulse experiments gave the same time course of turn-off. 4. When Ca inward current was reduced by lowering [Ca]o or by partial block by Cd the rate and extent of turn-off was reduced. 5. The inactivation curve (obtained using a double pulse with gap method) was U-shaped. The curve was not significantly changed by addition of quinine (0.2 mM) or by changing test pulse size. 6. Recovery of inward currents after a depolarizing prepulse was a double-exponential process, with time constants of 120 msec and 9.4 sec at 10--11 degrees C. 7. Our results are discussed in terms of possible Ca-dependent Ca inactivation and in terms of the possibility of development of an outward Ca-dependent K current.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELMAN W. J., TAYLOR R. E. Leakage current rectification in the squid giant axon. Nature. 1961 Jun 3;190:883–885. doi: 10.1038/190883a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
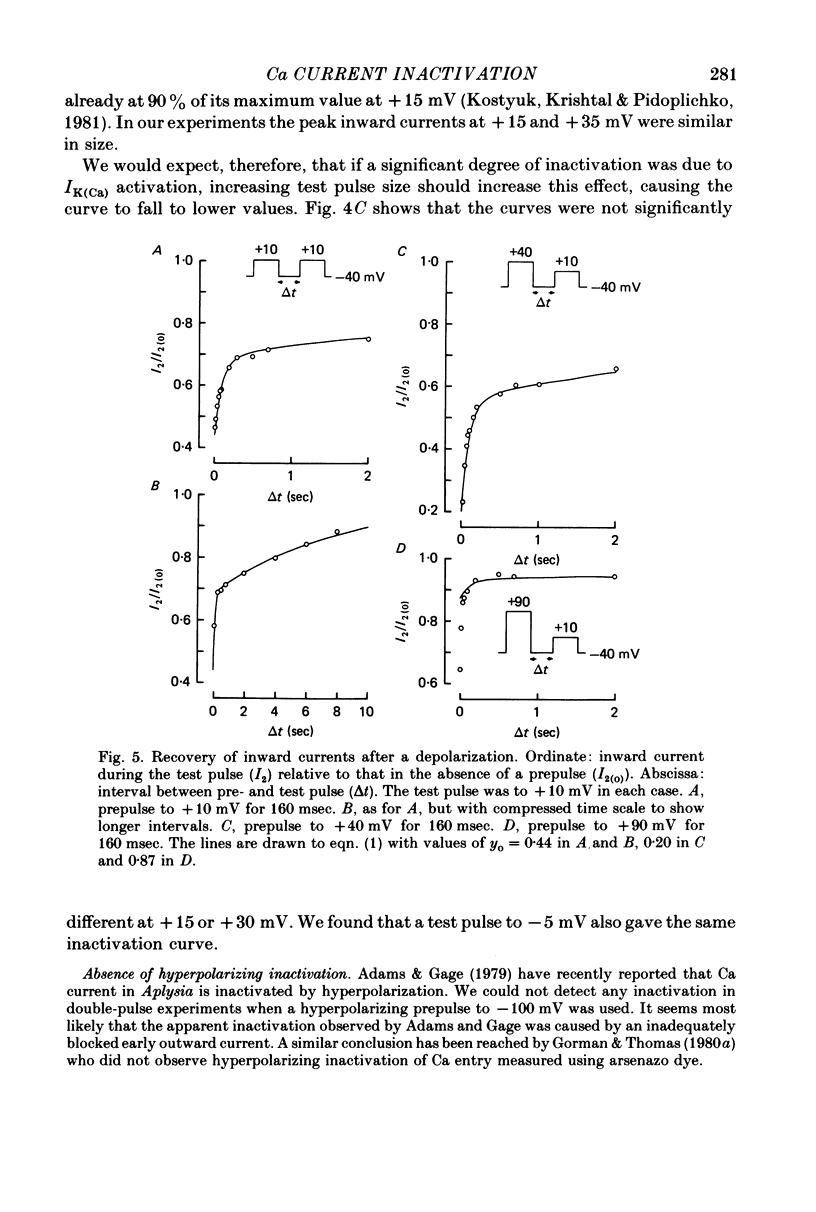
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W. Characteristics of sodium and calcium conductance changes produced by membrane depolarization in an Aplysia neurone. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:143–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. J., Smith S. J., Thompson S. H. Ionic currents in molluscan soma. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:141–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Lee K. S., Brown A. M. The calcium current of Helix neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):509–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Fink R., Palade P. T. Calcium depletion in frog muscle tubules: the decline of calcium current under maintained depolarization. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:177–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R. Calcium entry leads to inactivation of calcium channel in Paramecium. Science. 1978 Dec 15;202(4373):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.103199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R., Tillotson D. Calcium-mediated inactivation of calcium current in Paramecium. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:193–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Evidence for two types of sodium conductance in axons perfused with sodium fluoride solution. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):653–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Calcium current in molluscan neurones: measurement under conditions which maximize its visibility. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:41–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doroshenko P. A., Kostiuk P. G., Tsyndrenko A. Ia. Razdelenie kalievykh i kal'tsievykh kanalov v membrane somy nervnoi kletki. Neirofiziologiia. 1978;10(6):645–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geduldig D., Gruener R. Voltage clamp of the Aplysia giant neurone: early sodium and calcium currents. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;211(1):217–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. I., Meves H. The time course of sodium inactivation in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:289–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Intracellular calcium accumulation during depolarization in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:259–285. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Potassium conductance and internal calcium accumulation in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:287–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., SAITO N. Voltage-current relations in nerve cell membrane of Onchidium verruculatum. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:161–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca spike. Adv Biophys. 1973;4:71–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):349–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G. Calcium ionic channels in electrically excitable membrane. Neuroscience. 1980;5(6):945–959. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Doroshenko P. A. Calcium currents in snail neurones. II. The effect of external calcium concentration on the calcium inward current. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 11;348(2):95–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00586472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. Calcium inward current and related charge movements in the membrane of snail neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:403–421. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magura I. S. Long-lasting inward current in snail neurons in barium solutions in voltage-clamp conditions. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jul 14;35(3):239–256. doi: 10.1007/BF01869952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Aequorin response facilitation and intracellular calcium accumulation in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:167–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. Calcium and sodium ions as charge carriers in the action potential of an identified snail neurone. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):241–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. Voltage-clamp studies of the calcium inward current in an identified snail neurone: comparison with the sodium inward current. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):253–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D., Horn R. Inactivation without facilitation of calcium conductance in caesium-loaded neurones of Aplysia. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):312–314. doi: 10.1038/273312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. J., Lambert J. D., Woodruff G. N., Kerdut G. A. Action potential shape and frequency as criteria for neuron identification in the snail, Helix aspersa. Comp Gen Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;1(4):409–425. doi: 10.1016/0010-4035(70)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


