The title compound, a neutral bis{3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-[6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido}nickel(II) methanol disolvate, exhibits a distorted pseudooctahedral coordination environment around the metal ion. Due to the conical geometry and polar characteristics the molecules stack in one-dimensional columns that are connected by weak hydrogen bonds to form layers. These layers are arranged in a three-dimensional lattice without interlayer interactions closer than van der Waals distances.
Keywords: crystal structure, nickel(II) complexes, neutral complexes
Abstract
The unit cell of the title compound, [Ni(C16H10BrN6)2]·2CH3OH, contains a neutral complex and two methanol molecules. The NiII ion adopts a pseudooctahedral geometry, coordinated by two tridentate ligands via pyrazole, pyridine, and triazole N atoms. The average Ni—N bond length is 2.097 (4) Å. In the crystal, molecules form supramolecular chains through weak C–H⋯π interactions and further assemble into diperiodic layers via C—H⋯N/C interactions. Hirshfeld surface analysis shows H⋯H (32.1%), H⋯C/C⋯H (27.3%), H⋯N/N⋯H (14.9%), and H⋯Br/Br⋯H (14.6%) contacts. Interaction energies were evaluated using HF/3–21 G energy frameworks analysis. Structural parameters were compared to those of the chloro-containing analogue, and the effect of substituent variation was discussed.
1. Chemical context
A significant category of coordination compounds comprises 3d-metal complexes coordinated with tridentate bisazolepyridine ligands (Halcrow et al., 2019 ▸; Suryadevara et al., 2022 ▸), which have been employed in diverse applications including catalysis (Xing et al., 2014 ▸; Wei et al., 2015 ▸) and molecular magnetism (Suryadevara et al., 2022 ▸). Recently, we reported an NiII complex incorporating an asymmetric deprotonated chloro-substituted ligand, 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-[6-pyrazolyl(2-pyridyl)]-1H-1,2,4-triazole (KULRIW; Znovjyak et al., 2024 ▸).
In this study, we describe the synthesis and crystal structure determination of a new complex (1) featuring a bromo-substituted ligand, 3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(6-pyrazolyl(2-pyridyl))-1H-1,2,4-triazole. Comprehensive structural analyses were performed and the resulting calculated parameters were compared with those of the chloro-derivative (2).
2. Structural commentary
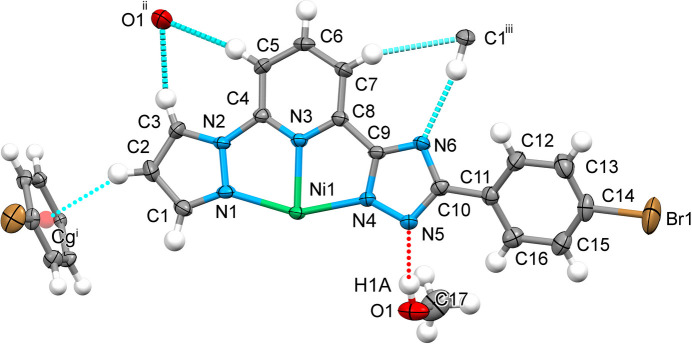
The two tridentate ligands span meridional and perpendicular coordination sites on the octahedron, forming a molecule with a compact coordination part and pending diverging 4-bromophenyl groups. The pendant group is tilted by 26.6 (2)° relative to the nearly planar pyrazole-pyridine-triazole (pz-py-trz) fragment (r.m.s. deviation = 0.074 Å). A methanol molecule forms an O—H⋯N5 hydrogen bond with the triazole ring of the ligand (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 1 ▸). The central Ni ion adopts a distorted octahedral N6 coordination sphere, formed by nitrogen atoms from two tridentate ligands, with an average Ni—N bond length of 2.097 (4) Å. The [NiN6] coordination polyhedron has a volume of 11.616 Å3. The trigonal distortion parameters are Σ = 119.3° (Σ = Σ112(|90 – φi|), where φi is the N—Ni—N′ angle; Drew et al., 1995 ▸) and Θ = 386.9° (Θ = Σ124(|60 – θi|), where θi is the angle from superposed opposite octahedral faces; Chang et al., 1990 ▸), indicating deviation from ideal octahedral geometry (Σ = Θ = 0). The continuous shape measure [CShM(Oh)] relative to ideal octahedral symmetry is 3.702 (Kershaw Cook et al., 2015 ▸). Compared to 2, compound 1 shows marginally higher distortion indices, reflecting the effect of varying pendant substituents (Table 2 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg is the centroid of the C11–C16 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3—H3⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.35 | 3.269 (8) | 162 |
| C5—H5⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.48 | 3.413 (7) | 167 |
| C1—H1⋯N6ii | 0.95 | 2.30 | 3.238 (6) | 171 |
| C7—H7⋯C1iii | 0.95 | 2.71 | 3.615 (7) | 161 |
| O1—H1A⋯N5 | 0.73 (6) | 2.08 (6) | 2.798 (6) | 168 (6) |
| C2—H2⋯Cgiv | 0.95 | 2.69 | 3.542 (6) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure in the asymmetric unit of the title compound and contact atoms with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. The strong O—H⋯N (red) and weak C—H⋯N/C/O/Cg (cyan) hydrogen bonds are shown with the nearest neighbors. Symmetry codes: (i) 1 − x, 1 + y,  − z; (ii)
− z; (ii)  + x,
+ x,  + y,
+ y,  − z; (iii)
− z; (iii)  + x, −
+ x, − + y,
+ y,  − z.
− z.
Table 2. Computed distortion indices for the title compound and for similar complexes reported in the literature.
| CSD refcode | <M—N> (Å) | Σ (°) | Θ (°) | CShM(Oh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.097 | 119.3 | 386.9 | 3.70 |
| 2_(KULRIW) | 2.095 | 119.4 | 387.3 | 3.71 |
| YOCFAZ | 2.088a | 120.8a | 397.6a | 3.65a |
| ZOCKOT | 2.086 | 121.0 | 375.9 | 3.78 |
| ZOTVIP | 2.110 | 124.9 | 382.4 | 3.55 |
Note: (a) averaged value.
3. Supramolecular features
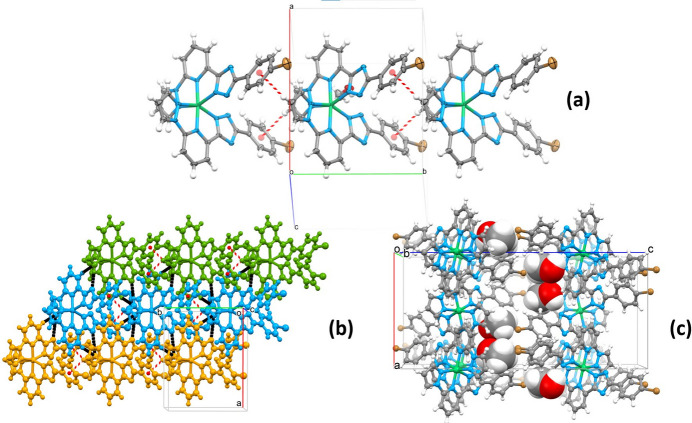
The title compound exhibits a packing similar to 2, with adjacent molecules interlocked and interacting via weak off-center non-perpendicular (73.0° angle) C—H(pz)⋯π(ph) contact between the pyrazole and phenyl groups [H2/C2⋯Cg(ph) = 2.686 (1)/3.542 (6) Å]. The formed one-dimensional chains extend along the b-axis direction with a periodicity of 10.1729 (4) Å (Fig. 2 ▸a), and are linked into corrugated layers in the ab plane by weak C—H(pz, py)⋯N/C(pz, trz) interactions [3.238 (6)–3.746 (7) Å; Fig. 2 ▸b]. The layers stack without interactions below the van der Waals radii, while methanol molecules occupy the interlayer voids and connect them through weak O⋯H—C(pz,py) interactions (Fig. 2 ▸c). Table 1 ▸ provides a summary of all intermolecular interactions. Compared to 2, the overall packing remains similar, with minor differences in the values of intermolecular contacts, which can be compared using Hirshfeld surface analysis.
Figure 2.
(a) A fragment of a monoperiodic supramolecular column formed by stacking of molecules along the b axis, with C—H⋯Cg contacts indicated by red dashed lines; (b) supramolecular diperiodic layers formed by stacking supramolecular columns in the ab plane. The C—H⋯N/C contacts between chains are indicated by black dashed cylinders. For a better representation, each column has a different color; (c) stacking of the diperiodic layers along the c axis with the methanol molecules in the voids.
4. Hirshfeld surface and two-dimensional fingerprint plots
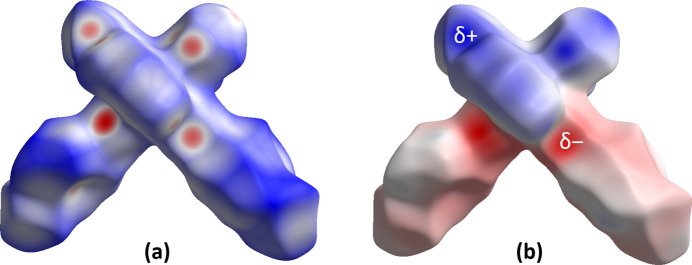
A Hirshfeld surface analysis was conducted and two-dimensional fingerprint plots were generated using CrystalExplorer 21.5 (Spackman et al., 2021 ▸), with a standard resolution for the three-dimensional dnorm surfaces plotted over a fixed color scale ranging from −0.6304 (red) to 1.6516 (blue) a.u. Red spots indicate short contacts and negative dnorm values on the surface, which correspond to the interactions described above. A projection of dnorm mapped over the Hirshfeld surfaces is presented in Fig. 3 ▸a. The two-dimensional fingerprint plots, along with their relative contributions to the Hirshfeld surface mapped over dnorm, are shown in Fig. 4 ▸a. H⋯H interactions account for the largest contribution to the overall crystal packing at 32.1%, and are situated in the middle region of the fingerprint plot. H⋯C/C⋯H contacts contribute 27.3%, while H⋯N/N⋯H contacts, seen as a pair of sharp spikes, represent a 14.9% contribution to the surface. Interactions of H⋯Br/Br⋯H make up 14.6%, forming pairs of characteristic wings. This is greater than the H⋯Cl/Cl⋯H interaction in 2, while other contributions are smaller due to the larger van der Waals radius of Br compared to Cl (1.85 vs 1.75 Å; Bondi, 1964 ▸) and the corresponding relative contribution to the surface area of the molecule. In Fig. 4 ▸b, the percentage contribution of contacts to the Hirshfeld surface for the two compounds is compared. In Fig. 4 ▸c, the different interactions are plotted onto the Hirshfeld surface. The electrostatic potential energy calculated using the HF/3-21G basis is shown in Fig. 3 ▸b. The negative charge is localized on the trz-ph moiety and the Br atom of the complex molecule, whereas the pz-py moieties exhibit relatively positive charges, supporting the stacking of molecules into columns and the arrangement of these columns into diperiodic two-dimensional layers.
Figure 3.
(a) A projection of dnorm mapped on Hirshfeld surfaces, showing the intermolecular interactions within the molecule. Red/blue and white areas represent regions where contacts are shorter/larger than the sum and close to the sum of the van der Waals radii, respectively. (b) Electrostatic potential for the title compound mapped on the Hirshfeld surface. Red/blue and white areas represent regions where the charge is negative/positive or close to zero.
Figure 4.

(a) Decomposition of the two-dimensional fingerprint plot of 1 into specific interactions and (b) comparison with those in 2; (c) a projection of dnorm mapped on the Hirshfeld surfaces, showing the intermolecular interactions within the molecule. Red/blue and white areas represent regions where contacts are shorter/larger than the sum and close to the sum of the van der Waals radii, respectively.
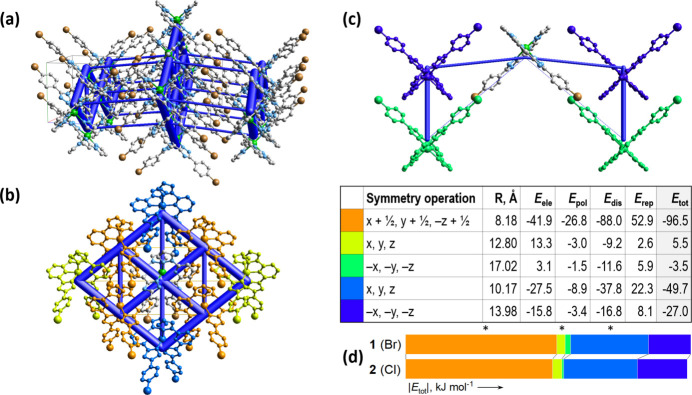
5. Energy framework analysis
The energy framework (Spackman et al., 2021 ▸), calculated at the HF/3-21G level, includes electrostatic (Eele), polarization (Epol), dispersion (Edis), repulsion (Erep) components and total energy (Etot). Cylindrical radii are scaled to the relative strength. Dispersion forces dominate in the crystal of neutral molecules, and the framework topology reflects the described intra- and interlayer interactions. Calculated Etot values are −49.7 kJ mol−1 (intrachain), down to −96.5 kJ mol−1 (interchain), and −27.0 kJ mol−1 (interlayer). Color-coded interaction mappings and detailed energy contributions within 3.8 Å of a central molecule are summarized in Fig. 5 ▸a–c. Fig. 5 ▸d presents a bar plot comparing the Etot values of 1 and 2. Despite identical molecular structures and packing arrangements, variations in the size and electronegativity of halogen substituents account for the differing strengths of intermolecular interactions in the two compounds. Consequently, interactions within a supramolecular layer are stronger in 1, whereas the interlayer interactions are comparatively weaker.
Figure 5.
(a) The calculated energy frameworks, showing the total energy diagrams (Etot), (b) decomposition of the energy framework into the part corresponding to the interactions within a supramolecular layer and (c) interlayer interactions. In the table, the corresponding color-coded energy values Etot are provided, including their Eele, Epol, Edis, and Erep components. Tube size is set at 100 scale, the blue color corresponds to the attractive interactions, yellow to the repulsive interactions; (d) Comparative plots of the absolute Etot values for 1 and 2. The color-coding of the bars corresponds to the symmetry operations in the table above. The asterisks distinguish the energy bars corresponding to the intralayer interactions.
6. Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.42; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) identifies neutral Ni complexes with tridentate bisazolpyridine ligands containing deprotonable azole groups, such as YOCFAZ (Yuan et al., 2014 ▸), ZOCKOT (Xing et al., 2014 ▸), and ZOTVIP (Wei et al., 2015 ▸). Table 2 ▸ summarizes the structural parameters of these complexes along with complex 2 (KULRIW).
7. Synthesis and crystallization
The ligand was synthesized by a modified procedure reported earlier (Seredyuk et al., 2022 ▸), and the synthesis of the title complex followed the method of 2 (Znovjyak et al., 2024 ▸). All chemicals were purchased from commercial suppliers and used without further purification (Merck, Enamine Ltd.).
3-(4-Bromophenyl)-5-(6-pyrazolyl(2-pyridyl))-1H-1,2,4-triazole (L). A Schlenk flask with an inert atmosphere was charged with 6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-ylboronic acid, (1.00 g, 5.3 mmol), 5-iodo-3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole (2.09 g, 4.8 mmol), [Pd(PPh3)4] (0.61 g, 0.53 mmol) and Na2CO3 (1.65 g, 15.6 mmol). Degassed 1,4-dioxane (20 mL) and degassed water (10 mL) were added, and the reaction mixture was heated to 373 K under vigorous stirring for 16 h. After filtering through a Celite pad, to the obtained solution HClaq (37%, 5 ml) was added dropwise and the obtained solution was stirred for 10 min. Thereafter the pH of the solution was brought to neutral with an aqueous solution of NaOH (10%). The resulting suspension was evaporated to dryness and resuspended in water, and the precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with water and recrystallized from chloroform-acetone (1:1). After drying in vacuo, the final compound was isolated as an analytically pure white crystalline powder. Yield: 1.02 g, 57%. Elemental analysis calculated for C16H11BrN6: C, 52.34; H, 3.02; N, 22.89. Found: C, 52.12; H, 3.11; N, 22.62. 1H NMR (300 MHz, 298 K, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 14.90 (1H, s, trzH), 9.16 (1H, s, pzH), 8.12–7.96 (5H, m, phH/pyH), 7.83 (1H, s, pzH), 7.64 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, phH), 6.62 (1H, s, pzH). 13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 161.5, 154.5, 150.9, 144.7, 143.0, 141.4, 132.1, 130.7, 128.7, 128.3, 122.9, 118.8, 113.1, 108.7.
Complex 1 was produced by a layering technique in a standard test tube. The layering sequence was as follows: the bottom layer contained a solution of [Ni(L2)](ClO4)2 prepared by dissolving L (101 mg, 0.274 mmol) and Ni(ClO4)2·6H2O (50 mg, 0.137 mmol) in boiling acetone, to which chloroform (5 ml) was then added. The middle layer was a methanol–chloroform mixture (1:10, 10 ml), which was covered by a layer of methanol (10 ml), to which 5 drops of NEt3 were added. The tube was sealed, and light violet plate-like single crystals appeared after 2 weeks (yield ca. 65%). Elemental analysis calculated for C34H28Br2N12NiO2: C, 47.75; H, 3.30; N, 19.65. Found: C, 47.52; H, 3.41; N, 19.73.
8. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. H atoms were refined as riding [C—H = 0.95–0.98 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C)]. The hydrogen atom H1A was refined freely.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Ni(C16H10BrN6)2]·2CH4O |
| M r | 855.21 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, Pbcn |
| Temperature (K) | 200 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 12.8038 (8), 10.1729 (4), 27.9377 (14) |
| V (Å3) | 3638.9 (3) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 2.78 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.3 × 0.2 × 0.03 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Xcalibur, Eos |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2024 ▸) |
| Tmin, Tmax | 0.534, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 11620, 3218, 2074 |
| R int | 0.064 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.595 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)], wR(F2), S | 0.061, 0.134, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 3218 |
| No. of parameters | 236 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.74, −0.81 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025007467/ee2019sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025007467/ee2019Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025007467/ee2019Isup3.cdx
CCDC reference: 2481668
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the FAIRE programme provided by the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC) for the opportunity to use the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) and associated software. Author contributions are as follows: Conceptualization, KZ and MS; methodology, KZ; formal analysis, SON; synthesis, SOM; single-crystal measurements, SS; writing (original draft), MS; writing (review and editing of the manuscript), OT, MS; visualization and calculations, KZ, YSM; funding acquisition, MS.
supplementary crystallographic information
Bis{3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-[6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido}nickel(II) methanol disolvate . Crystal data
| [Ni(C16H10BrN6)2]·2CH4O | Dx = 1.561 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 855.21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pbcn | Cell parameters from 1992 reflections |
| a = 12.8038 (8) Å | θ = 2.6–21.9° |
| b = 10.1729 (4) Å | µ = 2.78 mm−1 |
| c = 27.9377 (14) Å | T = 200 K |
| V = 3638.9 (3) Å3 | Plate, clear colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.3 × 0.2 × 0.03 mm |
| F(000) = 1720 |
Bis{3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-[6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido}nickel(II) methanol disolvate . Data collection
| Xcalibur, Eos diffractometer | 3218 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed X-ray tube, Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 2074 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.064 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1593 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.2° |
| ω scans | h = −8→15 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku OD, 2024) | k = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.534, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −33→23 |
| 11620 measured reflections |
Bis{3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-[6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido}nickel(II) methanol disolvate . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.061 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.134 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.042P)2 + 6.2503P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3218 reflections | Δρmax = 0.74 e Å−3 |
| 236 parameters | Δρmin = −0.81 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Bis{3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-[6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido}nickel(II) methanol disolvate . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Bis{3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-[6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido}nickel(II) methanol disolvate . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.66307 (8) | 0.02071 (7) | 0.48878 (3) | 0.0797 (4) | |
| Ni1 | 0.500000 | 0.70049 (8) | 0.750000 | 0.0216 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.5117 (3) | 0.8456 (4) | 0.80613 (15) | 0.0256 (10) | |
| N2 | 0.6139 (3) | 0.8692 (4) | 0.81923 (16) | 0.0248 (10) | |
| N3 | 0.6556 (3) | 0.7082 (4) | 0.76558 (14) | 0.0219 (10) | |
| N4 | 0.5627 (3) | 0.5623 (4) | 0.70264 (15) | 0.0231 (10) | |
| N5 | 0.5333 (3) | 0.4789 (4) | 0.66679 (15) | 0.0251 (10) | |
| N6 | 0.7063 (3) | 0.4515 (4) | 0.67934 (16) | 0.0259 (10) | |
| C1 | 0.4561 (4) | 0.9206 (5) | 0.83493 (19) | 0.0301 (13) | |
| H1 | 0.381986 | 0.925804 | 0.834432 | 0.036* | |
| C2 | 0.5201 (5) | 0.9917 (5) | 0.8664 (2) | 0.0390 (16) | |
| H2 | 0.498267 | 1.051486 | 0.890526 | 0.047* | |
| C3 | 0.6200 (5) | 0.9572 (5) | 0.8552 (2) | 0.0335 (14) | |
| H3 | 0.681998 | 0.988952 | 0.869887 | 0.040* | |
| C4 | 0.6923 (4) | 0.7938 (5) | 0.79686 (18) | 0.0241 (12) | |
| C5 | 0.7978 (4) | 0.8087 (5) | 0.80651 (19) | 0.0325 (14) | |
| H5 | 0.822350 | 0.871958 | 0.828859 | 0.039* | |
| C6 | 0.8649 (4) | 0.7276 (5) | 0.7822 (2) | 0.0377 (15) | |
| H6 | 0.938019 | 0.735362 | 0.787377 | 0.045* | |
| C7 | 0.8278 (4) | 0.6343 (5) | 0.7501 (2) | 0.0349 (14) | |
| H7 | 0.874470 | 0.577053 | 0.733845 | 0.042* | |
| C8 | 0.7215 (4) | 0.6267 (5) | 0.74235 (18) | 0.0237 (12) | |
| C9 | 0.6658 (4) | 0.5433 (5) | 0.70830 (18) | 0.0237 (12) | |
| C10 | 0.6212 (4) | 0.4151 (5) | 0.65395 (19) | 0.0260 (13) | |
| C11 | 0.6278 (4) | 0.3207 (5) | 0.61459 (19) | 0.0275 (13) | |
| C12 | 0.7116 (5) | 0.2340 (5) | 0.6123 (2) | 0.0380 (15) | |
| H12 | 0.762148 | 0.235364 | 0.637192 | 0.046* | |
| C13 | 0.7239 (5) | 0.1457 (6) | 0.5749 (2) | 0.0470 (17) | |
| H13 | 0.782299 | 0.088134 | 0.573719 | 0.056* | |
| C14 | 0.6488 (5) | 0.1440 (5) | 0.5396 (2) | 0.0403 (16) | |
| C15 | 0.5639 (5) | 0.2259 (5) | 0.5405 (2) | 0.0414 (16) | |
| H15 | 0.513185 | 0.222718 | 0.515651 | 0.050* | |
| C16 | 0.5530 (5) | 0.3147 (5) | 0.57862 (19) | 0.0345 (14) | |
| H16 | 0.494019 | 0.371228 | 0.579850 | 0.041* | |
| O1 | 0.3537 (4) | 0.5660 (5) | 0.61938 (19) | 0.0542 (14) | |
| H1A | 0.397 (5) | 0.548 (6) | 0.635 (2) | 0.05 (2)* | |
| C17 | 0.3843 (6) | 0.6447 (6) | 0.5808 (3) | 0.070 (2) | |
| H17A | 0.404825 | 0.588562 | 0.553908 | 0.105* | |
| H17B | 0.443564 | 0.699591 | 0.590398 | 0.105* | |
| H17C | 0.325855 | 0.700940 | 0.571141 | 0.105* |
Bis{3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-[6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido}nickel(II) methanol disolvate . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.1213 (9) | 0.0692 (5) | 0.0486 (5) | 0.0147 (5) | −0.0015 (5) | −0.0307 (4) |
| Ni1 | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0257 (5) | 0.0254 (5) | 0.000 | −0.0008 (5) | 0.000 |
| N1 | 0.016 (3) | 0.031 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.001 (2) | −0.006 (2) | 0.0002 (19) |
| N2 | 0.014 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.032 (3) | 0.0003 (19) | −0.002 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| N3 | 0.016 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0013 (19) | −0.001 (2) | −0.0033 (18) |
| N4 | 0.018 (3) | 0.026 (2) | 0.025 (2) | −0.0010 (19) | −0.001 (2) | −0.0036 (18) |
| N5 | 0.019 (3) | 0.030 (2) | 0.026 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.000 (2) | −0.0039 (19) |
| N6 | 0.017 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.033 (3) | −0.0011 (19) | 0.003 (2) | −0.0058 (19) |
| C1 | 0.022 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.031 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.001 (2) |
| C2 | 0.037 (4) | 0.045 (4) | 0.035 (3) | 0.010 (3) | 0.006 (3) | −0.013 (3) |
| C3 | 0.027 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.036 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.006 (3) | −0.015 (3) |
| C4 | 0.019 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.003 (2) | −0.004 (3) | −0.002 (2) |
| C5 | 0.024 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.032 (3) | −0.002 (3) | −0.006 (3) | −0.014 (3) |
| C6 | 0.016 (3) | 0.050 (4) | 0.047 (4) | 0.001 (3) | −0.007 (3) | −0.010 (3) |
| C7 | 0.018 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.043 (4) | 0.003 (3) | 0.001 (3) | −0.015 (3) |
| C8 | 0.019 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.023 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.000 (3) | 0.000 (2) |
| C9 | 0.015 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.027 (3) | −0.002 (2) | −0.002 (3) | 0.000 (2) |
| C10 | 0.025 (3) | 0.025 (3) | 0.028 (3) | −0.005 (2) | −0.001 (3) | 0.001 (2) |
| C11 | 0.029 (3) | 0.027 (3) | 0.026 (3) | −0.003 (2) | 0.004 (3) | 0.001 (2) |
| C12 | 0.039 (4) | 0.041 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.003 (3) | −0.007 (3) | −0.008 (3) |
| C13 | 0.050 (5) | 0.046 (4) | 0.045 (4) | 0.014 (3) | 0.006 (4) | −0.006 (3) |
| C14 | 0.062 (5) | 0.028 (3) | 0.031 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.006 (4) | −0.006 (2) |
| C15 | 0.053 (4) | 0.042 (4) | 0.028 (3) | −0.005 (3) | −0.004 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| C16 | 0.037 (4) | 0.029 (3) | 0.038 (3) | −0.001 (3) | −0.003 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| O1 | 0.032 (3) | 0.073 (3) | 0.058 (3) | −0.004 (3) | −0.009 (3) | 0.026 (3) |
| C17 | 0.094 (7) | 0.054 (4) | 0.063 (5) | −0.014 (4) | −0.021 (5) | 0.015 (4) |
Bis{3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-[6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido}nickel(II) methanol disolvate . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C14 | 1.903 (5) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| Ni1—N1i | 2.159 (4) | C5—C6 | 1.372 (7) |
| Ni1—N1 | 2.159 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| Ni1—N3 | 2.041 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.390 (7) |
| Ni1—N3i | 2.041 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| Ni1—N4i | 2.091 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.380 (7) |
| Ni1—N4 | 2.091 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.461 (7) |
| N1—N2 | 1.380 (5) | C10—C11 | 1.462 (7) |
| N1—C1 | 1.318 (6) | C11—C12 | 1.390 (7) |
| N2—C3 | 1.347 (6) | C11—C16 | 1.389 (7) |
| N2—C4 | 1.409 (6) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C4 | 1.320 (6) | C12—C13 | 1.386 (8) |
| N3—C8 | 1.349 (6) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| N4—N5 | 1.366 (5) | C13—C14 | 1.378 (8) |
| N4—C9 | 1.344 (6) | C14—C15 | 1.370 (8) |
| N5—C10 | 1.348 (6) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| N6—C9 | 1.339 (6) | C15—C16 | 1.404 (7) |
| N6—C10 | 1.352 (6) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | O1—H1A | 0.73 (6) |
| C1—C2 | 1.403 (7) | O1—C17 | 1.398 (8) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.364 (7) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.386 (7) | ||
| N1—Ni1—N1i | 93.7 (2) | C6—C5—C4 | 116.7 (5) |
| N3—Ni1—N1i | 101.33 (16) | C6—C5—H5 | 121.7 |
| N3i—Ni1—N1 | 101.33 (16) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 |
| N3i—Ni1—N1i | 75.58 (16) | C5—C6—C7 | 121.0 (5) |
| N3—Ni1—N1 | 75.58 (16) | C7—C6—H6 | 119.5 |
| N3i—Ni1—N3 | 175.6 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.8 |
| N3—Ni1—N4 | 77.64 (16) | C8—C7—C6 | 118.5 (5) |
| N3i—Ni1—N4 | 105.42 (16) | C8—C7—H7 | 120.8 |
| N3i—Ni1—N4i | 77.64 (16) | N3—C8—C7 | 120.4 (5) |
| N3—Ni1—N4i | 105.42 (16) | N3—C8—C9 | 111.5 (5) |
| N4i—Ni1—N1i | 153.21 (16) | C7—C8—C9 | 128.0 (5) |
| N4—Ni1—N1 | 153.21 (16) | N4—C9—C8 | 118.2 (4) |
| N4—Ni1—N1i | 91.54 (16) | N6—C9—N4 | 114.2 (4) |
| N4i—Ni1—N1 | 91.54 (16) | N6—C9—C8 | 127.6 (5) |
| N4i—Ni1—N4 | 95.5 (2) | N5—C10—N6 | 113.6 (4) |
| N2—N1—Ni1 | 112.2 (3) | N5—C10—C11 | 124.4 (5) |
| C1—N1—Ni1 | 143.3 (4) | N6—C10—C11 | 121.9 (5) |
| C1—N1—N2 | 104.5 (4) | C12—C11—C10 | 119.7 (5) |
| N1—N2—C4 | 117.6 (4) | C16—C11—C10 | 122.2 (5) |
| C3—N2—N1 | 111.6 (4) | C16—C11—C12 | 118.1 (5) |
| C3—N2—C4 | 130.6 (5) | C11—C12—H12 | 118.9 |
| C4—N3—Ni1 | 120.9 (3) | C13—C12—C11 | 122.2 (6) |
| C4—N3—C8 | 120.2 (4) | C13—C12—H12 | 118.9 |
| C8—N3—Ni1 | 118.9 (3) | C12—C13—H13 | 121.1 |
| N5—N4—Ni1 | 140.9 (3) | C14—C13—C12 | 117.9 (6) |
| C9—N4—Ni1 | 113.6 (3) | C14—C13—H13 | 121.1 |
| C9—N4—N5 | 105.5 (4) | C13—C14—Br1 | 118.4 (5) |
| C10—N5—N4 | 105.3 (4) | C15—C14—Br1 | 119.3 (5) |
| C9—N6—C10 | 101.3 (4) | C15—C14—C13 | 122.3 (5) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 124.3 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.6 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 111.4 (5) | C14—C15—C16 | 118.9 (6) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 124.3 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.6 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 127.1 | C11—C16—C15 | 120.6 (5) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 105.8 (5) | C11—C16—H16 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 127.1 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.7 |
| N2—C3—C2 | 106.7 (5) | C17—O1—H1A | 112 (5) |
| N2—C3—H3 | 126.6 | O1—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.6 | O1—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N3—C4—N2 | 113.6 (4) | O1—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N3—C4—C5 | 123.2 (5) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—N2 | 123.2 (5) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 121.7 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| Br1—C14—C15—C16 | 178.8 (4) | C1—N1—N2—C4 | 175.0 (4) |
| Ni1—N1—N2—C3 | −178.2 (3) | C1—C2—C3—N2 | −0.6 (6) |
| Ni1—N1—N2—C4 | −3.0 (5) | C3—N2—C4—N3 | 174.0 (5) |
| Ni1—N1—C1—C2 | 176.8 (4) | C3—N2—C4—C5 | −6.4 (9) |
| Ni1—N3—C4—N2 | 3.7 (6) | C4—N2—C3—C2 | −173.9 (5) |
| Ni1—N3—C4—C5 | −175.9 (4) | C4—N3—C8—C7 | −1.7 (7) |
| Ni1—N3—C8—C7 | 176.4 (4) | C4—N3—C8—C9 | −178.1 (4) |
| Ni1—N3—C8—C9 | 0.1 (5) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.9 (9) |
| Ni1—N4—N5—C10 | −177.8 (4) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 1.4 (9) |
| Ni1—N4—C9—N6 | 177.7 (3) | C6—C7—C8—N3 | −0.1 (8) |
| Ni1—N4—C9—C8 | −5.4 (6) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 175.6 (5) |
| N1—N2—C3—C2 | 0.5 (6) | C7—C8—C9—N4 | −172.4 (5) |
| N1—N2—C4—N3 | −0.2 (6) | C7—C8—C9—N6 | 4.0 (9) |
| N1—N2—C4—C5 | 179.4 (5) | C8—N3—C4—N2 | −178.2 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.5 (7) | C8—N3—C4—C5 | 2.2 (8) |
| N2—N1—C1—C2 | −0.2 (6) | C9—N4—N5—C10 | 0.6 (5) |
| N2—C4—C5—C6 | 179.5 (5) | C9—N6—C10—N5 | −0.8 (6) |
| N3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.9 (8) | C9—N6—C10—C11 | 175.8 (5) |
| N3—C8—C9—N4 | 3.6 (6) | C10—N6—C9—N4 | 1.2 (6) |
| N3—C8—C9—N6 | 180.0 (5) | C10—N6—C9—C8 | −175.3 (5) |
| N4—N5—C10—N6 | 0.1 (6) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −177.6 (5) |
| N4—N5—C10—C11 | −176.4 (4) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | 177.7 (5) |
| N5—N4—C9—N6 | −1.2 (6) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.0 (9) |
| N5—N4—C9—C8 | 175.7 (4) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −1.7 (8) |
| N5—C10—C11—C12 | −162.1 (5) | C12—C13—C14—Br1 | −178.7 (4) |
| N5—C10—C11—C16 | 18.4 (8) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.1 (9) |
| N6—C10—C11—C12 | 21.6 (8) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.0 (9) |
| N6—C10—C11—C16 | −157.8 (5) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.9 (8) |
| C1—N1—N2—C3 | −0.2 (6) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 1.8 (9) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, y, −z+3/2.
Bis{3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-[6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ido}nickel(II) methanol disolvate . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg is the centroid of the C11–C16 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C3—H3···O1ii | 0.95 | 2.35 | 3.269 (8) | 162 |
| C5—H5···O1ii | 0.95 | 2.48 | 3.413 (7) | 167 |
| C1—H1···N6iii | 0.95 | 2.30 | 3.238 (6) | 171 |
| C7—H7···C1iv | 0.95 | 2.71 | 3.615 (7) | 161 |
| O1—H1A···N5 | 0.73 (6) | 2.08 (6) | 2.798 (6) | 168 (6) |
| C2—H2···Cgv | 0.95 | 2.69 | 3.542 (6) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (iii) x−1/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (iv) x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (v) −x+1, y+1, −z+3/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D–H···A | D–H | H···A | D···A | D–H···A |
| C3–H3···O1i | 0.95 | 2.35 | 3.268 (7) | 162 |
| C5–H5···O1i | 0.95 | 2.48 | 3.410 (7) | 167 |
| C1–H1···N6ii | 0.95 | 2.30 | 3.238 (6) | 171 |
| C7–H7···C1ii | 0.95 | 2.71 | 3.615 (7) | 161 |
| O1–H1A···N5 | 0.73 (6) | 2.08 (6) | 2.798 (6) | 168 (6) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 1/2 + x, 1/2 + y, 1.5 - z; (ii) 1/2 + x, -1/2 + y, 1.5 - z
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: grants from the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine (grant No. 24BF037-03).
References
- Bondi, A. (1964). J. Phys. Chem.68, 441–451.
- Chang, H. R., McCusker, J. K., Toftlund, H., Wilson, S. R., Trautwein, A. X., Winkler, H. & Hendrickson, D. N. (1990). J. Am. Chem. Soc.112, 6814–6827.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst.42, 339–341.
- Drew, M. G. B., Harding, C. J., McKee, V., Morgan, G. G. & Nelson, J. (1995). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. pp. 1035–1038.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Halcrow, M. A., Capel Berdiell, I., Pask, C. M. & Kulmaczewski, R. (2019). Inorg. Chem.58, 9811–9821. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kershaw Cook, L. J., Mohammed, R., Sherborne, G., Roberts, T. D., Alvarez, S. & Halcrow, M. A. (2015). Coord. Chem. Rev.289, 2–12.
- Rigaku OD (2024). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Seredyuk, M., Znovjyak, K., Valverde-Munoz, F. J., da Silva, I., Munoz, M. C., Moroz, Y. S. & Real, J. A. (2022). J. Am. Chem. Soc.144, 14297–14309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, P. R., Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2021). J. Appl. Cryst.54, 1006–1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Suryadevara, N., Mizuno, A., Spieker, L., Salamon, S., Sleziona, S., Maas, A., Pollmann, E., Heinrich, B., Schleberger, M., Wende, H., Kuppusamy, S. K. & Ruben, M. (2022). Chem. Eur. J.28, e202103853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wei, S. Y., Wang, J. L., Zhang, C. S., Xu, X.-T., Zhang, X. X., Wang, J. X. & Xing, Y.-H. (2015). ChemPlusChem80, 549–558. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xing, N., Xu, L. T., Liu, X., Wu, Q., Ma, X. T. & Xing, Y. H. (2014). ChemPlusChem79, 1198–1207.
- Yuan, L.-Z., Ge, Q., Zhao, X.-F., Ouyang, Y., Li, S.-H., Xie, C.-Z. & Xu, J.-Y. (2014). Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem.44, 1175–1182.
- Znovjyak, K., Shova, S., Panov, D. M., Kariaka, N. S., Fritsky, I. O., Malinkin, S. O. & Seredyuk, M. (2024). Acta Cryst. E80, 1235–1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025007467/ee2019sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025007467/ee2019Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989025007467/ee2019Isup3.cdx
CCDC reference: 2481668
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report