Abstract
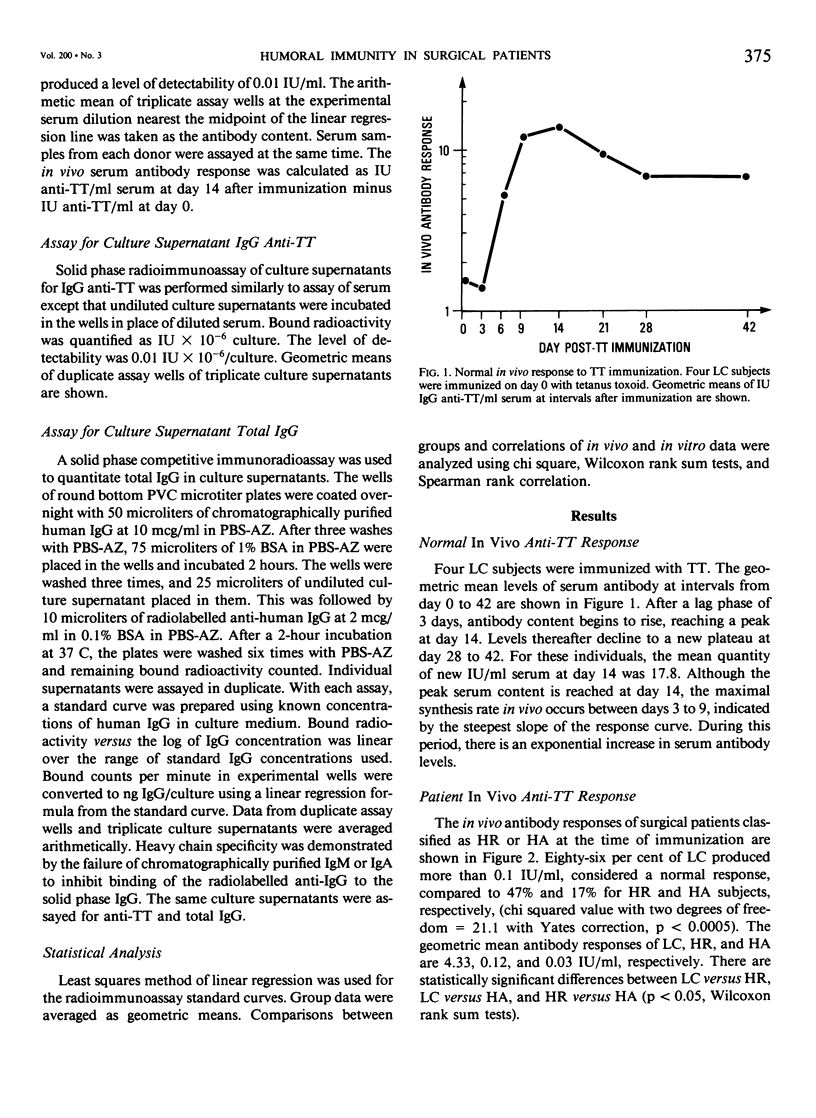
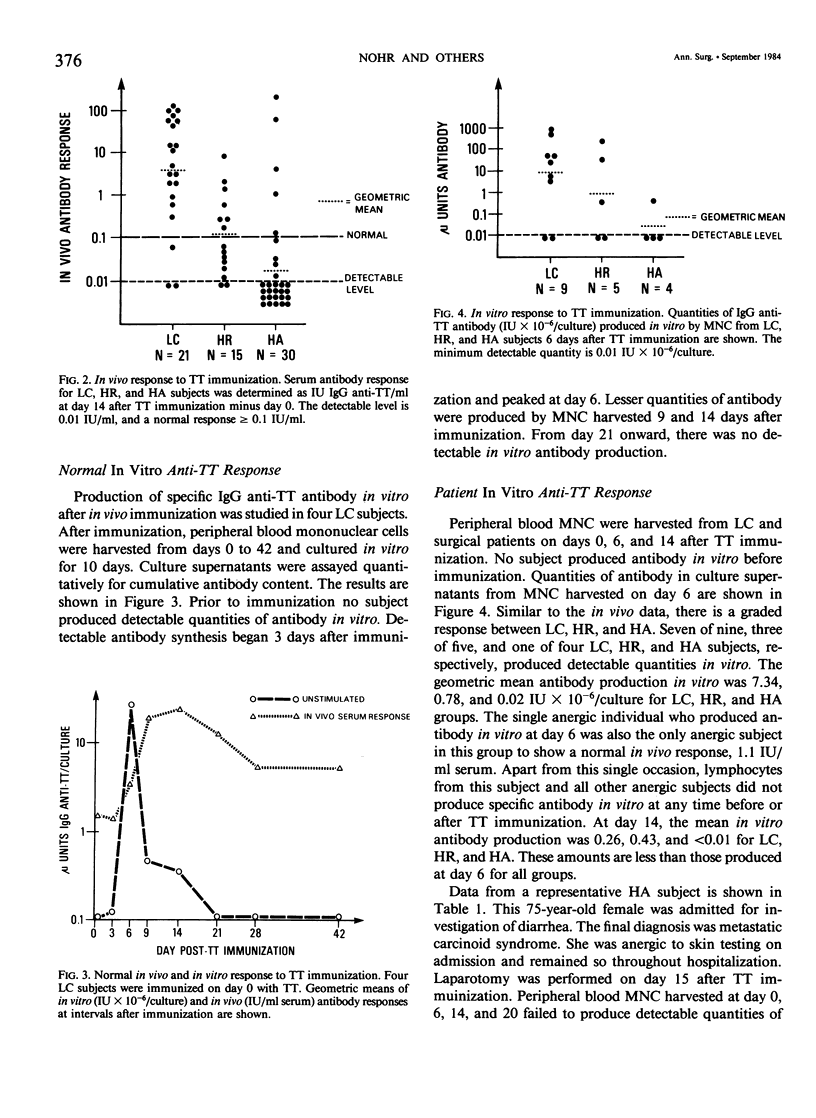
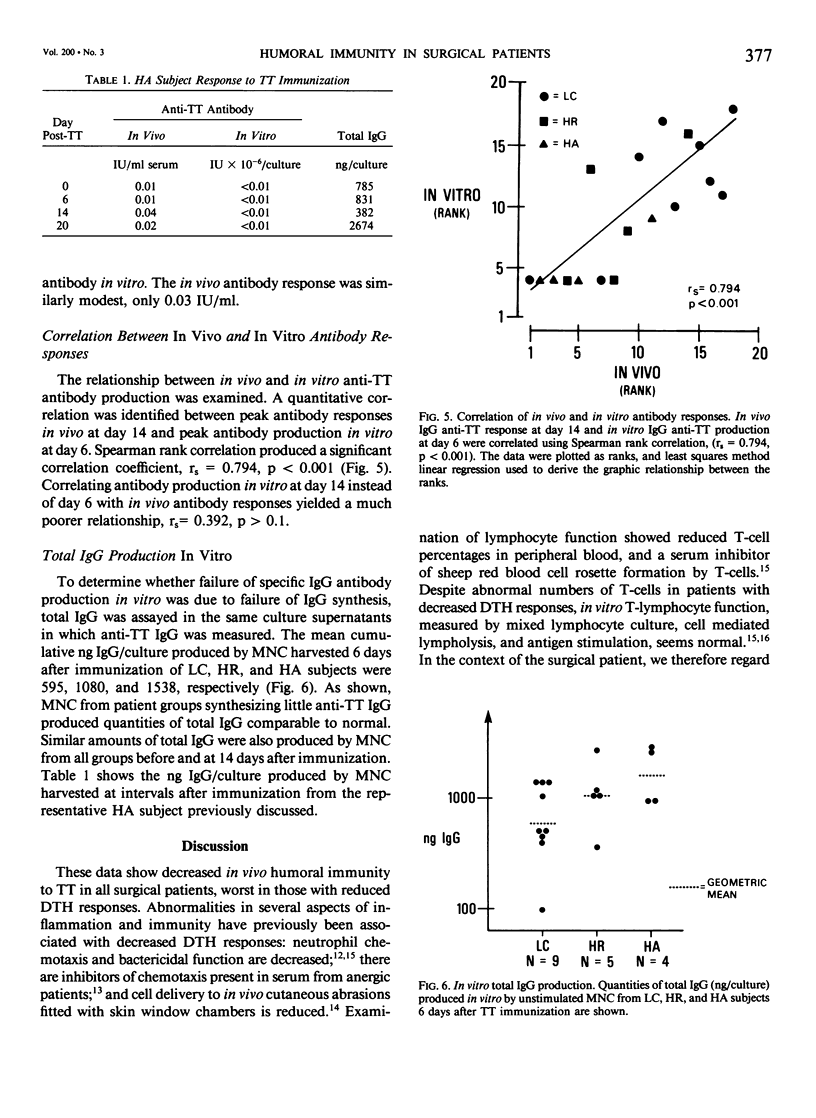
In vivo and in vitro humoral immunity was studied in surgical patients. Laboratory controls (LC), delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH) skin test reactive (HR), and anergic (HA) patients were immunized with tetanus toxoid. Maximum in vivo antibody levels occurred 14 days after immunization. Eighty-six, 47, and 17% of LC, HR, and HA subjects, respectively, showed a positive response (X2(2) = 21.1 with Yates, p less than 0.0005). Peak in vitro antibody production in unstimulated lymphocyte cultures occurred at day 6 after immunization. Antibody responses in vitro were reduced in all surgical patients, worst in HA, and correlated quantitatively with in vivo antibody responses at day 14 (Spearman rank correlation = 0.794, p less than 0.001). Total IgG production in vitro was not decreased; 595, 1080, and 1538 ng IgG/culture were produced by LC, HR, and HA, respectively. These data demonstrate decreased in vivo and in vitro humoral immunity in all surgical patients, worst in those with decreased DTH responses. There is a kinetic and quantitative correlation between in vivo and in vitro responses, the latter being a biologic reflection of the integrity and magnitude of the in vivo process. Finally, failure to produce specific antibody is not due to failure of total IgG synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benner R., Hijmans W., Haaijman J. J. The bone marrow: the major source of serum immunoglobulins, but still a neglected site of antibody formation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Oct;46(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L., Hallowell E., Heddle R. Protein status of general surgical patients. JAMA. 1974 Nov 11;230(6):858–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christou N. V., Meakins J. L. Neutrophil function in surgical patients: two inhibitors of granulocyte chemotaxis associated with sepsis. J Surg Res. 1979 Apr;26(4):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(79)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christou N. V., Meakins J. L. Phagocytic and bactericidal functions of polymorphonuclear neutrophils from anergic surgical patients. Can J Surg. 1982 Jul;25(4):444–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Gupta J. L. Controlled trial of Pseudomonas immunoglobulin and vaccine in burn patients. Lancet. 1980 Dec 13;2(8207):1263–1265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92334-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger B. E., Craven D. E., Carling P. C., McCabe W. R. Gram-negative bacteremia. III. Reassessment of etiology, epidemiology and ecology in 612 patients. Am J Med. 1980 Mar;68(3):332–343. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean L. D., Meakins J. L., Taguchi K., Duignan J. P., Dhillon K. S., Gordon J. Host resistance in sepsis and trauma. Ann Surg. 1975 Sep;182(3):207–217. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197509000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazaheri R., Rode H. N., Abikar K., Ing A., Nohr C., Gordon J. Dysfunction of humoral immunity in anergic surgical patients: absence of anti-tetanus IgG antibody production. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Jan;4(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00915289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakins J. L. Clinical importance of host resistance to infection in surgical patients. Adv Surg. 1981;15:225–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakins J. L., Pietsch J. B., Bubenick O., Kelly R., Rode H., Gordon J., MacLean L. D. Delayed hypersensitivity: indicator of acquired failure of host defenses in sepsis and trauma. Ann Surg. 1977 Sep;186(3):241–250. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197709000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode H. N., Christou N. V., Bubenik O., Superina R., Gordon J., Meakins J. L., MacLean L. D. Lymphocyte function in anergic patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jan;47(1):155–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. H., Macy E., Morrow C., Saxon A. Characterization of a circulating subpopulation of spontaneous antitetanus toxoid antibody producing B cells following in vivo booster immunization. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2498–2504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. H., Saxon A. Immunoregulation in humans: control of antitetanus toxoid antibody production after booster immunization. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1154–1160. doi: 10.1172/JCI109234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twomey P., Ziegler D., Rombeau J. Utility of skin testing in nutritional assessment: a critical review. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1982 Jan-Feb;6(1):50–58. doi: 10.1177/014860718200600150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Stevens P., Kaijser B. Gram-negative pathogens in septicaemic infections. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;31:78–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., McCutchan J. A., Fierer J., Glauser M. P., Sadoff J. C., Douglas H., Braude A. I. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and shock with human antiserum to a mutant Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 11;307(20):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211113072001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner S. H., McCabe W. R. Effects of IgM and IgG antibody in patients with bacteremia due to gram-negative bacilli. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):37–45. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


